- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Crystallography. Part 4: Crystal Forms Twinning презентация
Содержание
- 1. Crystallography. Part 4: Crystal Forms Twinning
- 2. Crystal Forms Habit: the general external shape
- 3. Unique Attributes of Crystal Forms NaCl
- 4. Form Indexes defined by the Miller index
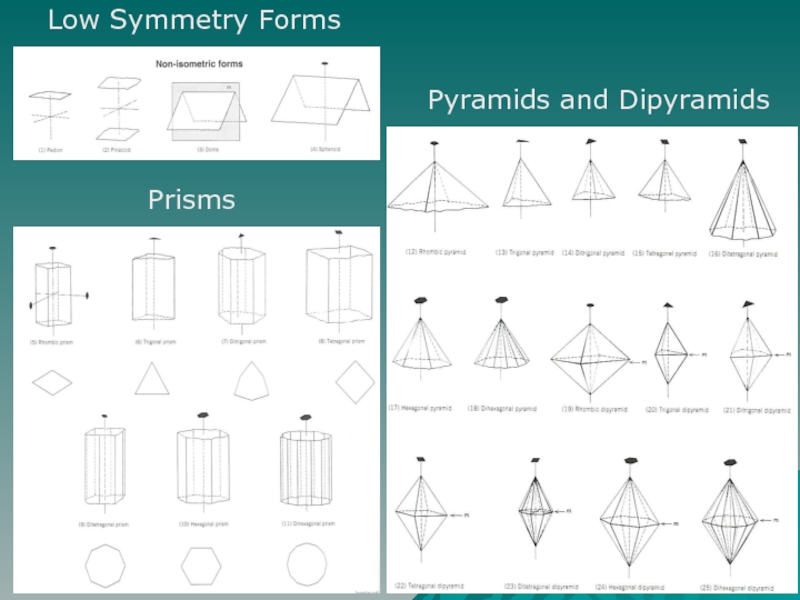
- 5. Pyramids and Dipyramids Prisms Low Symmetry Forms
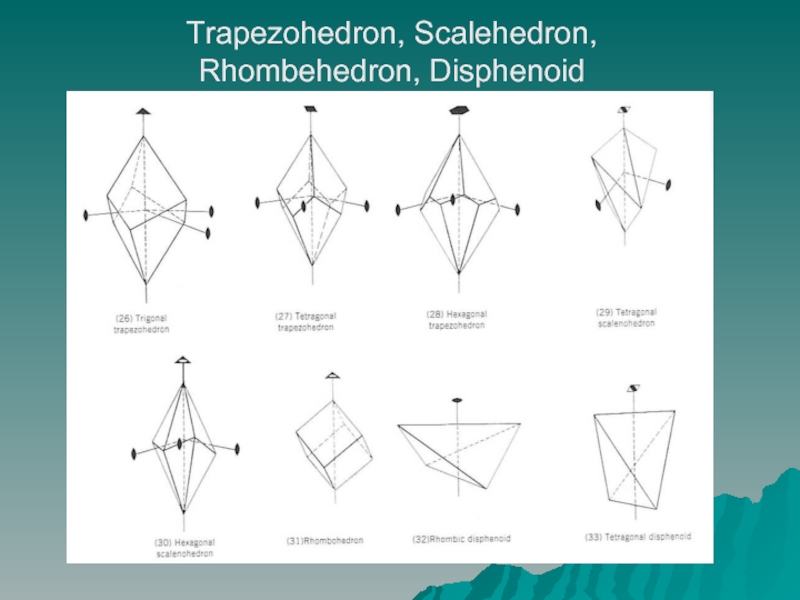
- 6. Trapezohedron, Scalehedron, Rhombehedron, Disphenoid
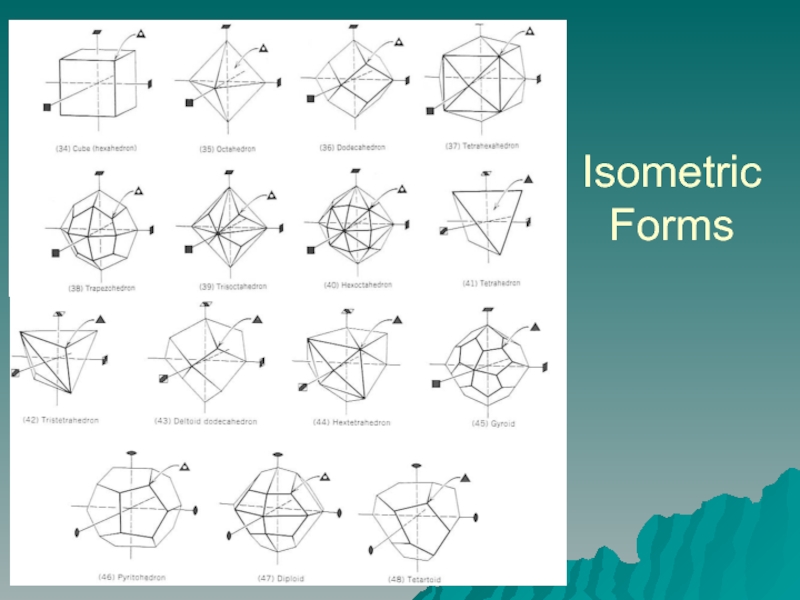
- 7. Isometric Forms
- 8. Twinning Symmetrical intergrowth of two or
- 9. Twin Types Potential Twin Plane (111)
- 10. Multiple Twins Formed from 3 or more
- 11. Twin Laws in the Triclinic System Albite
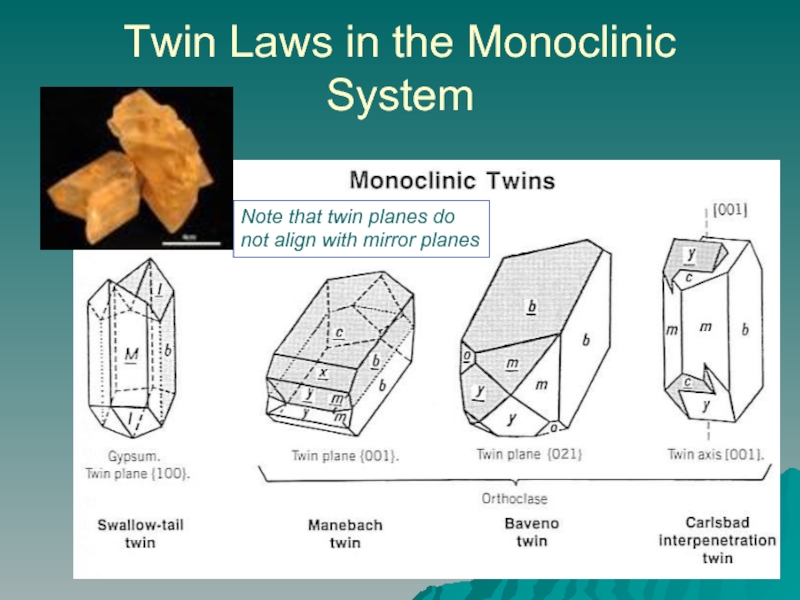
- 12. Twin Laws in the Monoclinic System Note
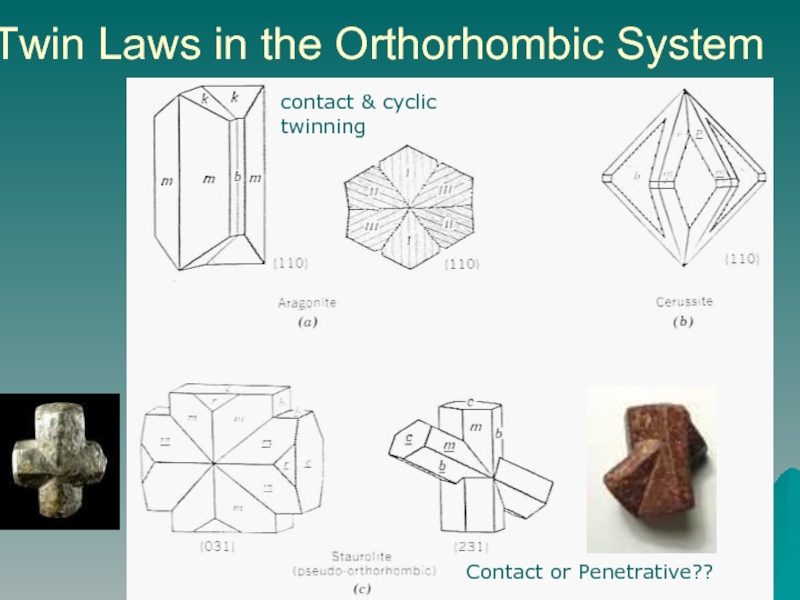
- 13. Twin Laws in the Orthorhombic System contact & cyclic twinning Contact or Penetrative??
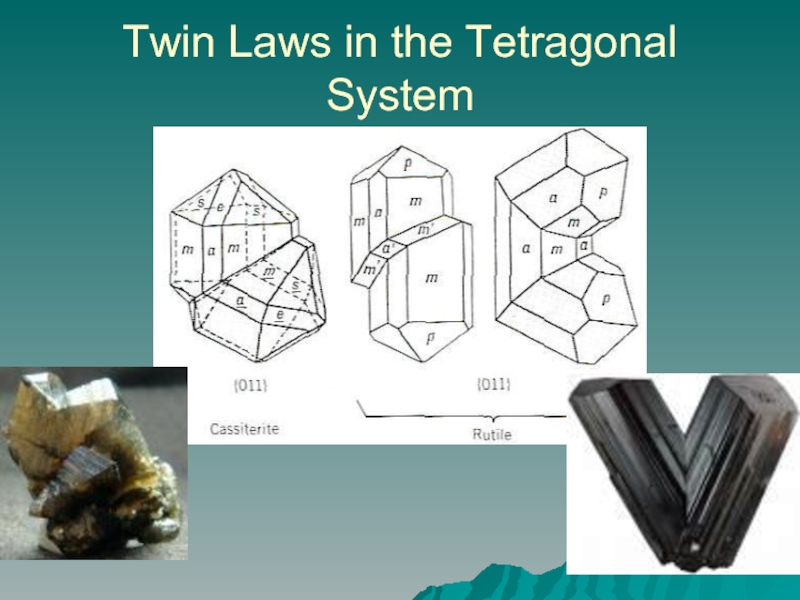
- 14. Twin Laws in the Tetragonal System
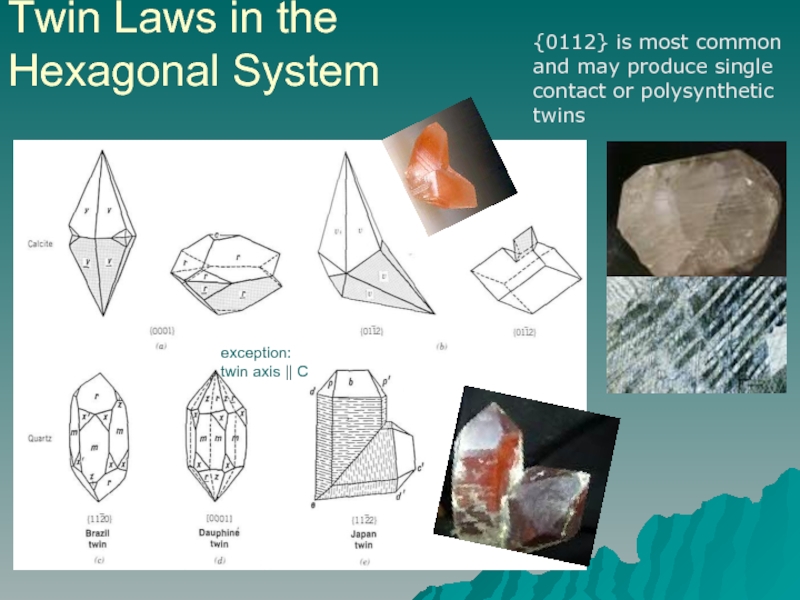
- 15. Twin Laws in the Hexagonal System {0112}
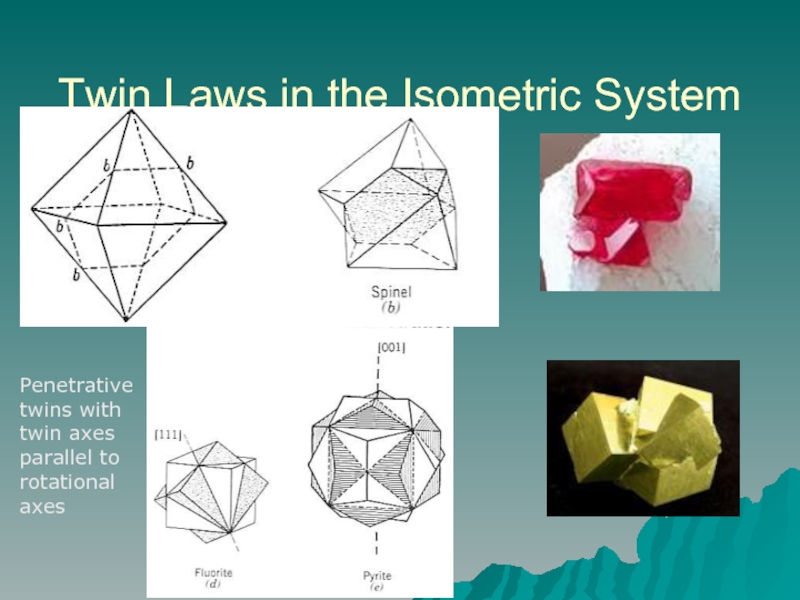
- 16. Twin Laws in the Isometric System Penetrative twins with twin axes parallel to rotational axes
- 17. Next Lecture No Lecture Next Week Yeah!!!
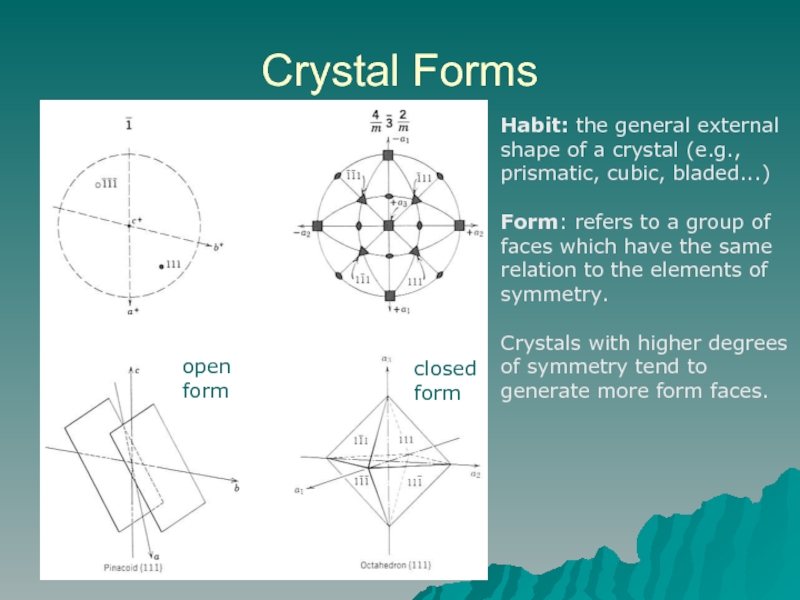
Слайд 2Crystal Forms
Habit: the general external shape of a crystal (e.g., prismatic,
Form: refers to a group of faces which have the same relation to the elements of symmetry.
Crystals with higher degrees of symmetry tend to generate more form faces.
open
form
closed
form
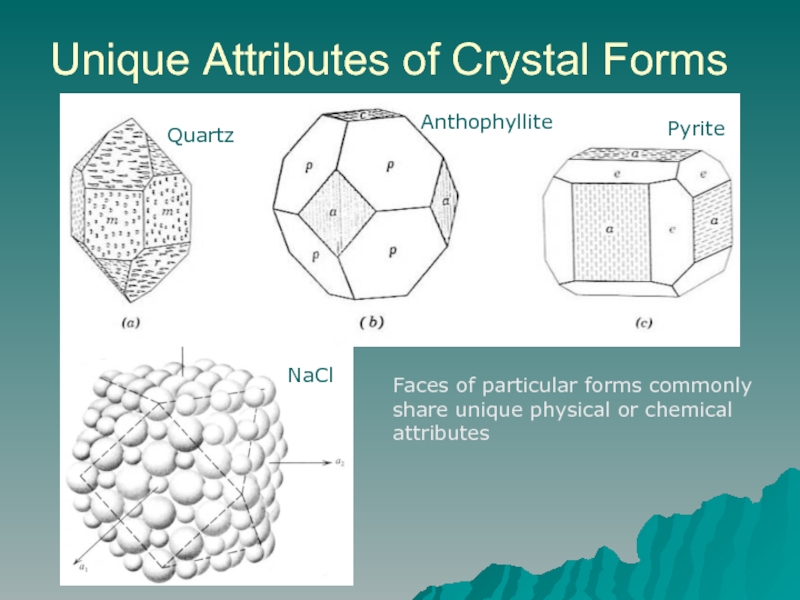
Слайд 3Unique Attributes of Crystal Forms
NaCl
Faces of particular forms commonly share
Quartz
Anthophyllite
Pyrite
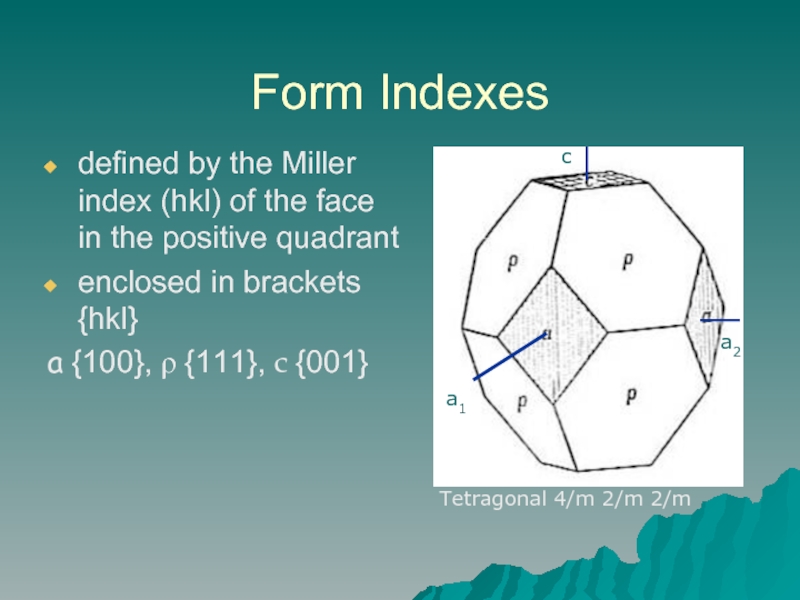
Слайд 4Form Indexes
defined by the Miller index (hkl) of the face in
enclosed in brackets {hkl}
a {100}, ρ {111}, c {001}
Tetragonal 4/m 2/m 2/m
a1
a2
c
Слайд 8Twinning
Symmetrical intergrowth of two or more crystals related to a
Twin elements includes mirrors, rotation axes (usually 2-fold) and roto-inversion that usually do not align with symmetry elements in the crystal.
Twin Laws define the twin element and its crystallographic orientation (twin planes are identified by its Miller index (hkl), twin axes are defined by a zone symbol [hkl]).
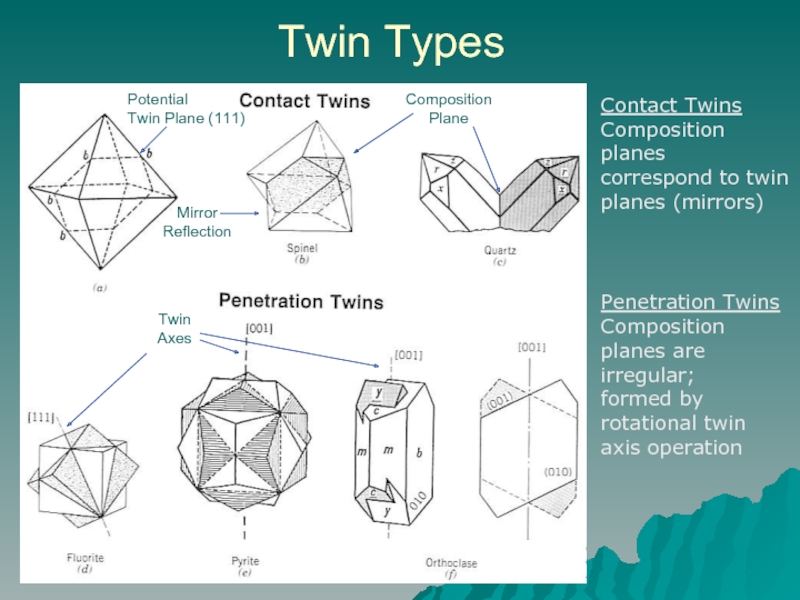
Слайд 9Twin Types
Potential
Twin Plane (111)
Mirror
Reflection
Composition
Plane
Contact Twins
Composition planes
correspond to twin planes
Penetration Twins
Composition planes are irregular;
formed by rotational twin axis operation
Twin
Axes
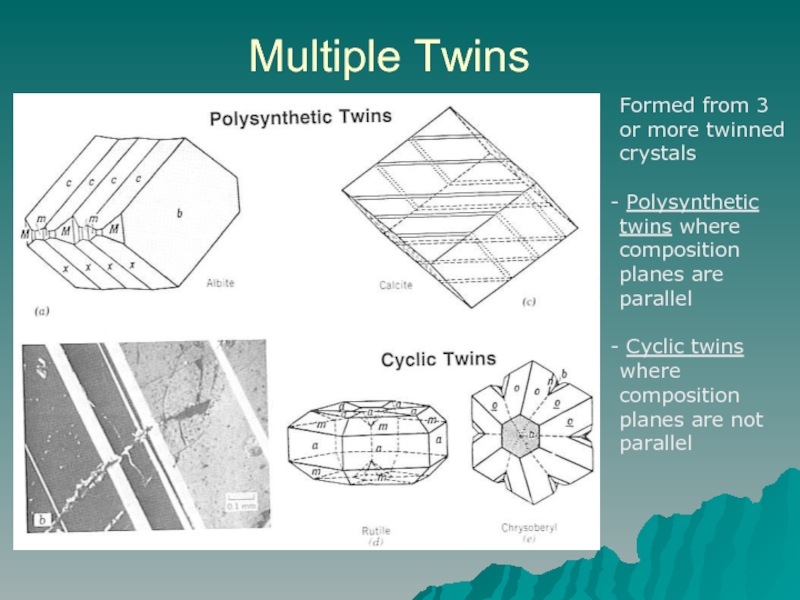
Слайд 10Multiple Twins
Formed from 3 or more twinned crystals
Polysynthetic twins where
Cyclic twins where composition planes are not parallel
Слайд 11Twin Laws in the Triclinic System
Albite Law
{010} twin plane
Albite combined
with
[010] twin axis
results in “tartan twinning” in microcline (K-feldspar)
Слайд 15Twin Laws in the Hexagonal System
{0112} is most common and may
exception:
twin axis || C


![Twin Laws in the Triclinic SystemAlbite Law{010} twin planeAlbite combined with Pericline Law[010] twin axisresults](/img/tmb/1/83667/8bf37c08494bd7a8f10798cb60ab6932-800x.jpg)