- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Healthcare Reporting: Centralized vs. Decentralized презентация
Содержание
- 1. Healthcare Reporting: Centralized vs. Decentralized
- 2. Healthcare Reporting One of the questions that
- 3. Healthcare Reporting At Health Catalyst we believe
- 4. Healthcare Reporting The approach is much like
- 5. Healthcare Reporting Suppose at the line of
- 6. Healthcare Reporting The purpose of analytics in
- 7. Basics of Centralized vs. Decentralized Organizations
- 8. Basics of Centralized vs. Decentralized Each
- 9. Centralized Reporting Pros The centralized model has
- 10. Centralized Reporting Pros Standards and best practices
- 11. Centralized Reporting Pros Flexibility Organizations that use
- 12. Centralized Reporting Pros Ability to support individuals
- 13. Centralized Reporting Pros Spot analytics trends vs.
- 14. Centralized Reporting Pros Better management of resources
- 15. Centralized Reporting Cons Specific departments do not
- 16. Play to Organizational Strengths Centralized vs. decentralized
- 17. Play to Organizational Strengths The primary benefit
- 18. More about this topic Hospital Data Warehouse:
- 19. For more information:
- 20. Other Clinical Quality Improvement Resources Click to
Слайд 2Healthcare Reporting
One of the questions that often comes up as healthcare
The answer I usually give is:
Слайд 3Healthcare Reporting
At Health Catalyst we believe in a concept touted by
Highly aligned means everyone shares the same strategic goals–team interactions are focused on strategies.
Loosely coupled means different groups have the flexibility to approach tactics differently as needed.
Слайд 4Healthcare Reporting
The approach is much like the offense on an NFL
The coaching staff develops a game plan and the overall strategic approach the team will take to win the game.
However, during the game, the offensive and defensive coordinators call the plays according to the game plan.
That is highly aligned.
Слайд 5Healthcare Reporting
Suppose at the line of scrimmage the quarterback sees a
He has the freedom to call an audible and make a tactical decision that is still highly aligned with the team’s overall strategy.
Слайд 6Healthcare Reporting
The purpose of analytics in a healthcare organization is to
Analysts are the conduits that collects various data points from different sources that allows non-analysts understand and act on it.
The tactics they use depend on the organizational structure.
Слайд 7Basics of Centralized vs. Decentralized
Organizations generally take one of two
One is a centralized model, where the analytics group is its own entity, independent of any particular group.
In a decentralized model, the analysts work directly for the different groups or departments.
Слайд 8Basics of Centralized vs. Decentralized
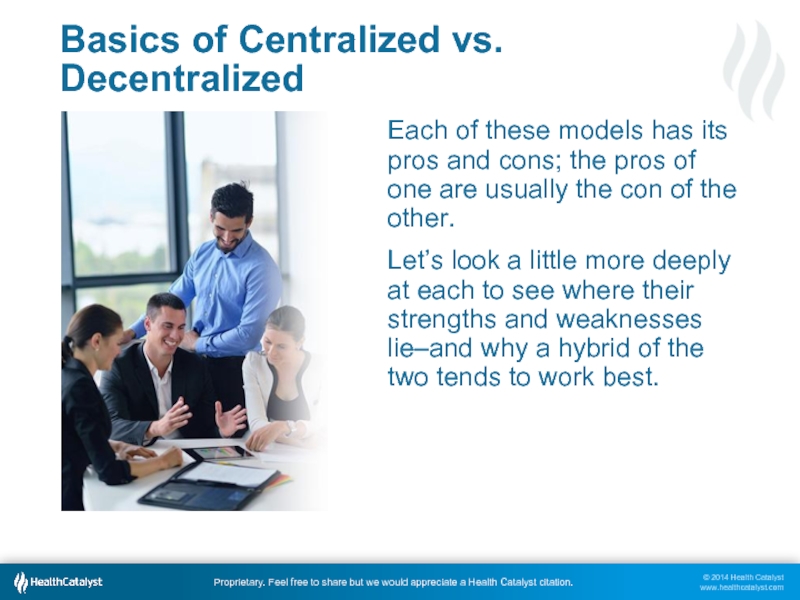
Each of these models has its
Let’s look a little more deeply at each to see where their strengths and weaknesses lie–and why a hybrid of the two tends to work best.
Слайд 9Centralized Reporting Pros
The centralized model has many advantages.
Overall, if you
The strengths of the centralized model follow:
Слайд 10Centralized Reporting Pros
Standards and best practices vs. a maverick approach
This begins
Having a standard set of reporting tools ensures it can be done almost instantly.
Слайд 11Centralized Reporting Pros
Flexibility
Organizations that use a centralized approach can shift resources
Слайд 12Centralized Reporting Pros
Ability to support individuals with different skillsets
In a centralized
Слайд 13Centralized Reporting Pros
Spot analytics trends vs. analytics islands
In a decentralized model;
When reporting is centralized the organization can aggregate reports from multiple areas and build customized dashboards that enables executives to get ahead of trends.
Слайд 14Centralized Reporting Pros
Better management of resources
In a centralized model, management is
Слайд 15Centralized Reporting Cons
Specific departments do not control their destiny
In many cases
A dissatisfied department Might say, “Fine, if IT can’t help me, I will go hire my own people.”
This common attitude is typically what drives organizations to go to a decentralized model.
Слайд 16Play to Organizational Strengths
Centralized vs. decentralized reporting doesn’t have to be
Organizations with the most success are the ones that combine the two to keep their reporting processes highly aligned yet loosely coupled – giving them the best of each while overcoming each model’s negatives.
Слайд 17Play to Organizational Strengths
The primary benefit is that analytic efforts are
With a lot of low-hanging fruit out there it’s easy to take advantage of immediate opportunities.
If their work aligns with the overall organization’s strategy they don’t need to follow the formal processes that are part of the centralized model.
Слайд 18More about this topic
Hospital Data Warehouse: The Best Tool for Efficient
Physician Reporting: The Secret to Useable, Engaging Reports Dr. Ed Corbett, Medical Officer
Data Analyst Saves Hospital Millions John Wadsworth, Vice President, Client Engagement
4 Ways Healthcare Data Analysts Can Provide Their Full Value Russ Staheli, Vice President, Analytics
Self-Service Hospital Reporting Possibilities Brian Eliason, Vice President, Client Engagement and Kristi Mousel, Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing Professional
Link to original article for a more in-depth discussion.
Healthcare Reporting: Centralized vs. Decentralized
Слайд 20Other Clinical Quality Improvement Resources
Click to read additional information at www.healthcatalyst.com
Russell Staheli joined Catalyst as a data architect in October 2011. He started his career as an Intern and later Outcomes Analyst at Intermountain Healthcare in the Institute for Health Care Delivery Research supporting the Advanced Training Program for Executives & QI Leaders (ATP) and the Primary Care Clinical Program. Before coming to Catalyst he worked as a Management Engineer Programmer Analyst for the Duke University Health System in their Performance Services department supporting their Infection Control and Epidemiology efforts.
While there, he also worked as an external consultant to advance the analytical work of the Duke Infection Control Outreach Network (DICON), a collaborative of over 30 community hospitals. Russ holds an Master of Public Health in Health Policy and Administration from University of North Carolina Chapel Hill and a Bachelor’s degree in Health Services Research from the University of Utah.