- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
3. Java Persistence API. 4. Java Persistence Query Language презентация
Содержание
- 1. 3. Java Persistence API. 4. Java Persistence Query Language
- 2. * Queries (1 of 2) In JPA:
- 3. * Queries (2 of 2) A query
- 4. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao
- 5. MerchantDaoImpl Class @Repository public class MerchantDaoImpl implements
- 6. MerchantServiceImpl Class @Named public class MerchantServiceImpl implements
- 7. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 8. * Java Persistence Query Language Java
- 9. * Filtering Results JP QL supports the
- 10. * Exercise: Find Payments Find all payments to the given merchant
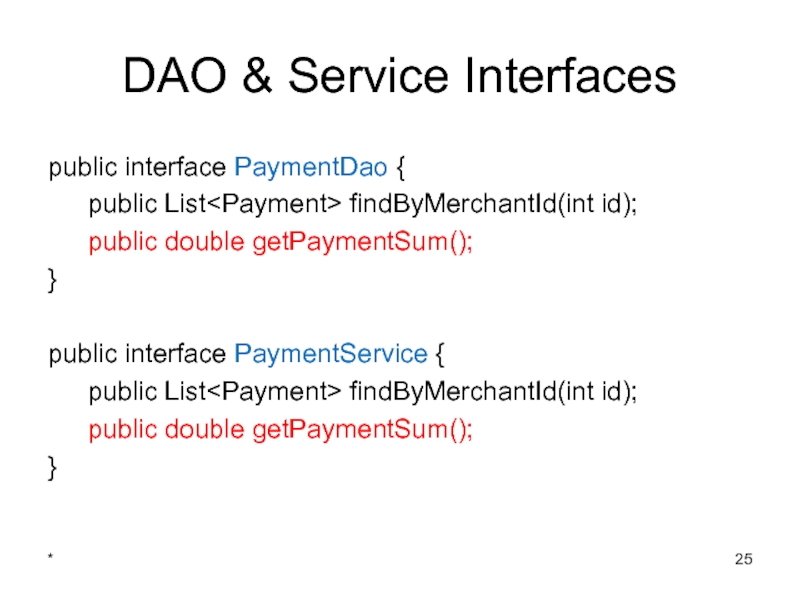
- 11. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao
- 12. PaymentDaoImpl Class @Repository public class PaymentDaoImpl implements
- 13. PaymentServiceImpl Class @Named public class PaymentServiceImpl implements
- 14. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 15. * Exercise: Find Payments See P342PaymentsWhere project for the full text
- 16. * Joins Between Entities Just
- 17. * Join Example Get names of customers
- 18. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface CustomerDao
- 19. CustomerDaoImpl Class public List getNames(double sumPayed){
- 20. CustomerServiceImpl Class public List getNames(double sumPayed){ return customerDao.getNames(sumPayed); } *
- 21. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 22. * Join Example See P343PaymentJoin project for the full text
- 23. * Aggregate Queries There are five supported
- 24. * Aggregate Example Find the sum of all payments
- 25. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao
- 26. PaymentDaoImpl Class public double getPaymentSum(){
- 27. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 28. * Aggregate Example See P344Aggregation project for the full text
- 29. * Query Positional Parameters Parameters are indicated
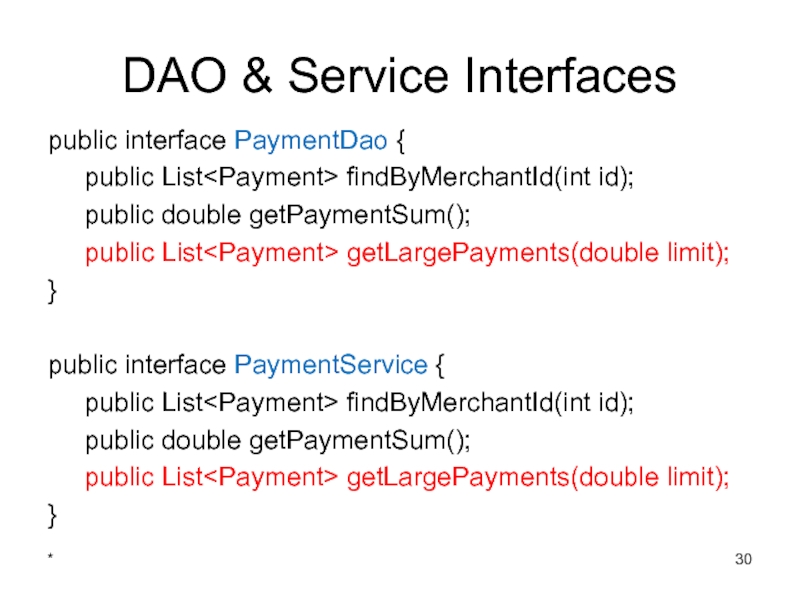
- 30. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface PaymentDao
- 31. PaymentDaoImpl Class public List getLargePayments(double limit){
- 32. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 33. * Query Named Parameters Named parameters may
- 34. PaymentDaoImpl Class public List getLargePayments(double limit){
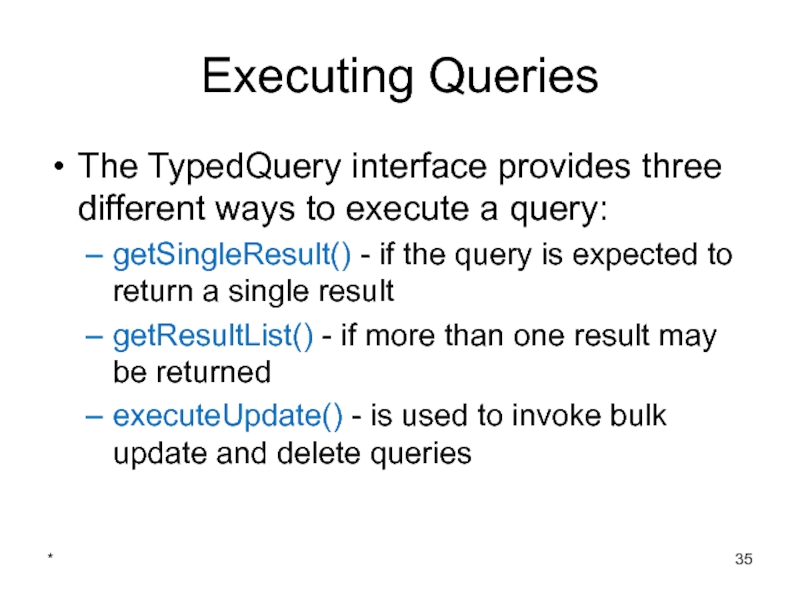
- 35. * Executing Queries The TypedQuery interface provides
- 36. * getResultList() Method Returns a collection containing
- 37. * Exercise: Sort Merchants Create a project
- 38. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao
- 39. MerchantDaoImpl Class public List getSortedByNeedToPay(){
- 40. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 41. * Exercise: Sort Merchants See P346Sort project for the full text
- 42. * getSingleResult() Method Instead of iterating to
- 43. * Working with Query Results The result
- 44. * Constructor expressions (1/2) Provide developers with
- 45. * Constructor expressions (2/2) The argument to
- 46. * Example: Grouping Payments Get
- 47. * Class Result public class Result {
- 48. DAO & Service Interfaces public interface MerchantDao
- 49. MerchantDaoImpl Class public List getTotalReport(){
- 50. Main Class @SuppressWarnings("resource") public static void main(String[]
- 51. * Example: Grouping Payments See P347Grouping project for the full text
Слайд 2*
Queries (1 of 2)
In JPA: SQL -> JP QL (Java Persistence
A query is implemented in code as a Query or TypedQuery object. They are constructed using the EntityManager as a factory
A query can be customized according to the needs of the application
Слайд 3*
Queries (2 of 2)
A query can be issued at runtime by
TypedQuery
List
listM = query.getResultList();
. . . . . . . . . . . .
See P341SelectMerchant project for the full text
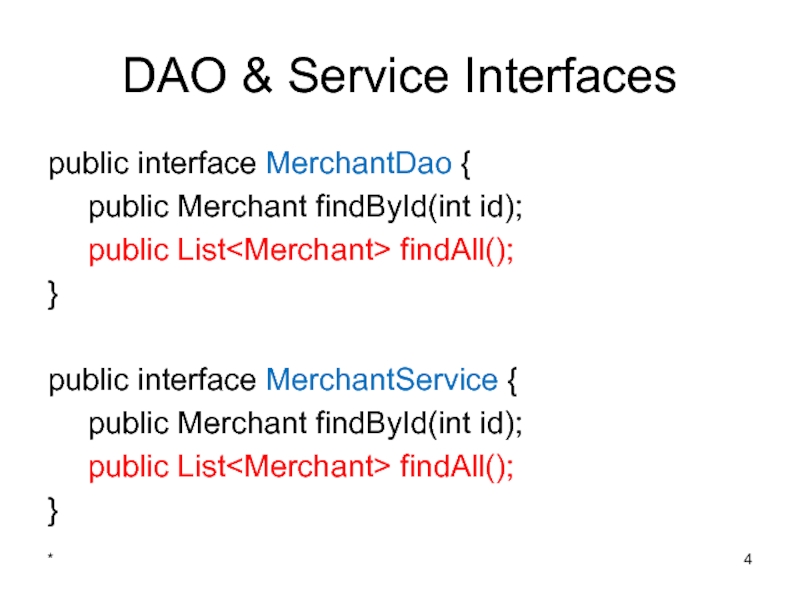
Слайд 4DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface MerchantDao {
public Merchant findById(int id);
public List
}
public interface MerchantService {
public Merchant findById(int id);
public List
}
*
Слайд 5MerchantDaoImpl Class
@Repository
public class MerchantDaoImpl implements MerchantDao{
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager
. . . . . . . . . . . .
public List
TypedQuery
em.createQuery("SELECT m FROM Merchant m", Merchant.class);
List
listM = query.getResultList();
return listM; }}
*
Слайд 6MerchantServiceImpl Class
@Named
public class MerchantServiceImpl implements MerchantService{
@Inject
private MerchantDao
. . . . . . . . . . . . .
public List
return merchantDao.findAll();
}
}
*
Слайд 7Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
MerchantService merchantService = context.getBean(MerchantService.class);
List
for(Merchant m: list)
System.out.println("name = " + m.getName() + " charge = " +m.getCharge());
}
*
Слайд 8*
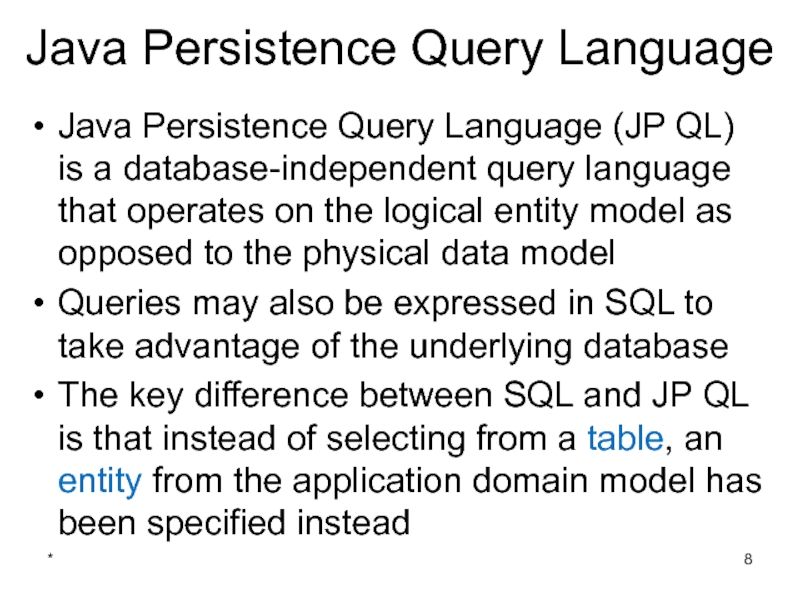
Java Persistence Query Language
Java Persistence Query Language (JP QL) is
Queries may also be expressed in SQL to take advantage of the underlying database
The key difference between SQL and JP QL is that instead of selecting from a table, an entity from the application domain model has been specified instead
Слайд 9*
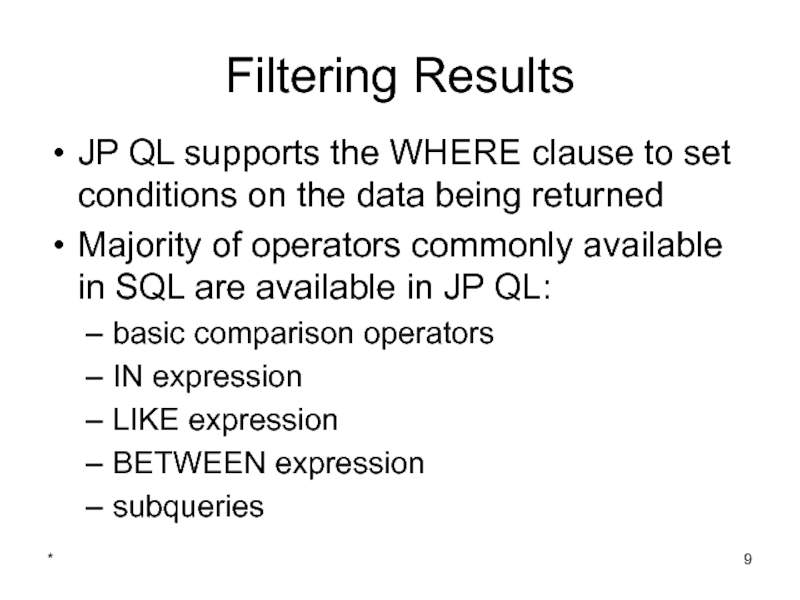
Filtering Results
JP QL supports the WHERE clause to set conditions on
Majority of operators commonly available in SQL are available in JP QL:
basic comparison operators
IN expression
LIKE expression
BETWEEN expression
subqueries
Слайд 11DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface PaymentDao {
public List findByMerchantId(int id);
}
public interface
public List
}
*
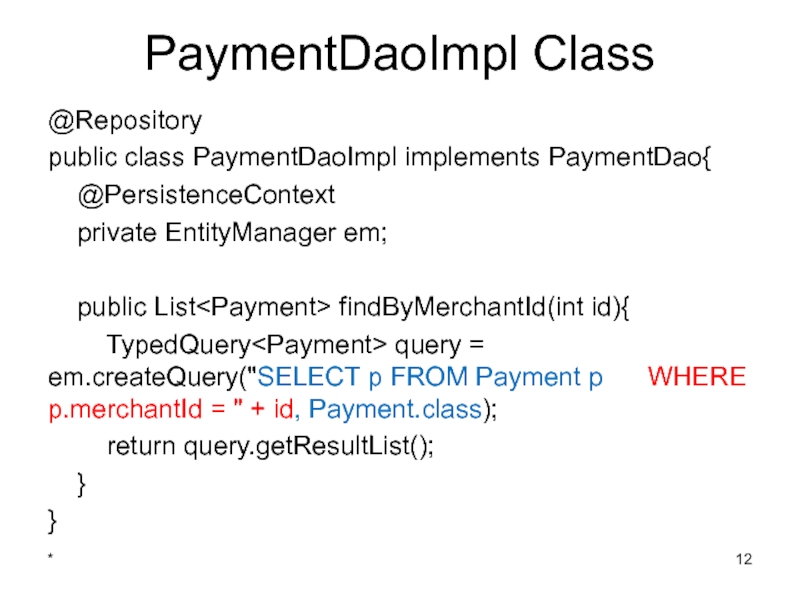
Слайд 12PaymentDaoImpl Class
@Repository
public class PaymentDaoImpl implements PaymentDao{
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager
public List
TypedQuery
return query.getResultList();
}
}
*
Слайд 13PaymentServiceImpl Class
@Named
public class PaymentServiceImpl implements PaymentService{
@Inject
private PaymentDao
public List
return paymentDao.findByMerchantId(id);
}
}
*
Слайд 14Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
PaymentService paymentService = context.getBean(PaymentService.class);
List
for(Payment p: list)
System.out.println(p.toString());
}
*
Слайд 16*
Joins Between Entities
Just as with SQL and tables, if
In JP QL, joins may also be expressed in the FROM clause using the JOIN operator
Слайд 18DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface CustomerDao {
public Customer findById(int id);
public List
}
public interface CustomerService {
public Customer findById(int id);
. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
public List
}
*
Слайд 19CustomerDaoImpl Class
public List getNames(double sumPayed){
String txt = "SELECT
txt += "Payment p, Customer c " ;
txt += "WHERE c.id = p.customerId AND p.sumPayed > " + sumPayed;
TypedQuery
return query.getResultList();
}
*
Слайд 20CustomerServiceImpl Class
public List getNames(double sumPayed){
return customerDao.getNames(sumPayed);
}
*
Слайд 21Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
CustomerService customerService = context.getBean(CustomerService.class);
List
for(String s: list)
System.out.println(s);
}
*
Слайд 23*
Aggregate Queries
There are five supported aggregate functions (AVG, COUNT, MIN, MAX,
Results may be grouped in the GROUP BY clause and filtered using the HAVING clause.
Слайд 25DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface PaymentDao {
public List findByMerchantId(int id);
public double
}
public interface PaymentService {
public List
public double getPaymentSum();
}
*
Слайд 26PaymentDaoImpl Class
public double getPaymentSum(){
TypedQuery query = em.createQuery ("SELECT SUM(p.sumPayed)
return query.getSingleResult();
}
*
Слайд 27Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
PaymentService paymentService = context.getBean(PaymentService.class);
double sum = paymentService.getPaymentSum();
System.out.println("total = " + sum);
}
*
Слайд 29*
Query Positional Parameters
Parameters are indicated in the query string by a
When the query is executed, the developer specifies the parameter number that should be replaced
Слайд 30DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface PaymentDao {
public List
public double getPaymentSum();
public List
}
public interface PaymentService {
public List
public double getPaymentSum();
public List
}
*
Слайд 31PaymentDaoImpl Class
public List getLargePayments(double limit){
TypedQuery query = em.createQuery
query.setParameter(1, limit);
return query.getResultList();
}
*
Слайд 32Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
PaymentService paymentService = context.getBean(PaymentService.class);
List
for (Payment p: list)
System.out.println(p.toString());
}
See P345Parameters project for the full text
*
Слайд 33*
Query Named Parameters
Named parameters may also be used and are indicated
When the query is executed, the developer specifies the parameter name that should be replaced
Слайд 34PaymentDaoImpl Class
public List getLargePayments(double limit){
TypedQuery query = em.createQuery
query.setParameter("limit", limit);
return query.getResultList();
}
See P245Parameters project for the full text
*
Слайд 35*
Executing Queries
The TypedQuery interface provides three different ways to execute a
getSingleResult() - if the query is expected to return a single result
getResultList() - if more than one result may be returned
executeUpdate() - is used to invoke bulk update and delete queries
Слайд 36*
getResultList() Method
Returns a collection containing the query results
If the query did
The return type is specified as a List instead of a Collection in order to support queries that specify a sort order
If the query uses the ORDER BY clause to specify a sort order, the results will be put into the result list in the same order
Слайд 37*
Exercise: Sort Merchants
Create a project to sort merchants by the value
Слайд 38DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface MerchantDao {
public Merchant findById(int id);
public List
}
public interface MerchantService {
public Merchant findById(int id);
public List
}
*
Слайд 39MerchantDaoImpl Class
public List getSortedByNeedToPay(){
String txt = "SELECT m FROM
TypedQuery
return query.getResultList();
}
*
Слайд 40Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
MerchantService merchantService = context.getBean(MerchantService.class);
List
for(Merchant m: list)
System.out.println("name = " + m.getName() + " sumToPay = " + m .getNeedToSend());
}
*
Слайд 42*
getSingleResult() Method
Instead of iterating to the first result in a collection,
Throws a NoResultException exception when no results are available
Throws a NonUniqueResultException exception if multiple results are available after executing the query
Слайд 43*
Working with Query Results
The result type of a query is determined
Basic types, such as String, the primitive types, and JDBC types
Entity types
An array of Object
User-defined types created from a constructor expression
Слайд 44*
Constructor expressions (1/2)
Provide developers with a way to map array of
Typically this is used to convert the results into JavaBean-style classes that provide getters for the different returned values
A constructor expression is defined in JP QL using the NEW operator in the SELECT clause
Слайд 45*
Constructor expressions (2/2)
The argument to the NEW operator is the fully
The only requirement on this class is that it has a constructor with arguments matching the exact type and order that will be specified in the query.
Слайд 47*
Class Result
public class Result {
private String name;
private double sum;
public Result(){
public Result(String name, double sum){
this.name = name;
this.sum = sum;
}
public String getName() { return name; }
. . . . . . .
Слайд 48DAO & Service Interfaces
public interface MerchantDao {
public Merchant findById(int id);
public List
public List
}
public interface MerchantService {
public Merchant findById(int id);
public List
public List
}
*
Слайд 49MerchantDaoImpl Class
public List getTotalReport(){
String txt = "SELECT new com.bionic.edu.Result
txt += "FROM Payment p, Merchant m WHERE m.id = p.merchantId GROUP BY m.name";
TypedQuery
return query.getResultList();
}
*
Слайд 50Main Class
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context
MerchantService merchantService = context.getBean(MerchantService.class);
List
for(Result r: list)
System.out.format("%1$25s %2$8.2f \n", r.getName(), r.getSum());
}
*