- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Navigation презентация
Содержание
- 1. Navigation
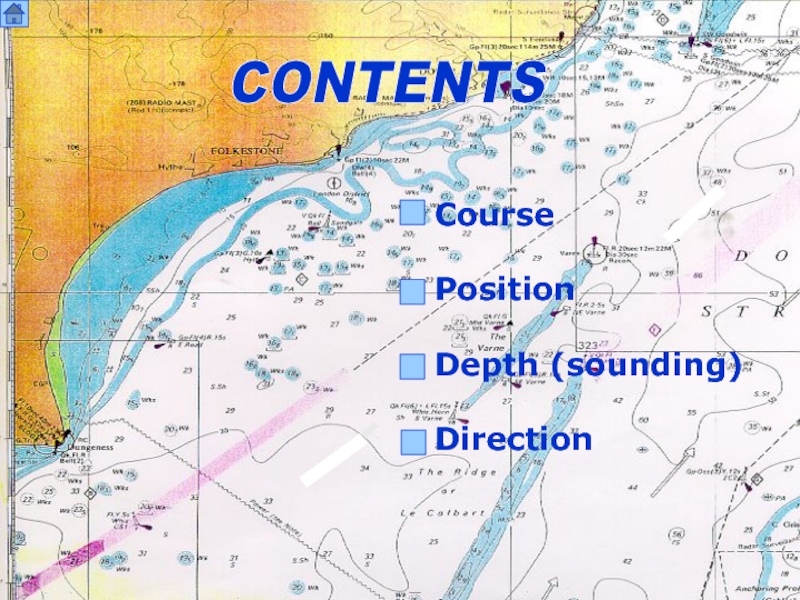
- 2. CONTENTS
- 3. SOUND
- 4. sound COURSE By course is meant: the
- 5. Do not confuse heading and
- 6. sound TRACK The track consists of one,
- 7. GREAT CIRCLE COURSE (TRACK) DEPARTURE DESTINATION
- 8. This implies that in
- 9. s sound COMPOSITE
- 10. sound DRIFT AND CURRENT A B
- 11. sound A By course made
- 12. sound A By course over
- 13. s POSITION
- 14. Pilotage (coastal navigation) Cross bearing The
- 15. When sailing along the coast, compass- bearings of conspicuous objects are taken at regular intervals.
- 16. A CONSPICUOUS OBJECT (CONSPIC) is an
- 17. Cross bearings form an
- 18. If a third conspicuous object is
- 19. X X X As the ship
- 20. When there is only one conspicuous object,
- 21. X Course line 16 50 380
- 22. 16 50 380 X 16 55
- 23. 16 50 380 X
- 24. X 16 50 380
- 25. sound By “Dead Reckoning” is meant
- 26. s ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION With astronomical
- 27. SEXTANT-BEARING
- 28. With the
- 29. SATELLITE-BEARING When taking a
- 30. sound s Sounding With the aid
- 31. TAKING SOUNDINGS A signal is
- 32. TAKING SOUNDINGS With multi-beam echo sounding
- 33. so
- 34. s Directions
- 35. Ahead Starboard Astern Port
- 36. On the stem On the
- 37. FINISHED
Слайд 3SOUND
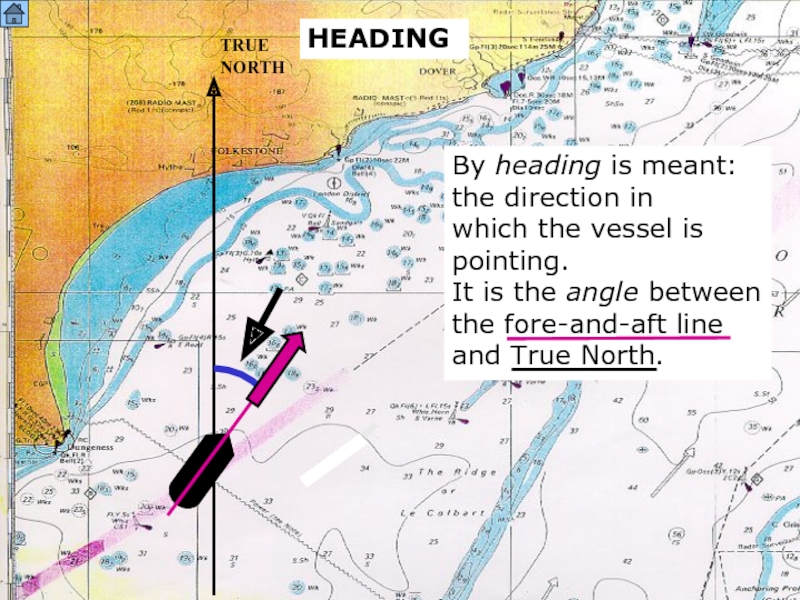
HEADING
TRUE
NORTH
By heading is
the direction in
which the vessel is
pointing.
It is the angle between
the fore-and-aft line
and True North.
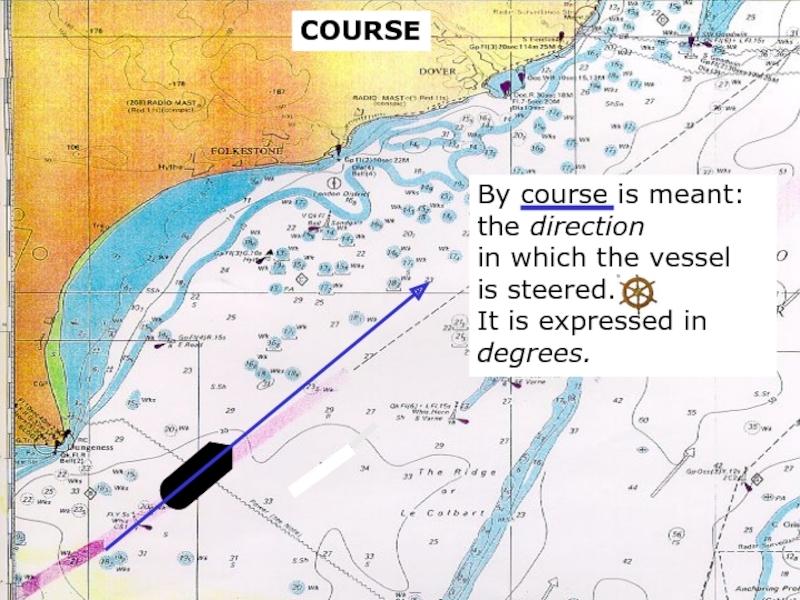
Слайд 4sound
COURSE
By course is meant:
the direction
in which the vessel
is steered.
It
degrees.
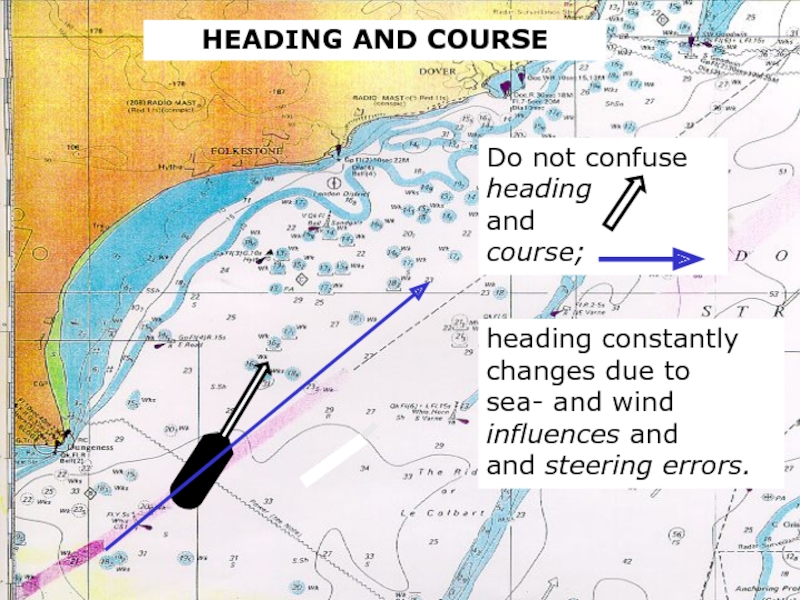
Слайд 5Do not confuse
heading
and
course;
HEADING AND COURSE
heading constantly
changes due to
sea- and
influences and
and steering errors.
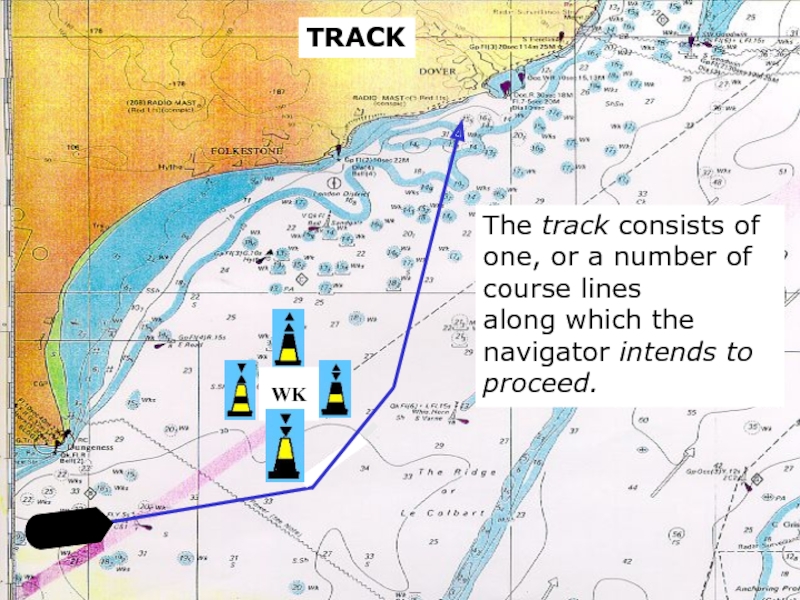
Слайд 6sound
TRACK
The track consists of one, or a number of
course lines
along which
navigator intends to proceed.
WK
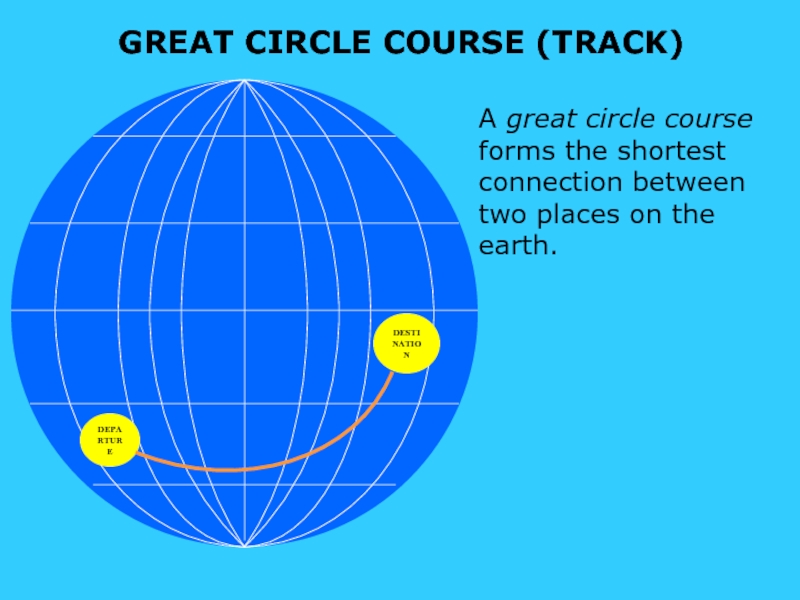
Слайд 7GREAT CIRCLE COURSE (TRACK)
DEPARTURE
DESTINATION
A great circle course forms the shortest connection
Слайд 8
This implies that in (Mercator) sea charts
the earth is
sound
DEPARTURE
DESTINATION
A Rhumb line
is a line whereby
all the angles made by the Meridians and the course line are equal.
RHUMB LINE (loxodrome)
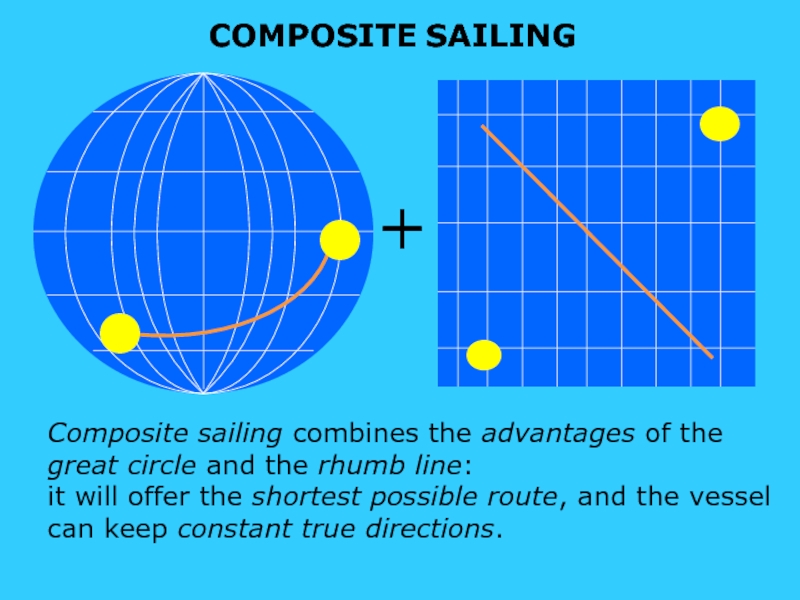
Слайд 9s
sound
COMPOSITE SAILING
+
Composite sailing combines the advantages of the
great circle and
it will offer the shortest possible route, and the vessel can keep constant true directions.
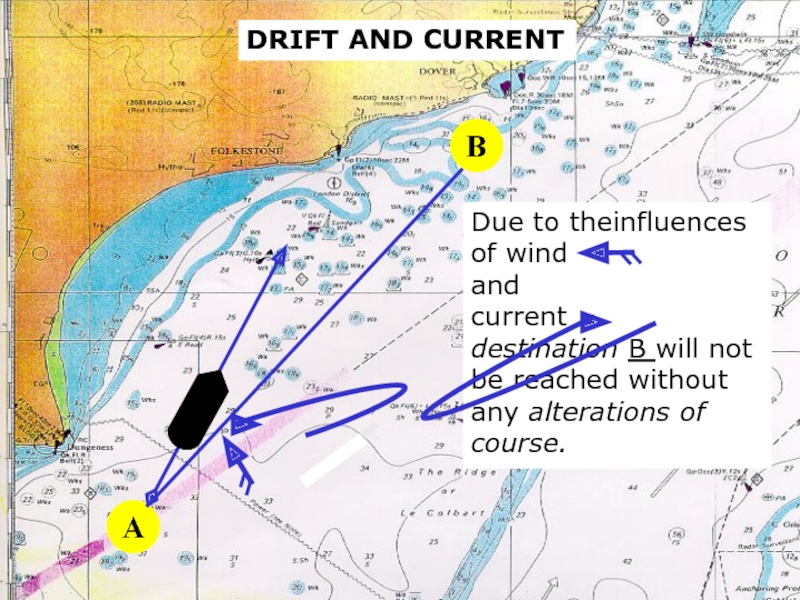
Слайд 10sound
DRIFT AND CURRENT
A
B
Due to theinfluences of wind
and
current
destination B will
Слайд 11sound
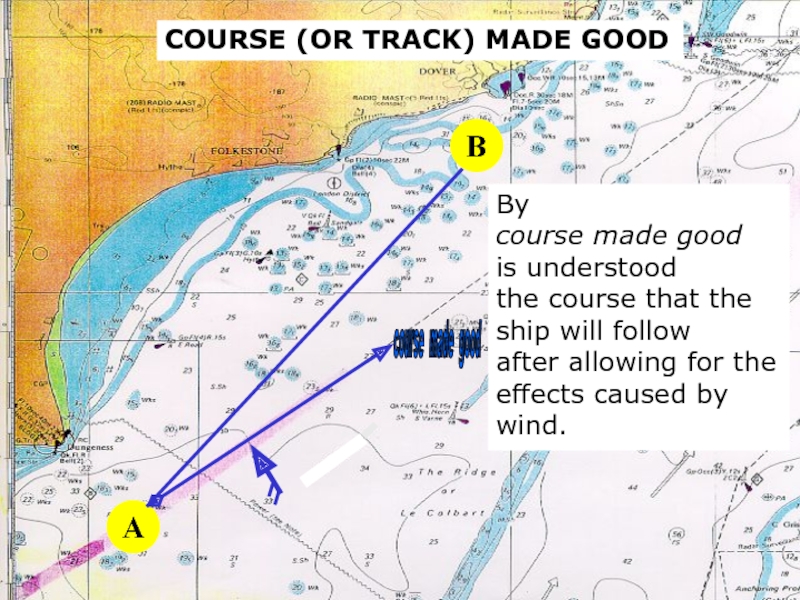
A
By
course made good
is understood
the course that the
ship will
after allowing for the effects caused by wind.
COURSE (OR TRACK) MADE GOOD
course made good
B
Слайд 12sound
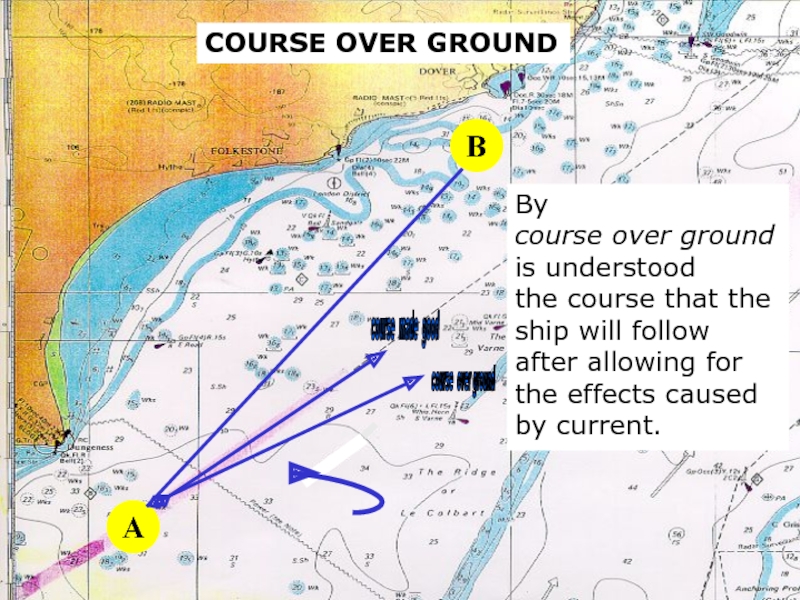
A
By
course over ground
is understood
the course that the
ship will
after allowing for the effects caused by current.
COURSE OVER GROUND
course over ground
course made good
B
Слайд 14Pilotage (coastal navigation)
Cross bearing
The cocked hat
A running fix
Dead reckoning
Astronomical
Satellite
s
Determining position
Слайд 15When sailing along the coast, compass- bearings of conspicuous objects are
Слайд 16A CONSPICUOUS OBJECT (CONSPIC)
is an object on land or at
mentioned and described in the pilot book.
Tower
Lighthouse
Oilrig
Слайд 17
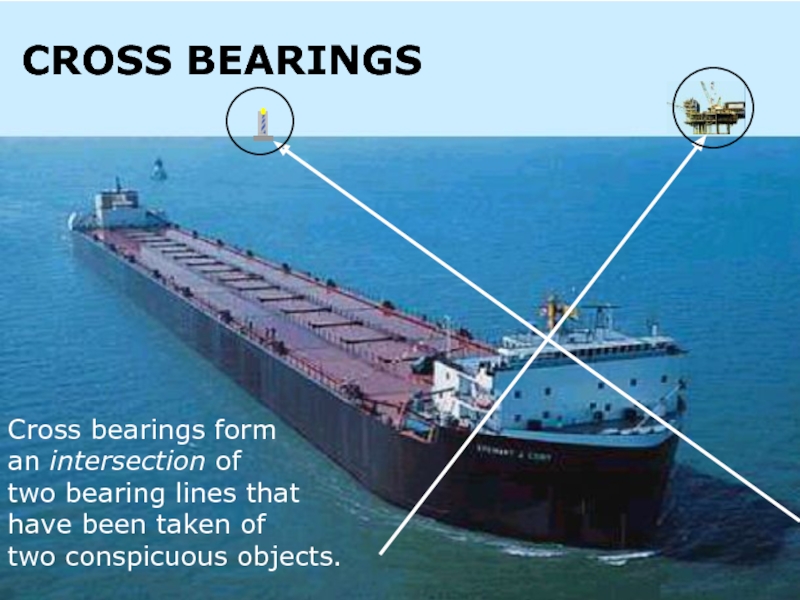
Cross bearings form
an intersection of
two bearing lines that
have been
two conspicuous objects.
CROSS BEARINGS
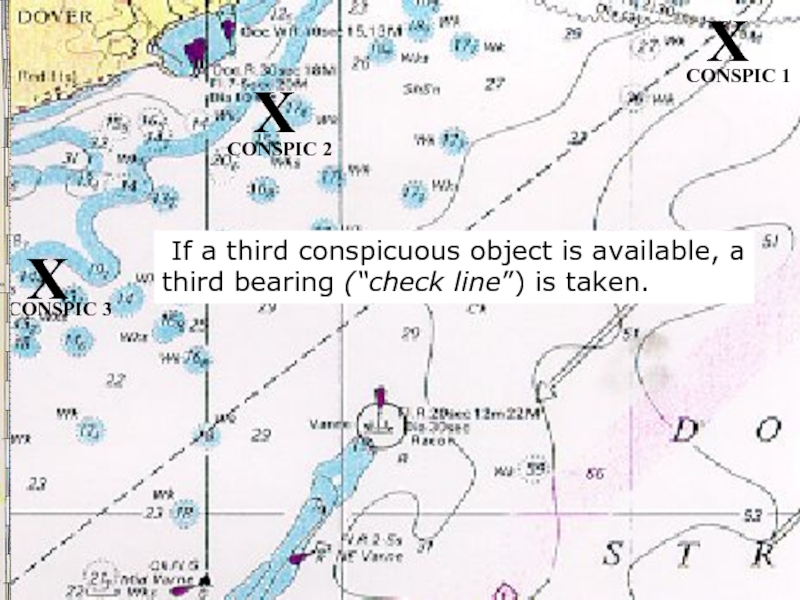
Слайд 18 If a third conspicuous object is available, a third bearing
X
X
CONSPIC 1
CONSPIC 2
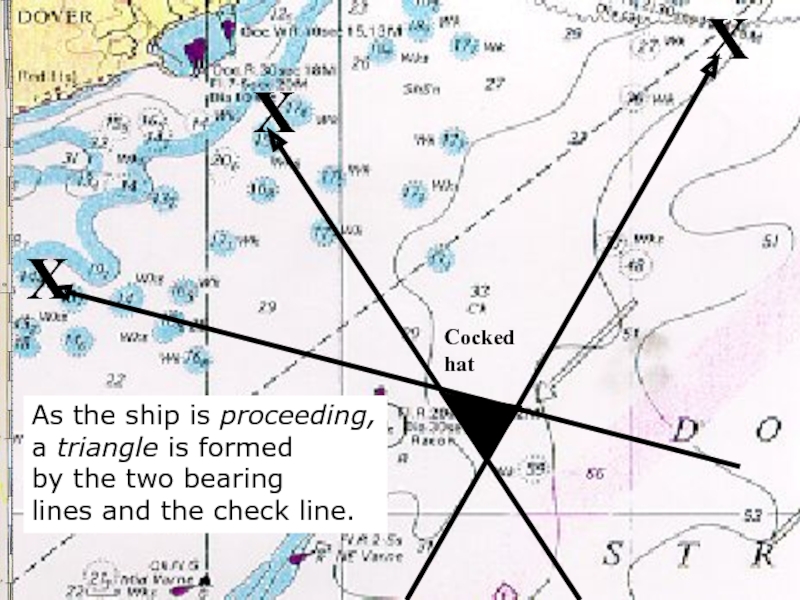
Слайд 19X
X
X
As the ship is proceeding,
a triangle is formed
by the two bearing
lines and the check line.
Cocked
hat
Слайд 20When there is only one
conspicuous object,
a position fix is made
by
of that same conspic
at interval.
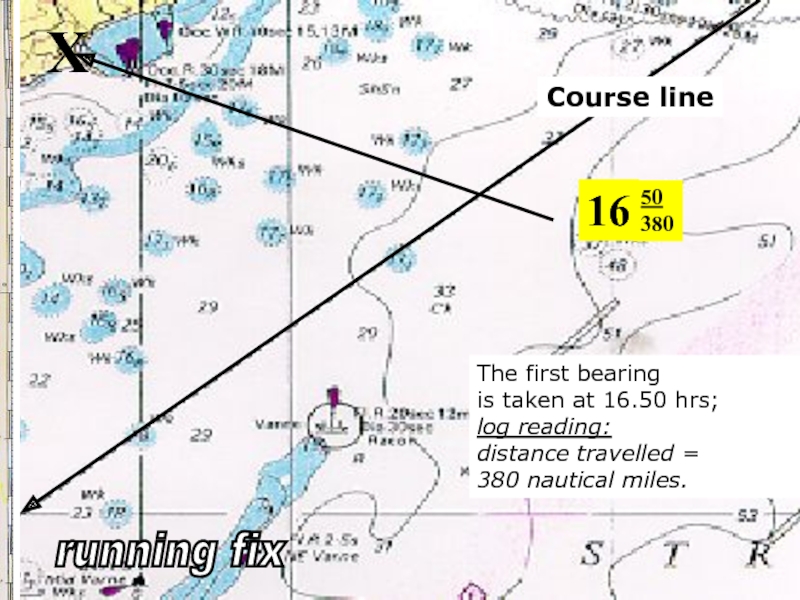
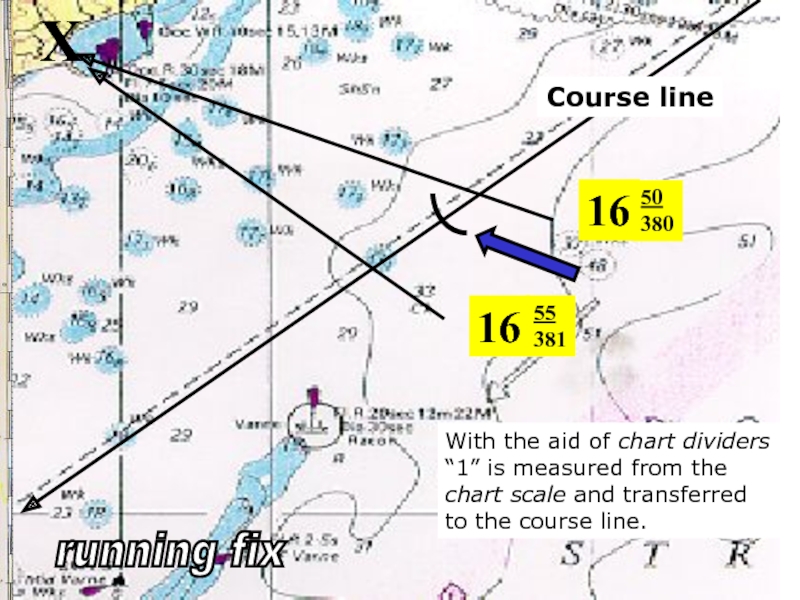
Слайд 21X
Course line
16
50
380
The first bearing
is taken at 16.50 hrs;
log reading:
distance travelled
380 nautical miles.
running fix
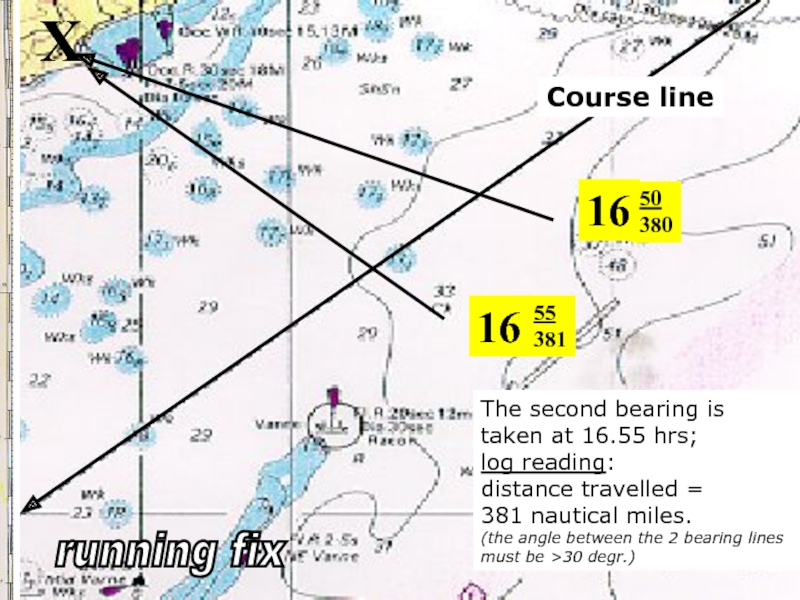
Слайд 2216
50
380
X
16
55
381
The second bearing is
taken at 16.55 hrs;
log reading:
distance travelled =
381 nautical miles.
(the angle between the 2 bearing lines must be >30 degr.)
running fix
Course line
Слайд 2316
50
380
X
With the aid of chart dividers
“1” is measured from the
to the course line.
running fix
16
55
381
Course line
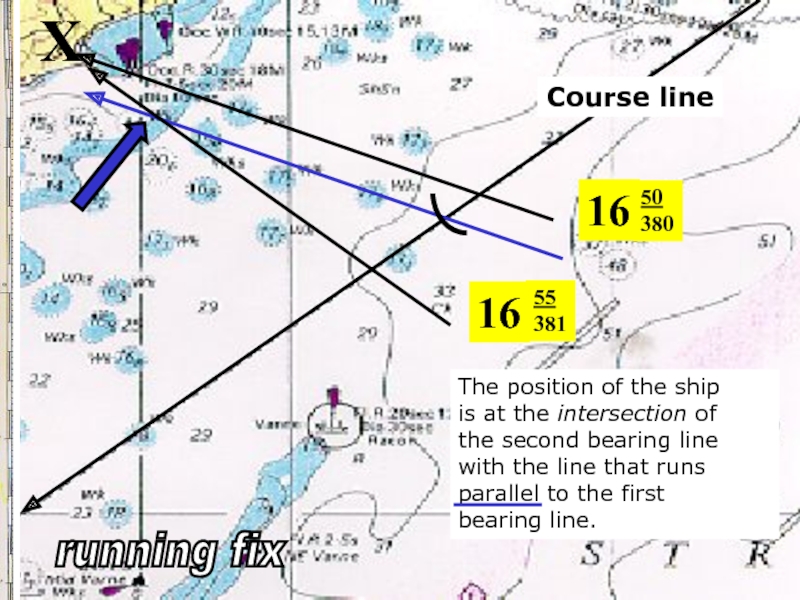
Слайд 24X
16
50
380
The position of the ship
is at the intersection of
the
with the line that runs
parallel to the first
bearing line.
running fix
16
55
381
Course line
Слайд 25 sound
By “Dead Reckoning” is meant
finding one’s position by
taking into
. last known position;
. course and speed;
. sea and weather conditions.
Dead Reckoning
Слайд 26 s
ASTRONOMICAL NAVIGATION
With astronomical navigation(celestial navigation)
observations are taken of the sun,
or the stars (celestial bodies) with the aid of
a sextant.
Слайд 28
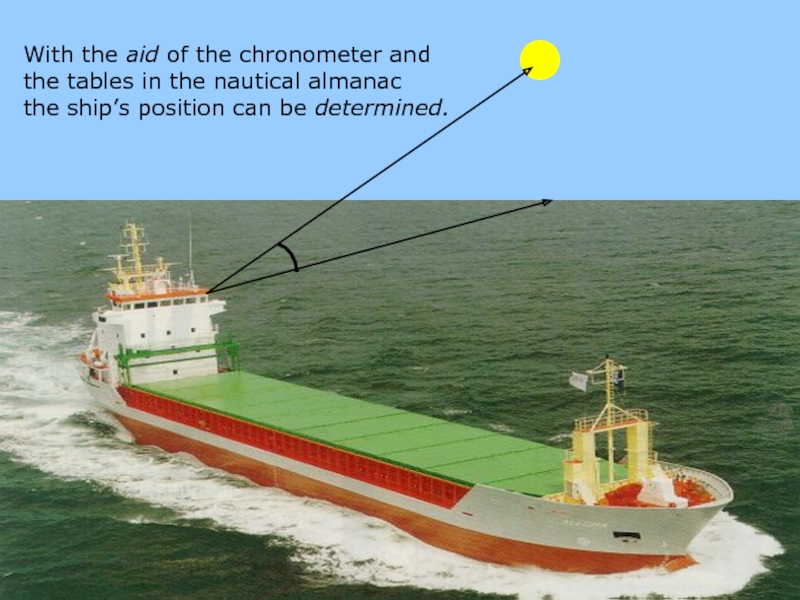
With the aid of the chronometer and
the tables in
the ship’s position can be determined.
Слайд 29
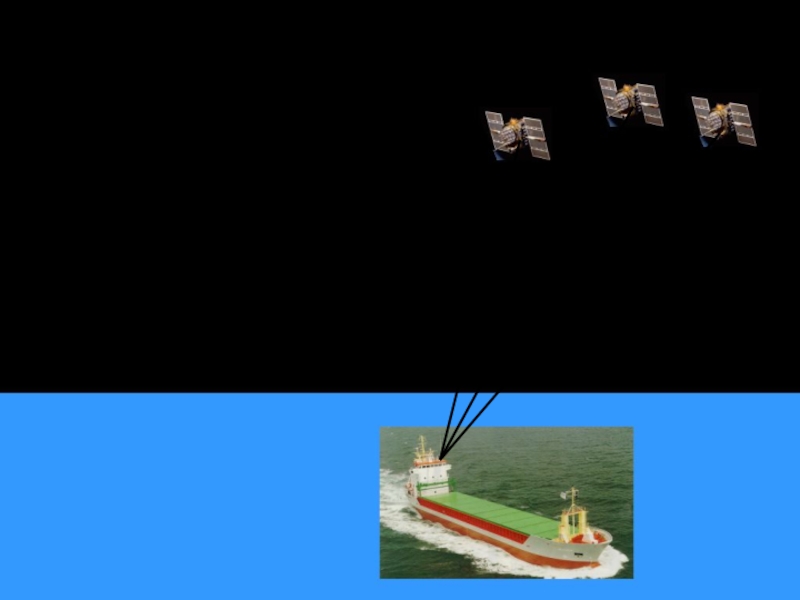
SATELLITE-BEARING
When taking a satellite bearing
by means of the
Global Positioning System
a
a satellite, indicating the vessel’s
position on the GPS - display.
Слайд 31
TAKING SOUNDINGS
A signal is transmitted to
the sea bed.
This signal “bounces
and is received again
by the echo sounder.
From the time elapsed
between transmission
and reception of the signal,
the depth of the water
can be determined.
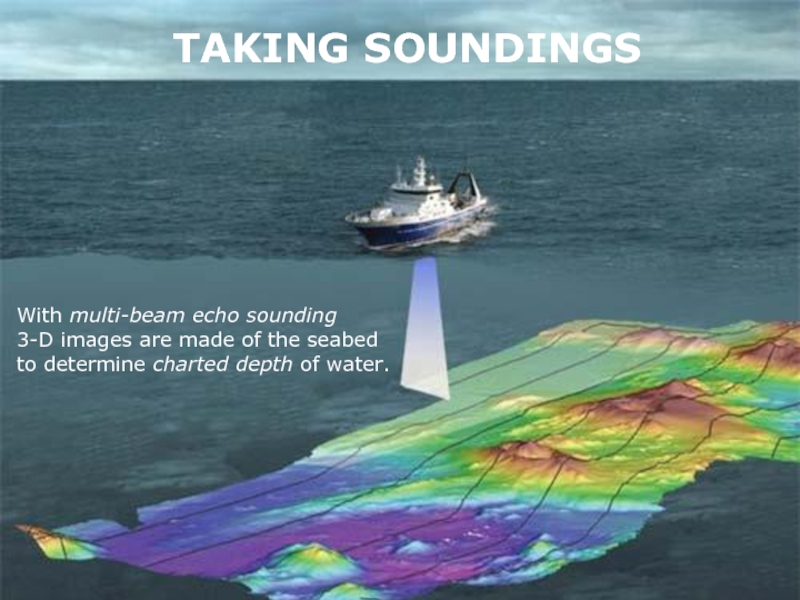
Слайд 32TAKING SOUNDINGS
With multi-beam echo sounding
3-D images are made of the
to determine charted depth of water.
Слайд 33so
WIRE SWEEPING
Depth over a protruding obstacle can also be obtained
wire sweeping, whereby a cable is swept over the sea bed
between two survey vessels.
However, this method of determining depth is obsolete.
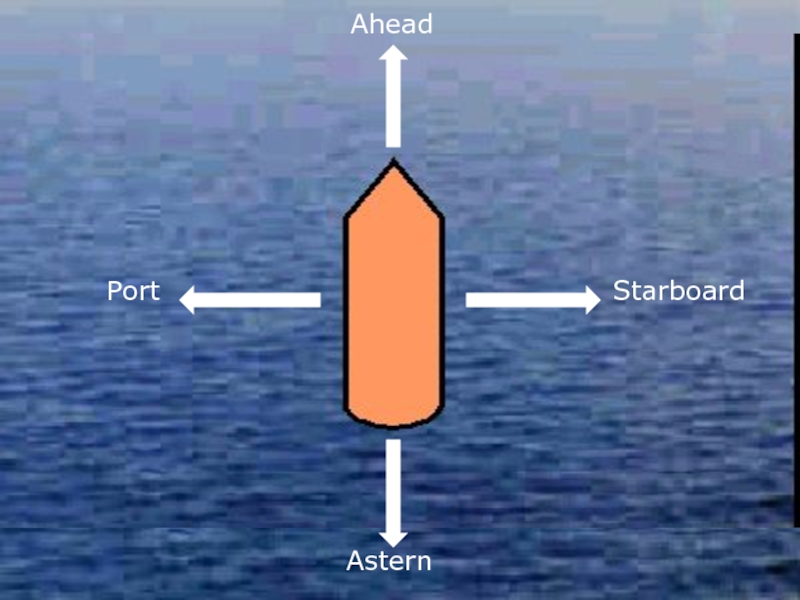
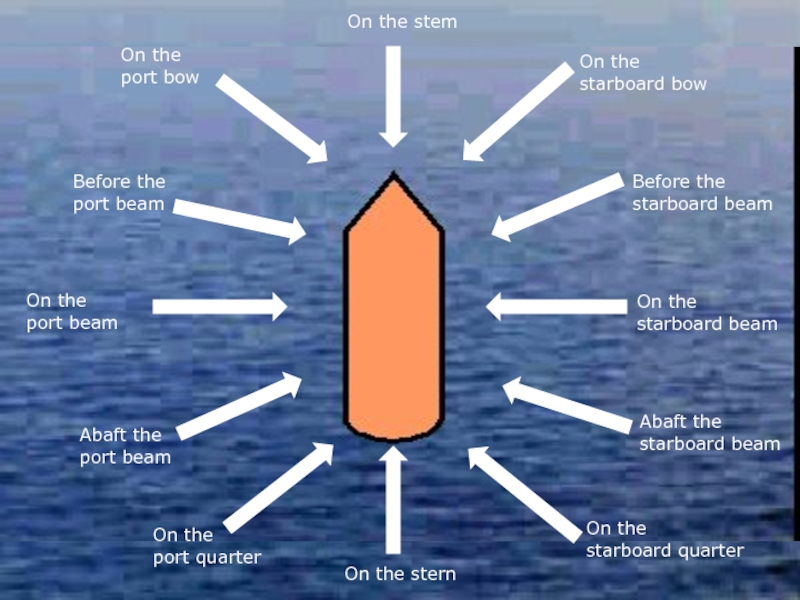
Слайд 36On the stem
On the
starboard bow
Before the
starboard beam
On the
starboard
Abaft the
starboard beam
On the
starboard quarter
On the stern
On the
port quarter
Abaft the
port beam
On the
port beam
Before the
port beam
On the
port bow