- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Assembly language презентация
Содержание
- 1. Assembly language
- 2. Overview and Aims LMC is a
- 3. What is in a Computer? Memory CPU I/O
- 4. Simple Computer Processor CPU Memory Data
- 5. Memory Each location has
- 6. Quiz – What is the Memory?
- 7. Registers (or Accumulators) Control lines
- 8. Memory I/O I/O CPU Write a program here
- 9. LMC CPU Structure Visible
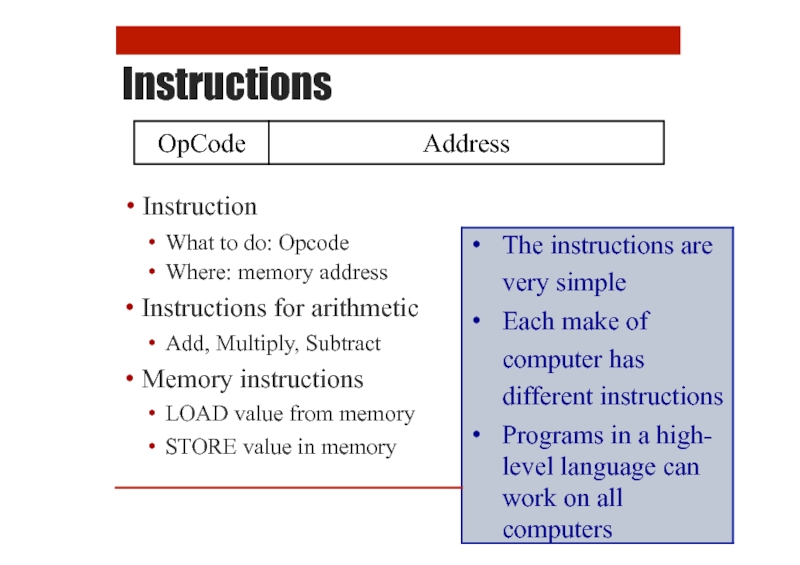
- 10. Instructions The primitive language of a computer
- 11. Instructions Instruction OpCode Address
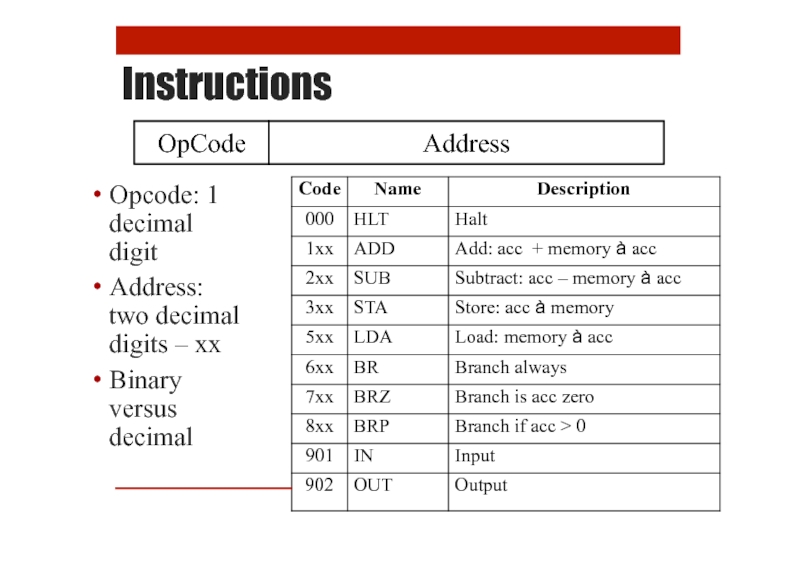
- 12. Instructions Opcode: 1 decimal digit Address: two
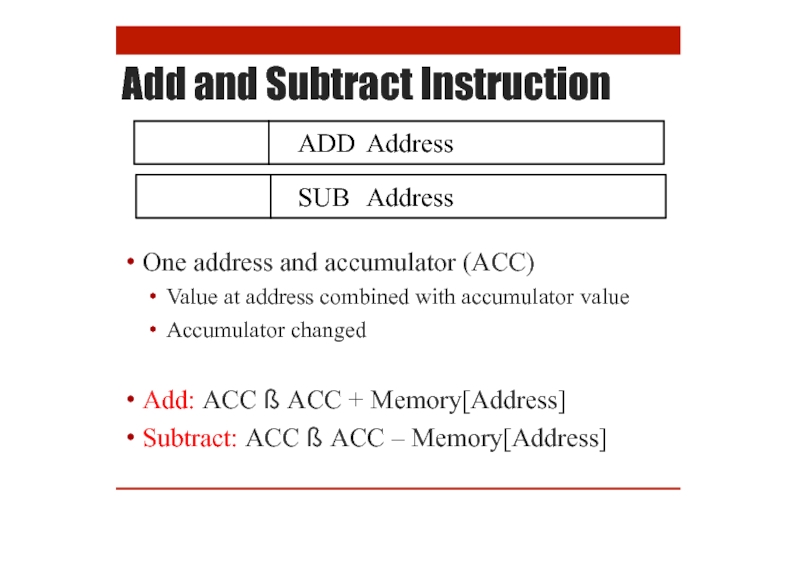
- 13. Add and Subtract Instruction
- 14. Load and Store Instruction
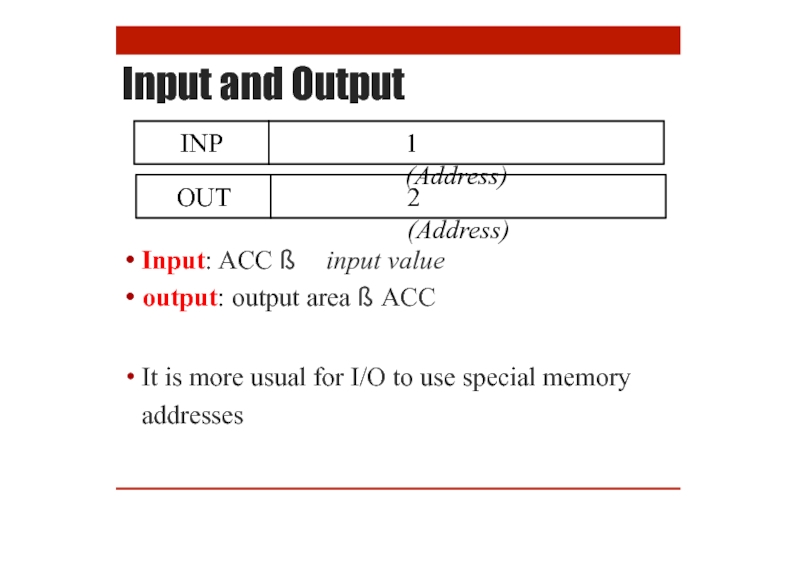
- 15. Input and Output Input: ACC ß input
- 16. Branch Instructions Changes program counter May
- 17. Assembly Code Numbers Memory holds
- 18. LMC Example
- 19. Simple Program x = y +
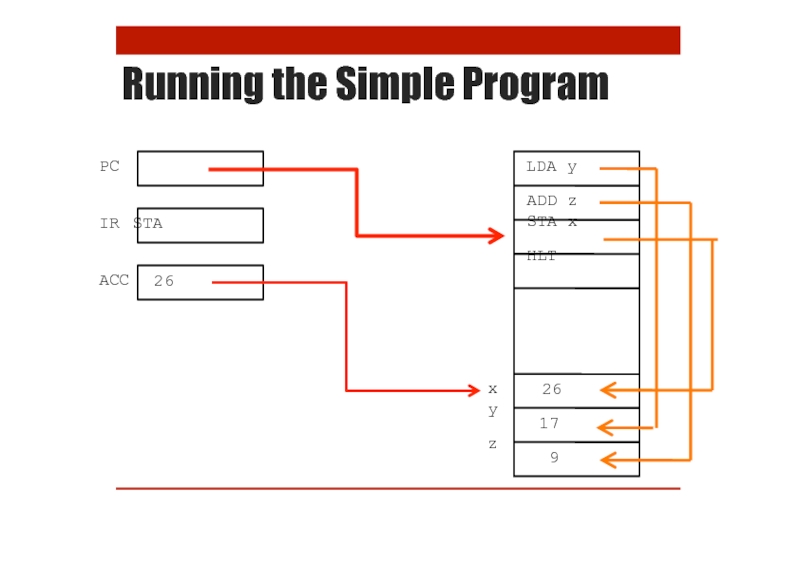
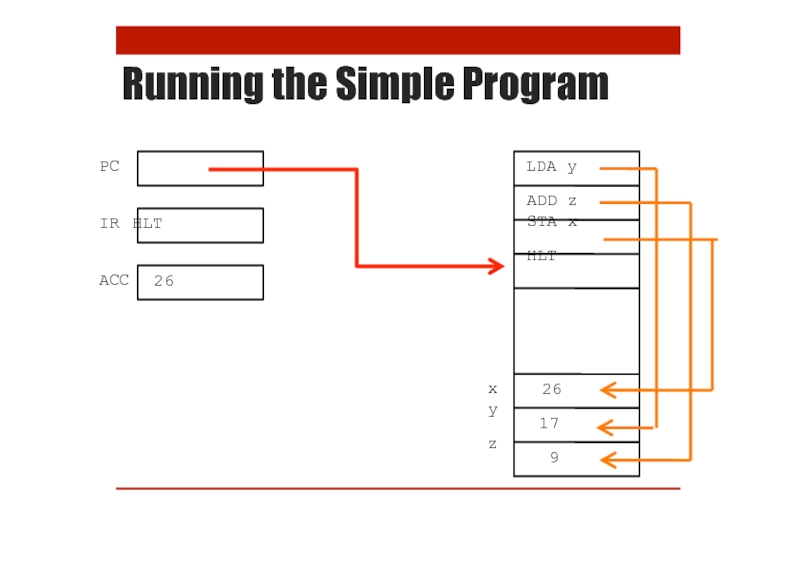
- 20. Running the Simple Program
- 21. Running the Simple Program
- 22. Running the Simple Program
- 23. Running the Simple Program
- 24. Practice Exercises Try the first three exercises on the practical sheet
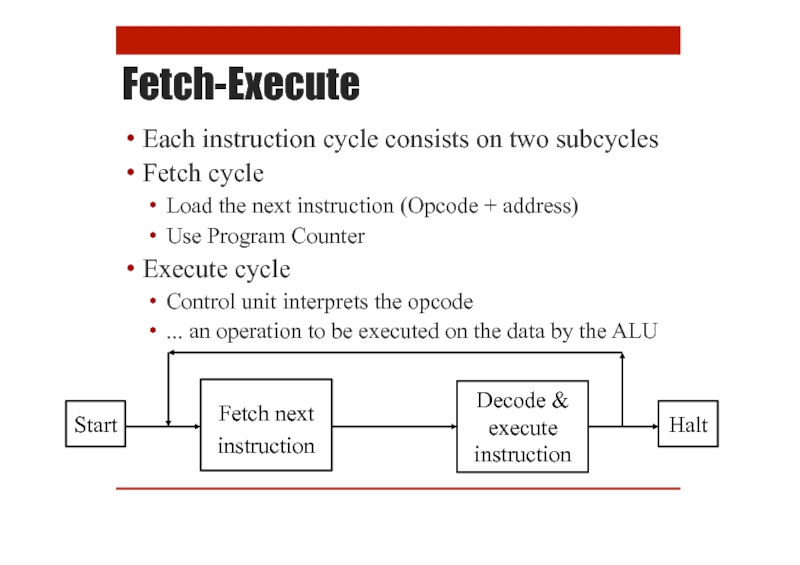
- 25. Fetch-Execute Cycle How the Computer Processes Instructions
- 26. Fetch-Execute Each instruction cycle consists on
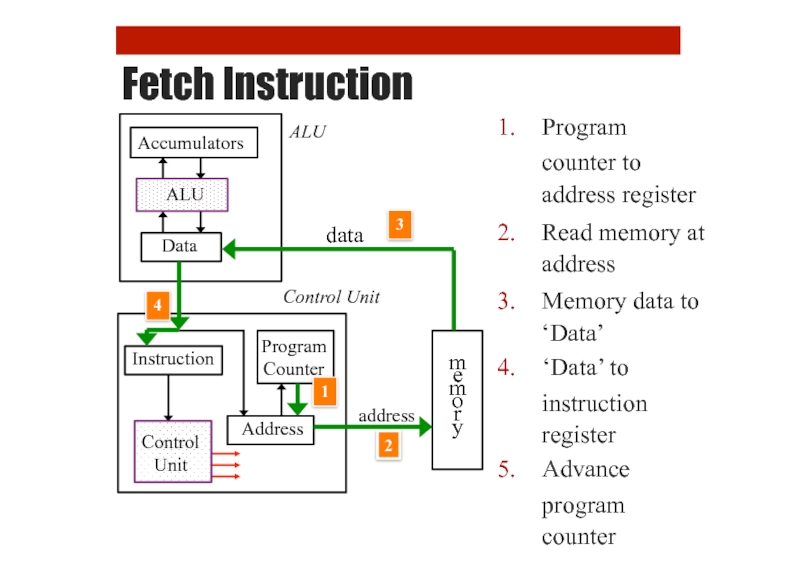
- 27. Fetch Instruction Program counter to
- 28. Execute Instruction Decode instruction Address
- 29. What We Can Learn from
- 30. Understanding Variables and Assignment What is
- 31. Understanding Variables and Assignment What is
- 32. Understanding If and Loops Calculate the
- 33. Compiler Compiler translates high level program
- 34. Why We Need An OS LMC
- 35. Summary of CPU Architecture Memory contains
- 36. Project: Writing an LMC Interpreter
- 37. Write a Simple LMC Emulator def fetch(memory):
Слайд 1
CAS London CPD Day 2016
Little Man Computer
Teaching London Computing
William Marsh School
Queen Mary University of London
Слайд 2
Overview and Aims
LMC is a computer simulator
… understanding how a computer
To program the LMC, must understand:
Memory addresses
Instructions
Fetch-execute cycle
Practical exercises
What we can learn from LMC
Слайд 4
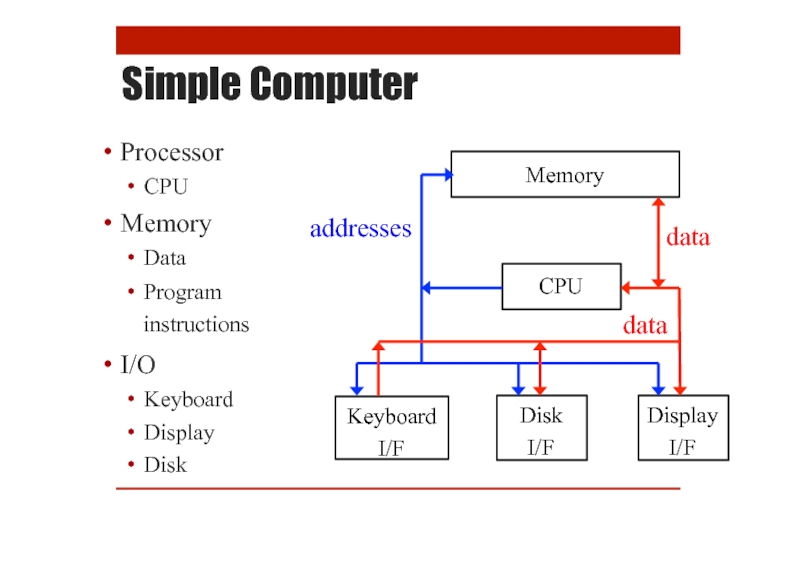
Simple Computer
Processor
CPU
Memory
Data
Program instructions
I/O
Keyboard
Display
Disk
Memory
Keyboard I/F
CPU
Disk I/F
Display I/F
data
data
addresses
Слайд 5
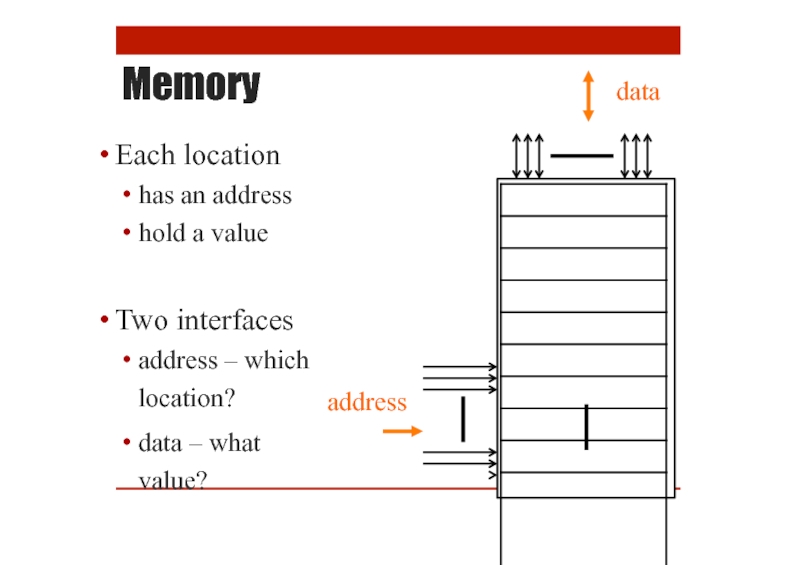
Memory
Each location
has an address
hold a value
Two interfaces
address – which location?
data –
address
data
Слайд 7
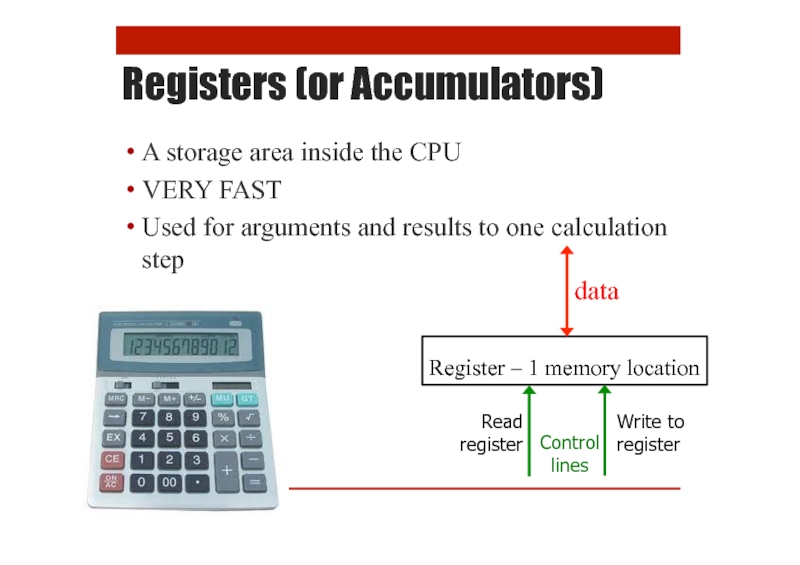
Registers (or Accumulators)
Control lines
A storage area inside the CPU
VERY FAST
Used for
data
Register – 1 memory location
Read register
Write to register
Слайд 9
LMC CPU Structure
Visible registers shown in red
Accumulators
Data for calculation
Data
Word to/from memory
PC
Address
Instruction
Address
For memory access
Program Counter
Mem Address
Instruction
MEM Data
ALU
Accumulator
Control
Unit
m
e
m
o
r
y
address
data
Control Unit
ALU
Слайд 12Instructions
Opcode: 1
decimal
digit
Address:
two decimal
digits – xx
Binary
versus
decimal
OpCode
Address
Слайд 13
Add and Subtract Instruction
ADD Address
SUB Address
One address and accumulator (ACC)
Value at address combined
Accumulator changed
Add: ACC ß ACC + Memory[Address]
Subtract: ACC ß ACC – Memory[Address]
Слайд 14
Load and Store Instruction
LDA Address
STA Address
Move data between memory and accumulator (ACC)
Load: ACC
Store: Memory[Address] ß ACC
Слайд 15
Input and Output
Input: ACC ß input value
output: output area ß ACC
It is
INP
1 (Address)
OUT
2 (Address)
Слайд 16
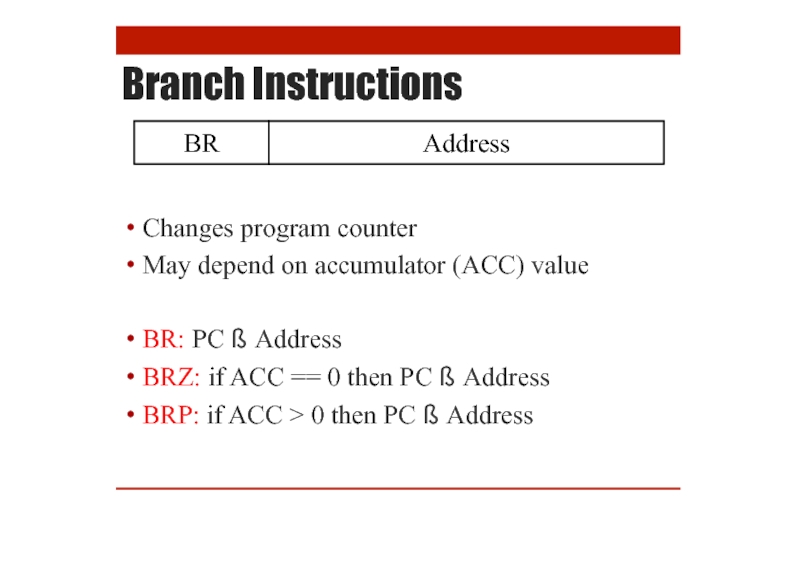
Branch Instructions
Changes program counter
May depend on accumulator (ACC) value
BR: PC ß
BRZ: if ACC == 0 then PC ß Address
BRP: if ACC > 0 then PC ß Address
BR
Address
Слайд 17
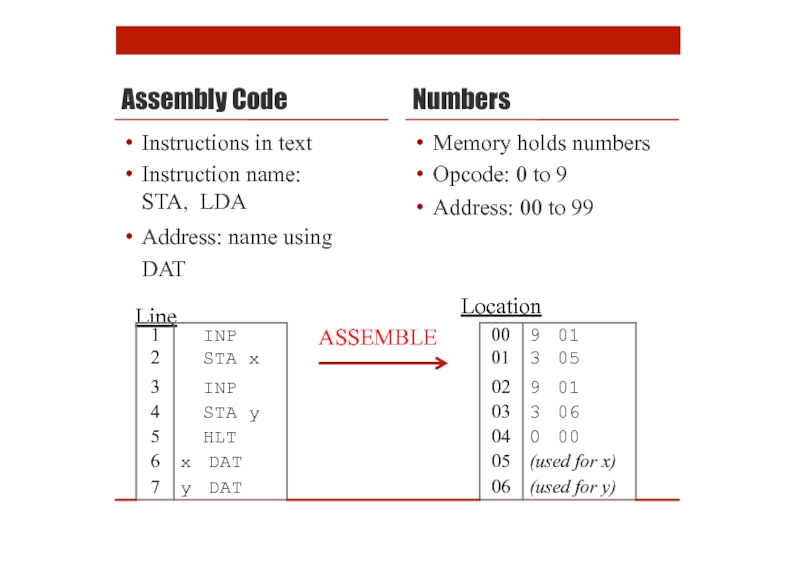
Assembly Code
Numbers
Memory holds numbers
Opcode: 0 to 9
Address: 00 to 99
Instructions in
Instruction name: STA, LDA
Address: name using DAT
Line
Location
Слайд 26
Fetch-Execute
Each instruction cycle consists on two subcycles
Fetch cycle
Load the next instruction
Use Program Counter
Execute cycle
Control unit interprets the opcode
... an operation to be executed on the data by the ALU
Start
Decode & execute instruction
Fetch next instruction
Halt
Слайд 27
Fetch Instruction
Program
counter to address register
Read memory at address
Memory data to ‘Data’
‘Data’
instruction register
Advance
program counter
Program
Counter
Address
Instruction
Data
Accumulators
m
e
m
o
r
y
address
data
Control Unit
ALU
1
2
3
4
ALU
Control
Unit
Слайд 28
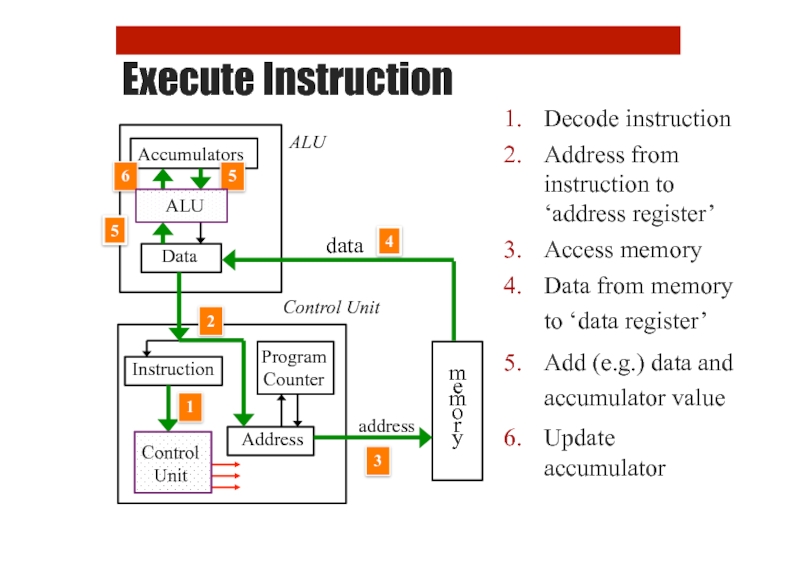
Execute Instruction
Decode instruction
Address from instruction to ‘address register’
Access memory
Data from memory
Add (e.g.) data and accumulator value
Update
accumulator
Program Counter
Address
Instruction
Data
Accumulators
m
e
m
o
r
y
address
data
Control Unit
ALU
1
2
3
4
5
5
6
ALU
Control
Unit
Слайд 29
What We Can Learn from LMC
How programming language work
What a compiler
Why we need an OS
Слайд 30
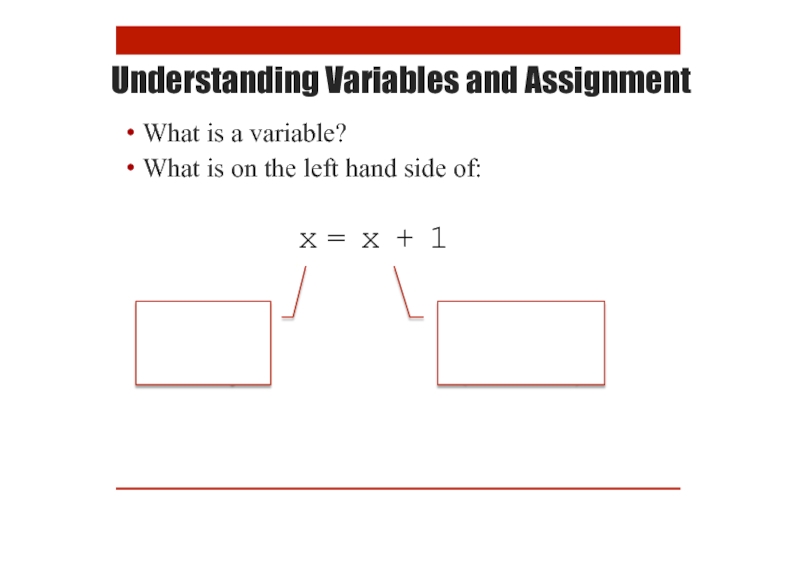
Understanding Variables and Assignment
What is a variable?
What is on the left
x = x + 1
Слайд 31
Understanding Variables and Assignment
What is a variable?
What is on the left
A[x+1] = 42
Слайд 32
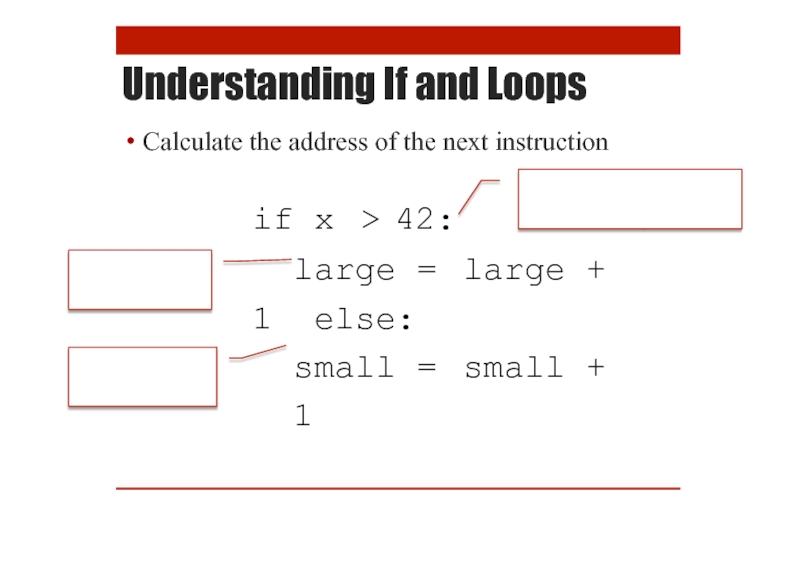
Understanding If and Loops
Calculate the address of the next instruction
if x > 42:
large
small = small + 1
Слайд 33
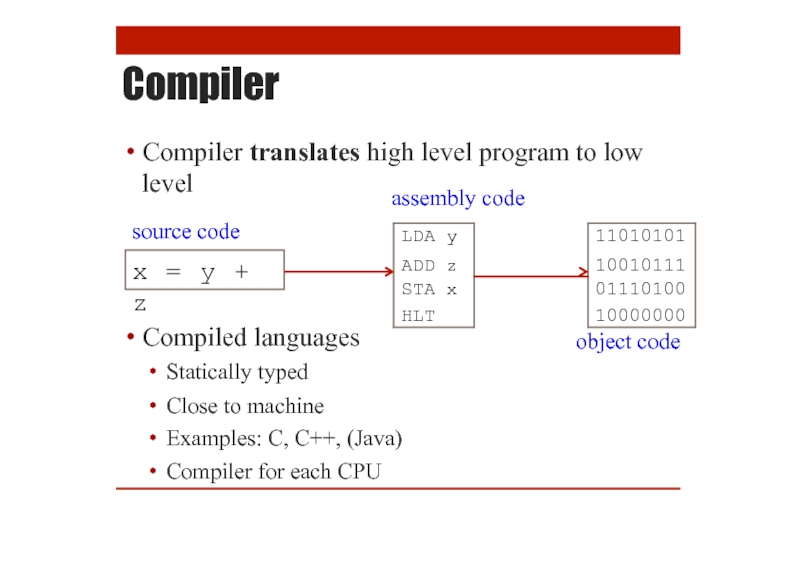
Compiler
Compiler translates high level program to low
Compiled languages
Statically typed
Close to machine
Examples:
Compiler for each CPU
level
source code
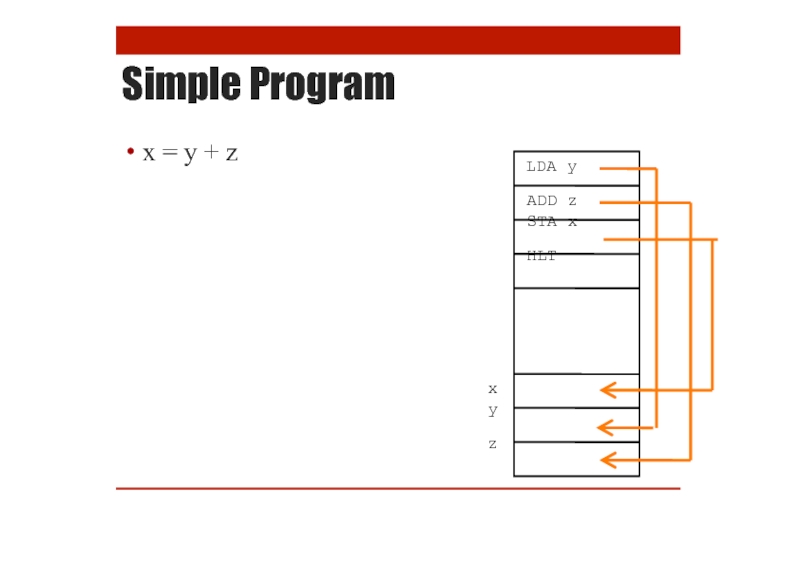
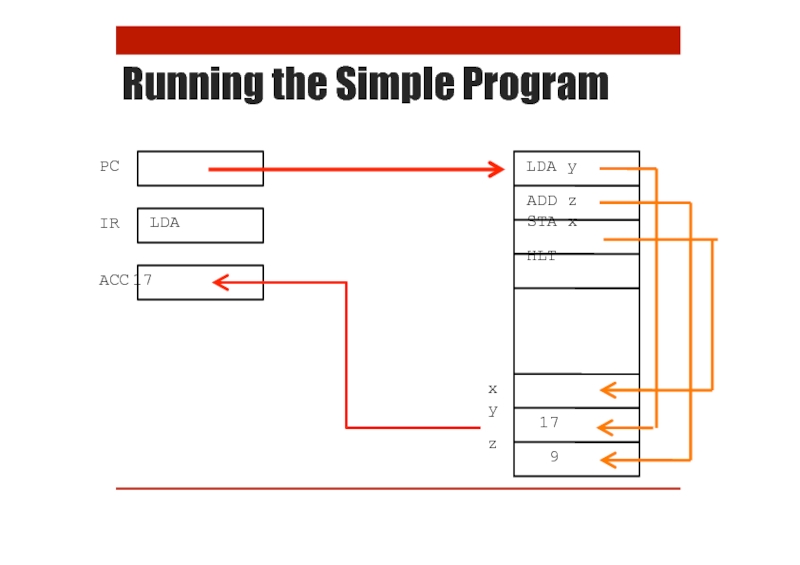
x = y + z
assembly code
object code
Слайд 34
Why We Need An OS
LMC
Only one program
Program at fixed place in
No
Disk
Screen
• …
Real Computer
Many programs at once
Program goes anywhere in memory
Complex I/O
Слайд 35
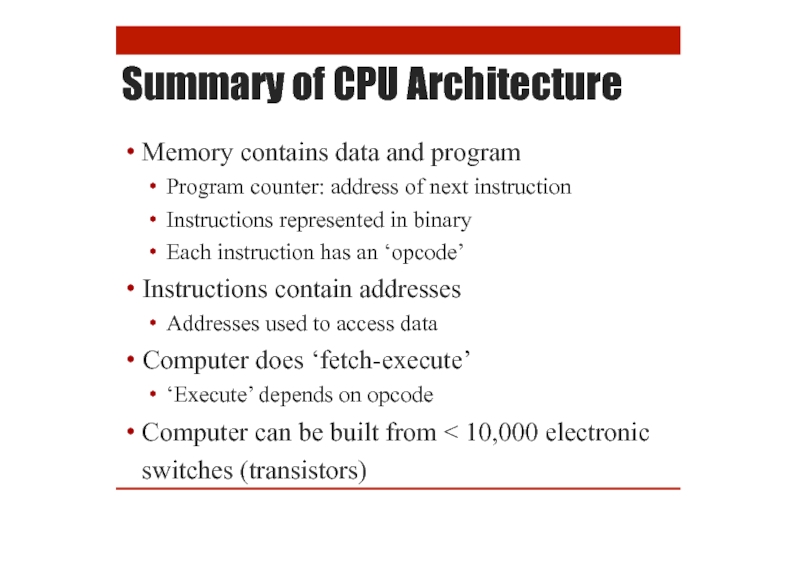
Summary of CPU Architecture
Memory contains data and program
Program counter: address of
Instructions represented in binary
Each instruction has an ‘opcode’
Instructions contain addresses
Addresses used to access data
Computer does ‘fetch-execute’
‘Execute’ depends on opcode
Computer can be built from < 10,000 electronic switches (transistors)
Слайд 37
Write a Simple LMC Emulator
def fetch(memory): global pc, mar mar = pc
pc = pc
readMem(memory)
def readMem(memory): global mdr
mdr = memory[mar]
acc = 0
mdr = 0
mar = 0
pc = 0 memory =
[504,105,306, 0,
11, 17,...]
def execute(memory, opcode,
arg):
global acc, mar, mdr, pc if opcode == ADD:
mar = arg
readMem(memory) acc = acc + mdr
elif opcode == SUB:
mar = arg readMem(memory) acc = acc – mdr
...






![Load and Store InstructionLDA AddressSTA AddressMove data between memory and accumulator (ACC)Load: ACC ß Memory[Address]Store: Memory[Address] ß ACC](/img/tmb/6/508821/37264f77960ca3ce5cf3a3b186651b8e-800x.jpg)





![Understanding Variables and AssignmentWhat is a variable?What is on the left hand side of:A[x+1] = 42](/img/tmb/6/508821/251035f661319fc0012681da77467fe3-800x.jpg)


![Write a Simple LMC Emulatordef fetch(memory): global pc, mar mar = pcpc = pc + 1readMem(memory)def readMem(memory): global mdrmdr = memory[mar]acc = 0mdr = 0mar = 0pc](/img/tmb/6/508821/c5729f9a54941aa6589aa7e74c74a4af-800x.jpg)





