- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
On Being an ePatient: презентация
Содержание
- 1. On Being an ePatient:
- 2. What is an ePatient? Equipped Enabled Empowered Engaged
- 3. My Life in Paper
- 4. Why I became an ePatient Several chronic
- 5. Personal Experiences Patient Centered Medical Home at
- 6. Personal Experience Focus on perfectionism Control! Compliance! Linking to support College!
- 7. Randomness and chaos is
- 8. Stigma - Barrier or Motivation? Barriers Misinformation
- 9. How I Became Involved JDRF Research
- 10. What Quality of Life Improvements Are Most Important? N=654 ©2013 DiabetesMine Patient Voices Survey
- 11. Diabetes Intrudes #DayOfDiabetes “Mommy, can
- 12. Characteristics of an ePatient Looking for
- 13. Caregivers are also ePatients 39% of
- 14. Self Trackers/Quantified Self Diabetics are by
- 15. How Do Patients Track? How do people
- 18. Health IT Changing ePatient Landscape Social Media
- 19. ePatients Online 31% of adults with chronic
- 20. Pew
- 21. What do ePatients Share? Treatment information Medications
- 22. What resources do ePatients turn to online?
- 23. Diabetes Online Community #DOC Diabulimia Helpline
- 24. ePatients Not Just Online Providers are
- 27. What Would Most Motivate You to Put
- 28. Change from Perfectionism to Positivism “Scott
- 29. How to engage and collaborate with an
- 30. Education - When ePatients Know More Healthcare
- 31. Educate Through Resources Reputable online websites
- 32. Collaborate – A Colleague in My Care
- 33. Coordinate Patients have multiple providers
- 34. ePatients at the Center Primary Care Doctor Me Hospital CDE Specialist
- 35. Support Support Groups Online Communities
- 36. Considerations when engaging Health literacy Cultural
- 37. Social Media (Facebook, Twitter, Online Communities)
- 38. Information Dissemination (Websites & Social Media)
- 39. New Technologies Pros Better management Allows patient
- 40. Mobile/Web Apps Pros Efficient Low Cost Innovative/Interactive
- 41. EHRs & Patient Portals Pros Records accuracy
- 42. PHRs Pros Ability to take your information
- 43. Medical Devices Pros Connect more and more
- 44. Telehealth Pros Reaches remote populations Cost efficient
- 45. e-Patient Dave on OpenNotes / Let Patients Help speech to AMSA, March 2014
- 46. e-Patient Dave on OpenNotes / Let Patients Help speech to AMSA, March 2014
- 47. The value of an ePatient Better management
- 48. As an ePatient I Am Equipped
Слайд 1On Being an ePatient:
Erin M. Gilmer
@GilmerHealthLaw
erin@gilmerhealthlaw.com
Equipped, Enabled, Empowered, Engaged
Слайд 4Why I became an ePatient
Several chronic conditions
Little support from friends and
In College
Personal struggles with coping
Socioecomic factors (insurance/costs)
Need for control
Personal Interest in health policy
Слайд 5Personal Experiences
Patient Centered Medical Home at Barbara Davis Center
Research studies
Adopting new
technologies
Слайд 8Stigma - Barrier or Motivation?
Barriers
Misinformation
Embarrassment
Depression
Motivation
Want to know the information & beat
Слайд 9How I Became Involved
JDRF
Research Studies
Diabetes Development
And Awareness at University of Colorado
Twitter
Conferences,
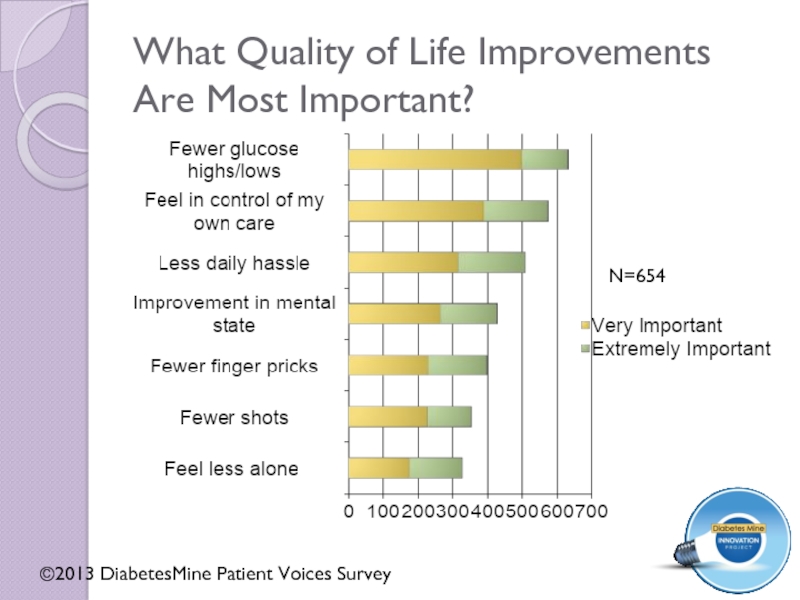
Слайд 10What Quality of Life Improvements Are Most Important?
N=654
©2013 DiabetesMine Patient Voices
Слайд 11Diabetes Intrudes
#DayOfDiabetes
“Mommy, can you please play with me?” Saying “not yet”
@Sixuntilme (Kerri)
Слайд 12Characteristics of an ePatient
Looking for information and trying to learn
Collaborate with
Share information across platforms
May have 1 or more chronic conditions and be a caregiver
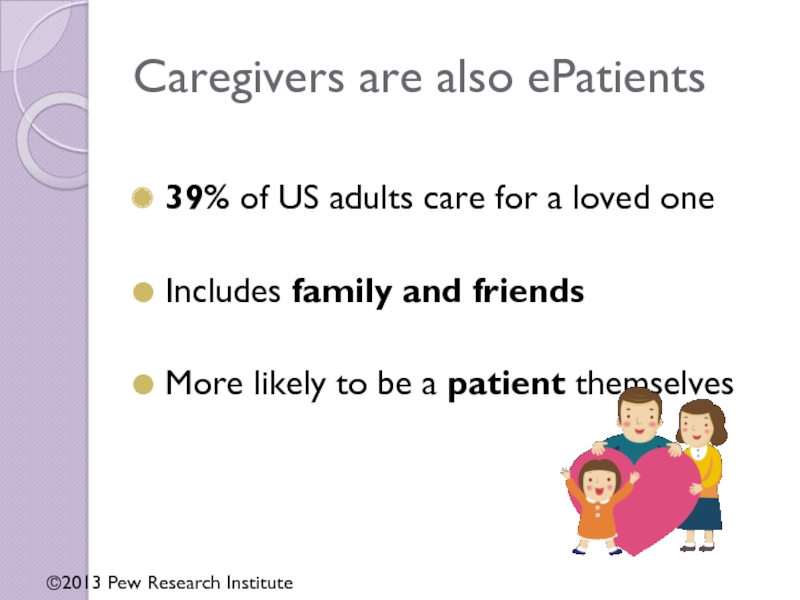
Слайд 13Caregivers are also ePatients
39% of US adults care for a loved
Includes family and friends
More likely to be a patient themselves
©2013 Pew Research Institute
Слайд 14Self Trackers/Quantified Self
Diabetics are by default self-trackers
“As patients it’s not enough
- Kim Vlasnik (Texting My Pancreas)
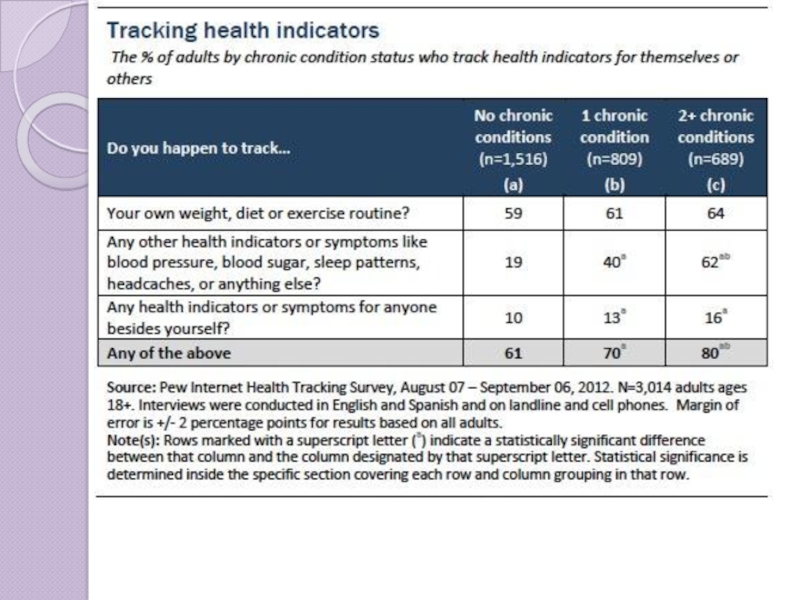
Слайд 15How Do Patients Track?
How do people track in general?
49% - in
34% - pencil and paper
8% - medical device (like glucometer)
7% - mobile app
5% - computer program
1% - websites
©2013 Pew Research Institute
Слайд 18Health IT Changing ePatient Landscape
Social Media (Twitter, Facebook, Online Communities)
Online Resources
New Technologies/Devices (CGM’s, Pumps)
Apps (Weight/Diet/Glucose Tracking)
EHRs & Patient Portals
Telehealth
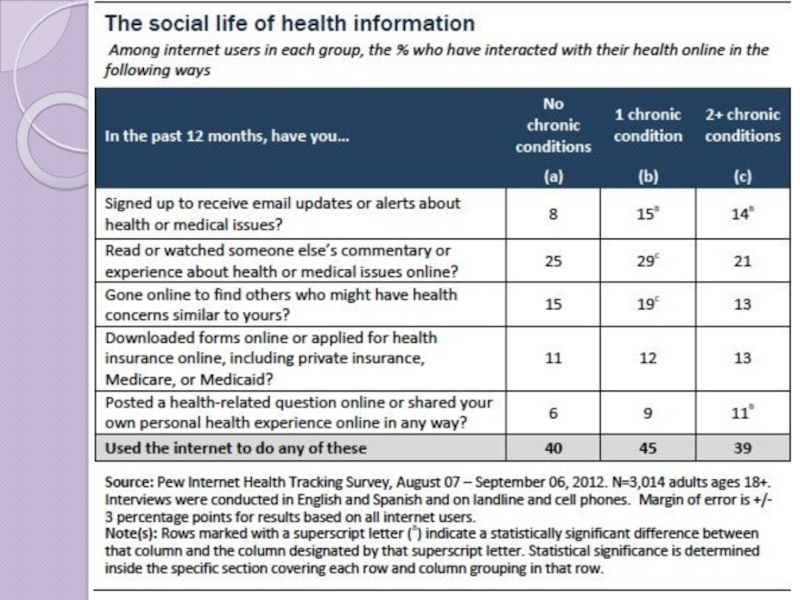
Слайд 19ePatients Online
31% of adults with chronic conditions go online to try
1 in 5 internet users have gone online to find patients like them
4 in 10 internet users share personal stories
©2013 Pew Research Institute
Слайд 21What do ePatients Share?
Treatment information
Medications
Technology
Personal Stories
Stories of other ePatients
Education/Research/News
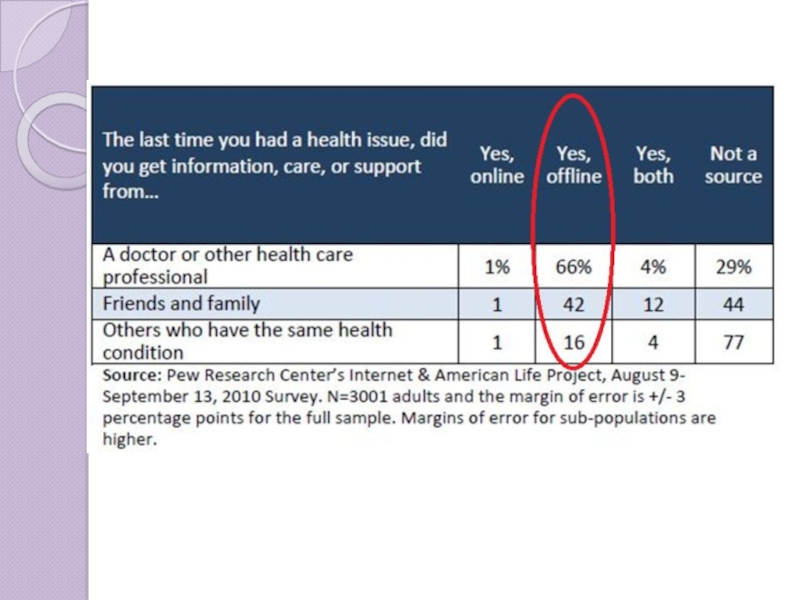
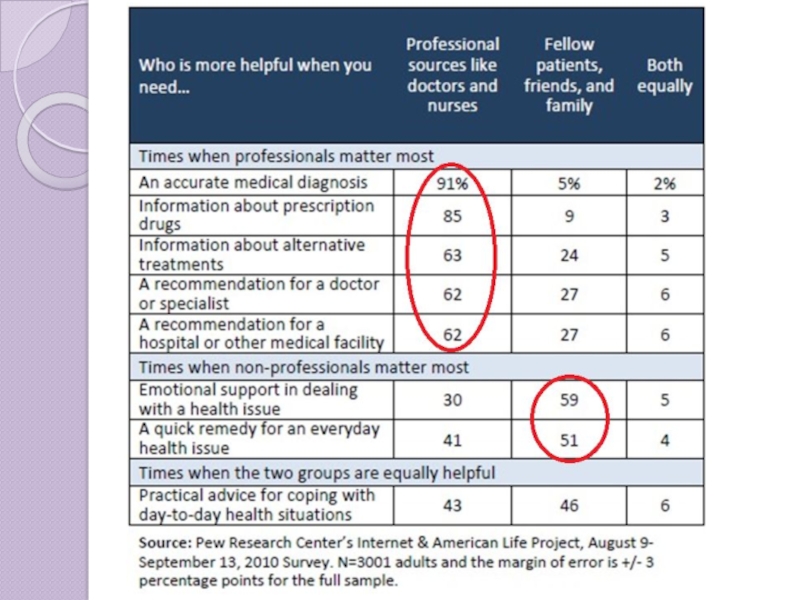
Слайд 24ePatients Not Just Online
Providers are still by far the most important
Only 5% receive information online with a healthcare professional or fellow patient
©2013 Pew Research Institute
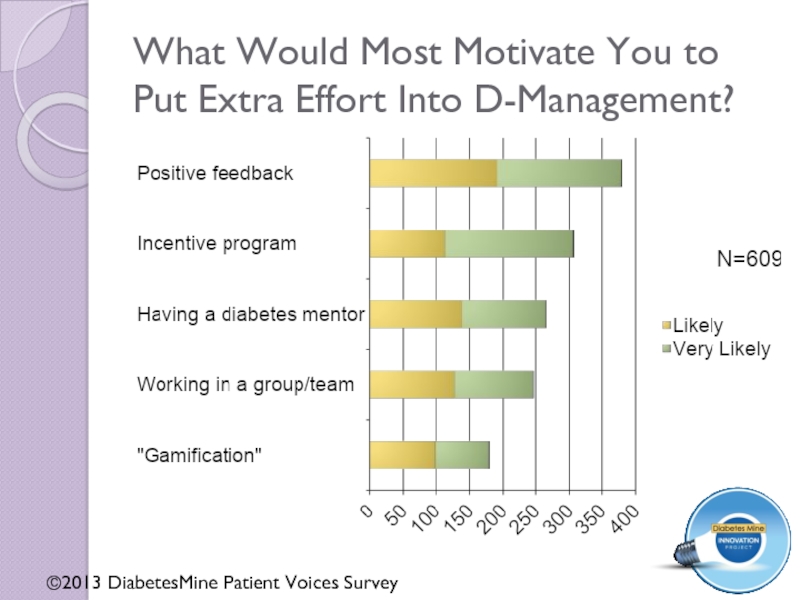
Слайд 27What Would Most Motivate You to Put Extra Effort Into D-Management?
©2013
Слайд 28Change from Perfectionism to Positivism
“Scott was diagnosed with Type 1 diabetes
- Scott Strange (@Strangely_T1)
Слайд 29How to engage and collaborate with an ePatient
Clinicians are the top
Need to
Educate
Collaborate
Coordinate
Support
Слайд 30Education - When ePatients Know More
Healthcare professionals cannot become experts in
Educated ePatients should be considered part of the healthcare team
If ePatients aren’t listened to:
Frustration and Feelings of loss of control
Medication errors and proper resources denied
BMJ article “What happens when patients know more than their doctors”
Слайд 31Educate Through Resources
Reputable online websites
Printed materials
Phone numbers for support groups
Apps
Слайд 32Collaborate – A Colleague in My Care
Ask where the patient is
Include in decision
making process
Include caregivers
Encourage use of EHRs (and PHRs)
Слайд 33Coordinate
Patients have multiple providers
Be a voice for patients
Encouraging providers to engage
Слайд 36Considerations when engaging
Health literacy
Cultural influences
Economic influences
At what level do they want
In what format do they want to engage?
Слайд 37Social Media
(Facebook, Twitter, Online Communities)
Pros
Support Systems
Sharing information
Cons
Privacy Issues
Слайд 38Information Dissemination
(Websites & Social Media)
Pros
Ability to research anything
Patient forums for
If you lose the pamphlets given to you, you can look it up
Cons
Not always accurate
Слайд 39New Technologies
Pros
Better management
Allows patient to be more engaged
Ease of sharing information
Cons
Expensive
Information Overload
Not all providers up-to-date on technology
Слайд 40Mobile/Web Apps
Pros
Efficient
Low Cost
Innovative/Interactive
Cons
Too many to consider – cannot decide which is
Doctors don’t know them
Слайд 41EHRs & Patient Portals
Pros
Records accuracy
E-prescribing attributes
Patient portals get test results to
Cons
Frustration by providers
All still in beta form
Portals not very meaningful
Слайд 42PHRs
Pros
Ability to take your information with you wherever you go
Ability to
Cons
Do not connect with Patient Portals in EHRs
Doctors may not pay attention to them
Слайд 43Medical Devices
Pros
Connect more and more to other mobile/web apps and EHRs
Ability
Cons
Security of devices
FDA regulation uncertain
Слайд 44Telehealth
Pros
Reaches remote populations
Cost efficient
Cons
Removed from in-person care that may be needed
Слайд 47The value of an ePatient
Better management
Greater coordination/collaboration of care
Increased health literacy
Educating
Patient Safety