- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
РНР hypertext preprocessor language презентация
Содержание
- 1. РНР hypertext preprocessor language
- 2. Include Files The include (or require) statement
- 3. Example of include
- 4. PHP include vs. require The require statement
- 5. File and file handleing Web Technology- IITU
- 6. Simple syntax to read file in php
- 7. File Open/Read/Close r Open a
- 8. Create and write on File // create
- 9. Forms and Files Web Technology- IITU
- 10. Create The HTML Form
- 11. Create The Upload File PHP Script
- 12. Check if File Already Exists // Check
- 13. Limit File Size // Check file size
- 14. Limit File Type // Allow certain file
- 15. Complete Upload File PHP Script (part 1)
- 16. Complete Upload File PHP Script (part 2)
- 17. Complete Upload File PHP Script (part 3)
- 18. PHP Images from Folder
- 19. Glob () The glob() function returns an
- 20. Count () The count() function returns the
- 21. Opendir () & Readdir () Opendir is
- 22. PHP pathinfo() Function The pathinfo() function returns
- 23. in_array () It searches for a value in an array
- 25. PHP Error Handling
- 26. Error Handling When creating scripts and web
- 27. Example of Error Handling Warning:
- 28. Exception handling Exception handling is used
- 29. Exception handling example When an exception is
- 30. Example of Try, throw and catch
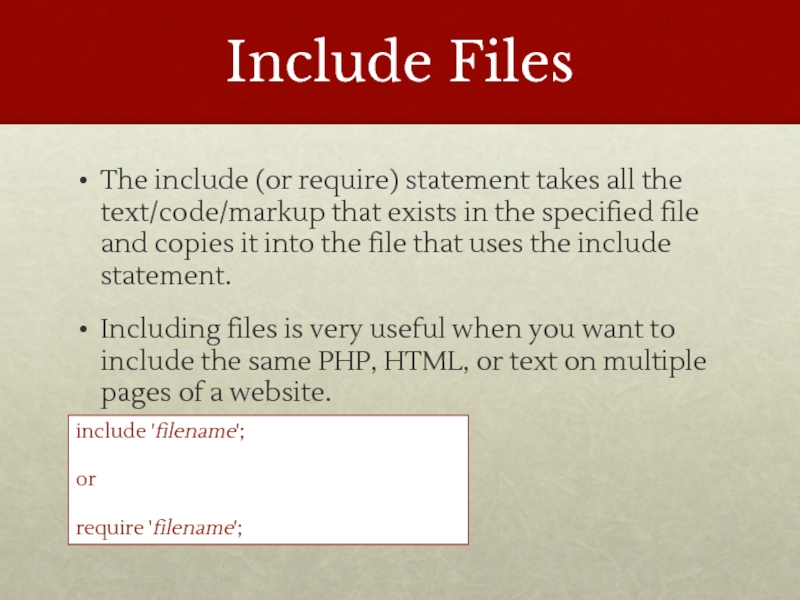
Слайд 2Include Files
The include (or require) statement takes all the text/code/markup that
exists in the specified file and copies it into the file that uses the include statement.
Including files is very useful when you want to include the same PHP, HTML, or text on multiple pages of a website.
Including files is very useful when you want to include the same PHP, HTML, or text on multiple pages of a website.
include 'filename';
or
require 'filename';
Слайд 3Example of include
Welcome to my home page!
Some
text.
Some more text.