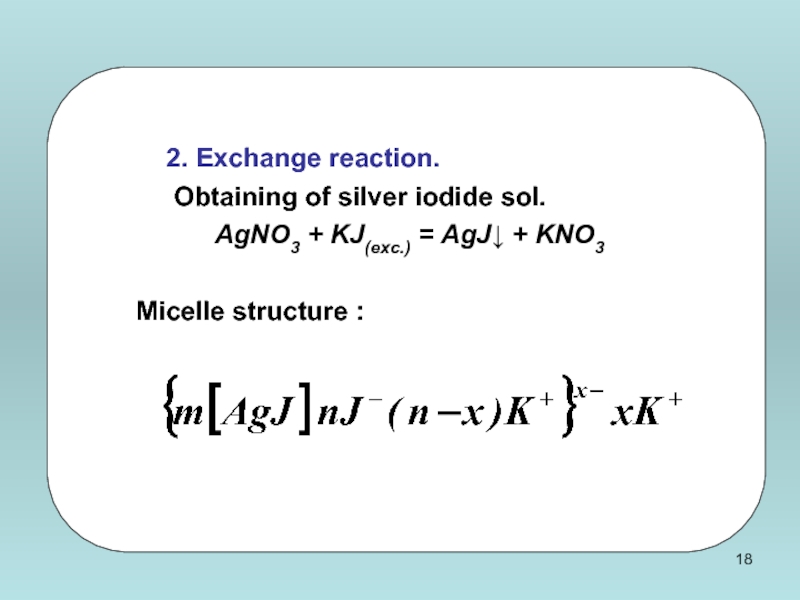- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Colloid chemistry презентация
Содержание
- 1. Colloid chemistry
- 2. Signs of colloid chemistry objects
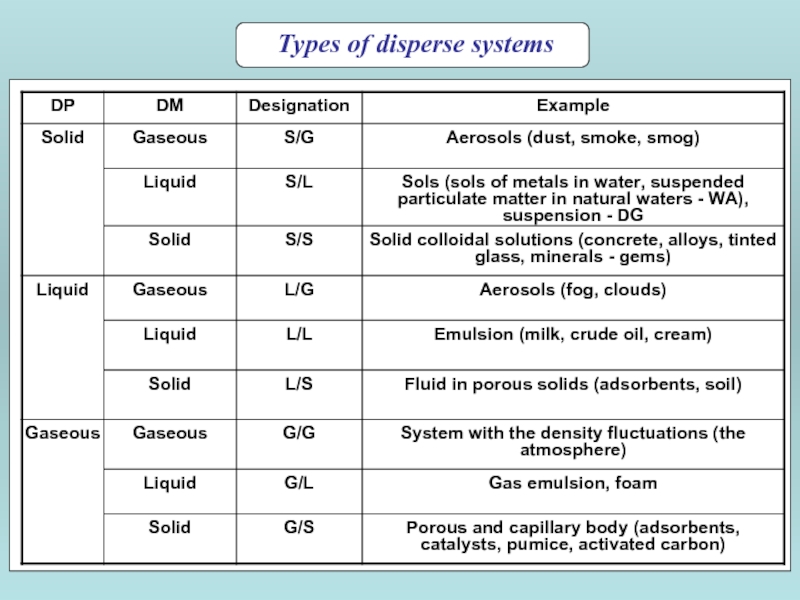
- 3. Types of disperse systems
- 4. Classification by degree of interaction dispersion
- 5. Features of colloidal systems 2. Thermodynamic instability 3. Irreproducibility 4. Capacity to structure formation
- 6. Obtaining disperse systems -grinding large sample substance to disperse particles sizes;
- 7. Colloid mills
- 8. INTENSIFICATION OF THE PROCESSES OF DISPERSION BY
- 9. based on the association of
- 10. Condensation stage 2. Growth of the
- 11. Physical condensation methods
- 12. STRUCTURE OF COLLOID MICELLES According to
- 13. STRUCTURE COLLOID MICELLES Micelle structure can
- 14. Some part of counterions adsorbed on
- 15. Rule Paneth-Fajans Determine
- 16. Chemical condensation methods
- 17. {[mFe4[Fe(CN)6]3·n[Fe(CN)6]4-]4n-·4 (n-х)K+}4x-·4xK+ {[m Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3·nFe3+] 3n+·3(n-х)Сl-}3x+·3xCl-
- 19. 3. Oxidation reaction Formation
- 20. 4. Hydrolysis reaction Obtaining ferric
- 21. Peptization method
- 22. Low molecular weight impurities destroy
- 23. Desalination by electrodialysis. Under the action
- 24. Low molecular weight impurities
- 25. Molecular-kinetic properties of dispersion systems Zaporozhye state medical University Department of physical and colloid chemistry
- 26. Brownian motion Colloidal particles by molecular-kinetic properties
- 27. Brownian motion The collision of particles is
- 28. Diffusion Diffusion - spontaneous process of alignment
- 29. The osmotic pressure Osmotic pressure in colloidal
- 30. Sedimentation Sedimentation (from Lat. Sedimentum - sediment)
- 31. Sedimentation analysis For sedimentation analysis of kinetically
- 32. Ultracentrifugation Modern ultracentrifugation allow to obtain a
- 33. Optical properties of disperse systems Zaporozhye state medical University Department of physical and colloid chemistry
- 34. The scattering of light This
- 35. The scattering of light Tyndall found
- 36. Electrical properties of disperse systems Zaporozhye state medical University Department of physical and colloid chemistry
- 37. DEL. Formation of a double electric layer
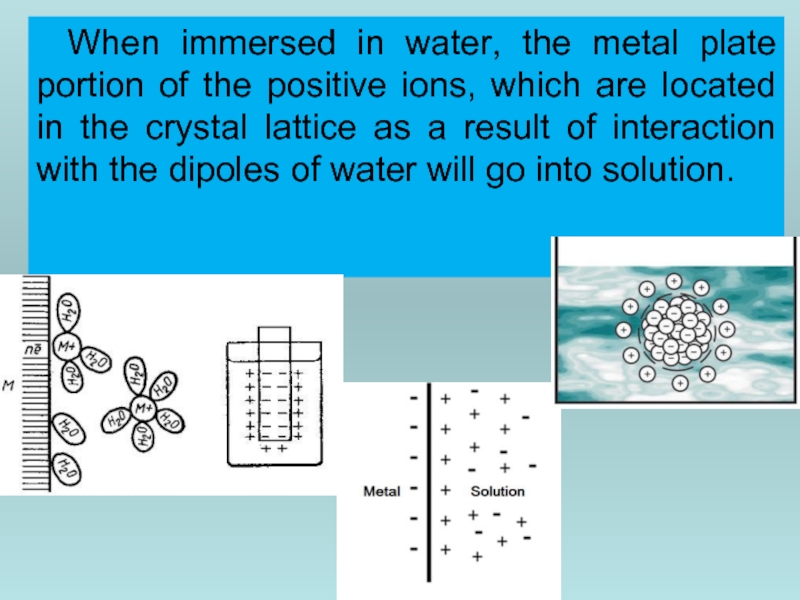
- 38. When immersed in water, the metal plate
- 39. Electric double layer 2nd version. In the
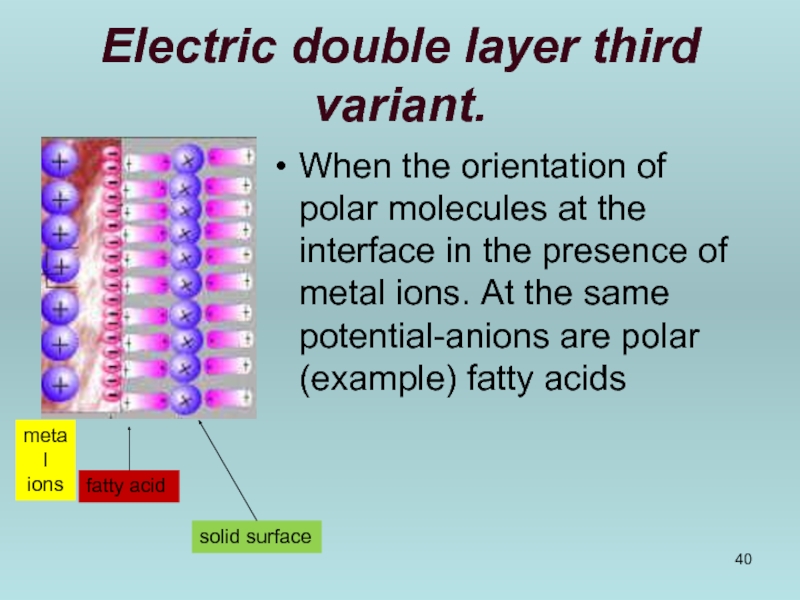
- 40. Electric double layer third variant. When the
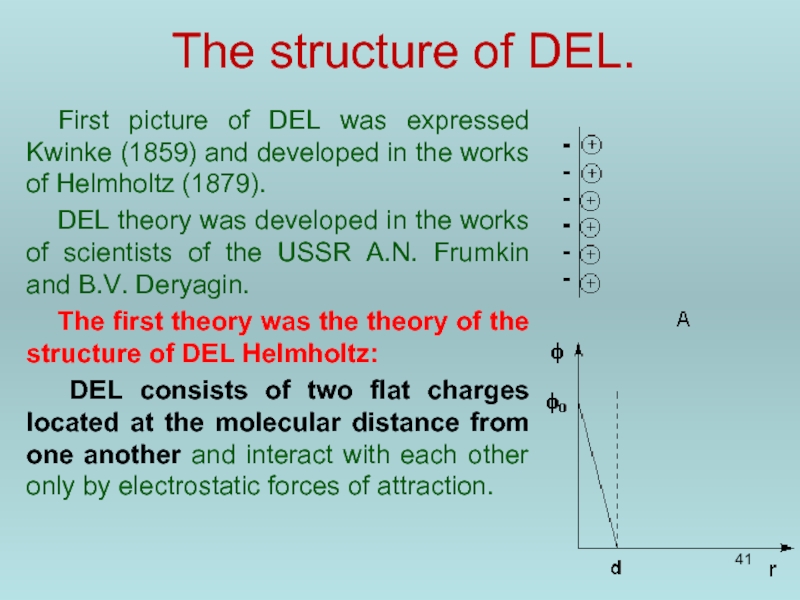
- 41. The structure of DEL. First picture of
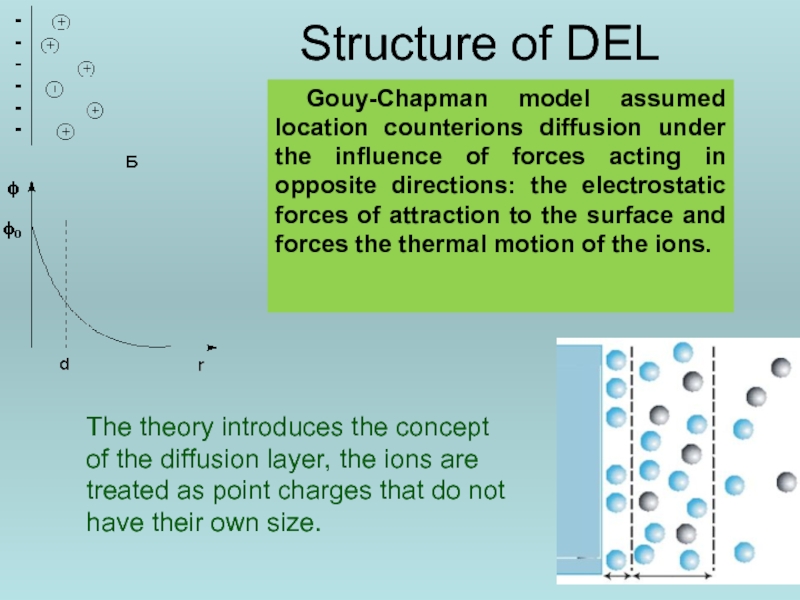
- 42. Structure of DEL Gouy-Chapman model assumed location
- 43. Structure of DEL According to modern concepts
- 44. Within the limits of DEL operates
- 45. To characterize the electrical properties of
- 46. Electrokinetic phenomena. Classification. Electrokinetic phenomena of the
- 47. Electrophoresis The presence of particles dispersed systems
- 48. Electrophoresis Particle velocity of the dispersed phase
- 49. Electroosmosis In the second experiment Reiss filled
- 50. Potential of leakage and sedimentation Potential
- 51. Stability and coagulation of colloidal systems Zaporozhye
- 52. Stability of disperse systems On
- 53. Coagulation is a process of adhesion of
- 54. Coagulation sols electrolytes All electrolytes at
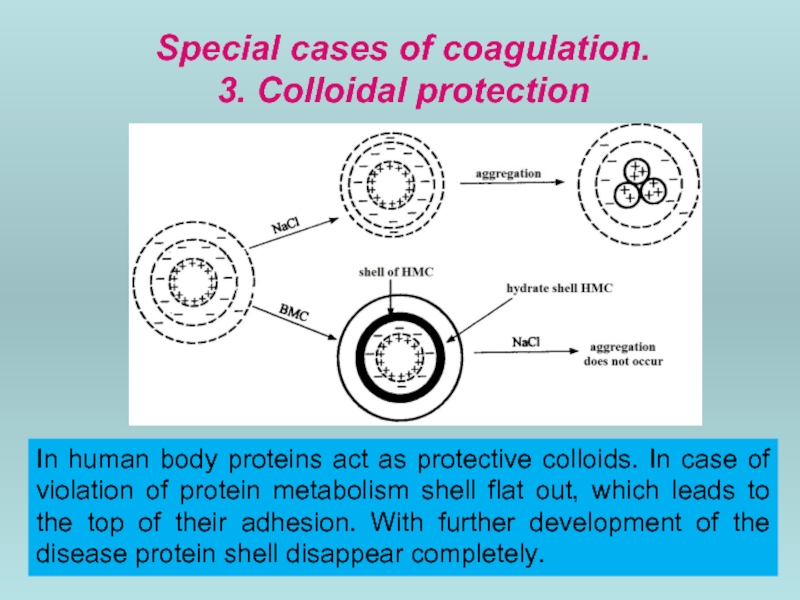
- 55. Special cases of coagulation. 3.
Слайд 1Zaporozhye state
medical University
Department of physical and
colloid chemistry
COLLOID CHEMISTRY
Слайд 2
Signs of colloid chemistry objects
Colloidal chemistry is sometimes called
PHYSICOCHEMISTRY
Слайд 4
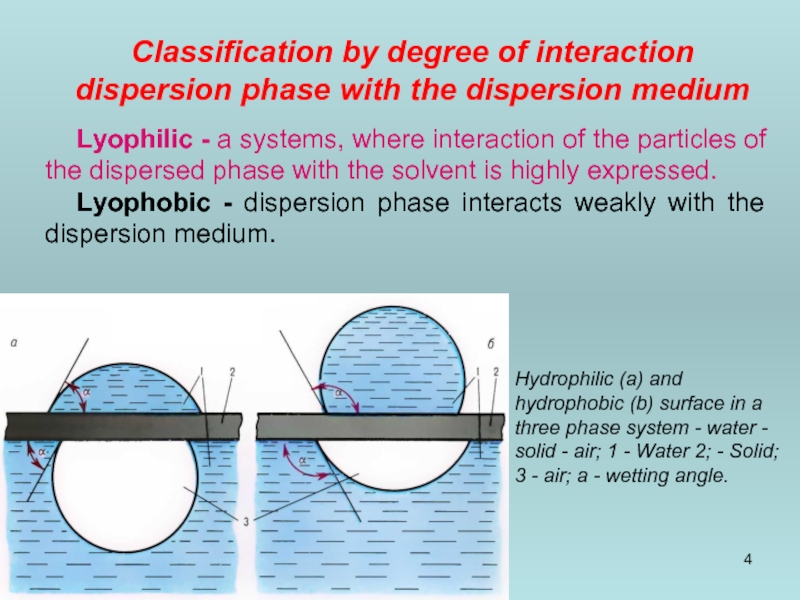
Classification by degree of interaction dispersion phase with the dispersion medium
Lyophilic
Lyophobic - dispersion phase interacts weakly with the dispersion medium.
Hydrophilic (a) and hydrophobic (b) surface in a three phase system - water - solid - air; 1 - Water 2; - Solid; 3 - air; a - wetting angle.
Слайд 5
Features of colloidal systems
2. Thermodynamic instability
3. Irreproducibility
4. Capacity to structure formation
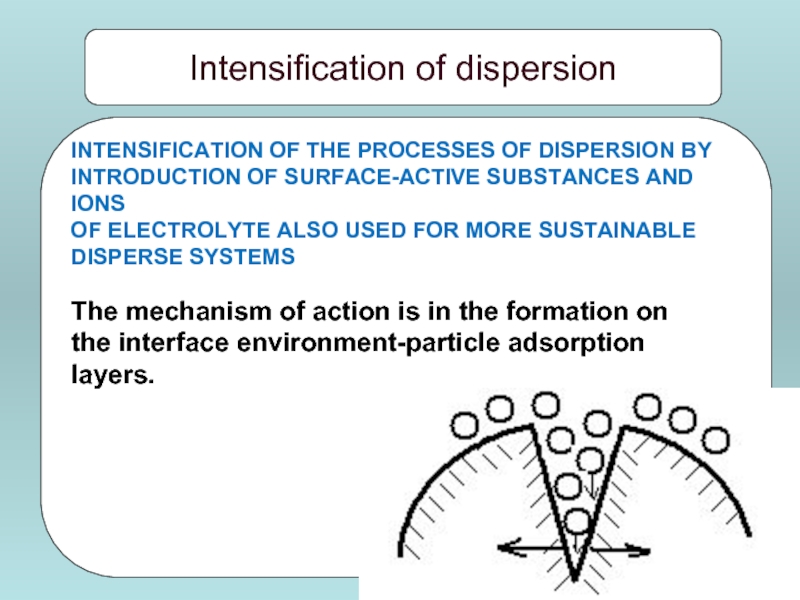
Слайд 8INTENSIFICATION OF THE PROCESSES OF DISPERSION BY
INTRODUCTION OF SURFACE-ACTIVE SUBSTANCES AND
OF ELECTROLYTE ALSO USED FOR MORE SUSTAINABLE
DISPERSE SYSTEMS
The mechanism of action is in the formation on
the interface environment-particle adsorption
layers.
Intensification of dispersion
Слайд 9
based on the association of molecules in aggregates from true solutions;
used to obtain highly dispersed systems;
do not require the cost of external work;
emergence of a new phase occurs at a supersaturation environment.
Condensation methods
Слайд 12
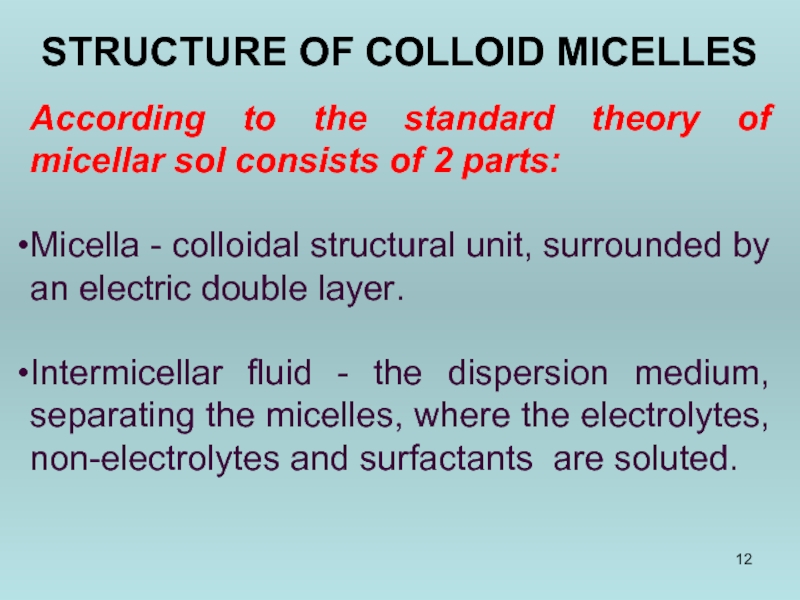
STRUCTURE OF COLLOID MICELLES
According to the standard theory of micellar sol
Micella - colloidal structural unit, surrounded by an electric double layer.
Intermicellar fluid - the dispersion medium, separating the micelles, where the electrolytes, non-electrolytes and surfactants are soluted.
Слайд 13
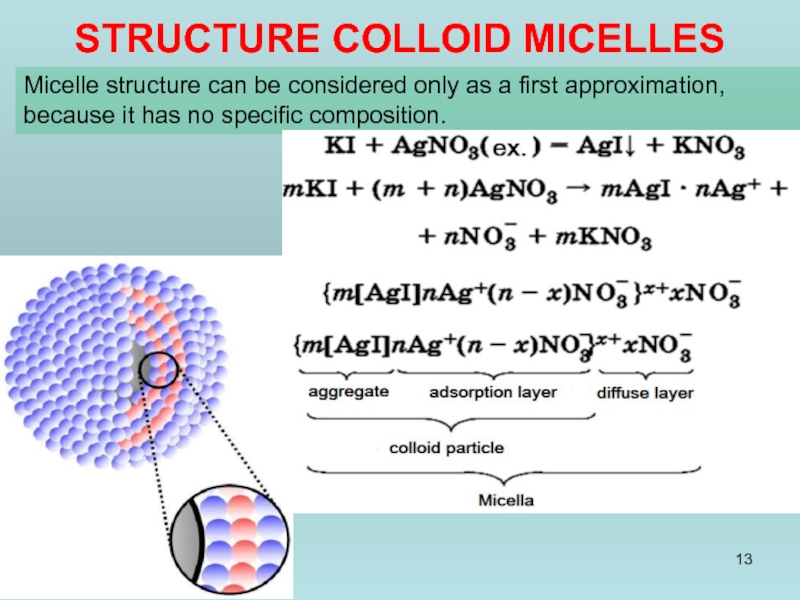
STRUCTURE COLLOID MICELLES
Micelle structure can be considered only as a first
Слайд 14
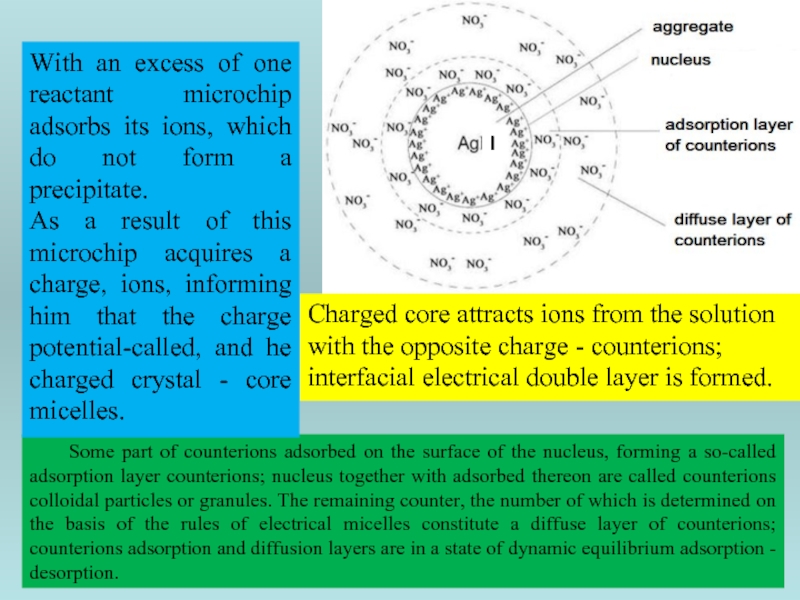
Some part of counterions adsorbed on the surface of the nucleus,
Charged core attracts ions from the solution with the opposite charge - counterions; interfacial electrical double layer is formed.
I
With an excess of one reactant microchip adsorbs its ions, which do not form a precipitate.
As a result of this microchip acquires a charge, ions, informing him that the charge potential-called, and he charged crystal - core micelles.
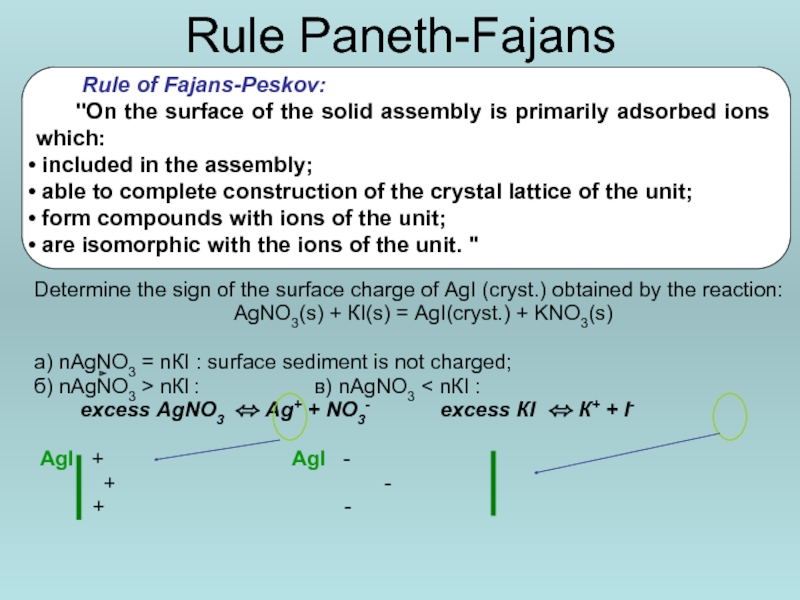
Слайд 15Rule Paneth-Fajans
Determine the sign of the surface charge of AgI (cryst.)
АgNО3(s) + КI(s) = АgI(cryst.) + KNO3(s)
а) nАgNО3 = nКI : surface sediment is not charged;
б) nАgNO3 > nКI : в) nАgNО3 < nКI :
excess АgNO3 ⬄ Аg+ + NО3- excess КI ⬄ К+ + I-
АgI + АgI -
+ -
+ -
Слайд 17{[mFe4[Fe(CN)6]3·n[Fe(CN)6]4-]4n-·4 (n-х)K+}4x-·4xK+
{[m Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3·nFe3+] 3n+·3(n-х)Сl-}3x+·3xCl-
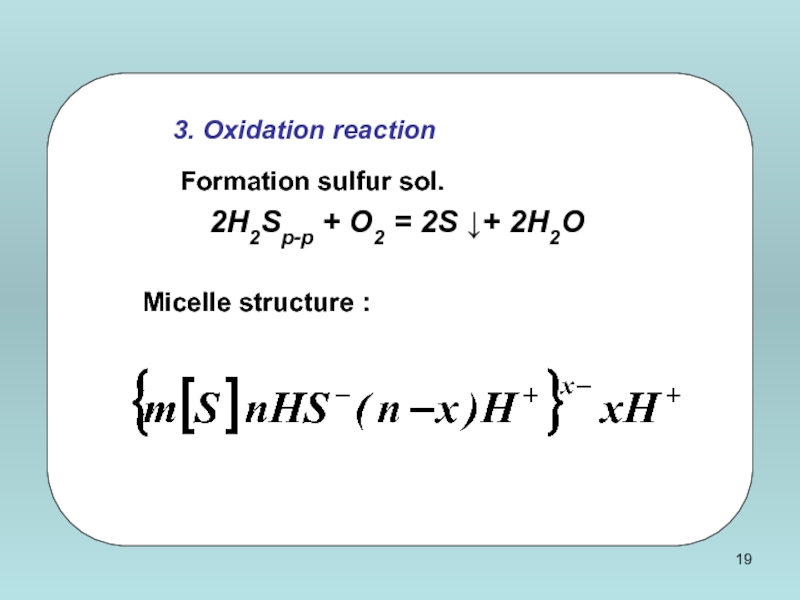
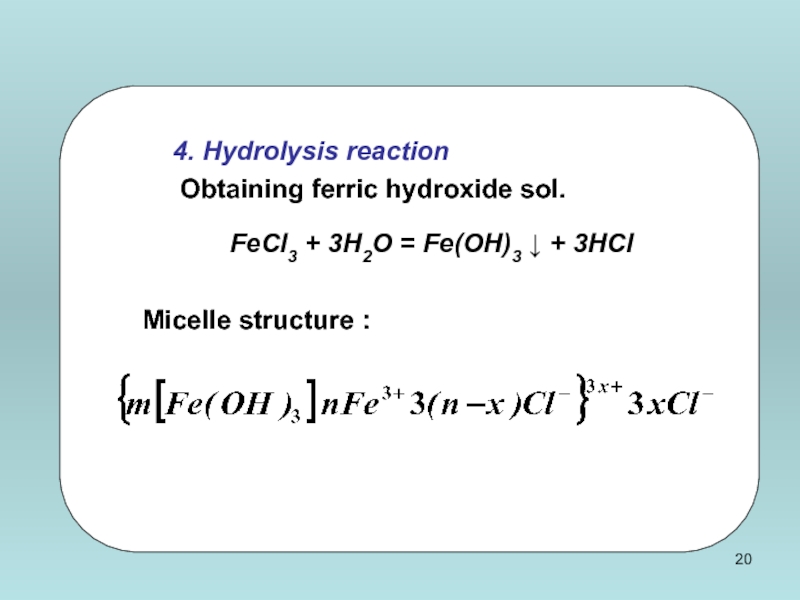
Слайд 20
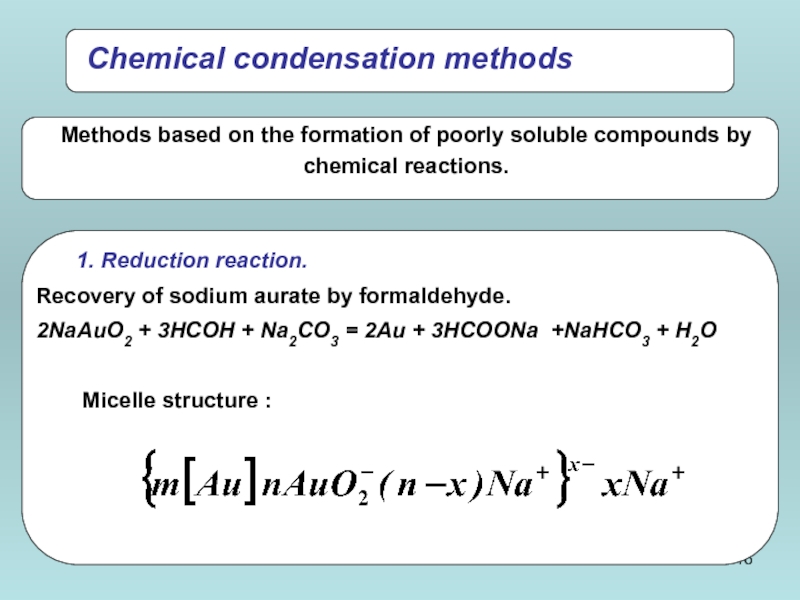
4. Hydrolysis reaction
Obtaining ferric hydroxide sol.
FeCl3 + 3H2O = Fe(OH)3
Micelle structure :
Слайд 22
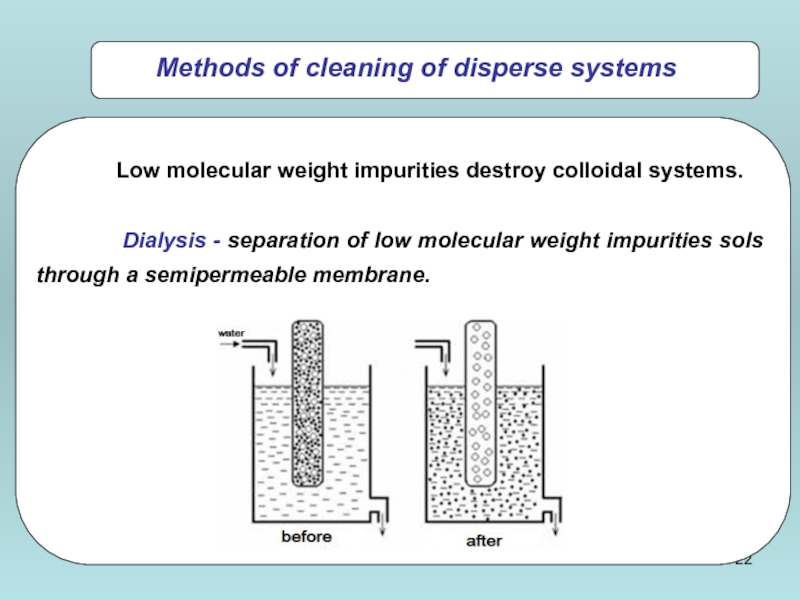
Low molecular weight impurities destroy colloidal systems.
Dialysis - separation of
Methods of cleaning of disperse systems
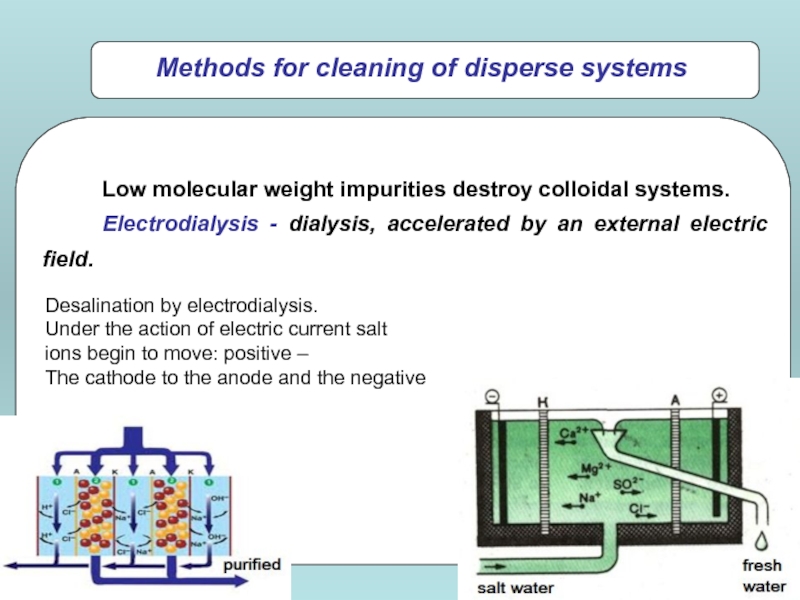
Слайд 23Desalination by electrodialysis.
Under the action of electric current salt
ions
The cathode to the anode and the negative
Low molecular weight impurities destroy colloidal systems.
Electrodialysis - dialysis, accelerated by an external electric field.
Methods for cleaning of disperse systems
Слайд 24
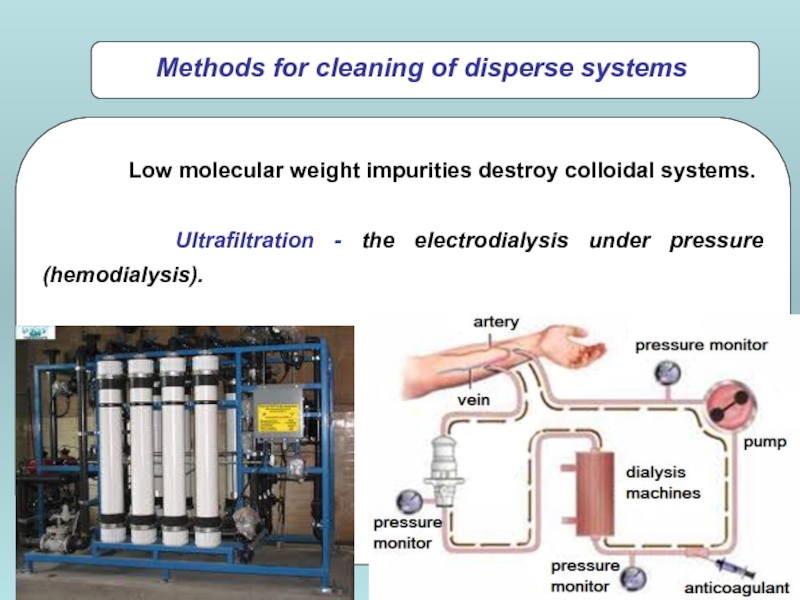
Low molecular weight impurities destroy colloidal systems.
Ultrafiltration - the
Methods for cleaning of disperse systems
Слайд 25Molecular-kinetic properties of dispersion systems
Zaporozhye state
medical University
Department of physical and
colloid chemistry
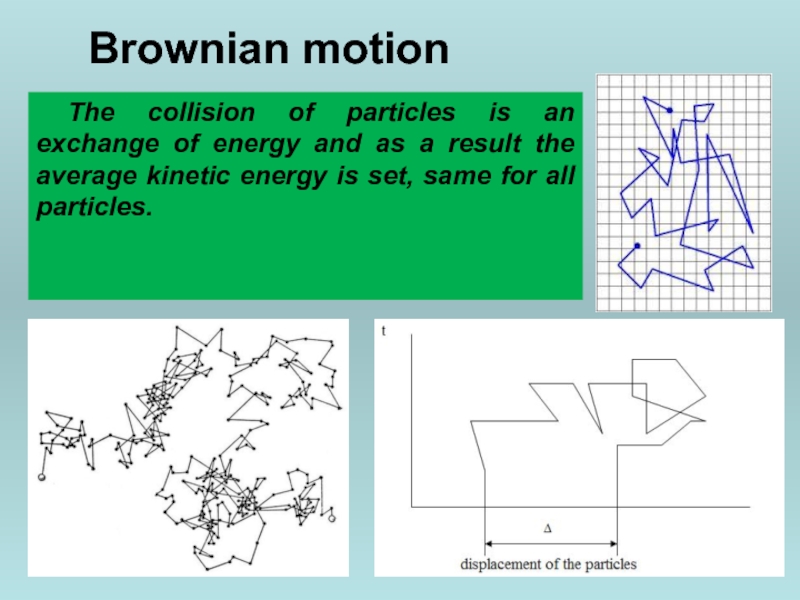
Слайд 26Brownian motion
Colloidal particles by molecular-kinetic properties are not fundamentally different from
Слайд 27Brownian motion
The collision of particles is an exchange of energy and
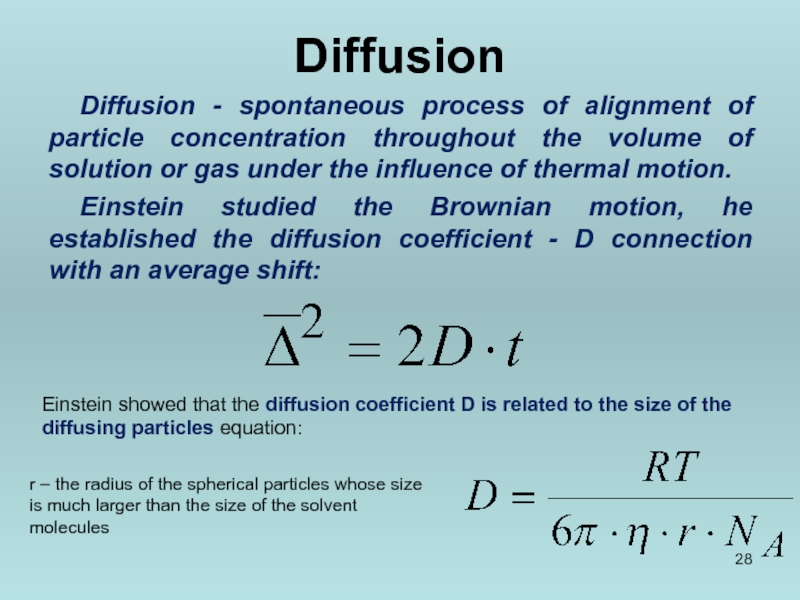
Слайд 28Diffusion
Diffusion - spontaneous process of alignment of particle concentration throughout the
Einstein studied the Brownian motion, he established the diffusion coefficient - D connection with an average shift:
Einstein showed that the diffusion coefficient D is related to the size of the diffusing particles equation:
r – the radius of the spherical particles whose size is much larger than the size of the solvent molecules
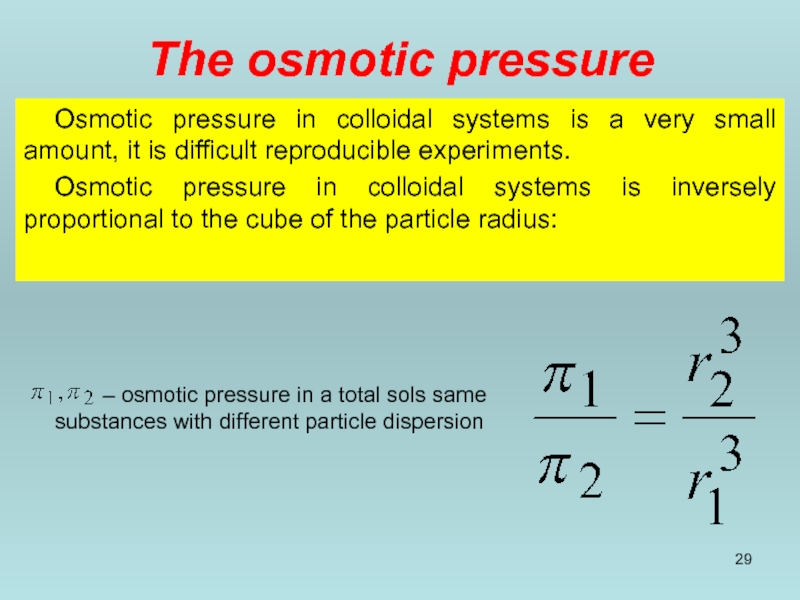
Слайд 29The osmotic pressure
Osmotic pressure in colloidal systems is a very small
Osmotic pressure in colloidal systems is inversely proportional to the cube of the particle radius:
– osmotic pressure in a total sols same substances with different particle dispersion
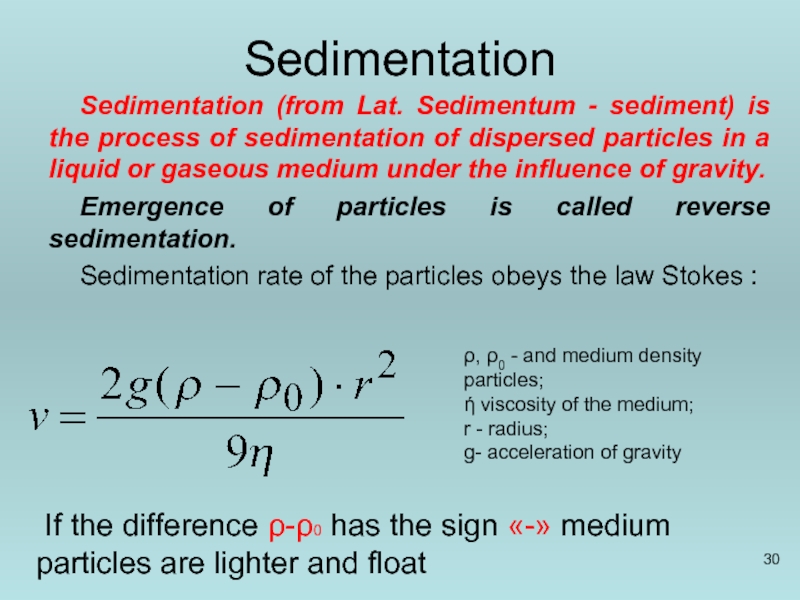
Слайд 30Sedimentation
Sedimentation (from Lat. Sedimentum - sediment) is the process of sedimentation
Emergence of particles is called reverse sedimentation.
Sedimentation rate of the particles obeys the law Stokes :
ρ, ρ0 - and medium density particles;
ή viscosity of the medium;
r - radius;
g- acceleration of gravity
If the difference ρ-ρ0 has the sign «-» medium particles are lighter and float
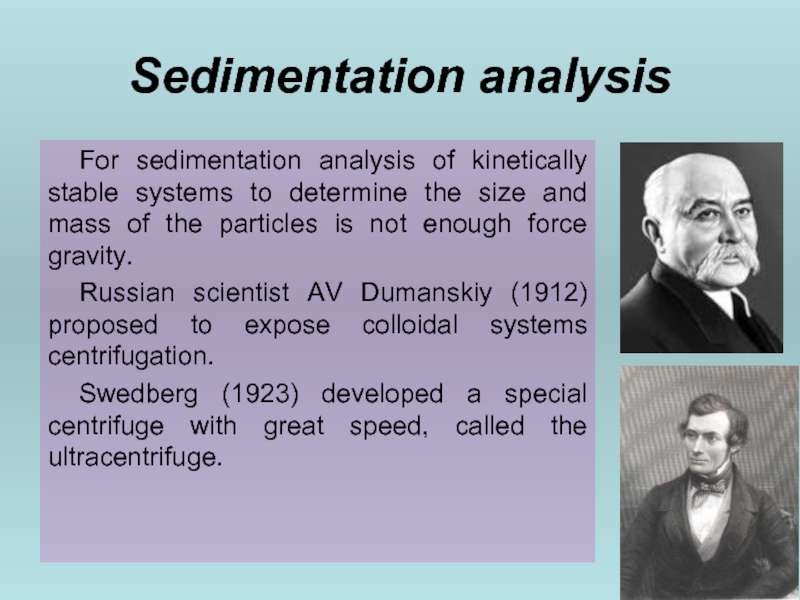
Слайд 31Sedimentation analysis
For sedimentation analysis of kinetically stable systems to determine the
Russian scientist AV Dumanskiy (1912) proposed to expose colloidal systems centrifugation.
Swedberg (1923) developed a special centrifuge with great speed, called the ultracentrifuge.
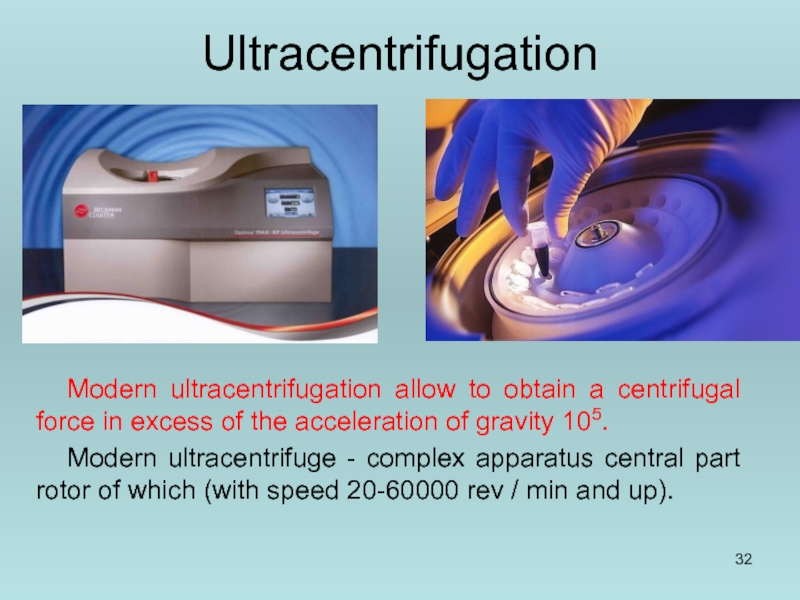
Слайд 32Ultracentrifugation
Modern ultracentrifugation allow to obtain a centrifugal force in excess of
Modern ultracentrifuge - complex apparatus central part rotor of which (with speed 20-60000 rev / min and up).
Слайд 33Optical properties of disperse systems
Zaporozhye state
medical University
Department of physical and
colloid chemistry
Слайд 34The scattering
of light
This is the most characteristic optical property of
This phenomenon was observed Faraday (1857) in the study of gold sol. The phenomenon Tyndall in 1868.
Through pure liquids and molecular solutions light just passes.
Through colloidal dispersions light ray meeting on the way a particle is not reflected, as if it skirts, and rejected several changes its direction (diffraction).
Faraday
Tyndall
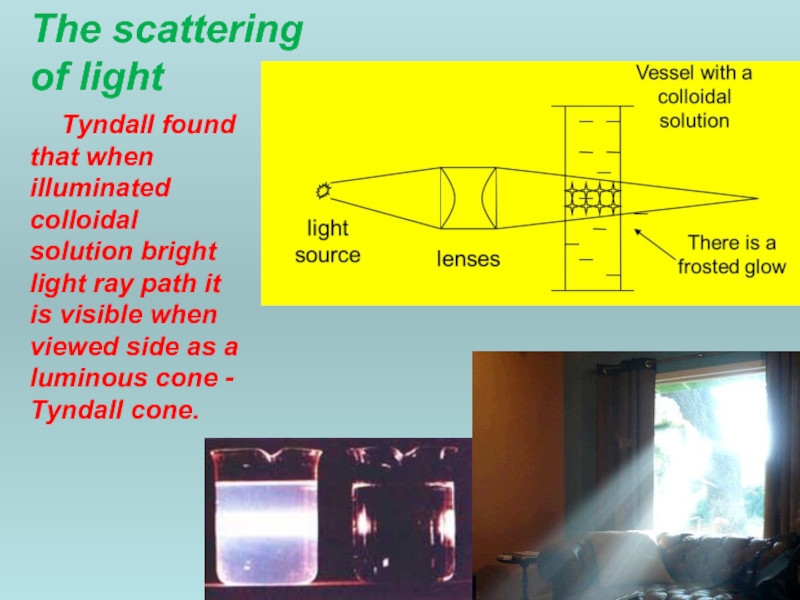
Слайд 35The scattering
of light
Tyndall found that when illuminated colloidal solution bright
Слайд 36Electrical properties of disperse systems
Zaporozhye state
medical University
Department of physical and
colloid chemistry
Слайд 37DEL. Formation of a double electric layer
DEL existence of ions and
These include: the electrode processes , electrocapillary and electrokinetic phenomena , phenomena associated with the electrostatic interaction of colloidal particles , largely determine the stability of the dispersed system .
All these phenomena are interconnected through DEL , called Electrosurface .
There are three possible mechanisms for the formation of DEL :
Due to the transition of electrons or ions from one phase to another ( 1st variant );
As a result of the selective adsorption of ions in the electrolyte interphase layer ( 2nd variant );
As a result of the orientation of the polar molecules conjugated phases in their interaction ( third variant ) .
Слайд 38When immersed in water, the metal plate portion of the positive
Слайд 39Electric double layer 2nd version. In the formation of AgI sol
Salt
Salt
Слайд 40Electric double layer third variant.
When the orientation of polar molecules at
metal ions
fatty acid
solid surface
Слайд 41The structure of DEL.
First picture of DEL was expressed Kwinke (1859)
DEL theory was developed in the works of scientists of the USSR A.N. Frumkin and B.V. Deryagin.
The first theory was the theory of the structure of DEL Helmholtz:
DEL consists of two flat charges located at the molecular distance from one another and interact with each other only by electrostatic forces of attraction.
Слайд 42Structure of DEL
Gouy-Chapman model assumed location counterions diffusion under the influence
The theory introduces the concept of the diffusion layer, the ions are treated as point charges that do not have their own size.
Слайд 43Structure of DEL
According to modern concepts (Stern’s theory) structure of DEL:
Слайд 44
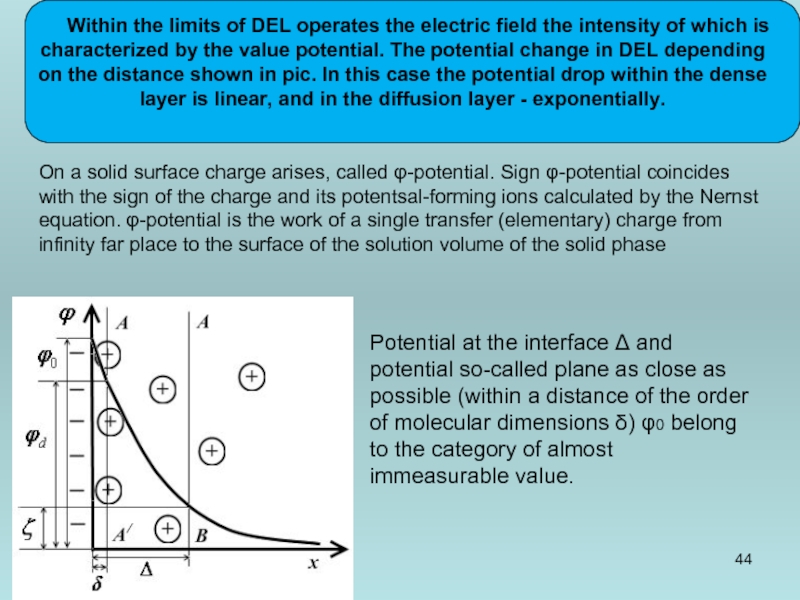
Within the limits of DEL operates the electric field the intensity
Potential at the interface Δ and potential so-called plane as close as possible (within a distance of the order of molecular dimensions δ) φ0 belong to the category of almost immeasurable value.
On a solid surface charge arises, called φ-potential. Sign φ-potential coincides with the sign of the charge and its potentsal-forming ions calculated by the Nernst equation. φ-potential is the work of a single transfer (elementary) charge from infinity far place to the surface of the solution volume of the solid phase
Слайд 45
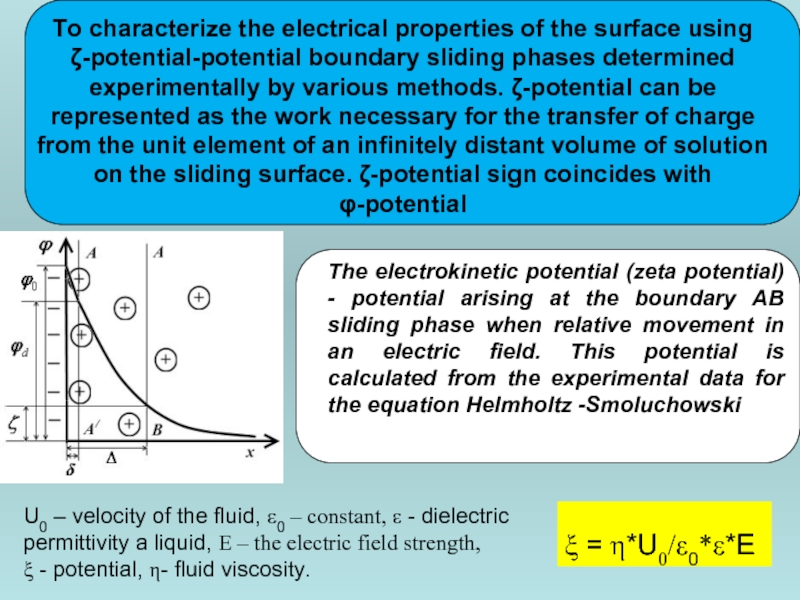
To characterize the electrical properties of the surface using ζ-potential-potential boundary
ξ = η*U0/ε0*ε*E
U0 – velocity of the fluid, ε0 – constant, ε - dielectric permittivity a liquid, E – the electric field strength,
ξ - potential, η- fluid viscosity.
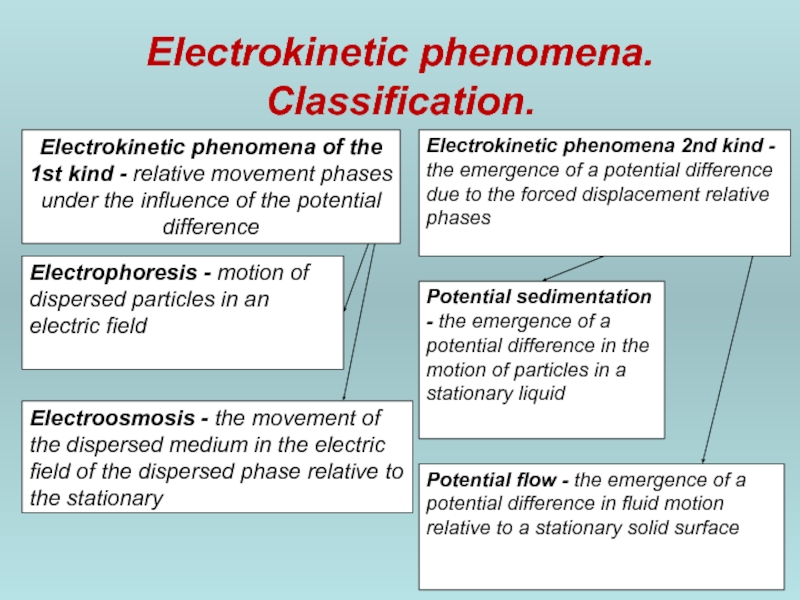
Слайд 46Electrokinetic phenomena. Classification.
Electrokinetic phenomena of the 1st kind - relative movement
Electrokinetic phenomena 2nd kind - the emergence of a potential difference due to the forced displacement relative phases
Electrophoresis - motion of dispersed particles in an electric field
Electroosmosis - the movement of the dispersed medium in the electric field of the dispersed phase relative to the stationary
Potential sedimentation - the emergence of a potential difference in the motion of particles in a stationary liquid
Potential flow - the emergence of a potential difference in fluid motion relative to a stationary solid surface
Слайд 47Electrophoresis
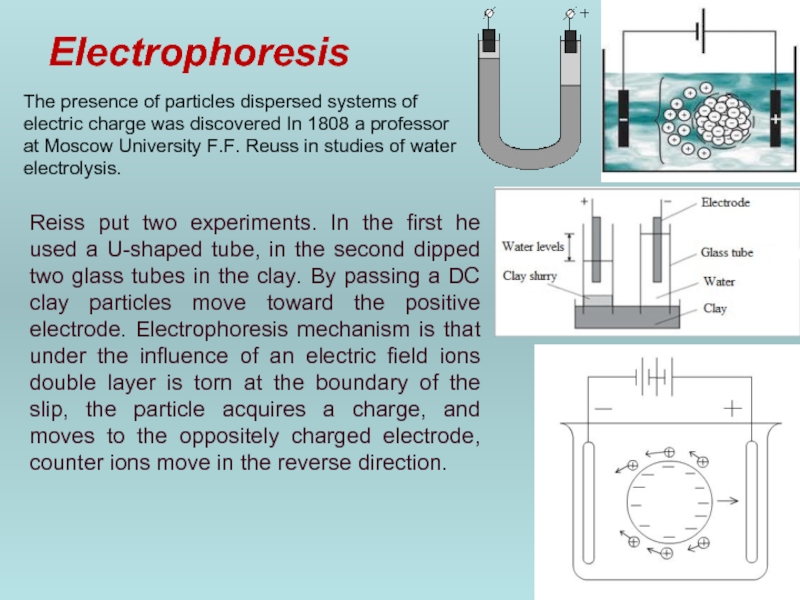
The presence of particles dispersed systems of electric charge was discovered
Reiss put two experiments. In the first he used a U-shaped tube, in the second dipped two glass tubes in the clay. By passing a DC clay particles move toward the positive electrode. Electrophoresis mechanism is that under the influence of an electric field ions double layer is torn at the boundary of the slip, the particle acquires a charge, and moves to the oppositely charged electrode, counter ions move in the reverse direction.
Слайд 48Electrophoresis
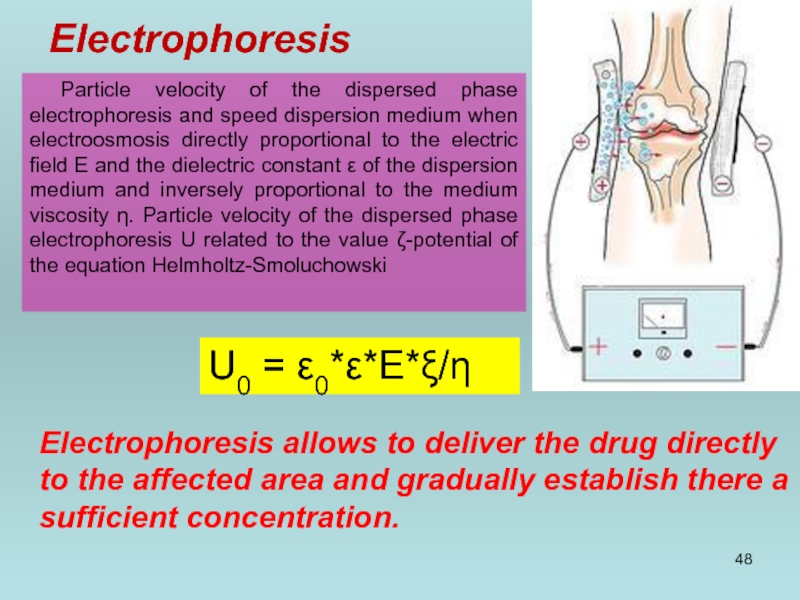
Particle velocity of the dispersed phase electrophoresis and speed dispersion medium
U0 = ε0*ε*E*ξ/η
Electrophoresis allows to deliver the drug directly to the affected area and gradually establish there a sufficient concentration.
Слайд 49Electroosmosis
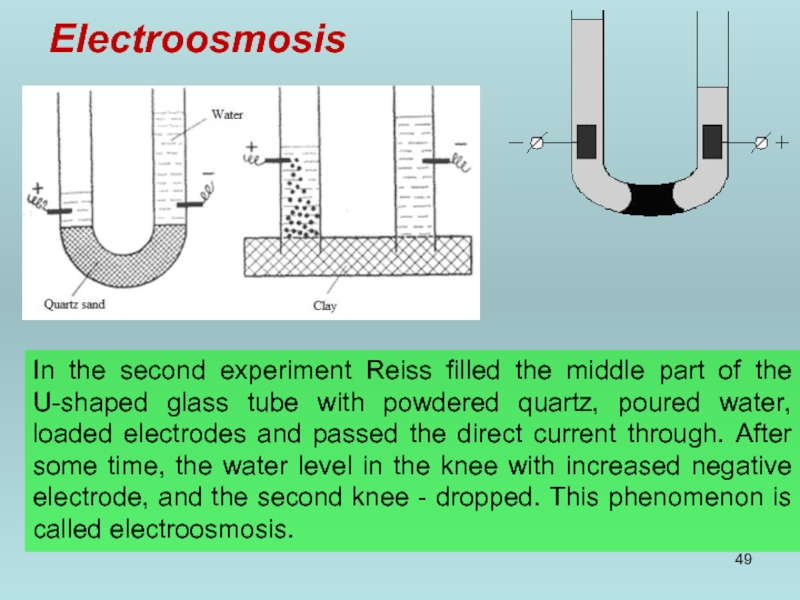
In the second experiment Reiss filled the middle part of the
Слайд 50Potential of
leakage and
sedimentation
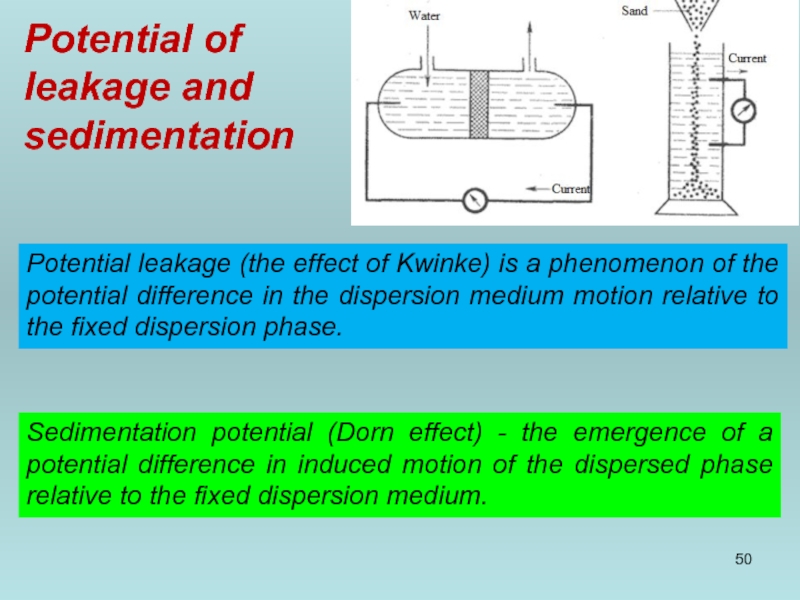
Potential leakage (the effect of Kwinke) is a
Sedimentation potential (Dorn effect) - the emergence of a potential difference in induced motion of the dispersed phase relative to the fixed dispersion medium.
Слайд 51Stability and coagulation of colloidal systems
Zaporozhye state
medical University
Department of physical and
colloid
Слайд 52
Stability of disperse systems
On the suggestion of NP Peskov (1920) the
Aggregate stability - the ability of the dispersed phase provide blocking resistance and thus maintain a certain degree of dispersion of this phase as a whole.
Слайд 53Coagulation is a process of adhesion of colloidal particles to form
introduction of electrolytes;
heating or freezing of the dispersed system;
mechanical action;
high-frequency oscillations;
ultracentrifugation.
Слайд 54
Coagulation sols electrolytes
All electrolytes at certain concentrations can cause coagulation of
Usually charge sign: sol coagulation that causes ion electrolyte sign of the charge which is opposite to the charge of the colloidal particle. This ion-ion called coagulator.
Each electrolyte in relation to the colloidal solution has a threshold of coagulation.





![{[mFe4[Fe(CN)6]3·n[Fe(CN)6]4-]4n-·4 (n-х)K+}4x-·4xK+{[m Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3·nFe3+] 3n+·3(n-х)Сl-}3x+·3xCl-](/img/tmb/2/155630/9a1ebbb30c7dbaeae5ad2b50dab57deb-800x.jpg)