Monaykina Yulia Vitalievna
2016
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Physics and chemistry of surface phenomena презентация
Содержание
- 1. Physics and chemistry of surface phenomena
- 2. Surface phenomena are the processes that occur
- 3. The substance which adsorbs the solute is
- 4. Adsorption at the gas-liquid and liquid-liquid
- 5. The ability of dissolved substances to change
- 6. The Duclos-Traube rule:
- 7. Molecules and atoms can attach themselves onto
- 8. Adsorption at the solid-solution interface Solutes
- 9. OTHER FACTORS AFFECTING ADSORPTION Surface area
- 10. Structure of biological membranes
Слайд 1 Zaporizhzhya State Medical University Analytical Chemistry Department PHYSICS AND CHEMISTRY OF SURFACE PHENOMENA Lecturer:
Слайд 2Surface phenomena are the processes that occur at the interface in
heterogeneous systems.
The spontaneous process of solute accumulation at the interface is called adsorption.
The spontaneous process of solute accumulation at the interface is called adsorption.
Слайд 3The substance which adsorbs the solute is called adsorbent.
The adsorbed solute
is called
adsorbate.
The interface may be: gas – liquid,
liquid – liquid,
solid – liquid,
solid – gas.
adsorbate.
The interface may be: gas – liquid,
liquid – liquid,
solid – liquid,
solid – gas.
Слайд 4
Adsorption at the gas-liquid and liquid-liquid interface
The resultant of the forces
acting on a molecule in a bulk is equal to zero.
The resultant of the forces acting on the molecules in a surface layer is directed to the bulk of the liquid phase perpendicularly to its surface.
The result is a surface layer with excess of surface energy that is the surface Gibbs free energy GS.
The resultant of the forces acting on the molecules in a surface layer is directed to the bulk of the liquid phase perpendicularly to its surface.
The result is a surface layer with excess of surface energy that is the surface Gibbs free energy GS.
Слайд 5 The ability of dissolved substances to change the surface tension of
the solvent is called surface activity.
A measure of the surface activity is a derivative of the surface tension on the concentration, taken with an opposite sign :
For narrow concentration ranges the formula is:
A measure of the surface activity is a derivative of the surface tension on the concentration, taken with an opposite sign :
For narrow concentration ranges the formula is:
Слайд 6
The Duclos-Traube rule:
The surface activity
increases about 3 -3,5 times with each addition of a methylene group to the homolog.
Слайд 7Molecules and atoms can attach themselves onto surfaces in two ways:
In
physisorption (physical adsorption), there is a weak van der Waals attraction of the adsorbate to the surface. During this process the chemical identity of the adsorbate remains intact, i.e. no breakage of the covalent structure of the adsorbate takes place.
In chemisorption (chemical adsorption), the adsorbate sticks to the solid by the formation of a chemical bond with the surface.
In chemisorption (chemical adsorption), the adsorbate sticks to the solid by the formation of a chemical bond with the surface.
Слайд 8Adsorption at the solid-solution interface
Solutes adsorption by solid adsorbents is more
complex as the solvent molecules can compete with adsorbate molecules for the adsorptive sites on the adsorbent surface as well as can interact with the adsorbate and adsorbent surface.
Two kinds of adsorption on a solid adsorbent are distinguished:
molecular
and
ionic adsorption.
Two kinds of adsorption on a solid adsorbent are distinguished:
molecular
and
ionic adsorption.
Слайд 9 OTHER FACTORS AFFECTING ADSORPTION
Surface area of adsorbent. Larger sizes of surface
area
imply a greater adsorption capacity.
Particle size of adsorbent. Smaller particle sizes reduce
internal diffusional and mass transfer limitation to the
penetration of the adsorbate inside the adsorbent (i.e.,
equilibrium is more easily achieved and nearly full
adsorption capability can be attained)
Contact time or residence time. The longer the time the
more complete the adsorption will be.
imply a greater adsorption capacity.
Particle size of adsorbent. Smaller particle sizes reduce
internal diffusional and mass transfer limitation to the
penetration of the adsorbate inside the adsorbent (i.e.,
equilibrium is more easily achieved and nearly full
adsorption capability can be attained)
Contact time or residence time. The longer the time the
more complete the adsorption will be.
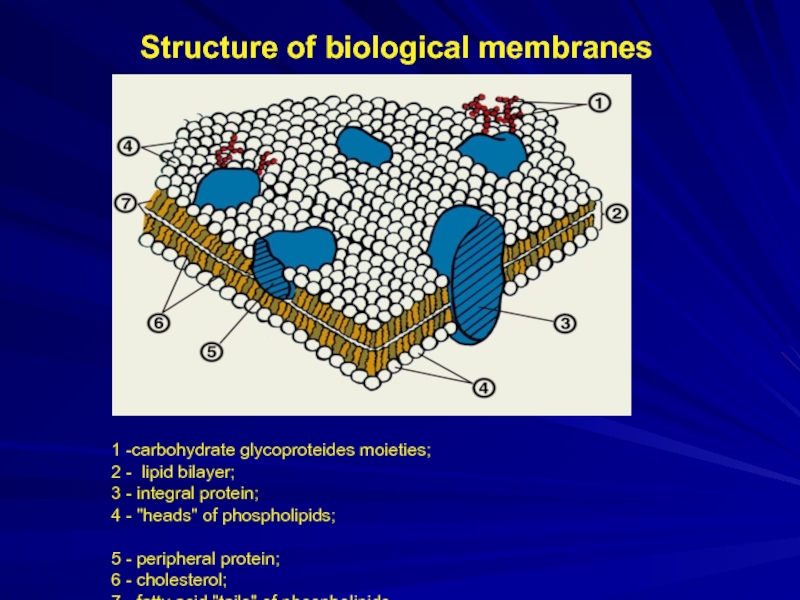
Слайд 10Structure of biological membranes
1 -carbohydrate glycoproteides moieties;
2 - lipid bilayer;
3
- integral protein;
4 - "heads" of phospholipids;
5 - peripheral protein;
6 - cholesterol;
7 - fatty acid "tails" of phospholipids
4 - "heads" of phospholipids;
5 - peripheral protein;
6 - cholesterol;
7 - fatty acid "tails" of phospholipids