that emits energetic electrons is called beta decay. Beta decay comes in two varieties. β- decay involves normal, negatively-charged electrons , while β+ decay involves positively-charged electrons or positrons. The energetic electrons or positrons are called beta particles in this context.)
Alpha decay
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Atomic mass презентация
Содержание
- 1. Atomic mass
- 2. Q2: Complete the following nuclear equations (the question marks)
- 3. Pre-lesson activity: What is the atomic
- 4. Theme of the lesson Atomic mass
- 5. Learning objectives Calculate relative atomic, molecular and
- 6. Success criteria Student achieves if He/she
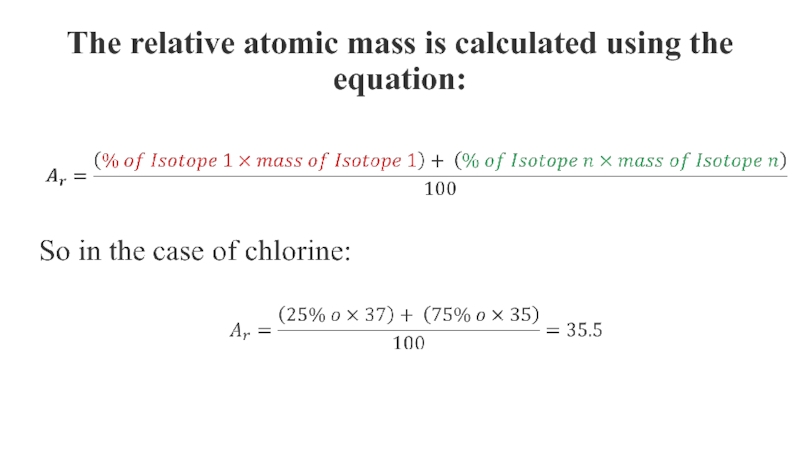
- 7. The relative atomic mass is calculated using the equation:
- 8.
Слайд 1Mark – scheme for RADIOACTIVITY quiz:
Delta.
True
Gamma
Alpha particles
Beta decay (Radioactive decay
Слайд 3Pre-lesson activity:
What is the atomic mass?
Why we do not use the
absolute atomic mass?
How the relative atomic mass was calculated?
What is the value of amu?
Why the atomic masses in the periodic table are not necessarily whole numbers?
How the relative atomic mass was calculated?
What is the value of amu?
Why the atomic masses in the periodic table are not necessarily whole numbers?
Слайд 5Learning objectives
Calculate relative atomic, molecular and formula masses.
Explain why the atomic
masses in the periodic table are not necessarily whole numbers.
Calculate relative isotopic ratios from molar mass.
Calculate relative isotopic ratios from molar mass.
Слайд 6Success criteria
Student achieves if
He/she will be able to calculate relative
atomic, molecular and formula masses
He/she can explain why the atomic masses in the periodic table are not necessarily whole numbers
He/she will be able to calculate relative isotopic ratios from molar mass
He/she can explain why the atomic masses in the periodic table are not necessarily whole numbers
He/she will be able to calculate relative isotopic ratios from molar mass