- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Creating and pricing products that satisfy customers презентация
Содержание
- 1. Creating and pricing products that satisfy customers
- 2. Learning Objectives Explain what a product is
- 3. Product …everything one receives in an exchange,
- 4. Product Good: a real, physical thing that
- 5. Product Classification Determines Distribution Promotion Pricing “The
- 6. Consumer Product …a product purchased to satisfy personal and family needs.
- 7. Consumer Product Classifications Convenience Inexpensive, frequently purchased
- 8. Business Product …a product bought for resale,
- 9. Business Product Classifications Raw material: becomes part
- 10. Source: “Attendance Required,” The B-to-B Media Handbook,
- 11. Product Life Cycle …a series of stages
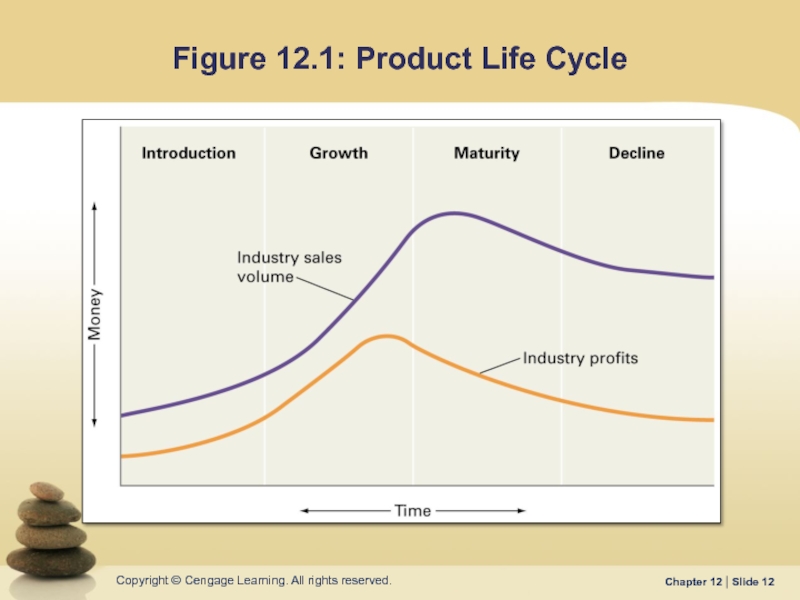
- 12. Figure 12.1: Product Life Cycle
- 13. Stages of Product Life Cycle Introduction Sales:
- 14. Product Line …a group of similar products that differ only in relatively minor characteristics.
- 15. Product Mix …all the products a firm offers for sale.
- 16. Dimensions of Product Mix Depth Width
- 17. Product Modification …the process of changing one or more of a product’s characteristics.
- 18. Effectiveness of Product Modification Product must be
- 19. Types of Modification Quality: dependability and durability
- 20. Line Extensions …development of a new product
- 21. Product Deletion …the elimination of one or more products from a product line.
- 22. New Product Categories Imitations: similar to and
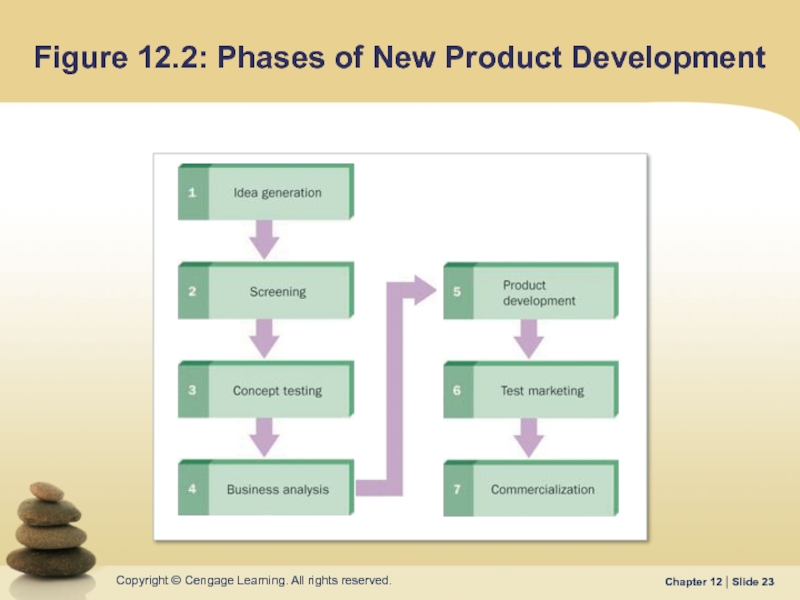
- 23. Figure 12.2: Phases of New Product Development
- 24. Table 12.1: Examples of Product Failures Sources:
- 25. Brand …a name, term, symbol, design, or
- 26. Brand Name …the part of a brand that can be spoken.
- 27. Market Value of Best Global Brands
- 28. Consumers’ Perceptions of Store and Manufacturers’ Brands
- 29. Brand Mark …the part of a brand that is a symbol or distinctive design.
- 30. Trademark …a brand name or brand mark
- 31. Trade Name …the complete and legal name of an organization.
- 32. Types of Brands Manufacturer/Producer Owned by a
- 33. Benefits of Branding Brand Loyalty: customer favorable
- 34. Choosing and Protecting a Brand Easy to
- 35. Branding Strategies Individual Branding Different brand for
- 36. Packaging …all the activities involved in developing
- 37. Packaging Functions Protects Product Adds Consumer Convenience
- 38. Functional problems Difficulty opening, breakage, inconvenience
- 39. Labeling …the presentation of information on a product or its package.
- 40. Federal Regulations on Labeling Garments Manufacturer, country,
- 41. Express Warranty …a written explanation of the
- 42. Pricing …the amount of money a seller
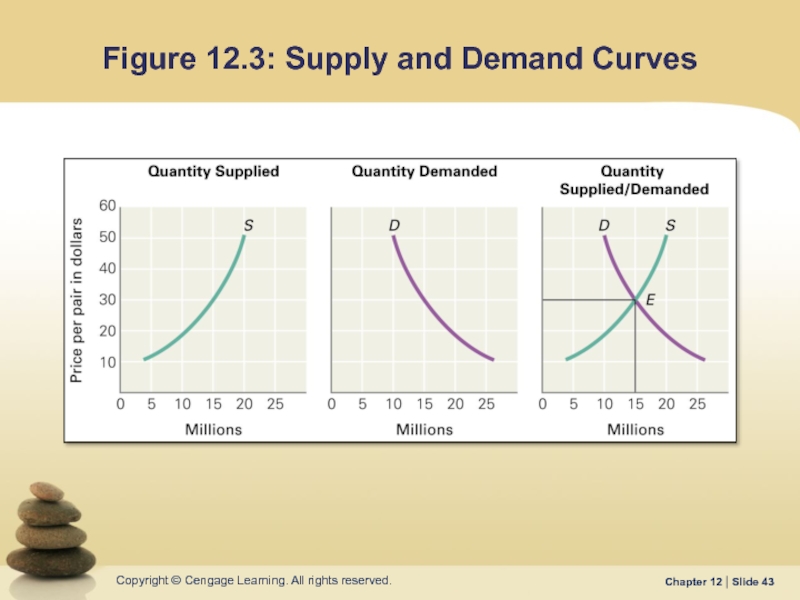
- 43. Figure 12.3: Supply and Demand Curves
- 44. Price Competition …an emphasis on setting a
- 45. Nonprice Competition …competition based on factors
- 46. Buyers’ Perceptions of Price Price Sensitivity Acceptance of Ranges Relation to Competing Products Quality
- 47. Spotlight Grocery Shopping Source: 2009 National Grocers Association—SupermarketGuru Consumer Panel Survey, November 2008–January 2009.
- 48. Pricing Objectives Survival Profit Maximization Target ROI Market-Share Goals Status Quo Pricing
- 49. Factors Affecting Price Setting Market determines price
- 50. Cost-Based Pricing Markup: amount seller adds to
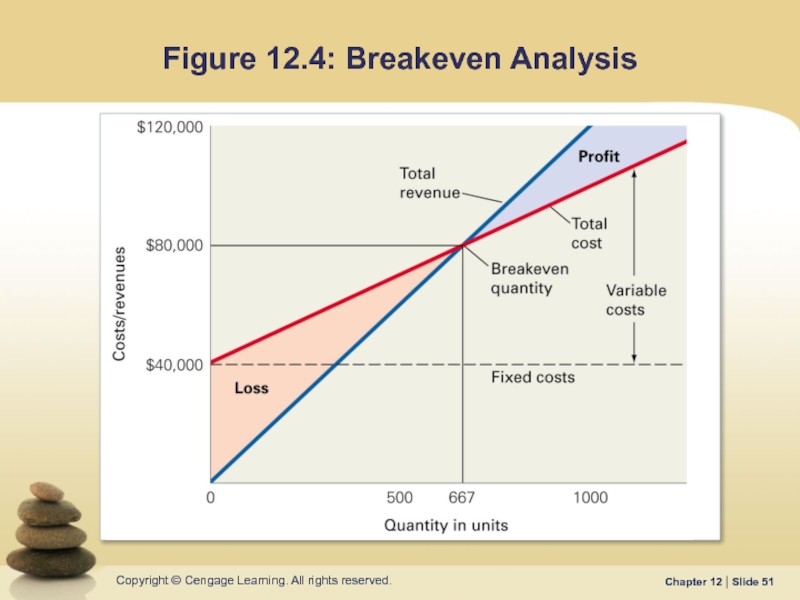
- 51. Figure 12.4: Breakeven Analysis
- 52. Other Pricing Strategies Demand-Based High price when
- 53. New Product Pricing Strategies Price Skimming Charge
- 54. Differential Pricing Negotiated Final price comes from
- 55. Psychological Pricing Odd-Number: use odd numbers just
- 56. Product-Line Pricing Captive Basic product priced
- 57. Promotional Pricing Price Leaders Below usual markup,
- 58. Pricing Business Products Geographic FOB Origin FOB Destination Transfer Discounting Trade Quantity Cash Seasonal Allowance
- 59. Using the Internet The U.S. government gateways
- 60. All of the following are characteristics of
- 61. If Samsonite decided to use better zippers
- 62. The Nike “swoosh” is a brand. generic
- 63. In setting prices, managers should consider the
- 64. The pricing strategy that requires the buyer
Слайд 2Learning Objectives
Explain what a product is and how products are classified.
Discuss
Define product line and product mix and distinguish between the two.
Identify the methods available for changing a product mix.
Explain the uses and importance of branding, packaging, and labeling.
Describe the economic basis of pricing and the means by which sellers can control prices and buyers’ perceptions of prices.
Identify the major pricing objectives used by businesses.
Examine the three major pricing methods that firms employ.
Explain the different strategies available to companies for setting prices.
Describe three major types of pricing associated with business products.
Слайд 3Product
…everything one receives in an exchange, including all tangible and intangible
Слайд 4Product
Good: a real, physical thing that we can touch
Service: the result
Idea: philosophies, lessons, concepts, or advice
Слайд 5Product Classification Determines
Distribution
Promotion
Pricing
“The buyer’s use of the product
determines the classification of
Слайд 7Consumer Product Classifications
Convenience
Inexpensive, frequently purchased item; buyers exert minimal effort
Shopping
Buyers willing
Specialty Possesses one or more unique characteristics; significant group of buyers willing to expend considerable purchasing effort
Слайд 8Business Product
…a product bought for resale, for making other products, or
Слайд 9Business Product Classifications
Raw material: becomes part of physical product
Major equipment: tools/machines
Accessory equipment: standardized equipment used in production or office activities
Component: part of physical product either as finished item or with little processing before assembly
Process material: directly in production of another product; not readily identifiable in finished product
Supply: facilitates production/operations, does not become part of finished product
Business service: intangible product used in operations
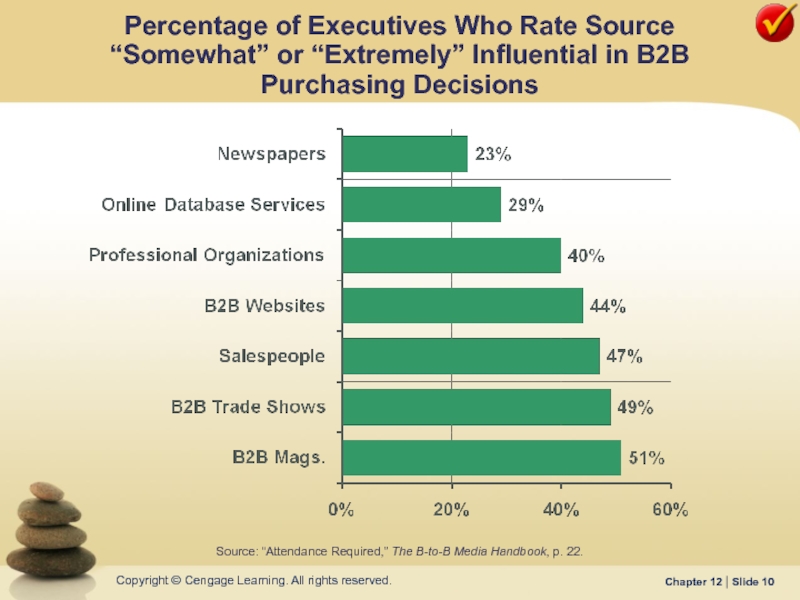
Слайд 10Source: “Attendance Required,” The B-to-B Media Handbook, p. 22.
Percentage of Executives
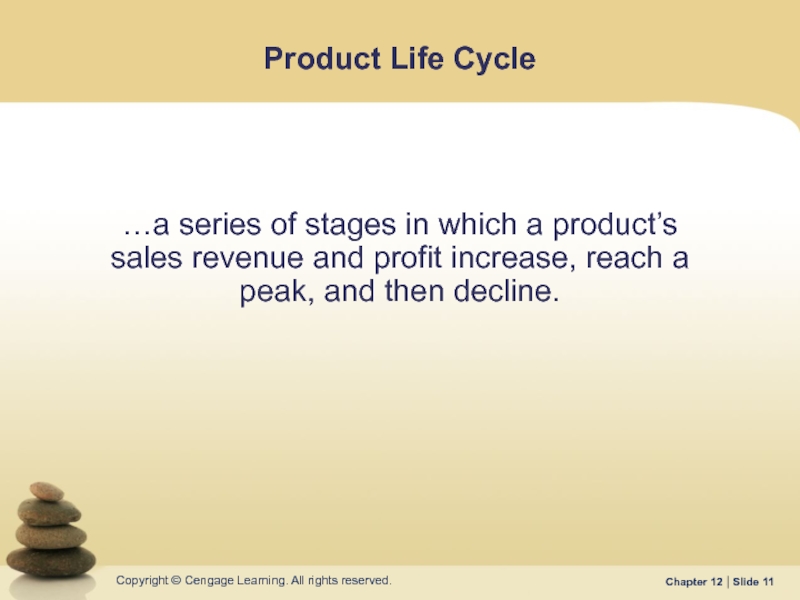
Слайд 11Product Life Cycle
…a series of stages in which a product’s sales
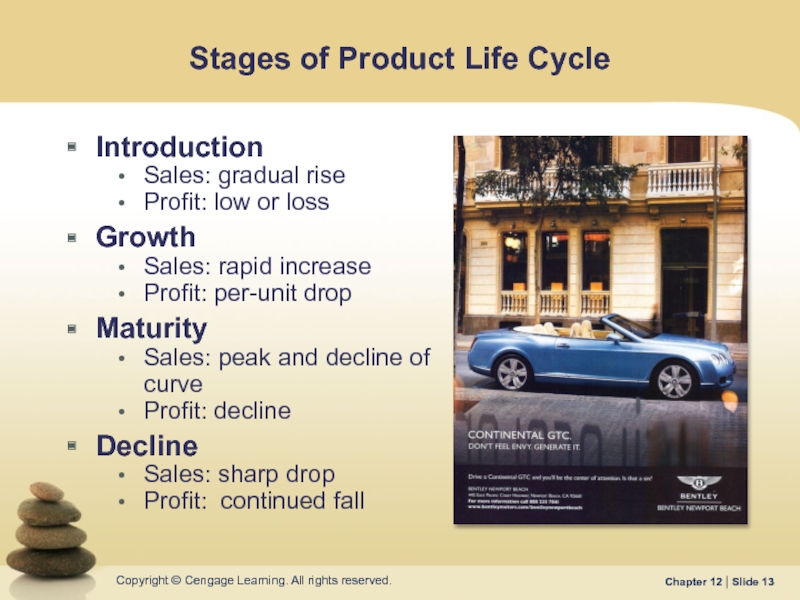
Слайд 13Stages of Product Life Cycle
Introduction
Sales: gradual rise
Profit: low or loss
Growth
Sales: rapid
Profit: per-unit drop
Maturity
Sales: peak and decline of curve
Profit: decline
Decline
Sales: sharp drop
Profit: continued fall
Слайд 14Product Line
…a group of similar products that differ only in relatively
Слайд 16Dimensions of Product Mix
Depth
Width
Ways to improve
Change existing product
Delete a product
Develop a
Слайд 18Effectiveness of Product Modification
Product must be modifiable
Existing customers must perceive modification
Modification makes product more consistent with customers’ desires
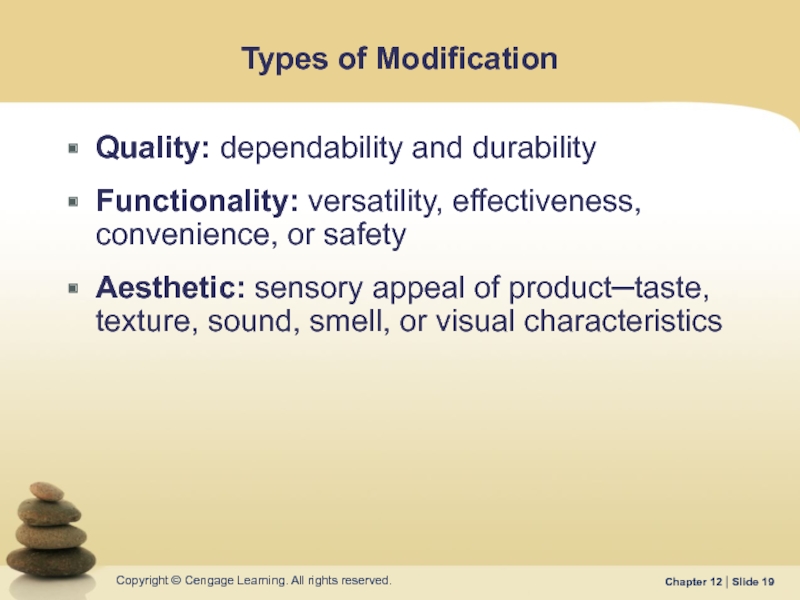
Слайд 19Types of Modification
Quality: dependability and durability
Functionality: versatility, effectiveness, convenience, or safety
Aesthetic:
Слайд 20Line Extensions
…development of a new product that is closely related to
More common than new products
Слайд 22New Product Categories
Imitations: similar to and competitive with existing products of
Adaptations: variations of existing products intended for an established market
Innovations: entirely new products
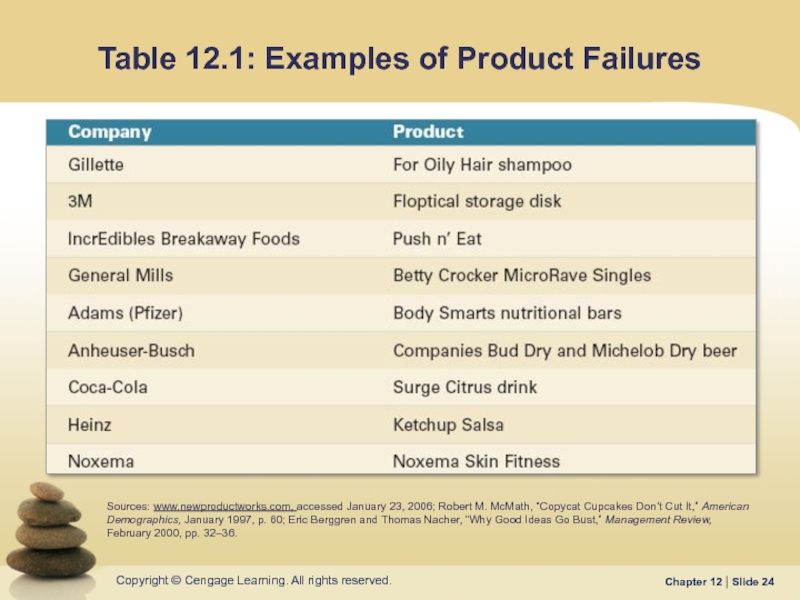
Слайд 24Table 12.1: Examples of Product Failures
Sources: www.newproductworks.com, accessed January 23, 2006;
Demographics, January 1997, p. 60; Eric Berggren and Thomas Nacher, “Why Good Ideas Go Bust,” Management Review, February 2000, pp. 32–36.
Слайд 25Brand
…a name, term, symbol, design,
or any combination of these that identifies
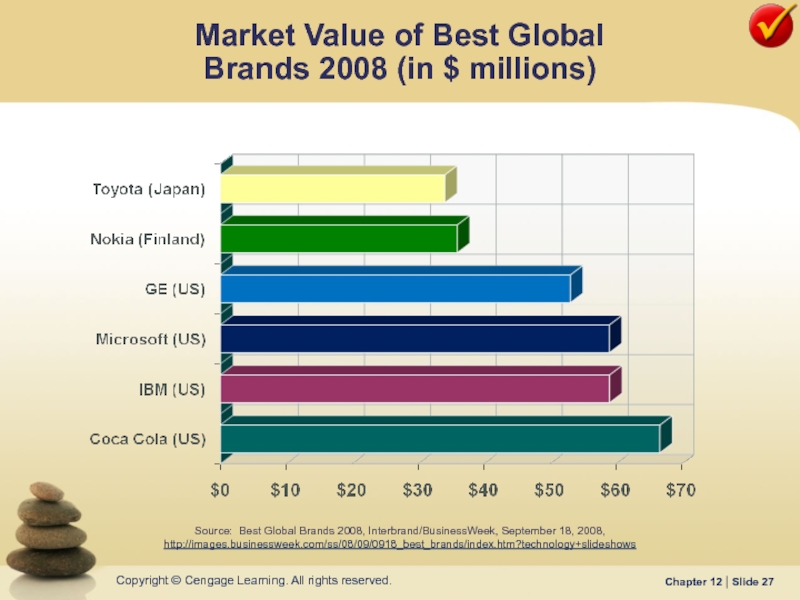
Слайд 27Market Value of Best Global
Brands 2008 (in $ millions)
Source: Best
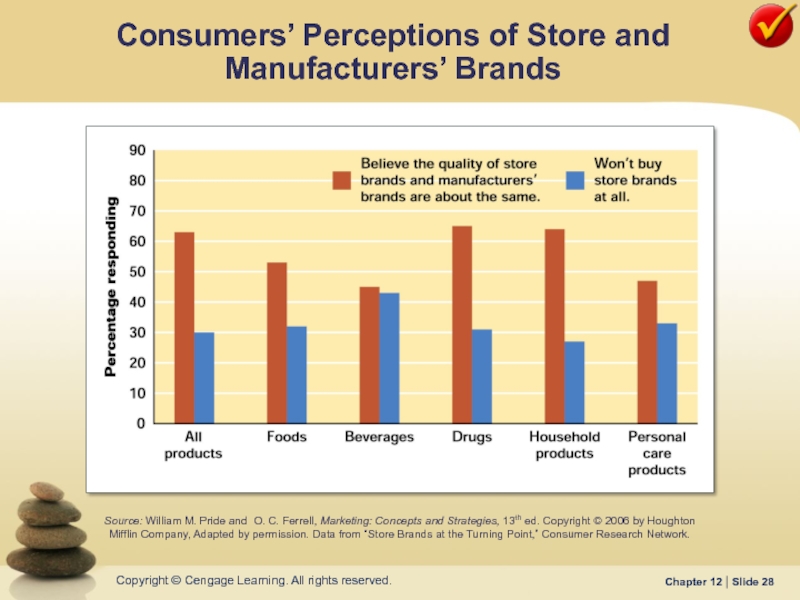
Слайд 28Consumers’ Perceptions of Store and Manufacturers’ Brands
Source: William M. Pride and
Слайд 30Trademark
…a brand name or brand mark that is registered with the
United States Patent and Trademark Office Home Page
Слайд 32Types of Brands
Manufacturer/Producer
Owned by a manufacturer
Store/Private
Owned by individual wholesaler or retailer
Generic
Слайд 33Benefits of Branding
Brand Loyalty: customer favorable toward specific brand
Brand Recognition
Brand Preference
Brand
Brand Equity: marketing/financial value associated with brand’s strength
Слайд 34Choosing and Protecting a Brand
Easy to say, spell, recall
Suggests product’s uses,
Distinctive enough to set it apart
Protect it through registration®.
Generic terms cannot be legally protected.
Слайд 35Branding Strategies
Individual Branding
Different brand for each of firm’s products
Family Branding
Same brand
Brand Extension Using an existing brand to brand new product in different product category
Слайд 36Packaging
…all the activities involved in developing and providing a container with
Слайд 37Packaging Functions
Protects Product
Adds Consumer Convenience
Promotes Product
Design Considerations
Cost
Single/multiple units
Family packaging: consistency
Needs of
Environmental responsibility
Слайд 38Functional problems
Difficulty opening, breakage, inconvenience
Safety
Tampering, sharp edges, breakable glass, health hazards of plastic and aerosol containers
Deception
Shape, design, colors may alter appearance of size; confusing size designations
Cost
Packaging costs being passed on to consumers
Criticisms of Packaging
Слайд 40Federal Regulations on Labeling
Garments
Manufacturer, country, fabric content, cleaning instructions
Food
Ingredients
Servings per container
Serving
Calories per serving
Calories from fat
Amounts of specific ingredients
Nutritional food: nutrition labeling
Nonedible items Safety precautions and instructions
Слайд 41Express Warranty
…a written explanation of the responsibilities of the producer in
Слайд 42Pricing
…the amount of money a seller is willing to accept in
Слайд 44Price Competition
…an emphasis on setting a price equal to or lower
www.mysimon.com
Price comparison shopping
Слайд 45Nonprice Competition
…competition based on factors
other than price.
Product Differentiation: the process
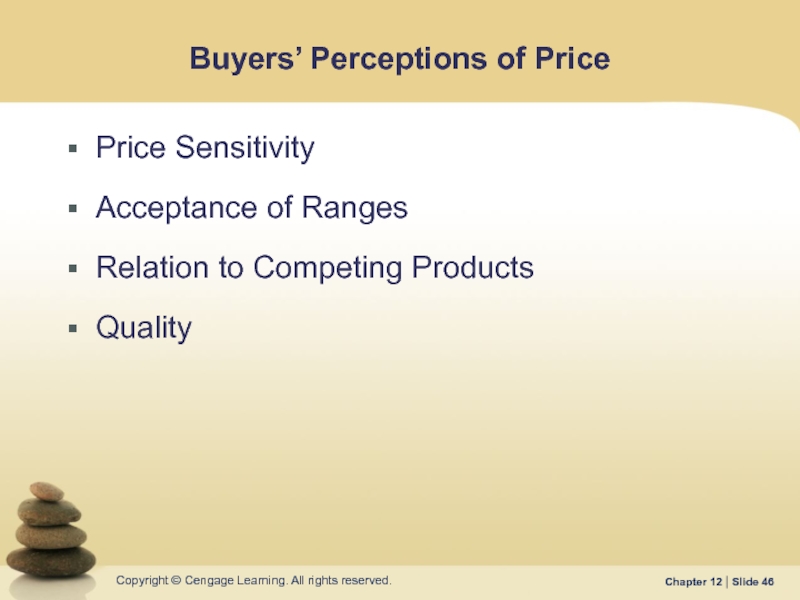
Слайд 46Buyers’ Perceptions of Price
Price Sensitivity
Acceptance of Ranges
Relation to Competing Products
Quality
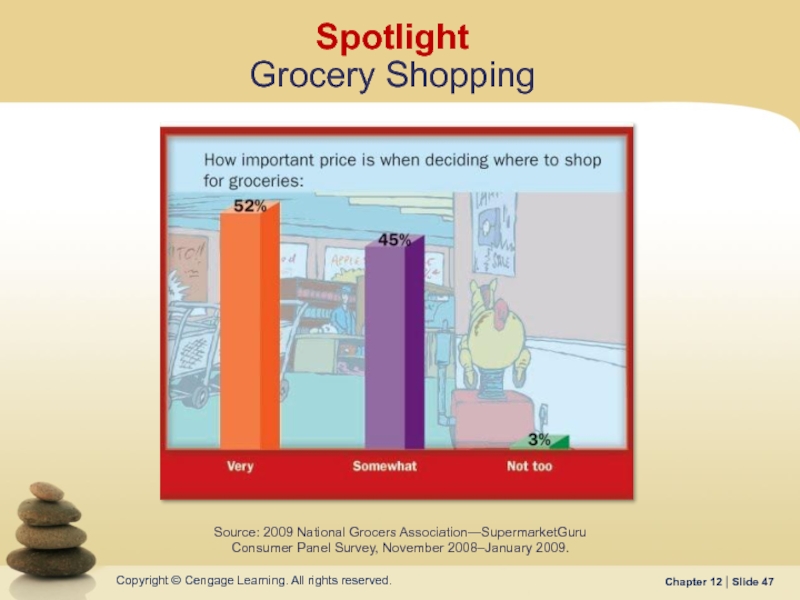
Слайд 47Spotlight
Grocery Shopping
Source: 2009 National Grocers Association—SupermarketGuru
Consumer Panel Survey, November 2008–January 2009.
Слайд 49Factors Affecting Price Setting
Market determines price
Costs and expected sales used only
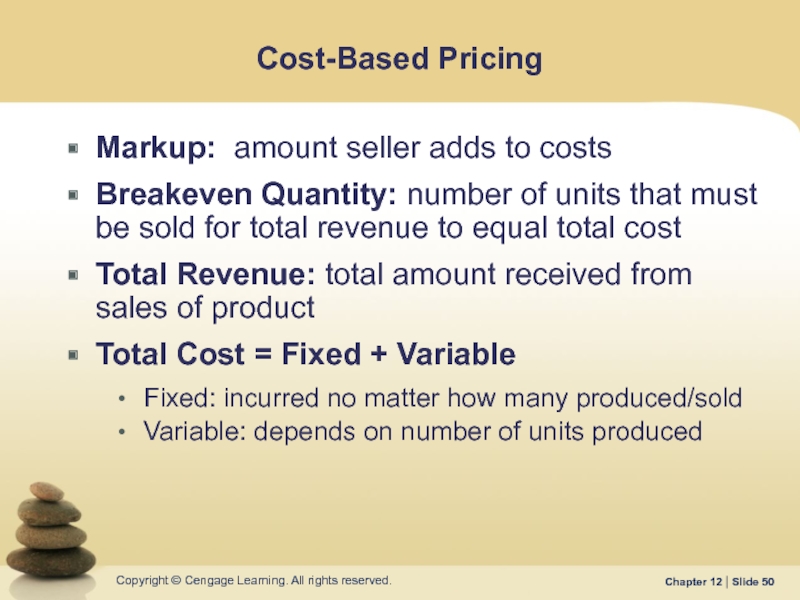
Слайд 50Cost-Based Pricing
Markup: amount seller adds to costs
Breakeven Quantity: number of units
Total Revenue: total amount received from sales of product
Total Cost = Fixed + Variable
Fixed: incurred no matter how many produced/sold
Variable: depends on number of units produced
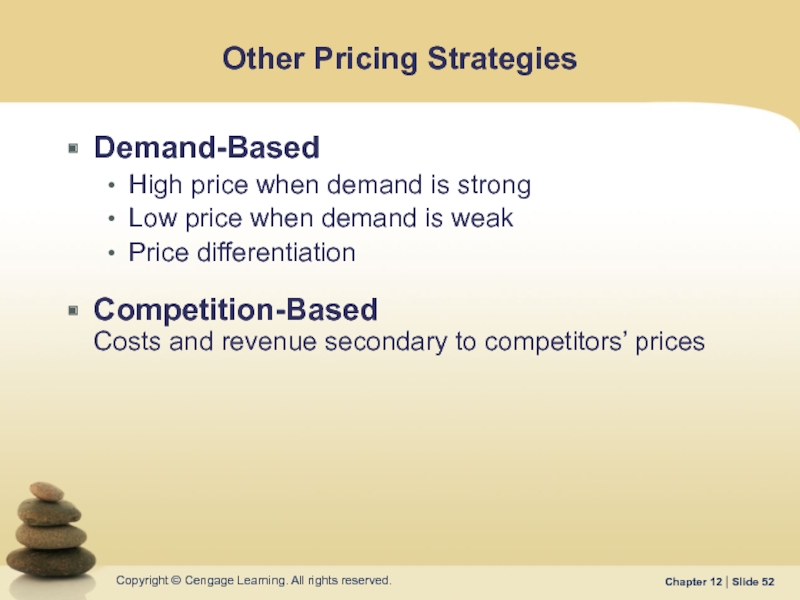
Слайд 52Other Pricing Strategies
Demand-Based
High price when demand is strong
Low price when demand
Price differentiation
Competition-Based Costs and revenue secondary to competitors’ prices
Слайд 53New Product Pricing Strategies
Price Skimming
Charge highest possible price during introduction stage
Penetration
Слайд 54Differential Pricing
Negotiated Final price comes from bargaining
Secondary Market
One price for primary
Periodic Discounting Temporary price reduction on patterned/systematic basis
Random Discounting Temporary price reduction on unsystematic basis
Charging different prices to different buyers for same quality and quantity
Слайд 55Psychological Pricing
Odd-Number: use odd numbers just below whole-dollar amounts
Multiple-Unit: single price
Reference: price at moderate level and positioning it near a more expensive model
Bundle: package 2+ products and selling for single price
EDLP: consistently low price
Customary: based on tradition
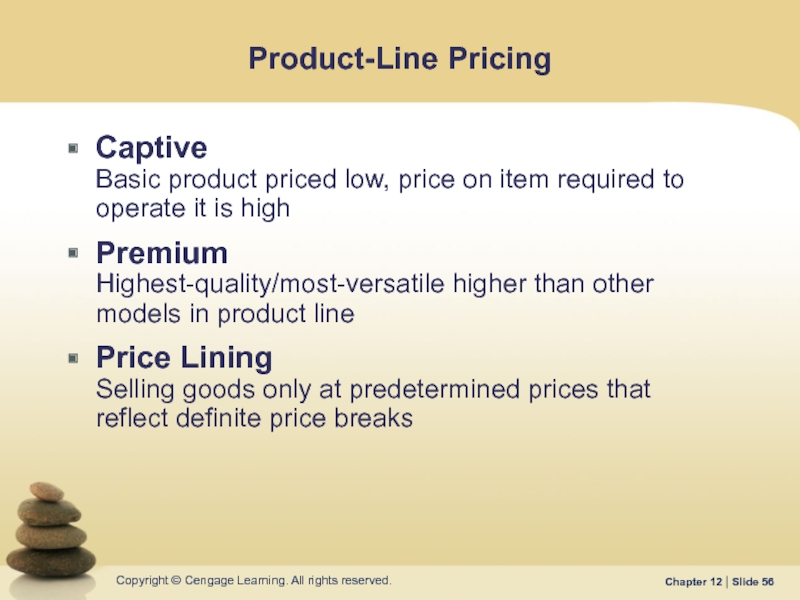
Слайд 56Product-Line Pricing
Captive
Basic product priced low, price on item required to
Premium Highest-quality/most-versatile higher than other models in product line
Price Lining Selling goods only at predetermined prices that reflect definite price breaks
Слайд 57Promotional Pricing
Price Leaders
Below usual markup, near or below cost
Special-Event
Price cutting linked
Comparison Discounting Set at specific level and compare with higher price
Слайд 58Pricing Business Products
Geographic
FOB Origin
FOB Destination
Transfer
Discounting
Trade
Quantity
Cash
Seasonal
Allowance
Слайд 59Using the Internet
The U.S. government gateways to consumer information about products,
www.pueblo.gsa.gov
www.consumer.gov
Слайд 60All of the following are characteristics of the growth stage of
a rapid increase in sales.
the introduction of competing products.
decreased unit prices but overall increase in total profits.
the introduction of modified versions of its products by the original firm.
a decline in the number of competing firms.
Chapter Quiz
Слайд 61If Samsonite decided to use better zippers on its luggage that
aesthetic
functional
texture
quality
market
Chapter Quiz
Слайд 62The Nike “swoosh” is a
brand.
generic symbol.
label.
brand mark.
Universal Product Code.
Chapter Quiz
Слайд 63In setting prices, managers should consider the __________ of people in
demographics
ages
price sensitivity
philosophy
occupations
Chapter Quiz
Слайд 64The pricing strategy that requires the buyer to pay the greatest
railhead pricing.
parcel post.
express delivery cost.
FOB origin pricing.
C.O.D. pricing.
Chapter Quiz