- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Mass transfer process in chemical technologies презентация
Содержание
- 1. Mass transfer process in chemical technologies
- 2. My specialties Chemical Reaction Engineering Nanomaterial Engineering
- 3. Question 1: What specialized courses have you
- 4. MODULE I: INTRODUCTION
- 5. biomass and ores. The raw materials are
- 6. Example 1: Traffic on the road A
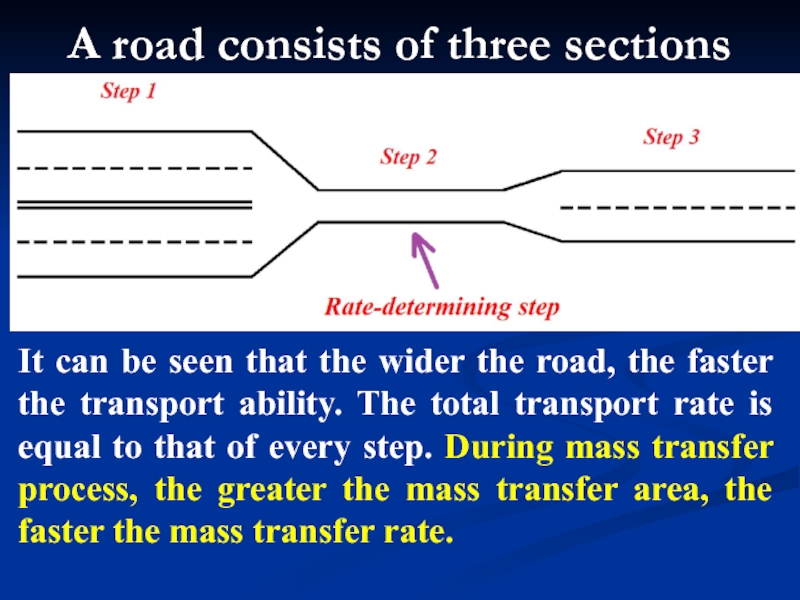
- 7. A road consists of three sections It
- 8. Example 2: Transport of bricks Three people
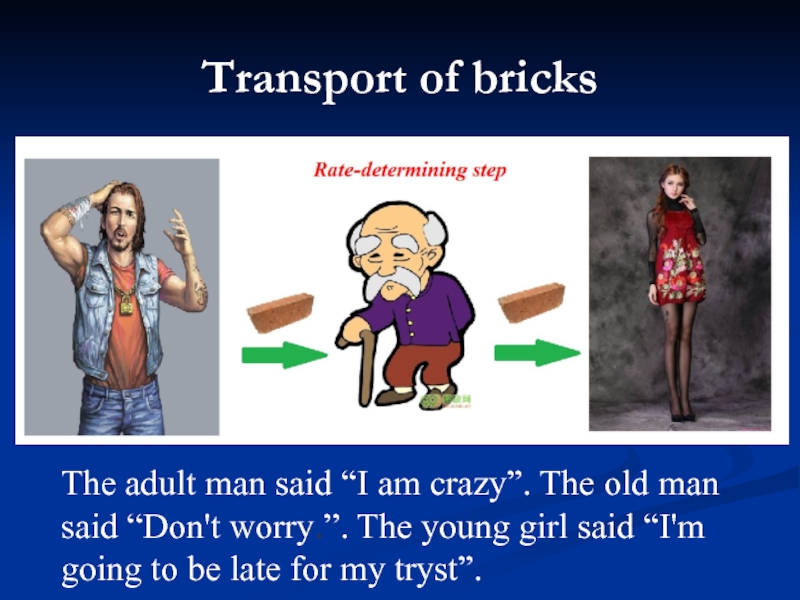
- 9. Transport of bricks The adult man said
- 10. Example 3: Process of crushing peanuts A stupid
- 11. The operation by the stupid woman is
- 12. Example 4: Process of rinsing clothes When
- 13. Washing clothes and then rinsing them.
- 14. The easiest method is that when you
- 15. The reason is that disrupting the sequence
- 16. 2. What is mass transfer process?
- 17. heterogeneous mass transfer processes. In chemical engineering,
- 18. is stemming from the random continuous motion
- 19. 4. Two modes of mass transfer Diffusion
- 20. Convection mass transfer is the movement of groups
- 21. For example: it
- 22. Typhoon is the most powerful rotating convection
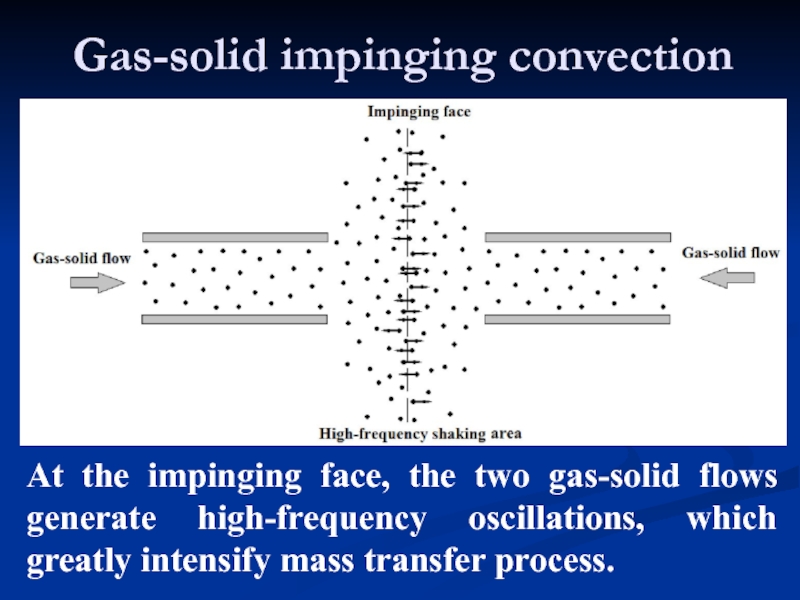
- 23. Gas-solid impinging convection At the impinging face,
- 24. Comparison of diffusion and convection mass transfer
- 25. A crawling turtle
- 26. Interface mass transfer
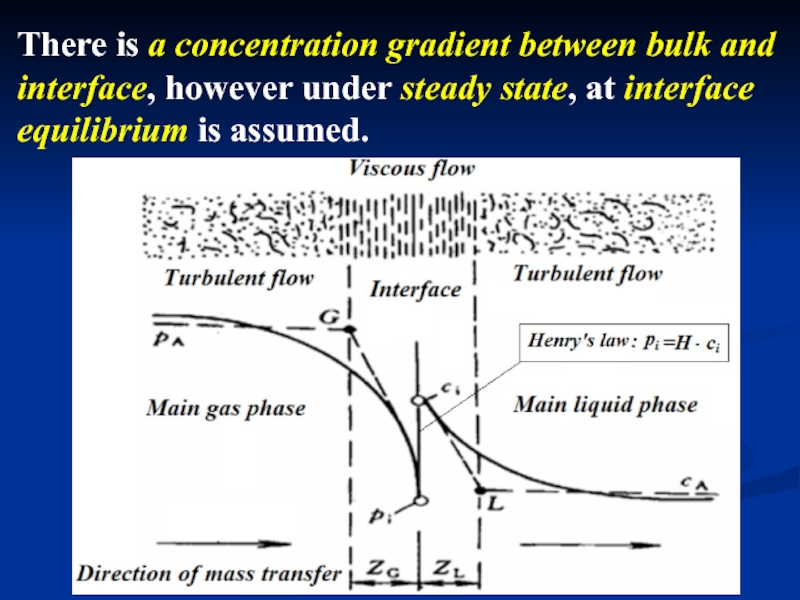
- 27. There is a concentration gradient between bulk
- 28. Double-film theory from Lewis-Whitman (1924) for the
- 29. A typical example: Your native language is
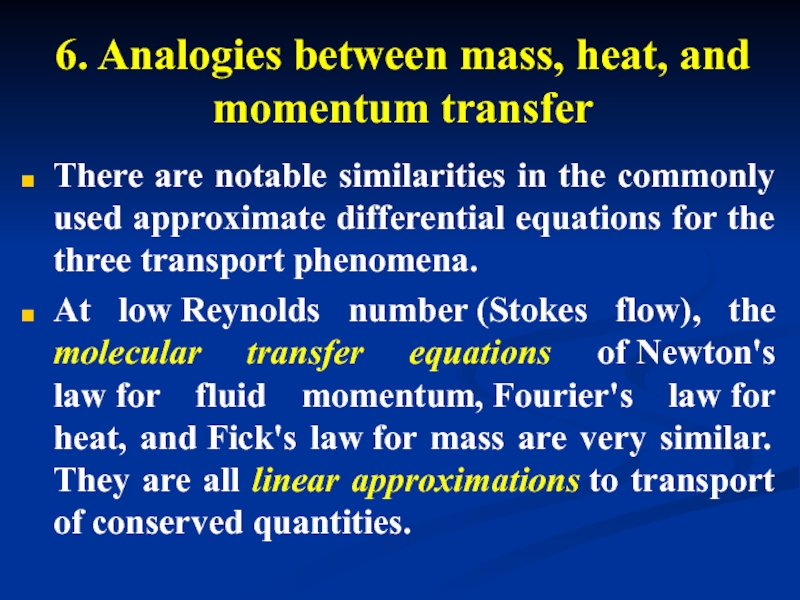
- 30. 6. Analogies between mass, heat, and momentum
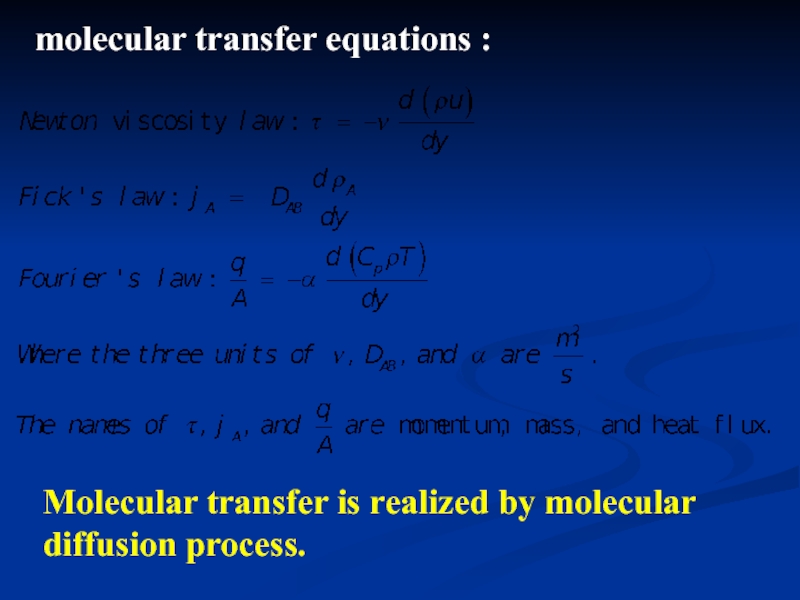
- 31. molecular transfer equations : Molecular transfer is realized by molecular diffusion process.
- 32. Take the momentum transfer in laminar flow
- 33. layer diffuse into the slow layer and
- 34. At high Reynolds number,
- 35. Mass transfer
- 36. From macroscopic point,
Слайд 2My specialties
Chemical Reaction Engineering
Nanomaterial Engineering
Chemical Process Intensification
All my specialties
Слайд 3Question 1: What specialized courses have you learned in chemical engineering?
Слайд 4
MODULE I: INTRODUCTION
Tall buildings are constructed by
Слайд 5biomass and ores. The raw materials are purified and transformed into
Слайд 6Example 1: Traffic on the road
A road is wide in some
1. Examples of transport process in
our daily life
Слайд 7A road consists of three sections
It can be seen that the
Слайд 8Example 2: Transport of bricks
Three people (including adult, young and old
Слайд 9Transport of bricks
The adult man said “I am crazy”. The old
Слайд 10Example 3: Process of crushing peanuts
A stupid woman crushes peanuts, and puts
Слайд 11The operation by the stupid woman is called “back-mixing”. Because she
Слайд 12Example 4: Process of rinsing clothes
When you have washed your clothes
Слайд 14The easiest method is that when you rinse clothes at second
Слайд 15The reason is that disrupting the sequence of rinsing clothes will
Слайд 162. What is mass transfer process?
A
Слайд 17heterogeneous mass transfer processes. In chemical engineering, mixing and separating operations
Слайд 18is stemming from the random continuous motion of molecules in fluids.
is
is irreversible process of statistical nature;
belongs to physical process;
3. Characteristics of mass transfer
Слайд 194. Two modes of mass transfer
Diffusion mass transfer (or single molecule
Слайд 20Convection mass transfer is the movement of groups of molecules within fluids, it is a
Слайд 21 For example: it is well-known that sweet-scented
Слайд 22Typhoon is the most powerful rotating convection in nature.
Now typhoon TALIM
Слайд 23Gas-solid impinging convection
At the impinging face, the two gas-solid flows generate
Слайд 24Comparison of diffusion and convection mass transfer processes
The rate of diffusion
Слайд 26 Interface mass transfer depends on molecules diffusing
5. Interphase mass transfer
Слайд 27There is a concentration gradient between bulk and interface, however under
Слайд 28Double-film theory from Lewis-Whitman (1924) for the fluid-phase mass transfer mechanism.
Слайд 29A typical example: Your native language is Russian, but my native
Слайд 306. Analogies between mass, heat, and momentum transfer
There are notable similarities
At low Reynolds number (Stokes flow), the molecular transfer equations of Newton's law for fluid momentum, Fourier's law for heat, and Fick's law for mass are very similar. They are all linear approximations to transport of conserved quantities.
Слайд 31molecular transfer equations :
Molecular transfer is realized by molecular diffusion process.
Слайд 32Take the momentum transfer in laminar flow as an example:
The unit
Слайд 33layer diffuse into the slow layer and collide with the slow
Слайд 34 At high Reynolds number, the analogy between mass,
Слайд 35 Mass transfer plays an important role
7. Mass transfer in separation operations
Слайд 36 From macroscopic point, chemical industry only consists
8. Mass transfer in reaction process