- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Risk management презентация
Содержание
- 1. Risk management
- 2. Where are we? 1. Introduction 2.
- 3. Outline What is Risk? Risk Identification: Threshold
- 4. Outcomes Understand the key parts of the
- 5. What is Risk? A risk is a
- 6. What is Risk? There are a very
- 7. What is Risk? Risk is the result
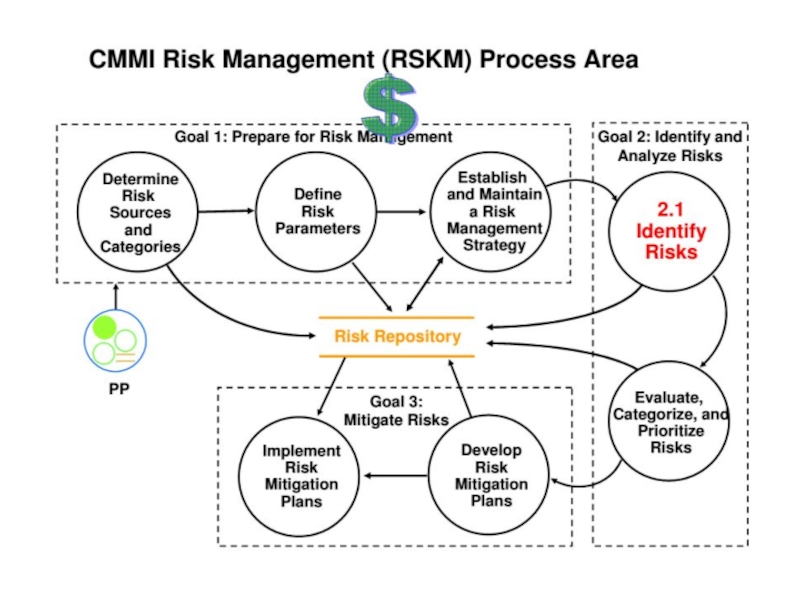
- 8. Key of Risk Management Risk Identification Risk
- 9. Key of Risk Management
- 10. Adult games A team is put
- 11. Threshold of Success Defining and committing to
- 12. Threshold of Success Clearly identifies what the
- 13. Threshold of Success A good Threshold of
- 14. Threshold of Success Building a Threshold of
- 15. Threshold of Success The threshold of success
- 16. Threshold of Success ToS statement:s We
- 17. As part of a larger, comprehensive project
- 18. Five main risk impact areas in SD:
- 19. New, unproven technologies. The majority of software projects
- 20. User and functional requirements. Software requirements capture all
- 21. Application and system architecture. Taking the wrong direction
- 22. Performance. It’s important to ensure that any risk
- 23. Organizational. Organizational problems may have adverse effects
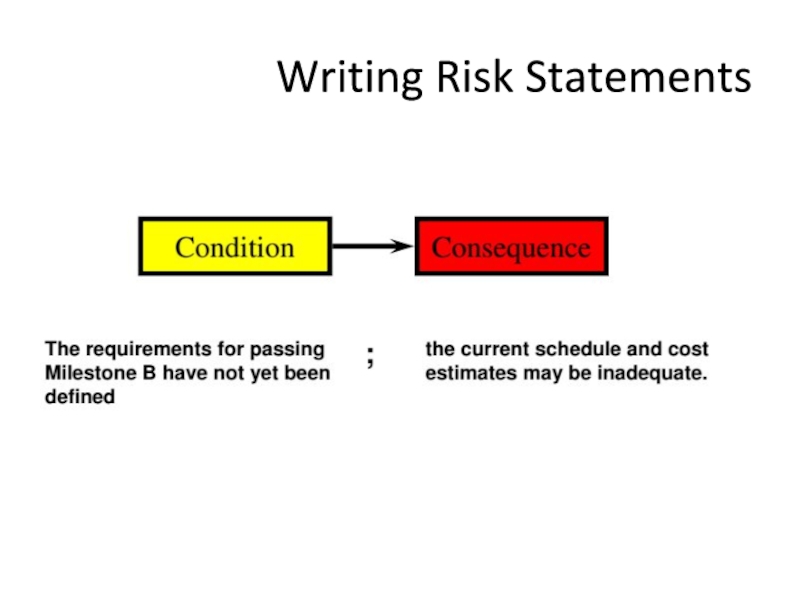
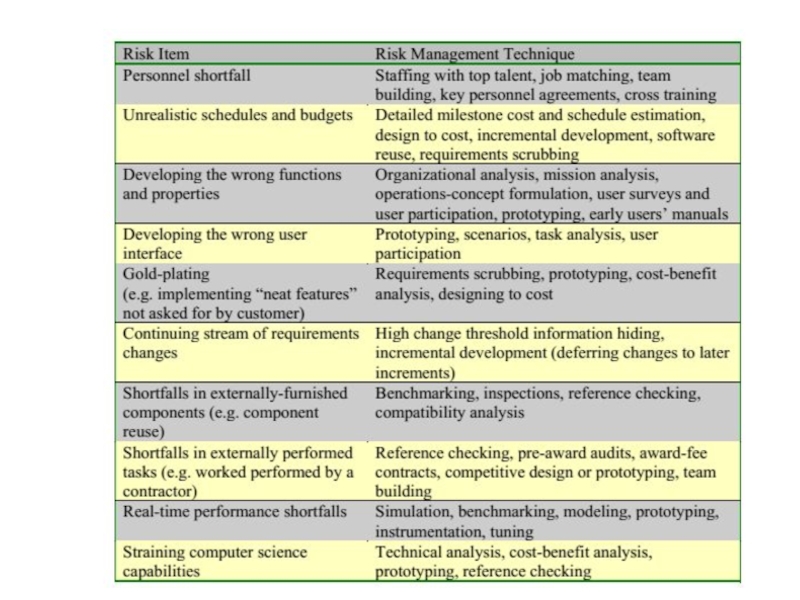
- 24. Writing Risk Statements
- 25. Writing Risk Statements
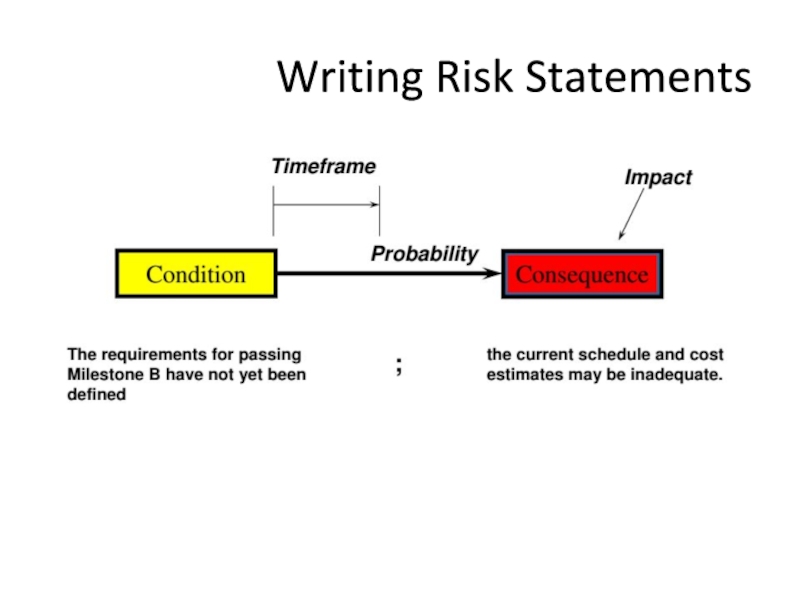
- 26. Writing Risk Statements
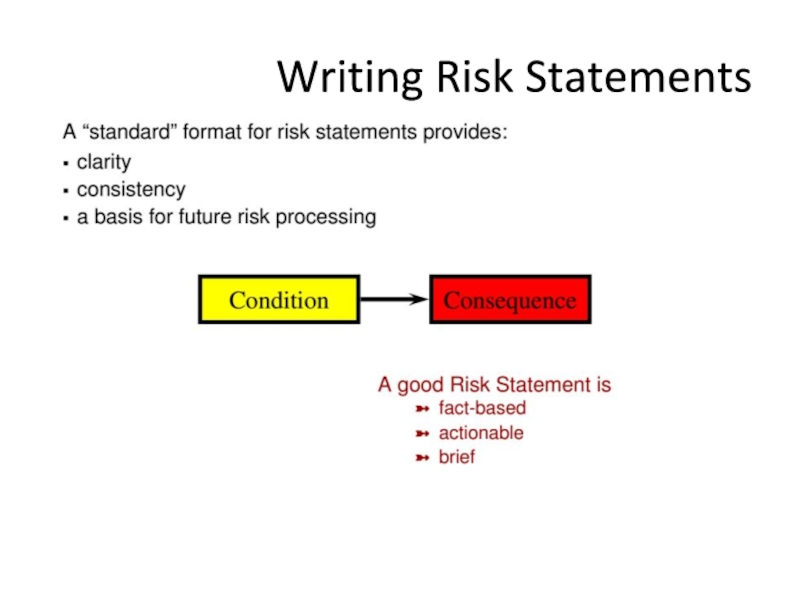
- 27. Writing Risk Statements
- 28. Lack of executive sponsorship (maybe because of
- 30. Risk prioritization Probability Very Improbable Improbable
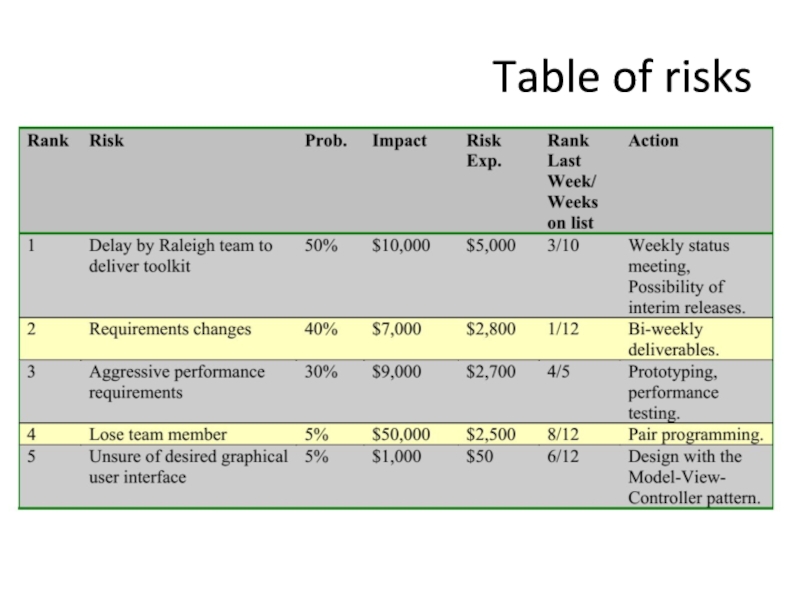
- 32. Table of risks
- 33. Key Ideas for Risk Management:
- 34. Risk management includes the following tasks:
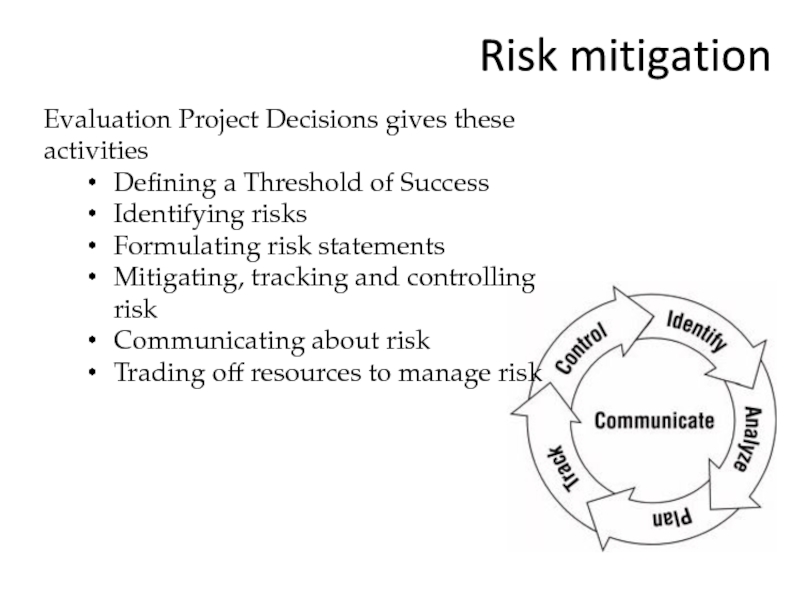
- 35. Risk mitigation Evaluation Project Decisions gives these
- 36. Summary: A work team identifying risks needs
Слайд 2
Where are we?
1. Introduction
2. Project Life Cycles
3. Project Artifacts
4. Work Elements,
5. Risk Management
Risk Management Plan
Optional Inclusions
Слайд 3Outline
What is Risk?
Risk Identification: Threshold of Success
Risk Management Plan
Monitoring and Mitigation
Слайд 4Outcomes
Understand the key parts of the Risk Management Plan
Know how to
Be able to write a TOS and begin writing Risks that can impact the TOS.
Have a clear understanding of what it means to mitigate a Risk.
Слайд 5What is Risk?
A risk is a potential future harm that may
(-> all risks have some probability rate of occurrence)
Слайд 6What is Risk?
There are a very few projects with no risk
Software
Risk management is an integral part of software project management
Слайд 7What is Risk?
Risk is the result of making decisions
Every decision has
Risk is neither good or bad it just is, the impact might be good or bad
Risk has a probability and an impact
“A problem is a risk whose time has come”
All Risks should be based on a fact
Examples:
Good: A condition exists therefore this event might occur…
Bad: A condition might exist therefore …
Слайд 8Key of Risk Management
Risk Identification
Risk Prioritization
Risk Mitigation
Also:
Risk Analysis – Take
Risk Monitoring – Have a method to identify the status of risks as they change
Слайд 10Adult games
A team is put together to build some software.
Слайд 11Threshold of Success
Defining and committing to a clear picture of success
Слайд 12Threshold of Success
Clearly identifies what the project must minimally do to
Establishes what are “must have” things versus “nice to have” items for the project
Provides a clear view of what must be done and therefore a clear view of what might impact what must be done
i.e., The risks of the project.
Слайд 13Threshold of Success
A good Threshold of Success is made up of
SMART is a mnemonic which stands for -
Short/Specific
Measurable
Achievable
Relevant
Time bound.
Слайд 14Threshold of Success
Building a Threshold of Success
The easiest way to create
Example: Failure for my current project might look something like this.
Essential features are not ready by the end of the second quarter.
Team members are dissatisfied or bored with their jobs.
Newly hired team members don't feel like they're part of the team by March 31.
There isn't enough money to continue development after this fiscal year and we have to fire people.
Слайд 15Threshold of Success
The threshold of success for my current project might
By the end of the second quarter, all "Must Have" features are implemented and pass acceptance tests with no known critical defects.
All team members give average score of 5 or better on a job satisfaction survey taken quarterly.
By March 31, the team has successfully executed at least three team building activities with all team members present.
Funds of at least $1 million are secured by December 31 to allow for future development without a reduction in team size.
Слайд 16Threshold of Success
ToS statement:s
We MUST do X or have shown
Слайд 17 As part of a larger, comprehensive project plan, the risk management
Risk management plan
Слайд 18Five main risk impact areas in SD:
New, unproven technologies
User and functional
Application and system architecture
Performance
Organizational
Risk management plan
Слайд 19New, unproven technologies. The majority of software projects entail the use of
Risk management plan
Слайд 20User and functional requirements. Software requirements capture all user needs with respect
Risk management plan
Слайд 21Application and system architecture. Taking the wrong direction with a platform, component,
Risk management plan
Слайд 22Performance. It’s important to ensure that any risk management plan encompasses user
Risk management plan
Слайд 23Organizational. Organizational problems may have adverse effects on project outcomes. Project
Risk management plan
Слайд 28Lack of executive sponsorship (maybe because of change in the Administration);
The majority of software-to-software interfaces are not defined & controlled; incomplete interfaces results in no benefits from [the project].
There has been inadequate schedule discipline (milestones, slippage, monitor progress, good project management) on this project; with no intervention the project will continue to slip & slide.
Example
Слайд 30Risk prioritization
Probability
Very Improbable
Improbable
Probable
Frequent
Impact
Negligible
Marginal
Critical
Catastrophic
Numerical Value
Risk Exposure (RE)= P * C
Слайд 34Risk management includes the following tasks:
Identify risks and their triggers
Classify and prioritize all
Craft a plan that links each risk to a mitigation
Monitor for risk triggers during the project
Implement the mitigating action if any risk materializes
Communicate risk status throughout project
Risk mitigation
Слайд 35Risk mitigation
Evaluation Project Decisions gives these activities
Defining a Threshold of Success
Identifying
Formulating risk statements
Mitigating, tracking and controlling risk
Communicating about risk
Trading off resources to manage risk
Слайд 36Summary:
A work team identifying risks needs to agree on an end-point
There needs to be a standard way of capturing (documenting) a risk.
Facilitators need practice to become comfortable writing risks in front of a group.
There are many ways for program management to support good risk identification:
Encourage documentation of risks privately at the working team level
Integrate risk identification and management into normal project management
Accept any risk identified into the repository – don’t “vet them out”
Acknowledge that the program’s decision-makers are the real “risk managers,” and have the decision-makers step up to the job