Cunningham, Xiaoya Li
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Nestle. Case study презентация
Содержание
- 1. Nestle. Case study
- 2. Largest nutrition
- 3. Key Figures Revenue 107.6
- 4. Nestle has 8500 brands
- 5. Growth Strategies
- 6. Emerging Markets
- 7. Profits of Adversity
- 8. Growth of Emerging
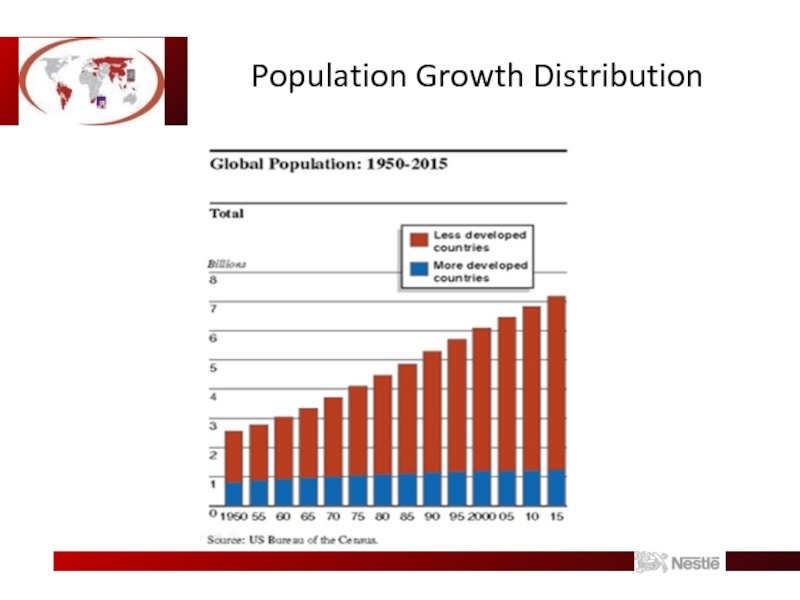
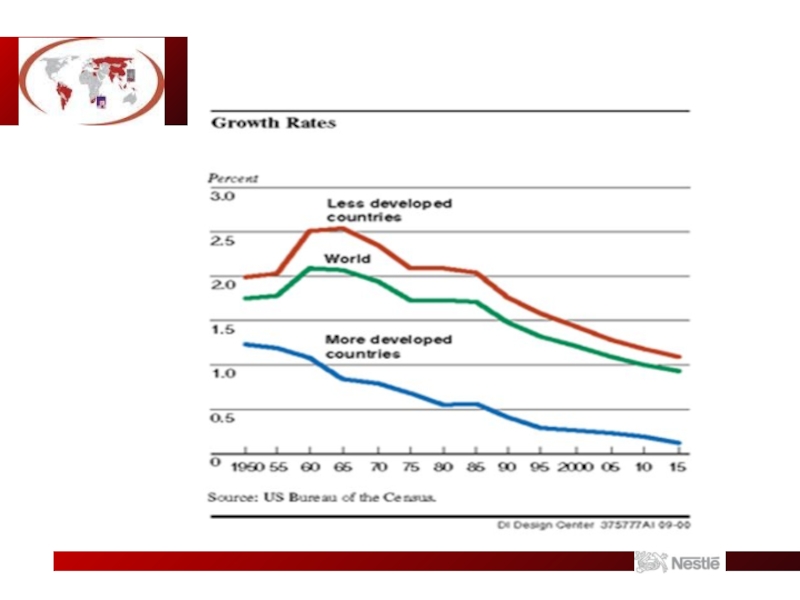
- 9. Population Growth Distribution
- 12. Investing In Emerging
- 13. Investing in Emerging
- 14. Strategy to work
- 15. The Nestle company
- 16. Nestlé's strategy in
- 17. Executing the strategy Flexibility Local adaptation A long-term focus
- 18. In Nigeria: the
- 19. Nestle Organizational Structure
- 20. Nestle Organizational Structure
- 22. Findings and Future
Слайд 2
Largest nutrition and foods company in the world
Founded and
headquarterd in Vevey, Switzerland
Nestle originated in a 1905 merger of the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company which was founded by Henri Nestle in 1866
Company grew significantly during the WWI and WWII
Operates in 86 countries
Employees 283,000 individuals.
Nestle originated in a 1905 merger of the Anglo-Swiss Milk Company which was founded by Henri Nestle in 1866
Company grew significantly during the WWI and WWII
Operates in 86 countries
Employees 283,000 individuals.
Слайд 3Key Figures
Revenue 107.6 billion
Operating Income 15.7 billion
Profit 10.43 billion
Total Assets 110.9 billion
Total Equity 53.63 billion (2009)
Total Assets 110.9 billion
Total Equity 53.63 billion (2009)
Слайд 4
Nestle has 8500 brands with a wide range of products
across a number
of markets including:
coffee
bottled water
other beverages
chocolate
ice cream
infant foods
confectionary
pet food
…
coffee
bottled water
other beverages
chocolate
ice cream
infant foods
confectionary
pet food
…
Слайд 5
Growth Strategies
Forced by Switzerlands small size
Established its
first foreign offices in U.S.A and Great Britain in the late 19th century
Australia, South America, Africa and Asia in the first three decades of the 20th century.
By the late 1990s, Nestle had 500 factories in 76 countries, sold products in 193 nations
3% of its employees are located in Switzerland
Australia, South America, Africa and Asia in the first three decades of the 20th century.
By the late 1990s, Nestle had 500 factories in 76 countries, sold products in 193 nations
3% of its employees are located in Switzerland
Слайд 6
Emerging Markets
Does it make sense for Nestle to focus on emerging
markets?
Infrastructure / Political difficulties ?!
Nestlé Emerging Markets Division imports products from more than 20 countries, and exporting products to more than 40 countries.
Infrastructure / Political difficulties ?!
Nestlé Emerging Markets Division imports products from more than 20 countries, and exporting products to more than 40 countries.
Слайд 7
Profits of Adversity
Nestlé's sales in emerging markets up 8.5% last year
Double
the rate of the company’s total revenue
Sales from those regions totaled $33.15 Billion, more than any rival.
Sales from those regions totaled $33.15 Billion, more than any rival.
Слайд 8
Growth of Emerging Markets Propensity
1 billion consumers in emerging markets will
increase their incomes enough to be able to afford Nestle products within the next decade.
1/3 of its revenue from emerging economies and aims to lift that to 45% within a decade.
- CEO Paul Bulcke
1/3 of its revenue from emerging economies and aims to lift that to 45% within a decade.
- CEO Paul Bulcke
Слайд 12
Investing In Emerging Markets
“Nestle will receive $28.1 billion from Novartis for
its majority stake in Alcon, the maker of Opti-Free contact lens cleaners, giving it a cash pile exceeding the $26.5 billion that Google had on its books at the end of March. The Swiss company is starting a new 10 billion-franc buyback programme, though Nestle would rather invest in its business or make acquisitions”
CFO Jim Singh said on June 22
CFO Jim Singh said on June 22
Слайд 13
Investing in Emerging Markets
“Nestle may purchase bottled water businesses in markets
such as China”
Frits van Dijk, head of Nestle’s Asian business, on June 22.
“Acquisitions would also be considered to expand its business selling nutrition products for athletes, such as PowerBar”
Nestle Nutrition CEO Richard Laube
Start cheap and introduce luxury later
Frits van Dijk, head of Nestle’s Asian business, on June 22.
“Acquisitions would also be considered to expand its business selling nutrition products for athletes, such as PowerBar”
Nestle Nutrition CEO Richard Laube
Start cheap and introduce luxury later
Слайд 14
Strategy to work effectively
Flexibility is another distinctive competencies which Nestle company
was able to achieve to react as quickly as possible to changing environments.
As a consequence, company was able to respond to changes in local demand, cultural barriers and political fluctuation.
Ethnocentric behavior must be avoided in any circumstances in order to approach the market in the appropriated .
As a consequence, company was able to respond to changes in local demand, cultural barriers and political fluctuation.
Ethnocentric behavior must be avoided in any circumstances in order to approach the market in the appropriated .
Слайд 15
The Nestle company uses that approach in order to the convenient
fact that the consumer is easier to reached because he is accustomed to this brand name and they think they know what they are buying.
The Nestle strategy was to be cultural awareness, which means a company should employ locals in order lower cultural barriers and resentments established by the foreigner.
Nestle believes that, the key to their success is customization rather than exaggerated globalization.
The Nestle strategy was to be cultural awareness, which means a company should employ locals in order lower cultural barriers and resentments established by the foreigner.
Nestle believes that, the key to their success is customization rather than exaggerated globalization.
Слайд 16
Nestlé's strategy in emerging markets
The Key strategy:
Customization rather than globalization.
Слайд 18
In Nigeria: the company hired local singers to go to towns
and villages offering a mix of entertainment and product demonstrations.
In China: Nestlé established its own distribution network, known as milk roads.
Executing the strategy
Слайд 19
Nestle Organizational Structure
Moving from Localization strategy to Transnational strategy
Includes first mover
advantage, local economies, global web, economies of scale
Strong local responsiveness, but production, training, and R&D becoming centralized
Management practices – spread knowledge, create learning effects, and transfer core competencies
“Glocal” philosophy and creating value
Strong local responsiveness, but production, training, and R&D becoming centralized
Management practices – spread knowledge, create learning effects, and transfer core competencies
“Glocal” philosophy and creating value
Слайд 20
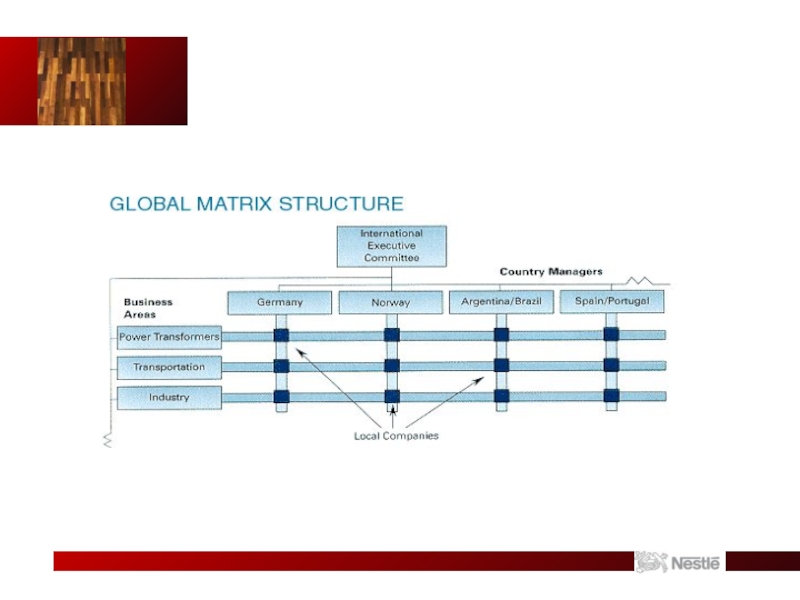
Nestle Organizational Structure
Seven global strategic business units classified by food type
(worldwide production divisional structure)
Five regional units by geography (worldwide area structure)
Has created a global matrix structure
Example of a global matrix structure:
Five regional units by geography (worldwide area structure)
Has created a global matrix structure
Example of a global matrix structure:
Слайд 22
Findings and Future
Strategy succeeding and applicable to markets and countries
Need for
tighter integration at matrix points
Focus on healthier, more nutritious products
Raise revenue from developing countries from 33% to 45% of total revenue within 10 years
Will receive $28.1 billion for its stake in Alcon
Focus on healthier, more nutritious products
Raise revenue from developing countries from 33% to 45% of total revenue within 10 years
Will receive $28.1 billion for its stake in Alcon