- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Introduction in bioorganic chemistry. Isomerism and structure of organic compounds презентация
Содержание
- 1. Introduction in bioorganic chemistry. Isomerism and structure of organic compounds
- 2. Organic chemistry — chemistry of carbon containing
- 3. Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (21 August 1816 –
- 4. In1853 C. Gerhardt elaborated «theory of the
- 5. Alexander Mikhaylovich Butlerov (September 15, 1828 –
- 6. Basic statements of structure theory of organic
- 7. 4) In organic molecules exists
- 8. Structural formula –
- 9. Structural formulas n-butane ethanol
- 10. 3D-models of organic compounds Sticks Ball & Stick spherical
- 11. Bond types covalent bond hydrogen bond Ionic bond
- 12. Covalent bond in organic molecules: Polar
- 13. Chemical properties of organic molecules caused
- 14. Structural isomerism caused by difference order and
- 15. Изомерия цепи primary atoms secondary atoms tertiary atoms Quatemary atoms
- 16. Positional isomerism
- 17. Functional group - atom or group
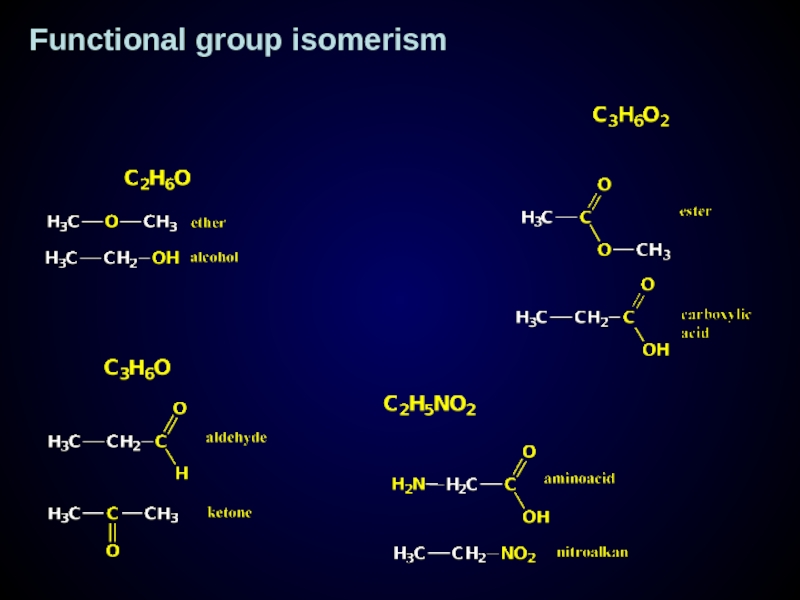
- 18. Functional group isomerism
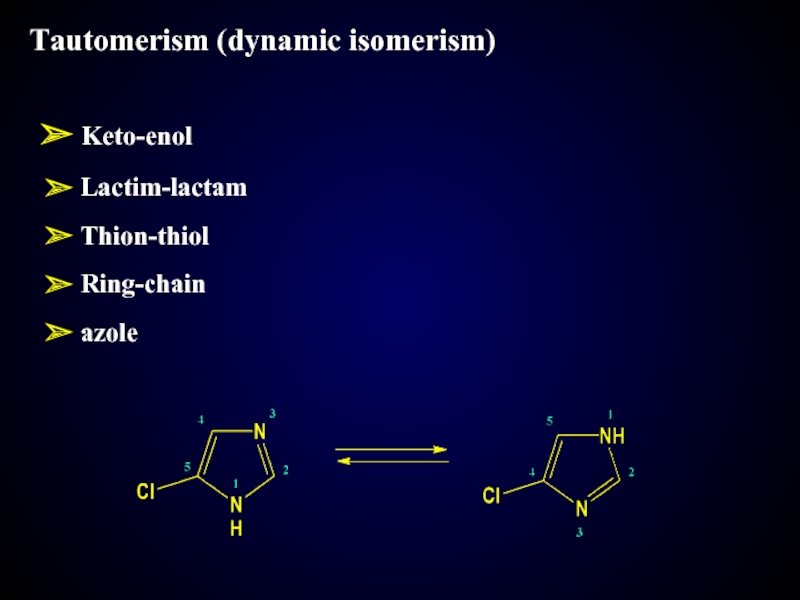
- 19. Tautomerism (dynamic isomerism) Keto-enol Lactim-lactam Thion-thiol Ring-chain azole
- 20. Stereoisomers are isomeric molecules that have the
- 21. Conformational stereoisomerism caused by difference location of
- 22. Conformations types
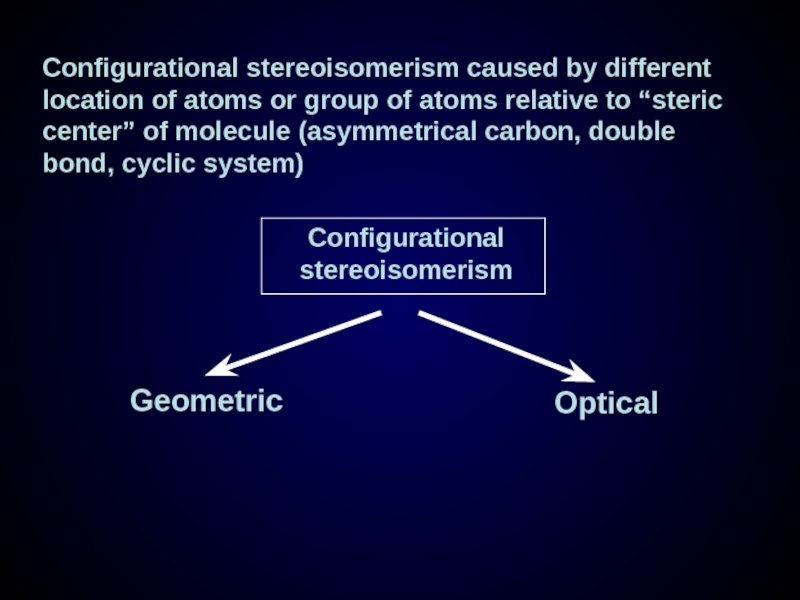
- 23. Configurational stereoisomerism caused by different location of
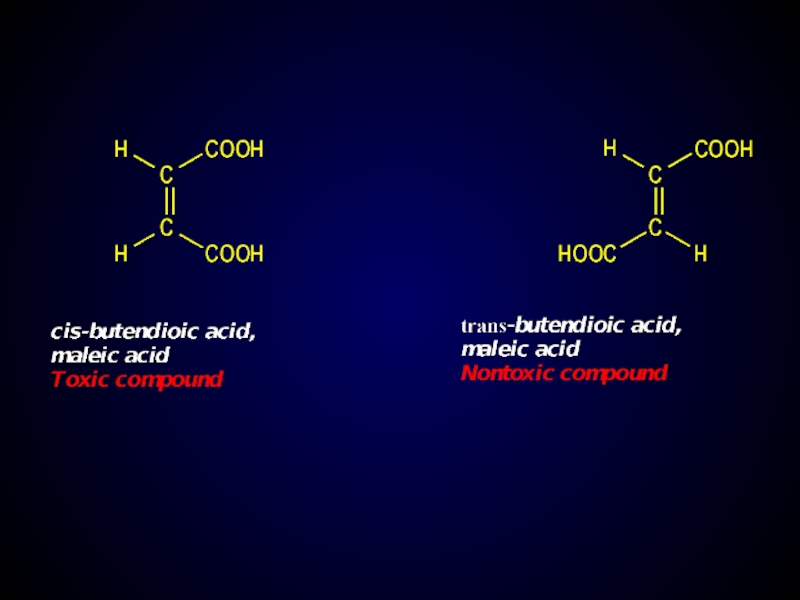
- 24. Geometric isomerism (cis-trans, E-Z-isomerism) Caused by difference
- 26. Optical isomerism caused by the presence in
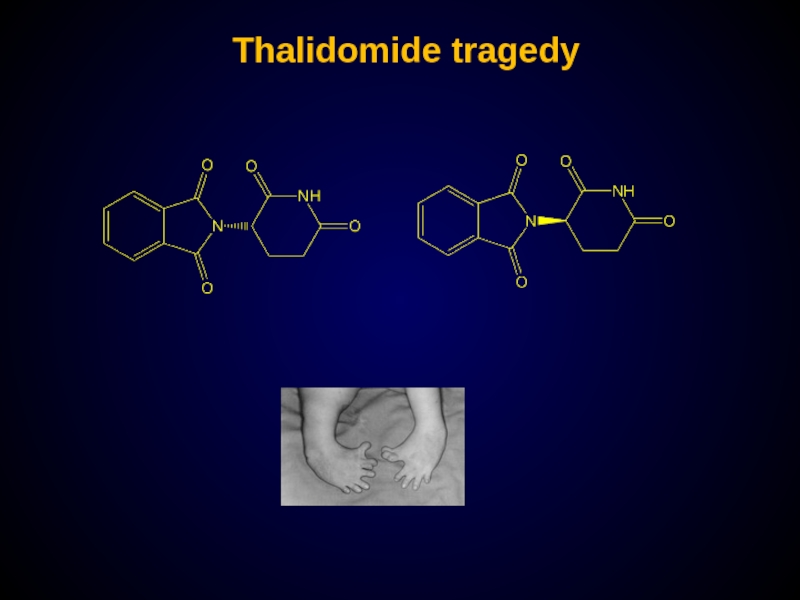
- 27. Thalidomide tragedy
- 28. Electronic effects in organic molecules Inductive effect
- 29. Electronic effects in organic molecules Mesomeric effect
- 30. Thank You for kind attention!
Слайд 1Lecture 1
Introduction in bioorganic chemistry. Isomerism and structure of organic compounds.
Слайд 2Organic chemistry — chemistry of carbon containing compounds
Elements Н, О, N,
Bioorganic chemistry— scientific discipline that combines organic chemistry and biochemistry. In most cases bioorganic chemistry deals with the study of biological processes using chemical methods. (Wiki)
Слайд 3Charles Frédéric Gerhardt (21 August 1816 – 19 August 1856). French
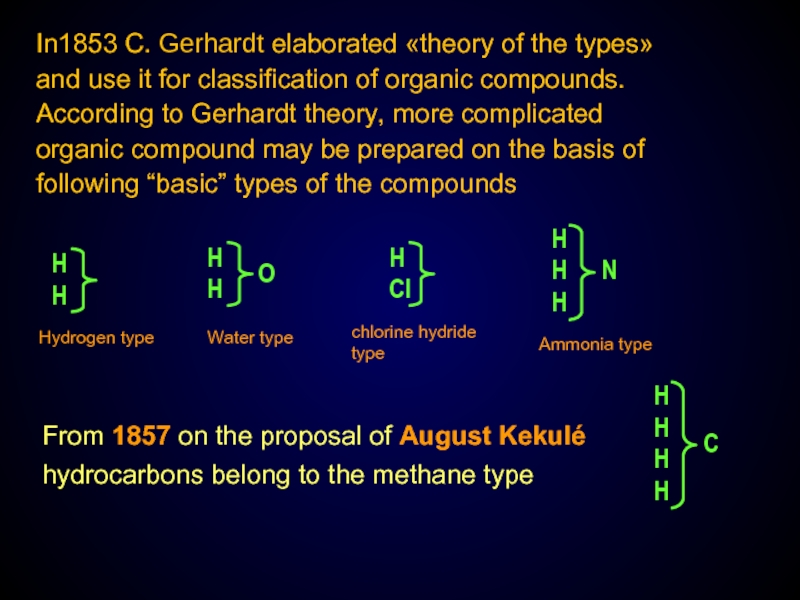
Слайд 4In1853 C. Gerhardt elaborated «theory of the types» and use it
From 1857 on the proposal of August Kekulé hydrocarbons belong to the methane type
Слайд 5Alexander Mikhaylovich Butlerov (September 15, 1828 – August 17, 1886) -
Слайд 6Basic statements of structure theory of organic compounds(1861)
1) In organic molecules
2) In organic molecules atoms bonded to each other in appointed order, what caused the chemical structure of molecule;
3) Chemical properties of organic molecules caused not only by quantity and nature of atoms, but on chemical structure of molecule.
Слайд 7
4) In organic molecules exists mutual effects between as bonded, so
5) Chemical structure of organic compounds may be defined by its chemical transformations and chemical properties may be predicted from the structure.
Basic statements of structure theory of organic compounds(1861)
Слайд 8
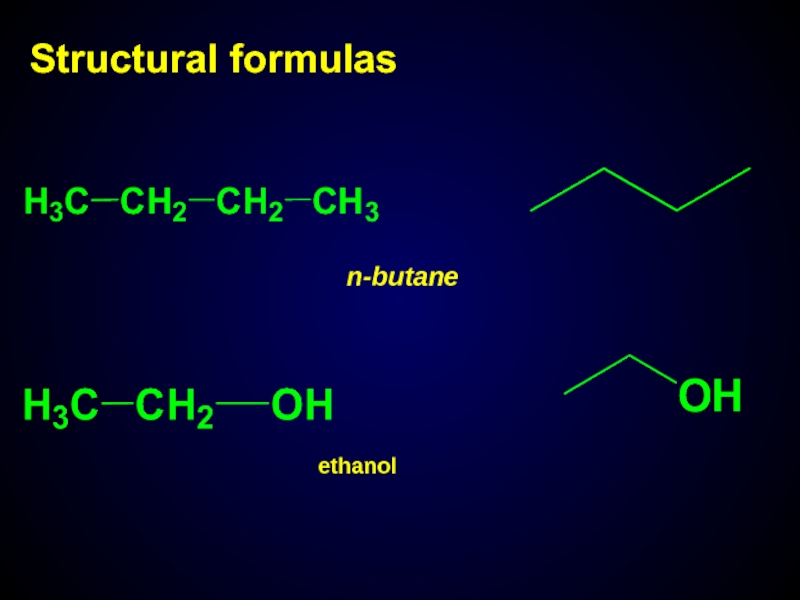
Structural formula – representation of bonds order in molecules
Empirical formula– СН4О
Structural formula
Basic statements of structure theory of organic compounds(1861)
Слайд 12Covalent bond in organic molecules:
Polar
Non-polar
Single (σ-bond)
Double or
Hydrogen bond in organic molecules:
Intermolecular
Intermolecular
Слайд 13
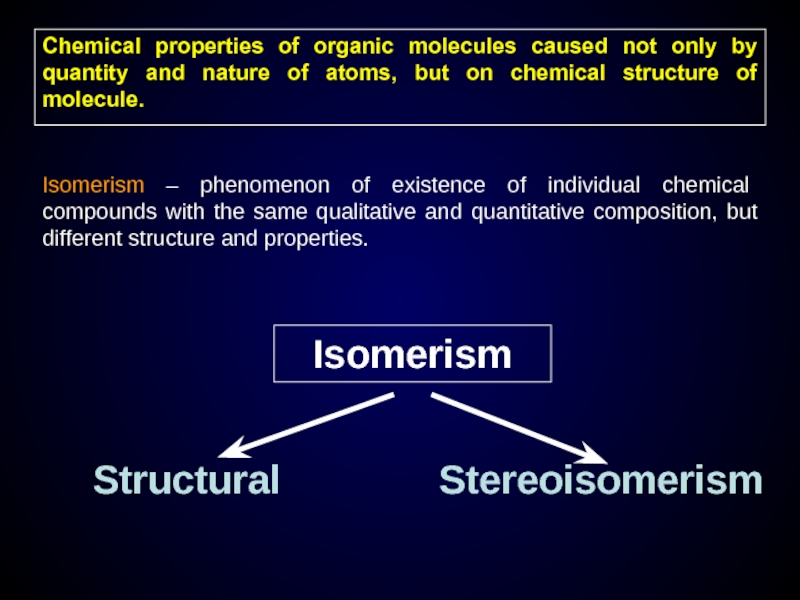
Chemical properties of organic molecules caused not only by quantity and
Isomerism – phenomenon of existence of individual chemical compounds with the same qualitative and quantitative composition, but different structure and properties.
Isomerism
Structural
Stereoisomerism
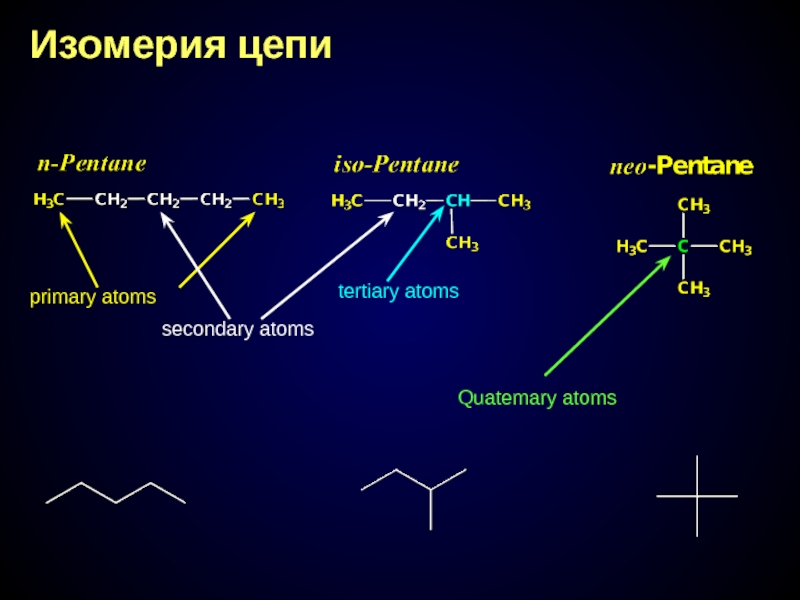
Слайд 14Structural isomerism caused by difference order and bonding type of atoms
Position isomerism
Functional group isomerism
Tautomerism (dynamic isomerism)
Слайд 17Functional group - atom or group of atom which contain elements differ
Слайд 20Stereoisomers are isomeric molecules that have the same molecular formula and
Stereoisomerism
Conformational
Configurational
Слайд 21Conformational stereoisomerism caused by difference location of molecular fragments caused by
Слайд 23Configurational stereoisomerism caused by different location of atoms or group of
Geometric
Optical
Configurational stereoisomerism
Слайд 24Geometric isomerism (cis-trans, E-Z-isomerism)
Caused by difference location of atoms and groups
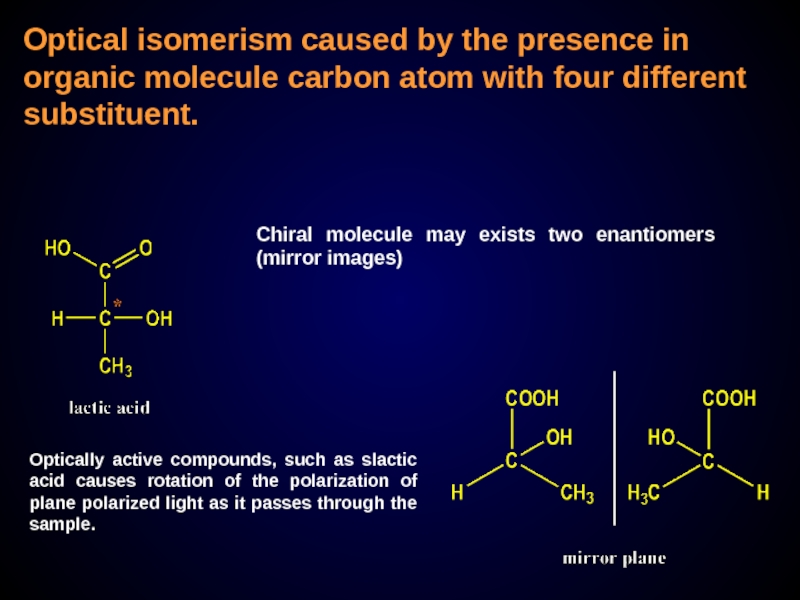
Слайд 26Optical isomerism caused by the presence in organic molecule carbon atom
Chiral molecule may exists two enantiomers (mirror images)
Optically active compounds, such as slactic acid causes rotation of the polarization of plane polarized light as it passes through the sample.