- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Alkali metals презентация
Содержание
- 1. Alkali metals
- 3. GENERAL PROPERTIES OF 1A *By giving their
- 4. They are solids at room temperature. They
- 5. OCCURRENCE Since the alkali metals are the
- 6. Potassium, K Potassium constitutes 1.5% of the
- 7. CHEMICAL PROPERTIES 1)Alkali metals are strong reducing
- 8. 2) Hydrides are formed as a result
- 9. 3) They react with water violently.
- 10. 4) They may form oxides, peroxides or
- 11. 5. All of them react with halogens
- 12. 6. They do not react with bases
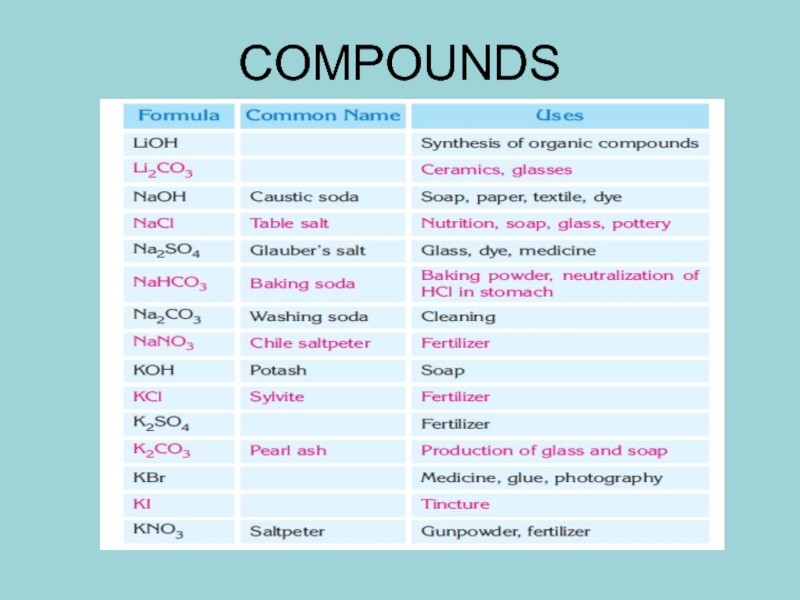
- 13. COMPOUNDS
Слайд 1I – A
GROUP ELEMENTS
Li-lithium
Na-sodium
K-potassium
Rb-rubidium
Cs-cesium
Fr-francium
ALKALI METALS
Слайд 2
INTRODUCTION
Name of this family comes from the properties of alkali metals to form hydroxides with water. Compounds containing hydroxide ion is basic and called alkali.
Name of this family comes from the properties of alkali metals to form hydroxides with water. Compounds containing hydroxide ion is basic and called alkali.
They are very active ,so in the nature they are not found in elemental forms. They exist in various compounds.
Слайд 3GENERAL PROPERTIES OF 1A
*By giving their valence electron easily in chemical
reactions, they form +1 charged ions.
* Alkali metals are the elements which have the least ionization energy and the highest atomic radius, in each period
* They are a group of most active metals.
* The activity of metals increase from top to bottom
* The element cesium, Cs, is the most active metal
* Francium is a radioactive element
* Alkali metals are the elements which have the least ionization energy and the highest atomic radius, in each period
* They are a group of most active metals.
* The activity of metals increase from top to bottom
* The element cesium, Cs, is the most active metal
* Francium is a radioactive element
Слайд 5OCCURRENCE
Since the alkali metals are the most active metals, they are
not found free in nature, but as compounds.
Sodium, Na
The most important compound of sodium is sodium chloride, NaCl. The important sodium sources are Chile saltpeter (NaNO3), washing soda (Na2CO3) and baking soda (NaHCO3). The most important sodium minerals are kryolite (Na3AlF6), borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O), sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and albite (NaAlSi3O8).
Sodium, Na
The most important compound of sodium is sodium chloride, NaCl. The important sodium sources are Chile saltpeter (NaNO3), washing soda (Na2CO3) and baking soda (NaHCO3). The most important sodium minerals are kryolite (Na3AlF6), borax (Na2B4O7.10H2O), sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) and albite (NaAlSi3O8).
Слайд 6Potassium, K
Potassium constitutes 1.5% of the earth’s crust. Potassium is found
as the minerals sylvite (KCl) and carnallite (KCl · MgCl2 ·6H2O) and as the silicates of orthoclas (KAlSi3O8) and mica (KH2Al3(SiO4)3). The main sources of potassium are K2SO4 and KNO3, which are used as fertilizers.
Слайд 7CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
1)Alkali metals are strong reducing agents.
nM0 + Y+n → nM+ + Y0(s)
(Y : any metal with low activity,
M : any alkali metal)
0 +3 +1 0
6Na(s) + Al2O3(s) → 3Na2O(s) + 2Al(s)
0 +3 +1 0
3K(s) + CrCl3(s) → 3KCl(s) + Cr(s)
(Y : any metal with low activity,
M : any alkali metal)
0 +3 +1 0
6Na(s) + Al2O3(s) → 3Na2O(s) + 2Al(s)
0 +3 +1 0
3K(s) + CrCl3(s) → 3KCl(s) + Cr(s)
Слайд 82) Hydrides are formed as a result of alkali metals reactions
with hydrogen. Hydrides contain a +1 charged alkali metal and –1 charged hydrogen
2K(s) + H2(g) ⎯→ 2KH(s) potassium hydride
2Na(s) + H2(g) ⎯→ 2NaH(s) sodium hydride
2K(s) + H2(g) ⎯→ 2KH(s) potassium hydride
2Na(s) + H2(g) ⎯→ 2NaH(s) sodium hydride
Слайд 9
3) They react with water violently. As a result of this
reaction H2 gas and a base solution form.
2M(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2MOH(aq) + H2(g) +heat
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat
2M(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2MOH(aq) + H2(g) +heat
2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) + heat
Слайд 104) They may form oxides, peroxides or superoxides by reacting with
oxygen in the air.
As a result of reactions with excess oxygen, lithium forms oxide, Li2O, sodium forms peroxide Na2O2 and potassium, rubidium and cesium form superoxides, such as KO2, RbO2, CsO2.
4Li(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ 2Li2O(s)
2Na(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ Na2O2(s)
K(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ KO2(s)
As a result of reactions with excess oxygen, lithium forms oxide, Li2O, sodium forms peroxide Na2O2 and potassium, rubidium and cesium form superoxides, such as KO2, RbO2, CsO2.
4Li(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ 2Li2O(s)
2Na(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ Na2O2(s)
K(s) + O2(g) ⎯→ KO2(s)
Слайд 115. All of them react with halogens to form alkali halides
(salts of alkali metals).
2M(s) + X2(g) ⎯→ 2MX(s)
(M : alkali metal, X : halogen,
MX ; alkali metal halides)
2Li(s) + F2(g) ⎯→ 2LiF(s)
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) ⎯→ 2NaCl(s)
2M(s) + X2(g) ⎯→ 2MX(s)
(M : alkali metal, X : halogen,
MX ; alkali metal halides)
2Li(s) + F2(g) ⎯→ 2LiF(s)
2Na(s) + Cl2(g) ⎯→ 2NaCl(s)
Слайд 126. They do not react with bases
M(s) + OH–(aq) ⎯→
No reaction
7. When they react with acids, the produce salts andliberate H2 gas.
M(s) + HX(aq) ⎯→ MX(aq) + 1/2H2(g)
(HX : Halo acid, MX : salt of an alkali)
2K(s) + 2HCl(aq) ⎯→ 2KCl(aq) + H2(g)
2Na(s) + 2HBr(aq) ⎯→ 2NaBr(aq) + H2(g)
7. When they react with acids, the produce salts andliberate H2 gas.
M(s) + HX(aq) ⎯→ MX(aq) + 1/2H2(g)
(HX : Halo acid, MX : salt of an alkali)
2K(s) + 2HCl(aq) ⎯→ 2KCl(aq) + H2(g)
2Na(s) + 2HBr(aq) ⎯→ 2NaBr(aq) + H2(g)