- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
DIARRHOEA презентация
Содержание
- 1. DIARRHOEA
- 3. Introduction Diarrhoea is defined as passage of
- 4. Types & Causes Based on Clinical Syndrome
- 5. Diarrhoea: types, etiology, pathogenesis Acute (up
- 6. TRANSMISSION Most of the diarrheal agents are
- 8. Pathophysiological Mechanisms secretory diarrhea (increased intestinal secretion)
- 9. secretory diarrhea (increased intestinal secretion) Osmotic diarrhea
- 10. Symptoms Accompany Diarrhoea 1. Dehydration Diarrhea can
- 11. Signs of dehydration in infants and young
- 12. SIGNS OF DEHYDRATION
- 13. 2. Functional bowel disorders: Diarrhea can
- 15. LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS Stool microscopy Dark field microscopy
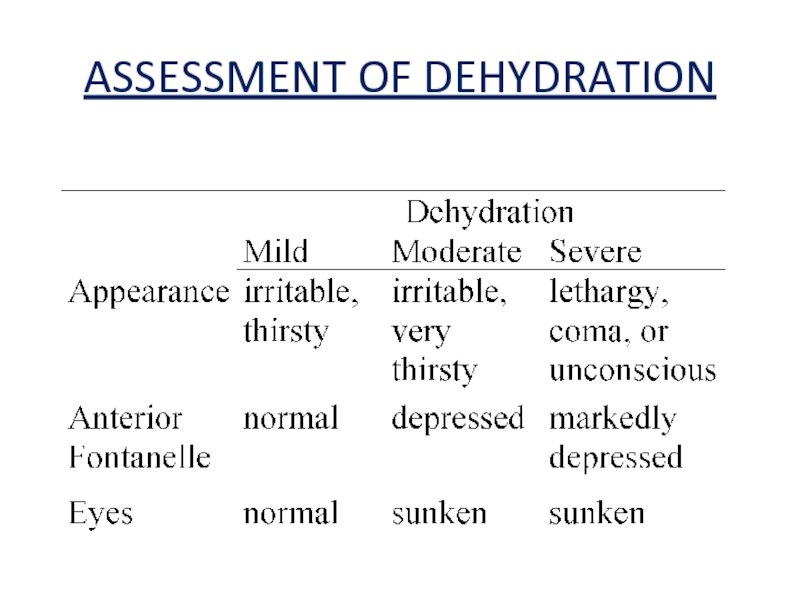
- 16. ASSESSMENT OF DEHYDRATION
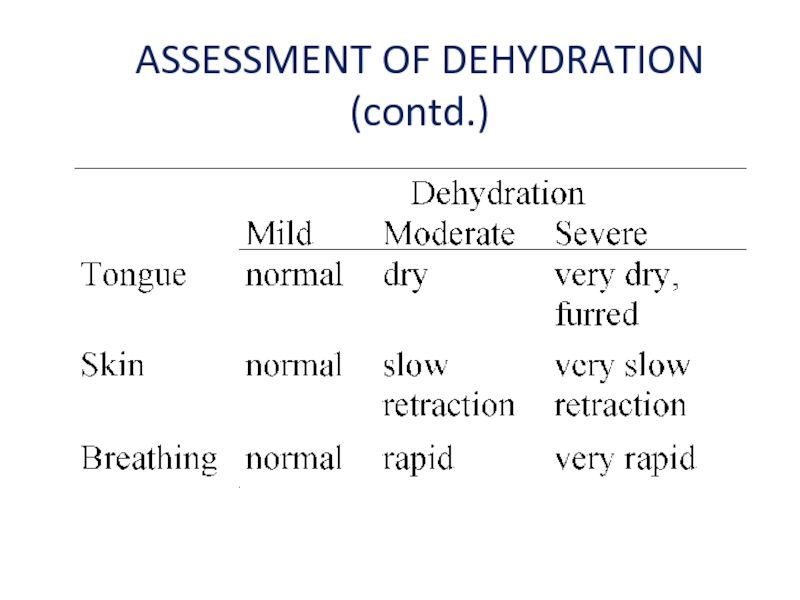
- 17. ASSESSMENT OF DEHYDRATION (contd.)
- 18. ASSESSMENT OF DEHYDRATION (contd.)
- 19. DIARRHOEA: PREVENTION AND CONTROL
- 20. When should
- 21. When should children with diarrhea
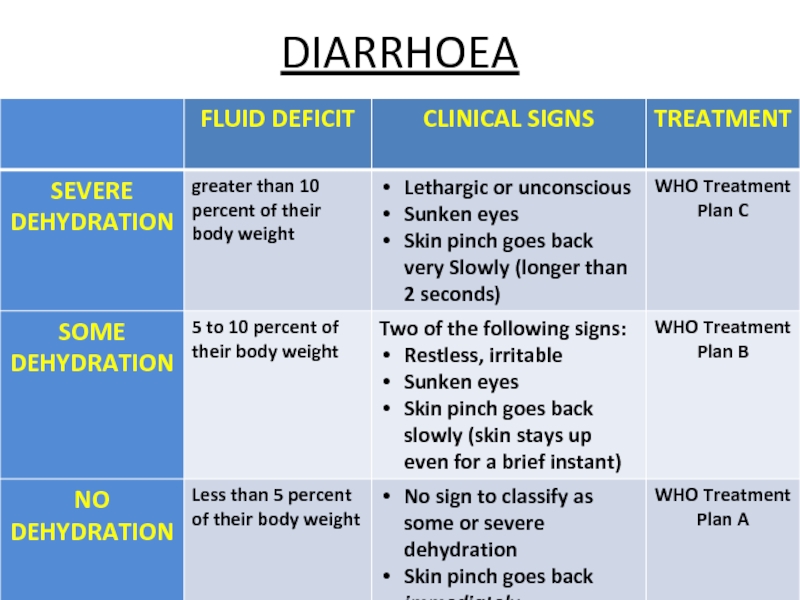
- 23. DIARRHOEA
- 24. WHO Treatment Plan C Severe dehydration require
- 25. Ringer's lactate solution is the preferred commercially
- 26. WHO Treatment Plan B Some dehydration The
- 27. WHO Treatment Plan A Plan A focuses
- 28. ORAL REHYDRATION SALT(ORS) It is a balanced
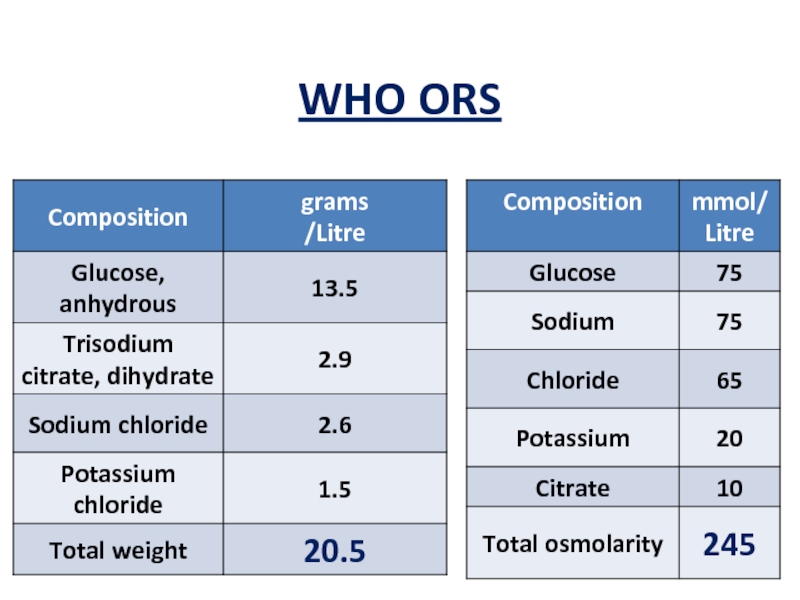
- 29. WHO ORS
- 30. RICE BASED ORS Tastes better and provides
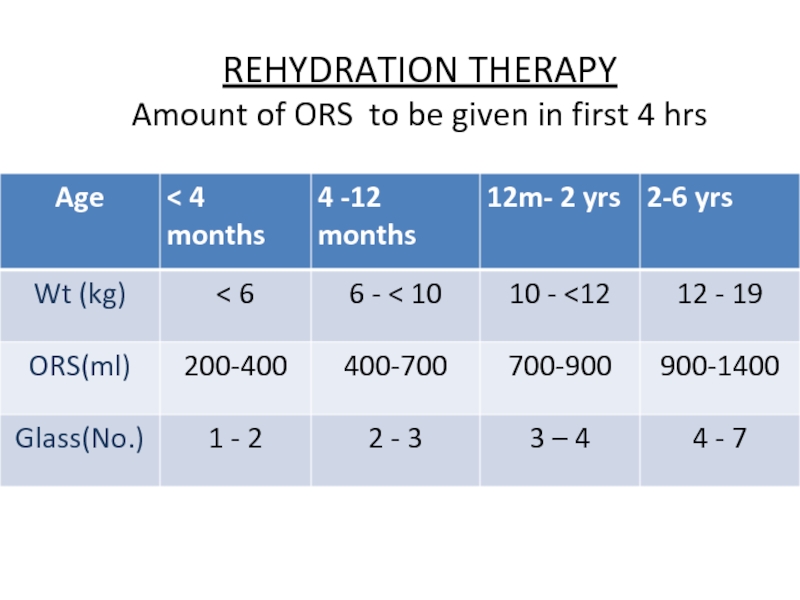
- 31. REHYDRATION THERAPY Amount of ORS to be given in first 4 hrs
- 32. Rate & Quantities of I/V infusion for severe dehydration
- 33. ZINC THERAPY 10 mg/day orally for 14 days in children
- 34. Role of Probiotics
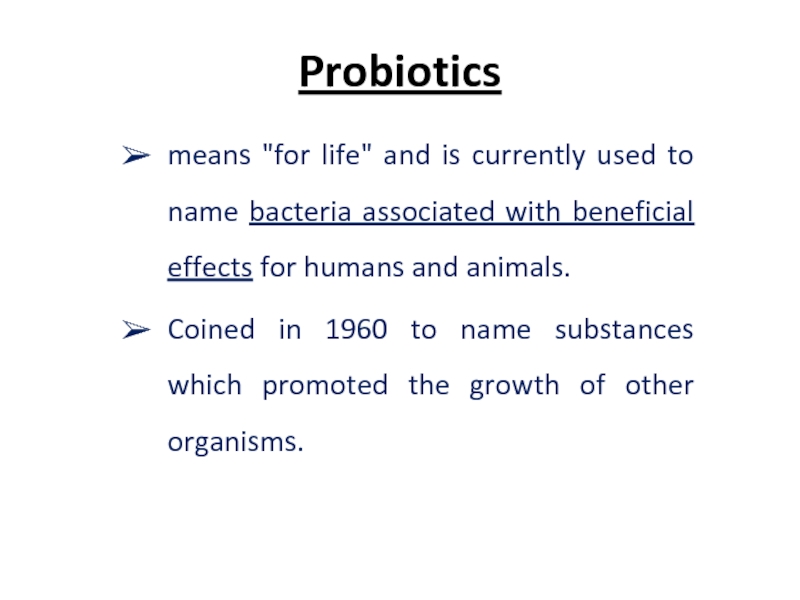
- 35. Probiotics means "for life" and is currently
- 36. Effect of probiotics in diarrhoea- The strongest
- 37. POTENTIAL USES OF PROBIOTICS Diarrhoea Helicobacter
- 38. FEEDING IN DIARRHOEA Children should continue to
- 39. To make foods-energy dense some of preparation
- 40. Rota virus vaccination Rotashield vaccine -1999 Withdrawn
- 42. -
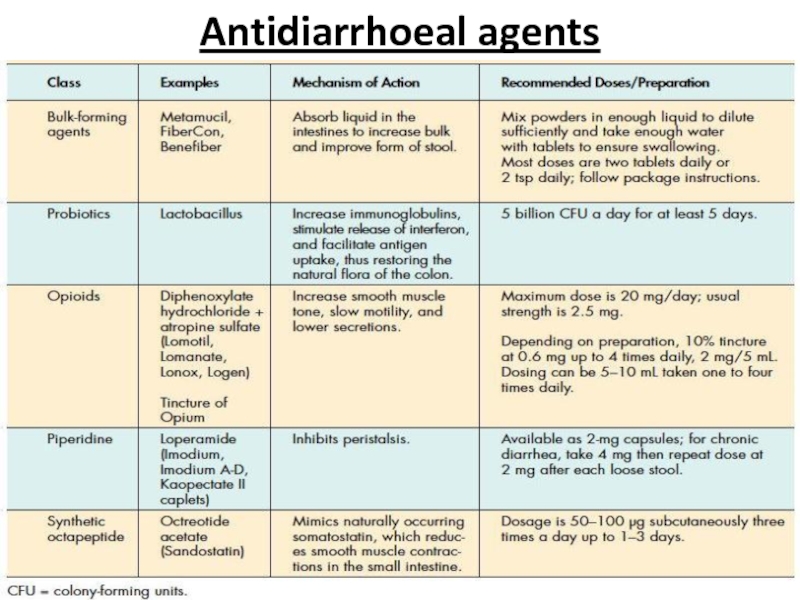
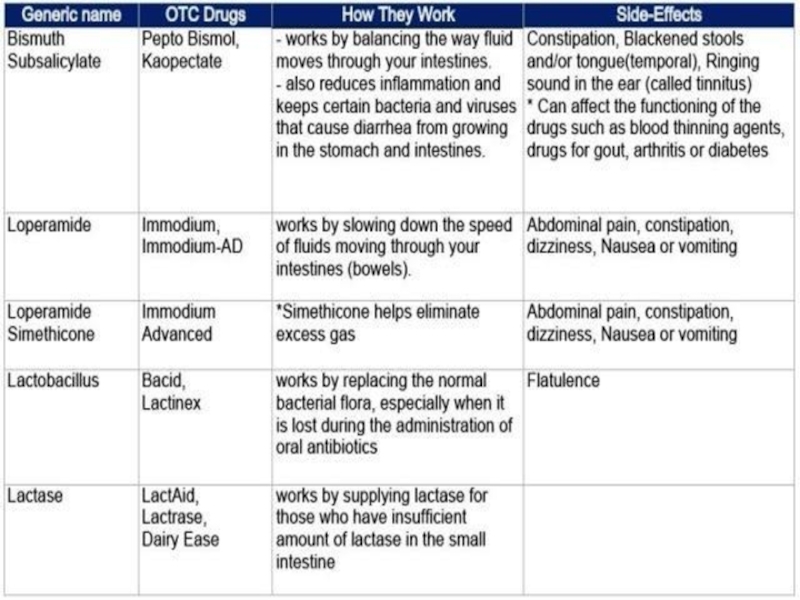
- 43. Antidiarrhoeal agents
- 45. Thanks
Слайд 3Introduction
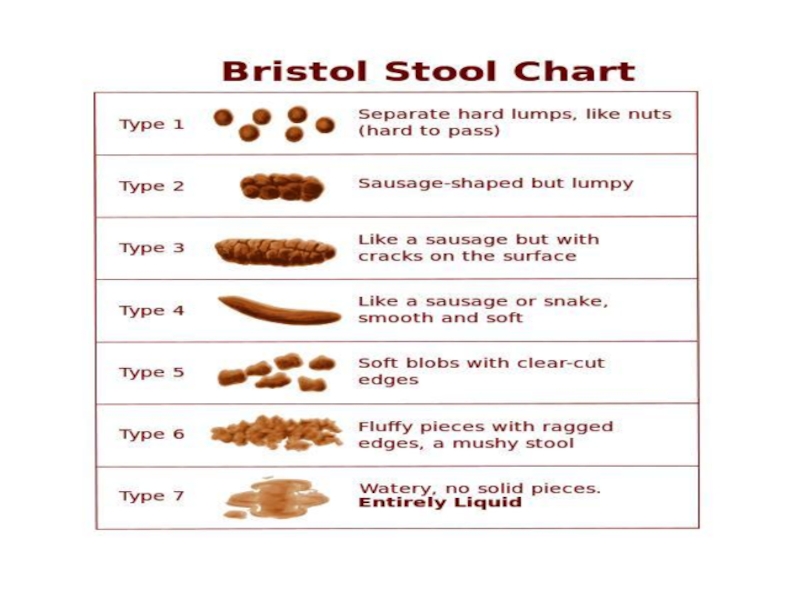
Diarrhoea is defined as passage of unusually loose or watery stools
For adults stool weight >200 g/d can generally be considered diarrhoeal.
Passage of even one large watery stool in young child is diarrhoea.
Frequent passage of normal stool is no diarrhoea.
Слайд 4Types & Causes Based on Clinical Syndrome
Diarrhoea
Persistent
Multiple cause
Dysentery
Bacillary
Amoebic
Watery
Cholera
E. coli
Rotavirus
Слайд 5Diarrhoea: types, etiology, pathogenesis
Acute (up to 1-2 weeks)
Food poisoning (due for
Bacterial infections: E.coli, Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter, Yersinia
Viral infections: Rotavirus
Protozoan infections: Entamoeba, Giardia lamblia
Drugs:
antibiotics (Сl.deficile)
laxatives
antacids (Mg)
anticholinesterase drugs
colchicin
preparations with Au
quinidine
cardiac glycosides
Chronic (> 4 weeks)
Osmotic diarrhoea (osmotic laxatives and lactose)
Secretory diarrhoea (bacterial toxins, hormones, fatty and bile acids, laxatives)
Inflammatory diarrhoea (infections, inflammatory bowl diseases, celiacia, lymphoma, iscemia)
Hypermotoric diarrhoea (irritated bowl syndrome)
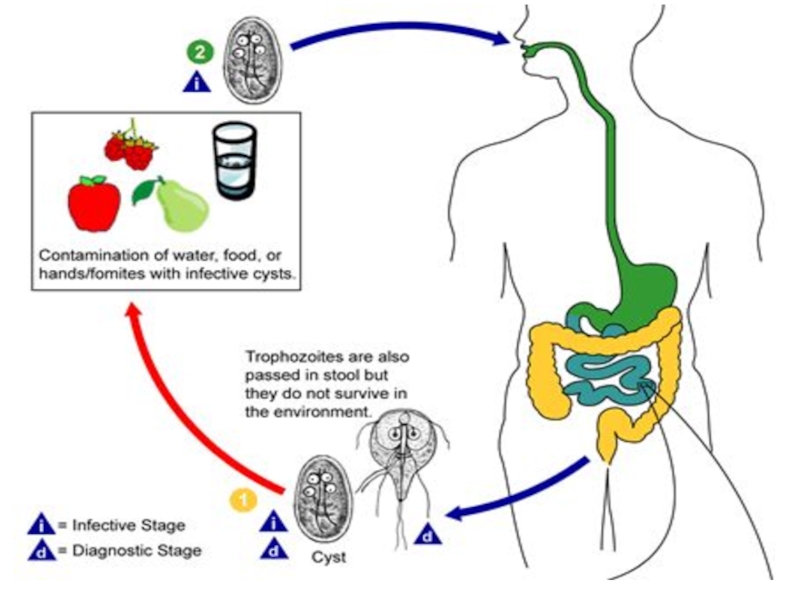
Слайд 6TRANSMISSION
Most of the diarrheal agents are transmitted by the fecal-oral route
Cholera:
Some viruses (such as rotavirus) can be transmitted through air
Nosocommial transmission is possible
Shigellosis (blood dysentery) is mainly transmitted person-to-person
Shigellosis is a water-washed disease; transmitted more when there is scarcity of water
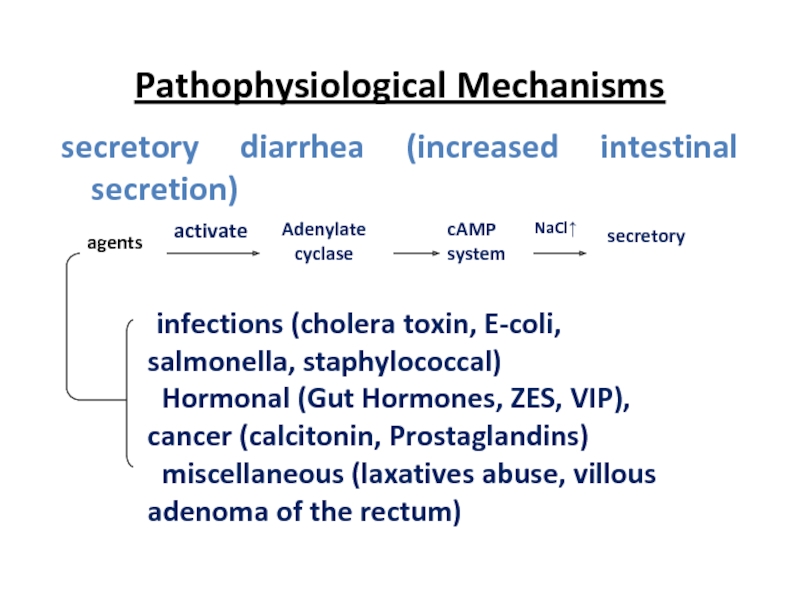
Слайд 8Pathophysiological Mechanisms
secretory diarrhea (increased intestinal secretion)
infections (cholera toxin, E-coli, salmonella,
Hormonal (Gut Hormones, ZES, VIP), cancer (calcitonin, Prostaglandins)
miscellaneous (laxatives abuse, villous adenoma of the rectum)
agents
Adenylate cyclase
cAMP system
secretory diarrhea
activate
NaCl↑
Слайд 9secretory diarrhea (increased intestinal secretion)
Osmotic diarrhea
Decreased intestinal surface area and/or intestinal
Inflammatary diarrhea
Rapid transit of intestinal contents (shortened transit time)
secretory diarrhea (increased intestinal secretion)
Osmotic diarrhea
Decreased intestinal surface area and/or intestinal absorption
Inflammatary diarrhea
Rapid transit of intestinal contents (shortened transit time)
Pathophysiological Mechanisms
Слайд 10Symptoms Accompany Diarrhoea
1. Dehydration
Diarrhea can cause dehydration. Loss of electrolytes through
Signs of dehydration in adults include:
• thirst
• less frequent urination than usual
• dark-colored urine
• dry skin
• fatigue
• dizziness
• light-headedness
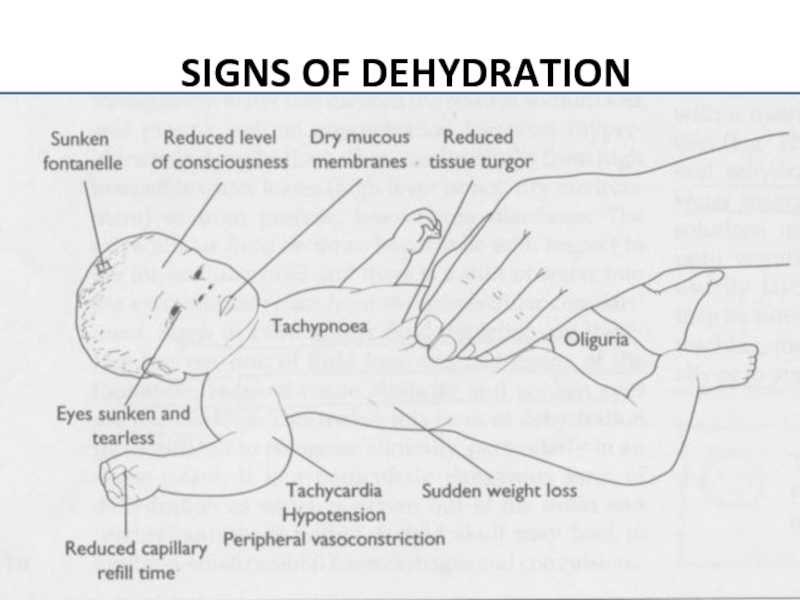
Слайд 11Signs of dehydration in infants and young
children include:
dry mouth
no tears when crying
no wet diapers for 3 hours or more
sunken eyes, cheeks, or soft spot in the skull
high fever
listlessness or irritability
Слайд 13
2. Functional bowel disorders: Diarrhea can be a symptom of irritable
3. Intestinal diseases: Inflammatory bowel disease, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, and celiac disease often lead to diarrhea.
4. Food intolerances and sensitivities: Some people have difficulty digesting certain ingredients, such as lactose, the sugar found in milk and milk products. Some people may have diarrhea if they eat certain types of sugar substitutes in excessive quantities.
5. Reaction to medicines: Antibiotics, cancer drugs, and antacids containing magnesium can all cause diarrhea.
Слайд 15LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
Stool microscopy
Dark field microscopy of stool for cholera
Stool cultures
ELISA for
Immunoassays, bioassays or DNA probe tests to identify E. coli strains
Слайд 20
When should adults with diarrhea see a health care provider?
Adults
should see a health care provider:
signs of dehydration
diarrhea for more than 24 hours
a fever of 102 degrees or higher
stools containing blood or pus
stools that are black and tarry
Слайд 21
When should children with diarrhea see a health care
provider?
Children with any
should see a health care provider:
signs of dehydration
diarrhea for more than 24 hours
a fever of 102 degrees or higher
stools containing blood or pus
stools that are black and tarry
Слайд 24WHO Treatment Plan C
Severe dehydration require immediate IV infusion, nasogastric or
Give 100 ml/kg IV fluids.
Слайд 25Ringer's lactate solution is the preferred commercially available solution.
If IV
When referral takes more than 30 minutes, fluids should be given by nasogastric tube.
If none of these are possible and the child can drink, ORS must be given by mouth.
Слайд 26WHO Treatment Plan B
Some dehydration
The approximate amount of ORS required is
After four hours, the child is reassessed and reclassified for dehydration, and feeding should begin
If dehydration persists- the same amount of ORS may be repeated for another 4 hours.
If the child is breastfed, breast-feeding should continue
Слайд 27WHO Treatment Plan A
Plan A focuses on the three rules of
Give extra fluids,
Continue feeding, and
Advise the caretaker when to return to the health facility
if the child develops blood in the stool, drinks poorly, becomes sicker, or is not better in 48 hours
Слайд 28ORAL REHYDRATION SALT(ORS)
It is a balanced mixture of glucose and electrolytes
Almost
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Sodium promotes absorption of water from the intestine
Glucose promotes the absorption of sodium and water from the intestine
Слайд 30RICE BASED ORS
Tastes better and provides more calories than the glucose-based
Culturally acceptable,
Reduces stool volume (by about 40 %)
Shortens the duration of diarrhea in both cholera and other severe diarrheal diseases.
Starches other than rice, including wheat flour and maize, have also been shown to reduce stool volume in patients with cholera.
Reduce diarrhea by adding more substrate to the gut lumen without increasing osmolality, thus providing additional glucose molecules for glucose-mediated absorption.
Слайд 33ZINC THERAPY
10 mg/day orally for 14 days in children
20 mg/day orally for 14 days in children ≥6 months of age
It is used as adjunct therapy (in all cases of diarrhoea) that decreases the duration and severity of the episode and the likelihood of subsequent infections on the 2-3 months following treatment.
Слайд 35Probiotics
means "for life" and is currently used to name bacteria associated
Coined in 1960 to name substances which promoted the growth of other organisms.
Слайд 36Effect of probiotics in diarrhoea-
The strongest evidence of a beneficial effect
These probiotics are effective for both treatment and prevention of acute diarrhoea caused mainly by rotavirus in children
Antibiotic associated diarrhoea has also been found to respond when probiotics have been used as prophylaxis and also for therapy
Слайд 37POTENTIAL USES OF PROBIOTICS
Diarrhoea
Helicobacter pylori infection
Inflammatory bowel disease
Cancers
To increase Immunity
Allergy
Heart disease
Urogenital
Слайд 38FEEDING IN DIARRHOEA
Children should continue to be fed during diarrhoea.
Milk
Milk can also be given as milk cereal mixture e.g. dalia, milk-rice mixture.
This technique reduces the lactose load & preserving energy density.
Слайд 39To make foods-energy dense some of preparation are:-
- Khichri with
- Rice with curd & sugar
- Mashed banana with milk or curd
- Mashed potatoes with oil.
Breast feeding should be continued uninterrupted even during rehydration with ORS.
FEEDING IN DIARRHOEA
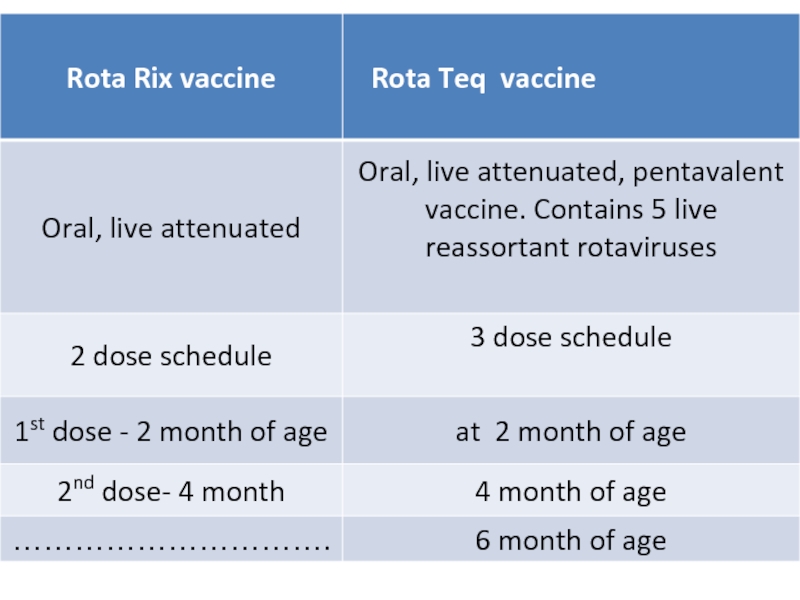
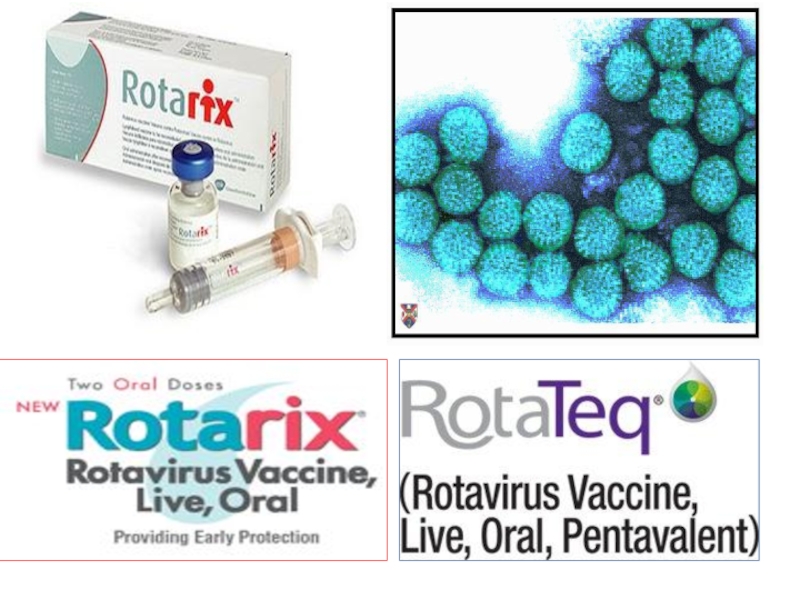
Слайд 40Rota virus vaccination
Rotashield vaccine -1999
Withdrawn because of its association with intussuscption
Two
The first dose administered between ages 6-10 weeks .
subsequent doses at intervals 4-10 weeks.
Vaccination should not be initiated before 6weeks and after 12 weeks of age.
All doses should be administered before 32 weeks.