- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Quantum computers, quantum computations презентация
Содержание
- 1. Quantum computers, quantum computations
- 2. Take-home message The quest for a quantum
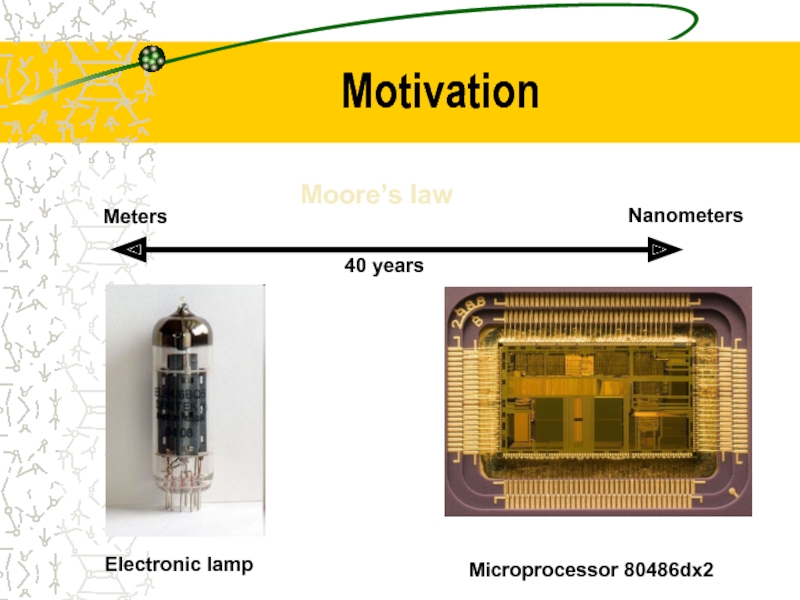
- 3. Motivation Microprocessor 80486dx2 Electronic lamp Meters Nanometers Moore’s law 40 years
- 4. Outline History Principles of quantum computation Di
- 5. History in facts 1982 – R. Feynman
- 6. 2012 – S. Haroche & D.
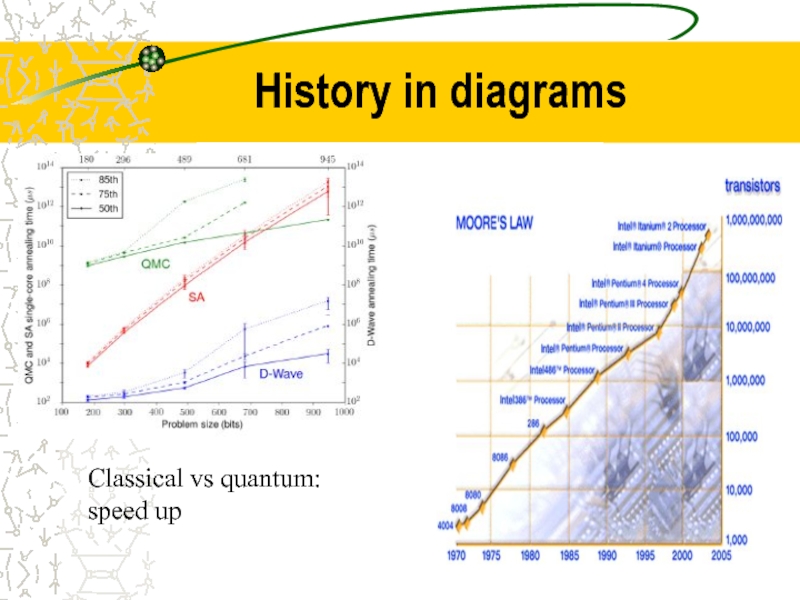
- 7. History in diagrams Classical vs quantum: speed up
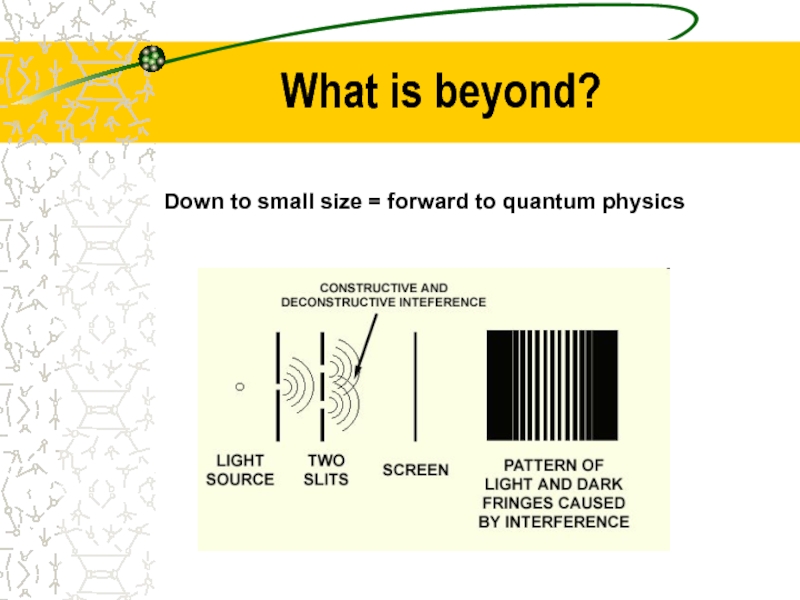
- 8. What is beyond? Down to small size = forward to quantum physics
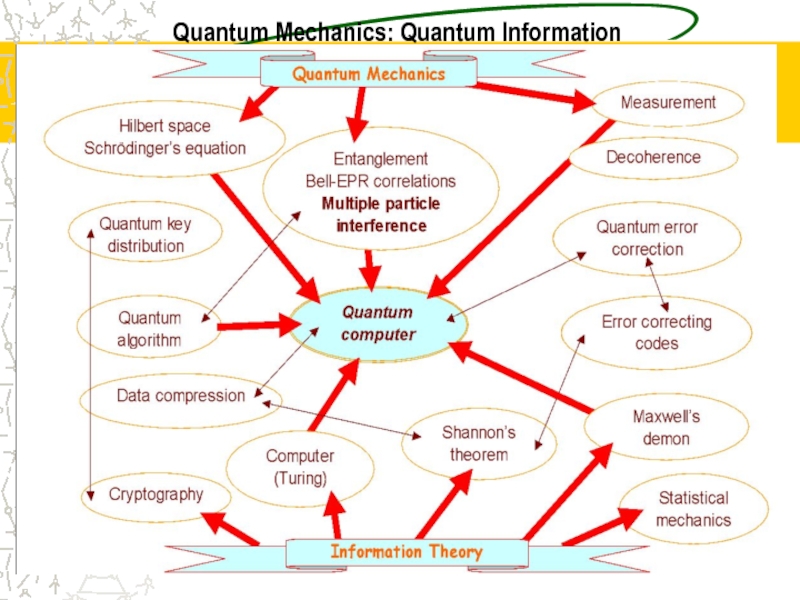
- 9. Quantum Mechanics: Quantum Information
- 10. What is all about or new applications
- 11. What is QC? QC is the physical
- 12. Classical ≠ Quantum
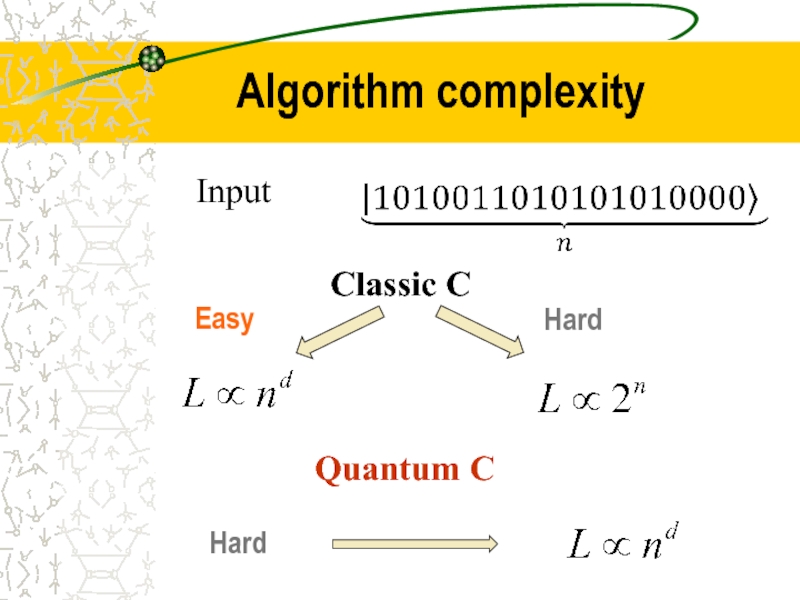
- 13. Algorithm complexity Easy Hard Input Classic
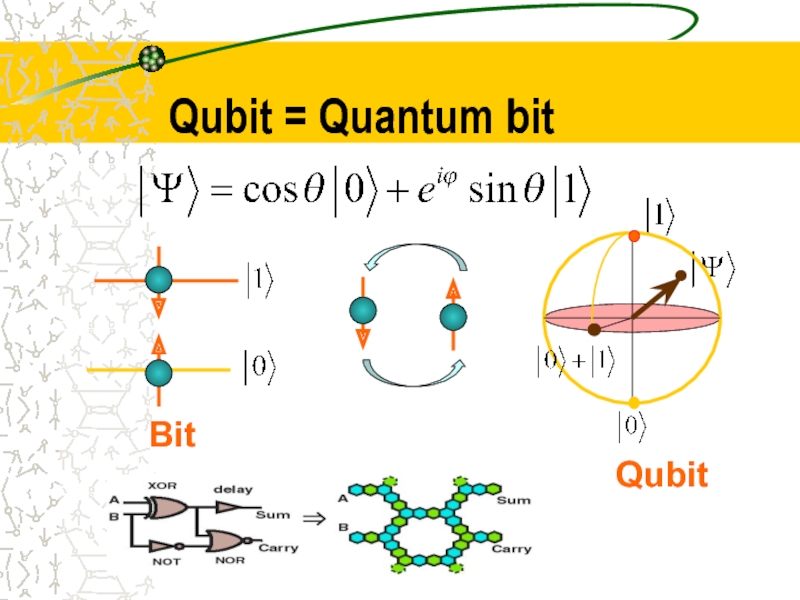
- 14. Qubit = Quantum bit Bit Qubit
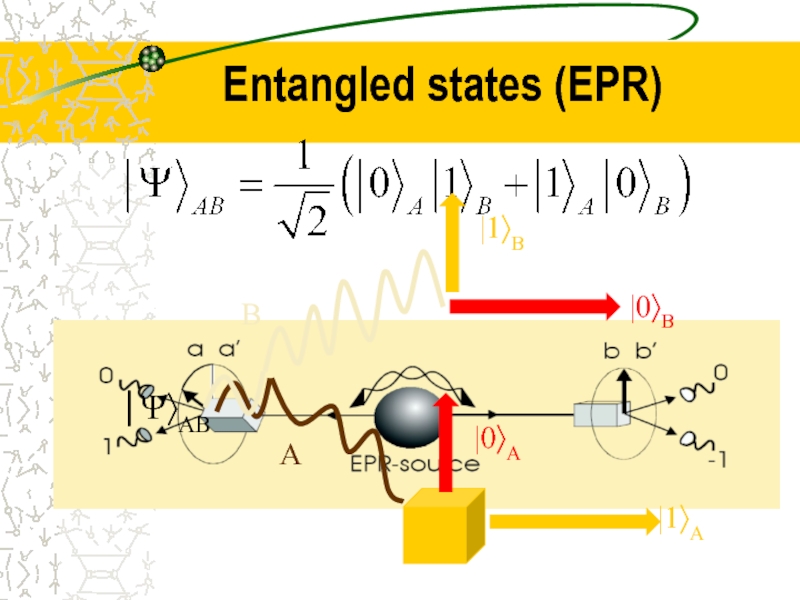
- 15. Entangled states (EPR)
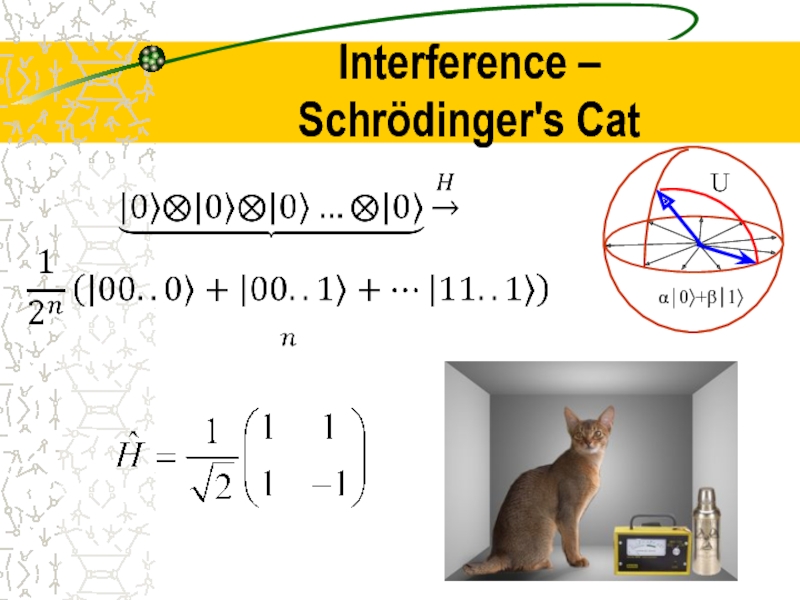
- 16. Interference – Schrödinger's Cat
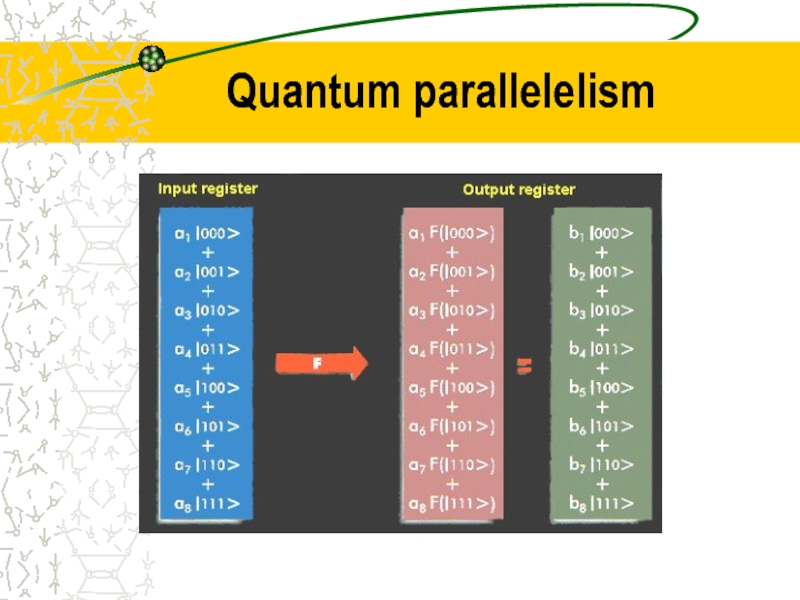
- 17. Quantum parallelelism
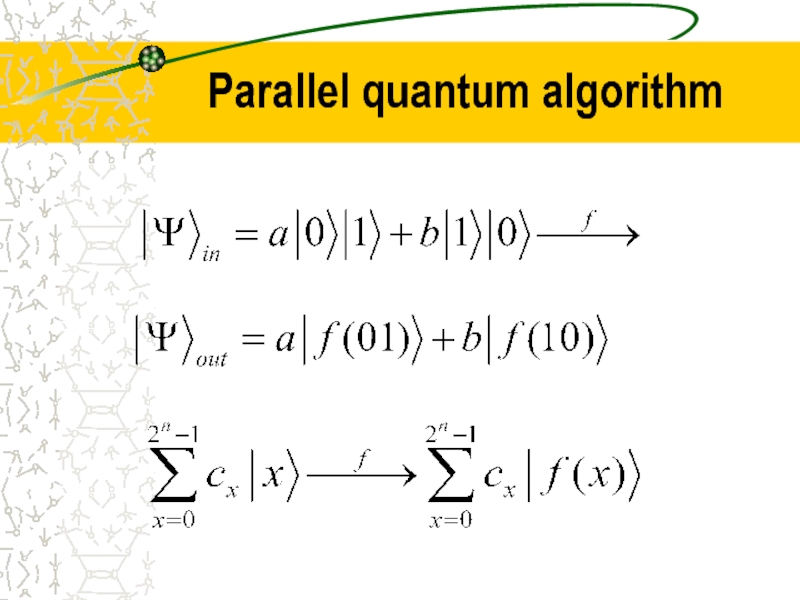
- 18. Parallel quantum algorithm
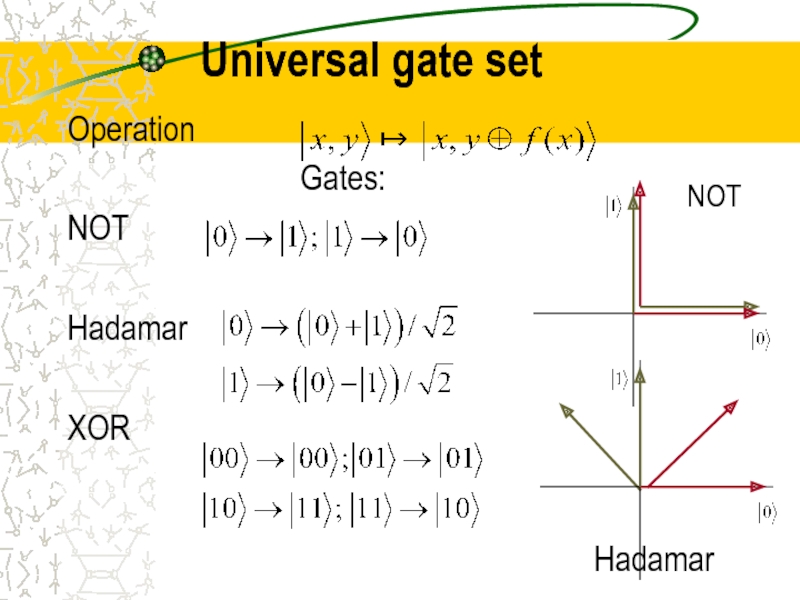
- 19. Universal gate set Operation Gates: NOT Hadamar XOR
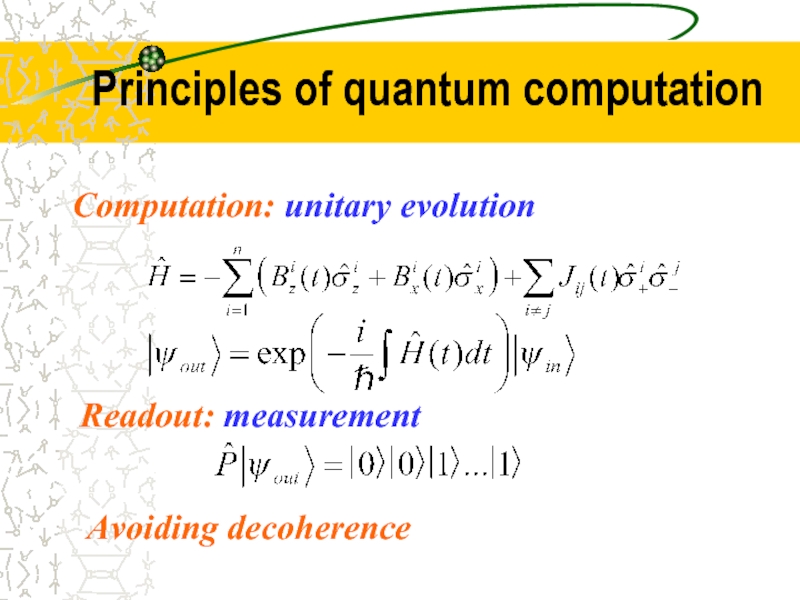
- 20. Principles of quantum computation Computation: unitary evolution Readout: measurement Avoiding decoherence
- 21. Di Vincenzo criteria Selectivity (addressing each qubit)
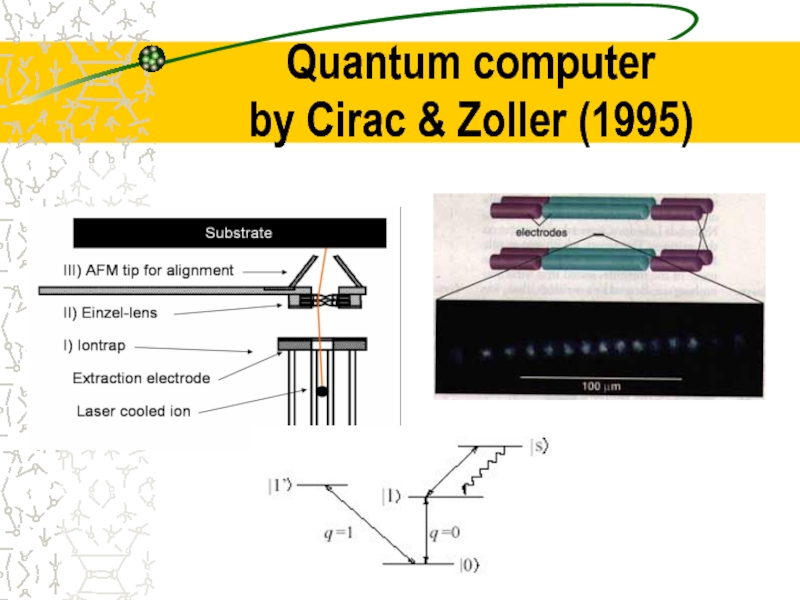
- 22. Quantum computer by Cirac & Zoller (1995)
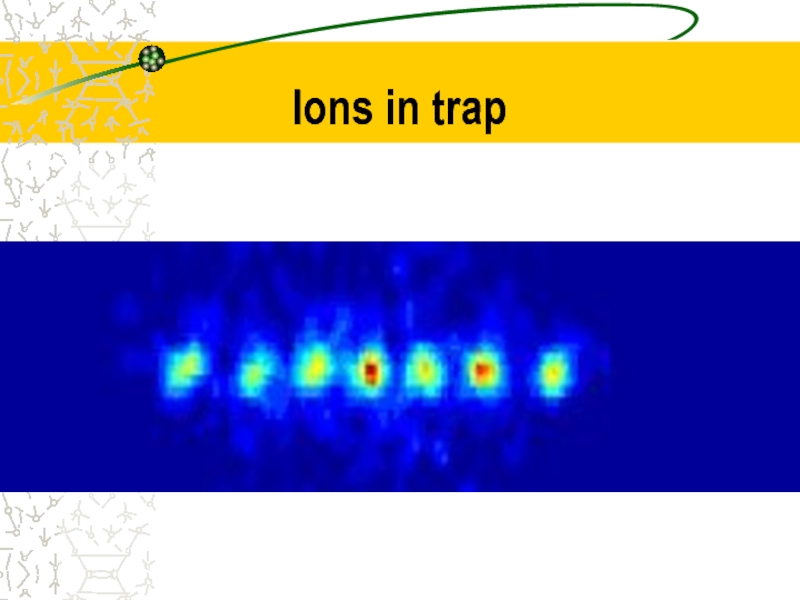
- 23. Ions in trap
- 24. Qubit: micro or macro? Measurement duration:
- 25. Superconductors: macroatoms Qubit: charge or phase Control:
- 26. Superconducting qubit: overcoming decoherence Shnyrkov et al,
- 27. Flux qubit: theory
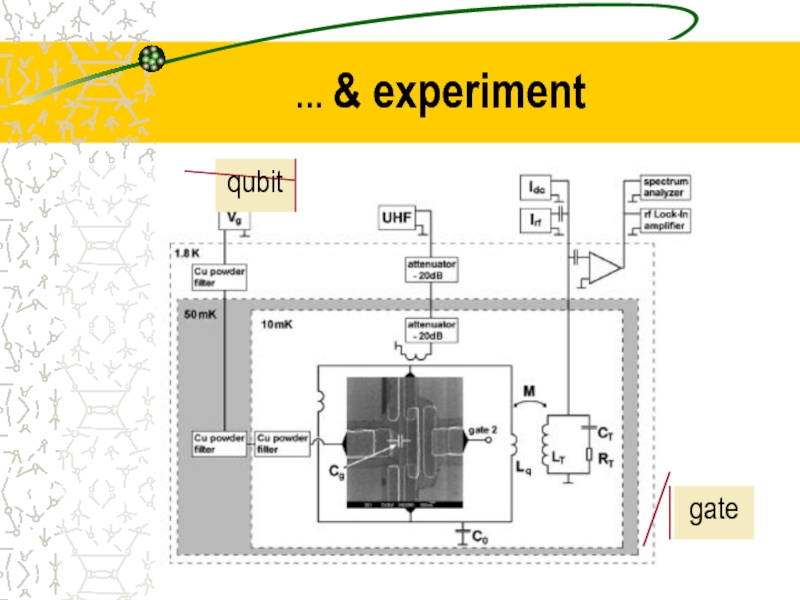
- 28. … & experiment qubit gate
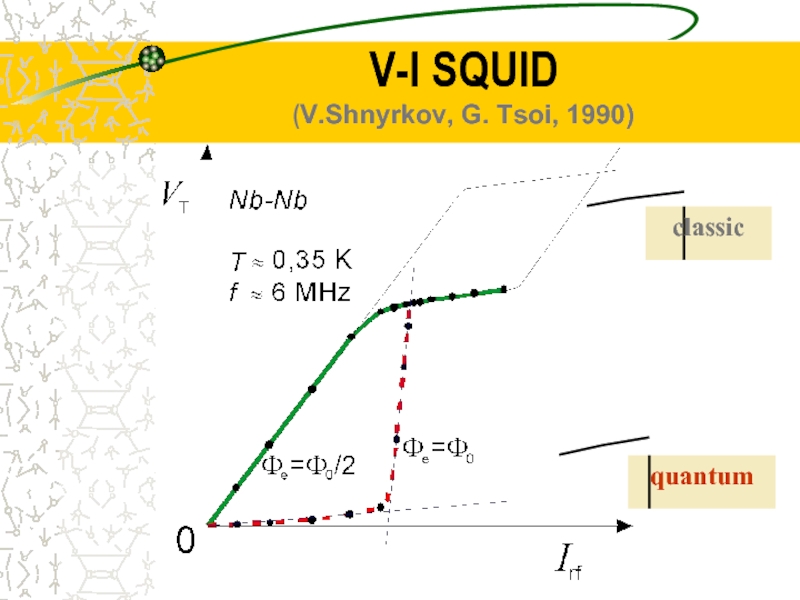
- 29. V-I SQUID (V.Shnyrkov, G. Tsoi, 1990) quantum classic
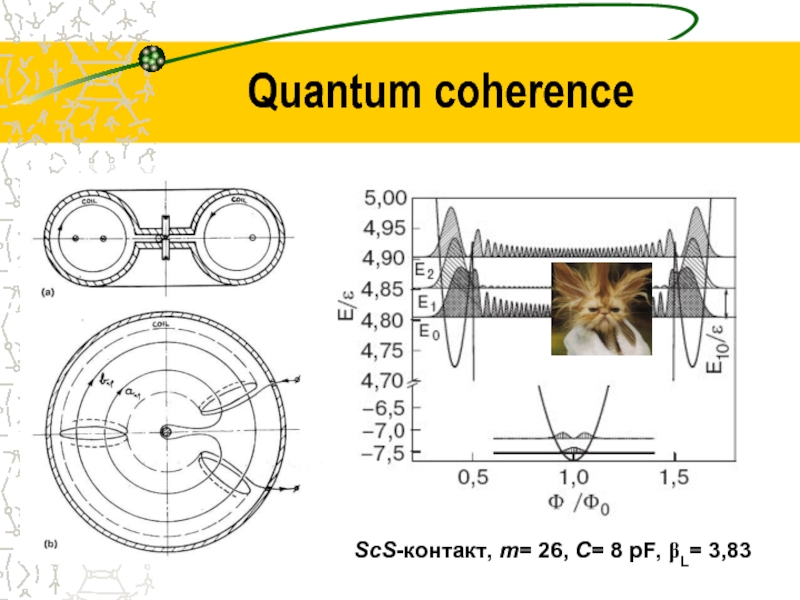
- 30. ScS-контакт, m= 26, C= 8 pF, βL= 3,83 Quantum coherence
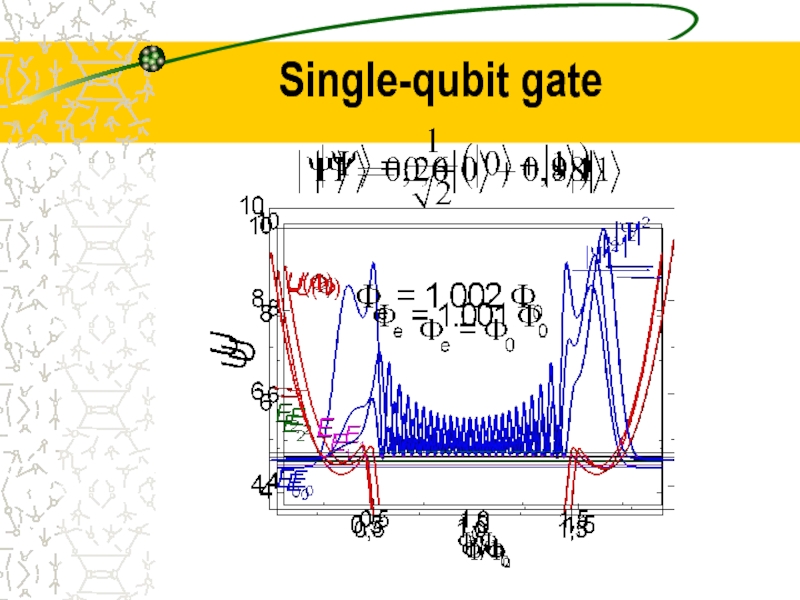
- 31. Single-qubit gate
- 32. Experimental results for the charge-phase qubit
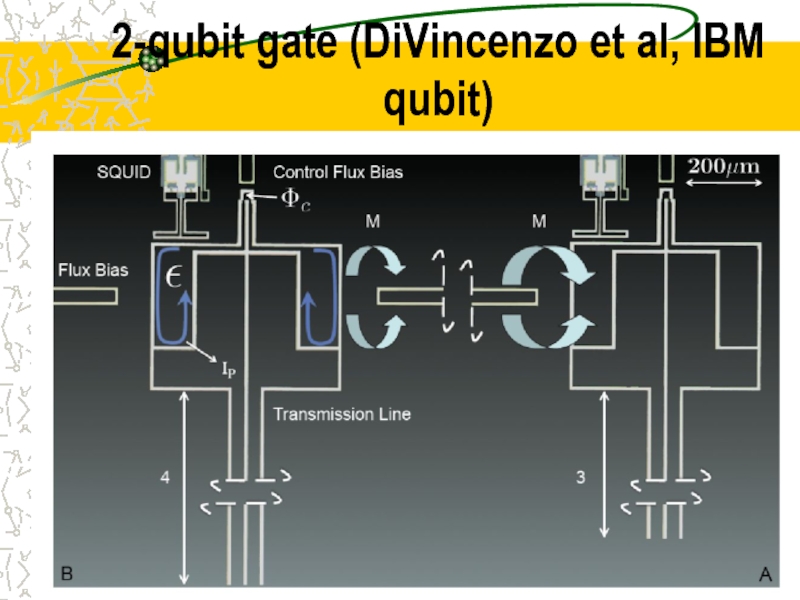
- 33. 2-qubit gate (DiVincenzo et al, IBM qubit)
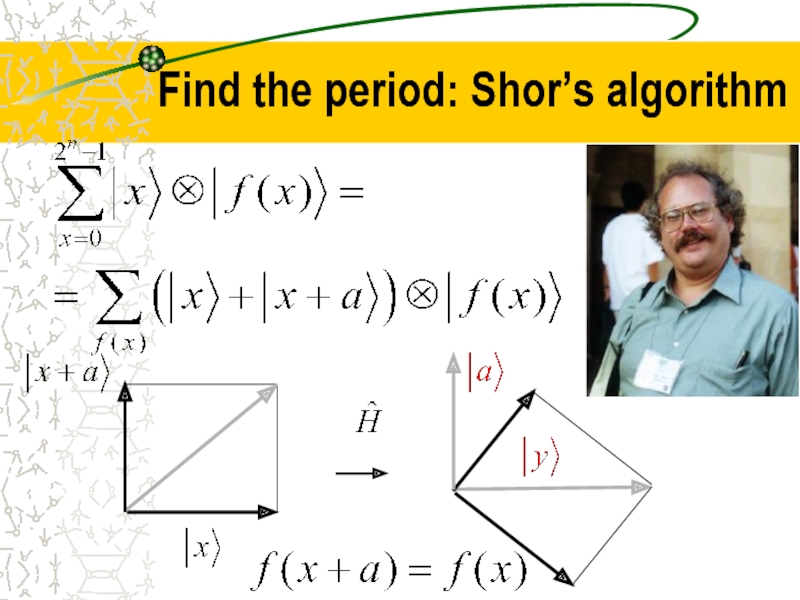
- 34. Find the period: Shor’s algorithm
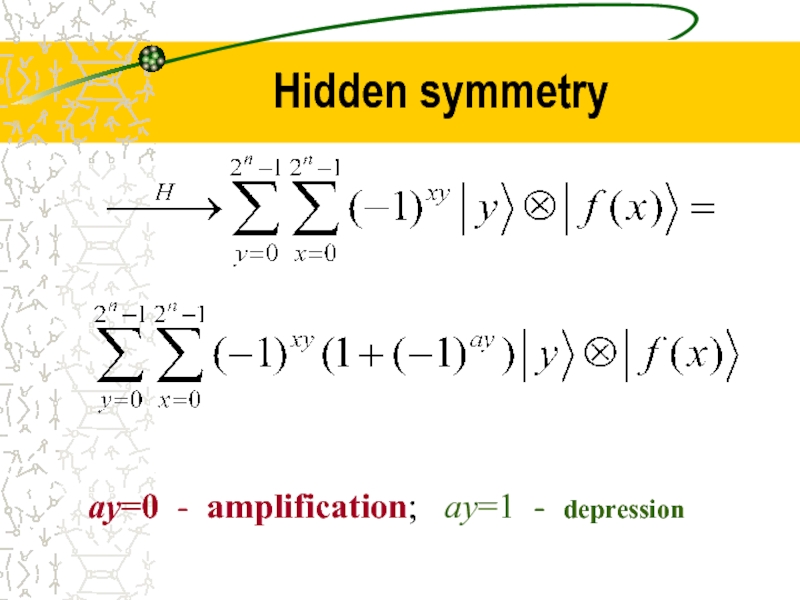
- 35. Hidden symmetry ay=0 - amplification; ay=1 - depression
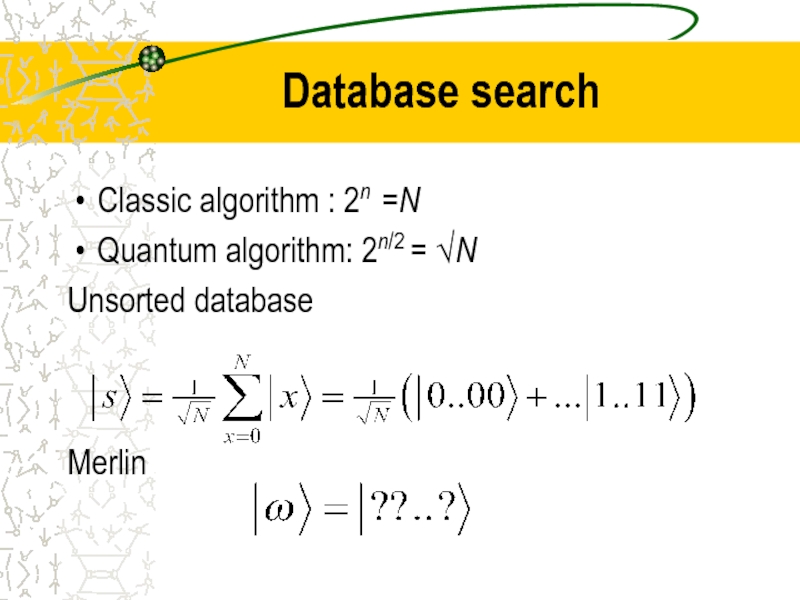
- 36. Classic algorithm : 2n =N Quantum algorithm:
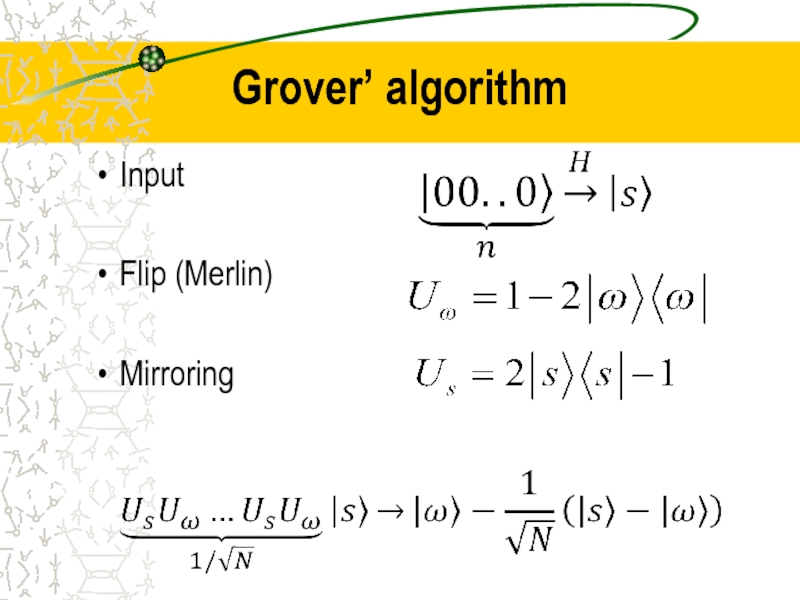
- 37. Grover’ algorithm Input Flip (Merlin) Mirroring
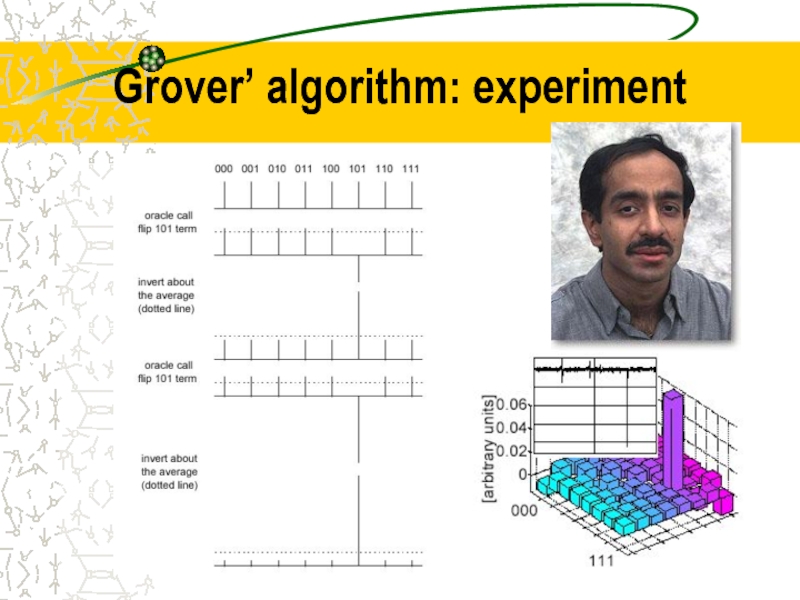
- 38. Grover’ algorithm: experiment
- 39. 4-level system QIR=Quantum Intermediate Representation QASM=Quantum Assembly
- 40. Quantum computer: challenges Decoherence (state instability) Scaling
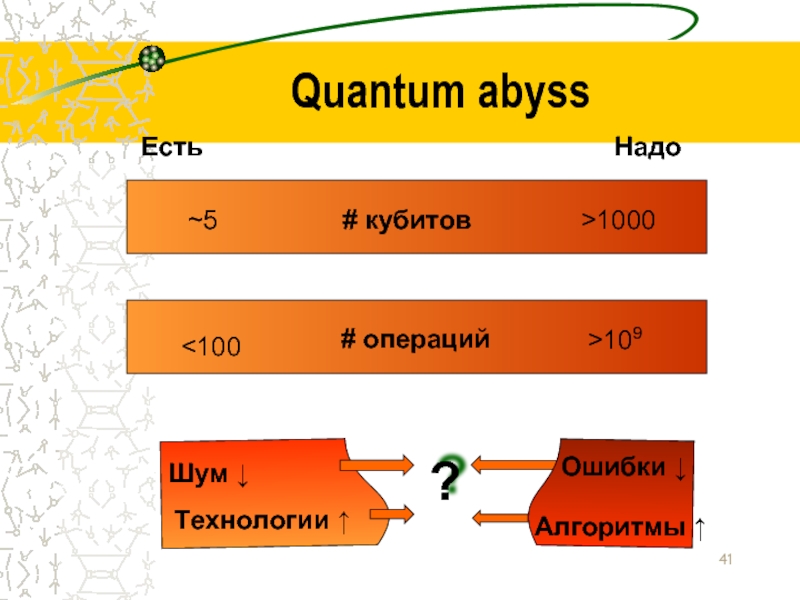
- 41. Quantum abyss # кубитов
- 42. When, Where, Who & hoW? 2 qb
- 43. Alumni Vadym Kliuchnikov Post doc researcher
- 44. QUANTUM COMPUTING JOIN THE TEAM!
Слайд 1Quantum computers, quantum computations
H. Gomonay
National Technical University of Ukraine
JGU, Mainz, Germany
Слайд 2Take-home message
The quest for a quantum computer reminds me of the
Слайд 4Outline
History
Principles of quantum computation
Di Vincenzo criteria
Superconducting qubit
Some algorithms
Architecture
Challenges and problems
Слайд 5History in facts
1982 – R. Feynman predicts possibility of quantum computations
1935
2007 – D-Wave Systems presents 16 qubit quantum processor Orion
Слайд 6
2012 – S. Haroche & D. J. Wineland winn Nobel prize
2015 – Google tests the D-Wave 2X quantum annealer, ~1000 qb
Слайд 10What is all about or new applications of quantum physics
“Hacking” crypto
Keeping
Data search speed up
Bioinformatics
Outer space opening
Fundamental problems
Factorization of 256-digit number:
Classic – 2N ≈1070 years
Quantum – N2 ~ 10 seconds
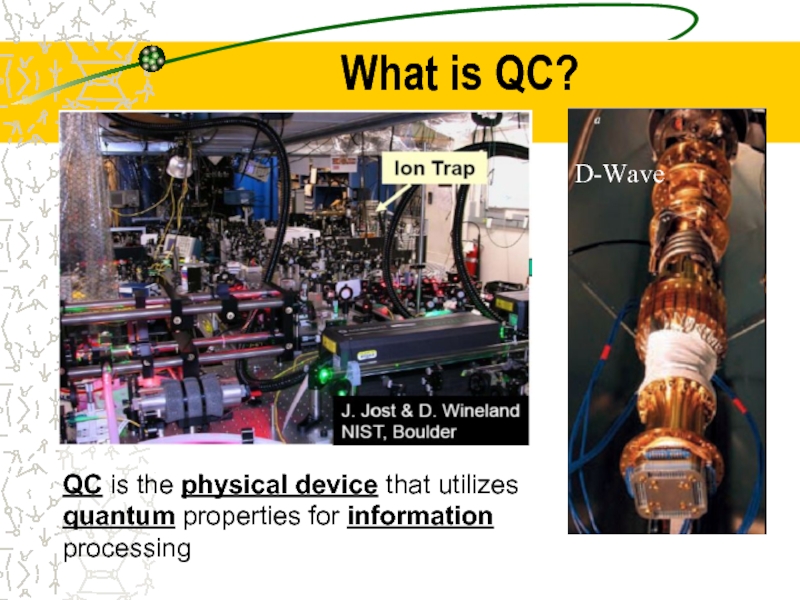
Слайд 11What is QC?
QC is the physical device that utilizes quantum properties
D-Wave
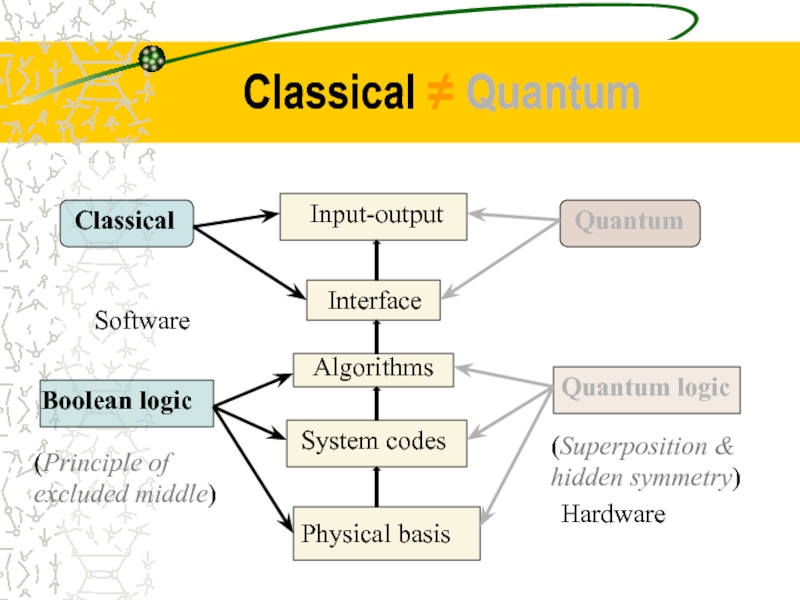
Слайд 12
Classical ≠ Quantum
Hardware
Software
Boolean logic
Quantum logic
Classical
Quantum
(Principle of
excluded middle)
(Superposition & hidden symmetry)
Слайд 20Principles of quantum computation
Computation: unitary evolution
Readout: measurement
Avoiding decoherence
Слайд 21Di Vincenzo criteria
Selectivity (addressing each qubit)
High sensitivity = Good control
Large decoherence
Readout ⇒ Measurability
Scalability (>100 qubits)
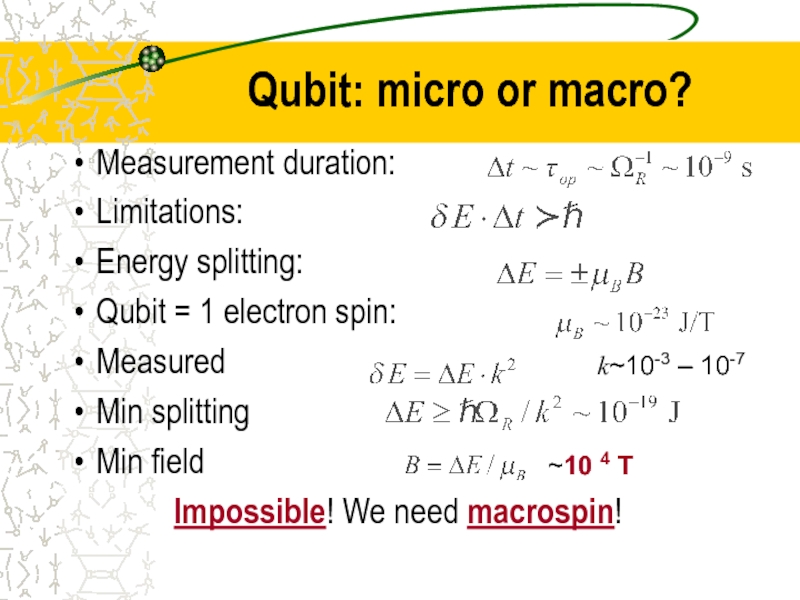
Слайд 24Qubit: micro or macro?
Measurement duration:
Limitations:
Energy splitting:
Qubit = 1 electron
Measured
Min splitting
Min field
Impossible! We need macrospin!
k~10-3 – 10-7
~10 4 T
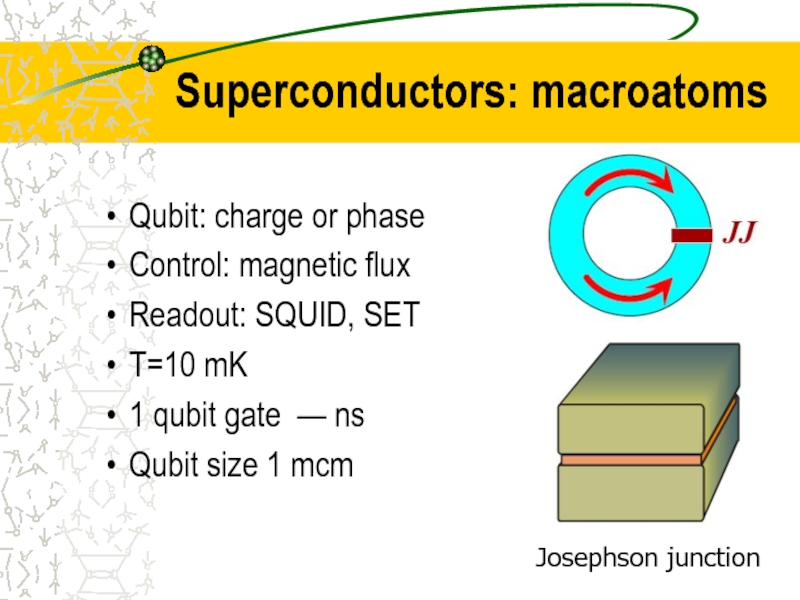
Слайд 25Superconductors: macroatoms
Qubit: charge or phase
Control: magnetic flux
Readout: SQUID, SET
T=10 mK
1 qubit
Qubit size 1 mcm
Josephson junction
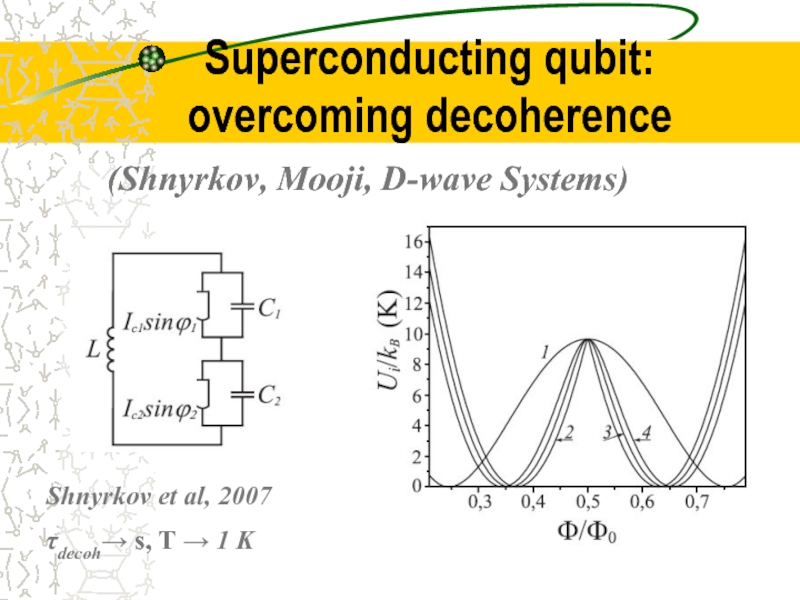
Слайд 26Superconducting qubit: overcoming decoherence
Shnyrkov et al, 2007
τdecoh→ s, T → 1
(Shnyrkov, Mooji, D-wave Systems)
Слайд 32
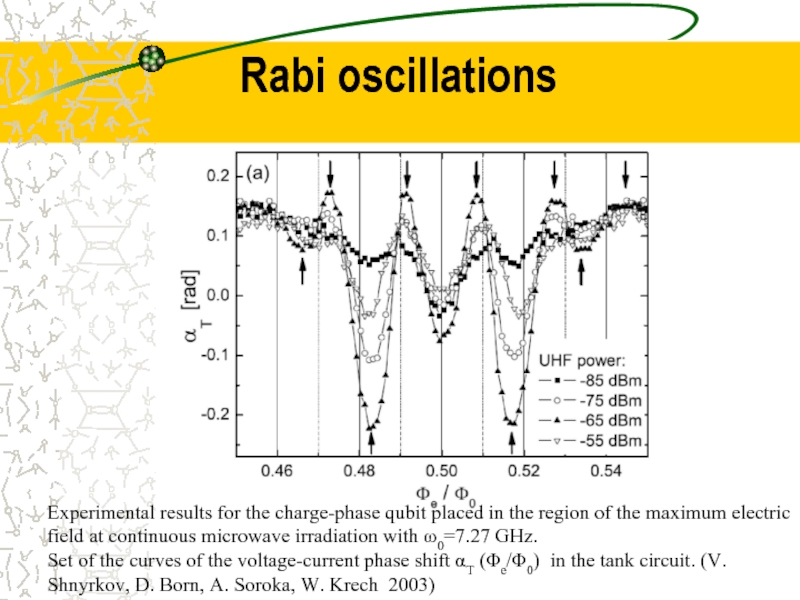
Experimental results for the charge-phase qubit placed in the region of
Rabi oscillations
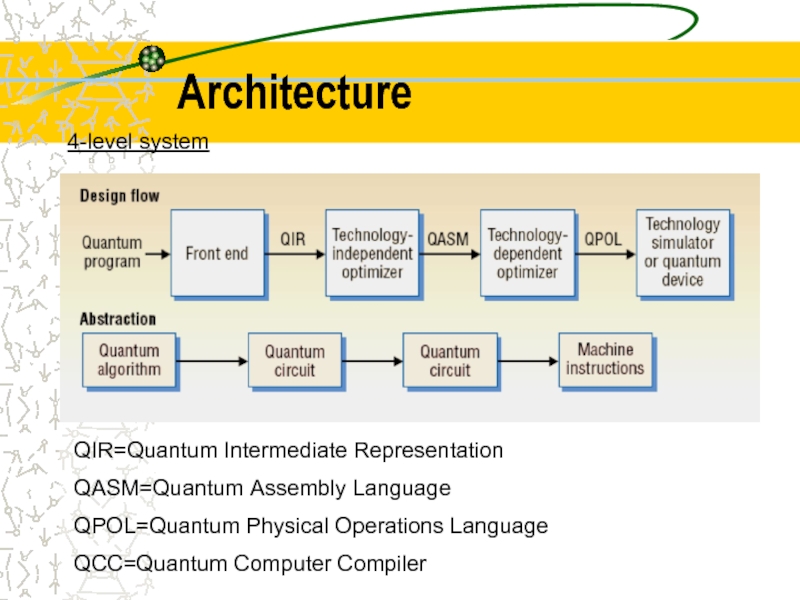
Слайд 394-level system
QIR=Quantum Intermediate Representation
QASM=Quantum Assembly Language
QPOL=Quantum Physical Operations Language
QCC=Quantum Computer Compiler
Architecture
Слайд 40Quantum computer: challenges
Decoherence (state instability)
Scaling (few number of qubits)
Input-output control
Extreme
New math algorithms development
Consumer friendly implementation
Weak measurement
Слайд 42When, Where, Who & hoW?
2 qb — 1999, 7 qb —
NP — 2012,1000 qb —2015, on-table -- 20xx?
~ 1000 experimental groups over the world
Physics, math, computer science, engineering?
Semi- or super-conductors or?
Слайд 43Alumni
Vadym Kliuchnikov
Post doc researcher @ Microsoft Research
http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/people/vadym/
Sergii Strelchuk
Junior Research Fellow
http://www.qi.damtp.cam.ac.uk/node/72