Түркістан 2017
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Heterogeneous catalysis презентация
Содержание
- 1. Heterogeneous catalysis
- 2. SIW plan : Smart-мақсат Lecture :Heterogeneous
- 3. Интерактивті тақта арқылы студенттерге гетерогенді катализ және
- 4. PLAN: The basic concept of heterogeneous catalysis
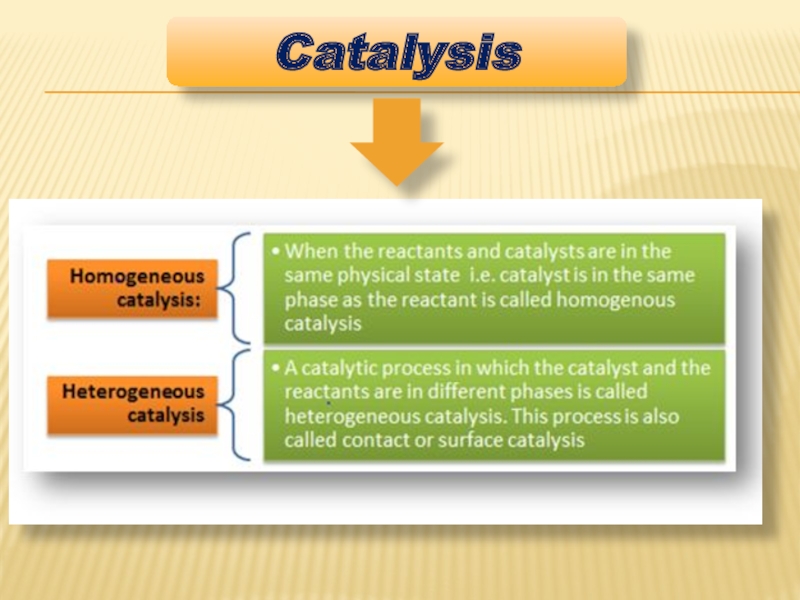
- 5. Catalysis
- 6. HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSIS In chemistry, heterogeneous catalysis refers
- 7. Describes the catalytic processes that occur at
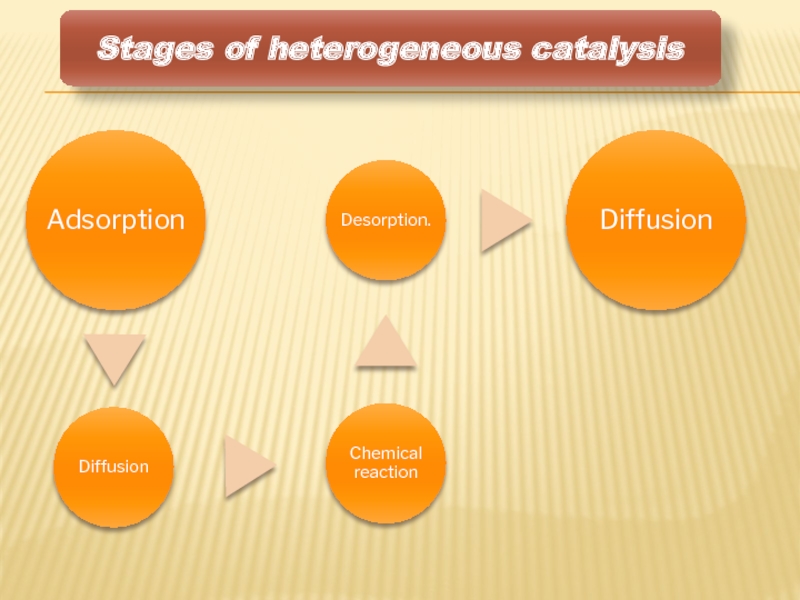
- 8. Stages of heterogeneous catalysis
- 9. Reactive molecules diffuse to the surface of
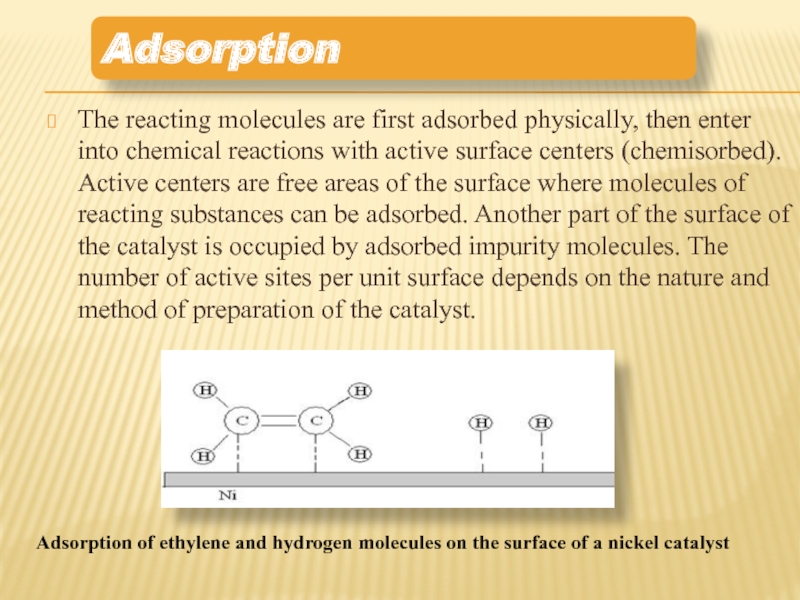
- 10. The reacting molecules are first adsorbed physically,
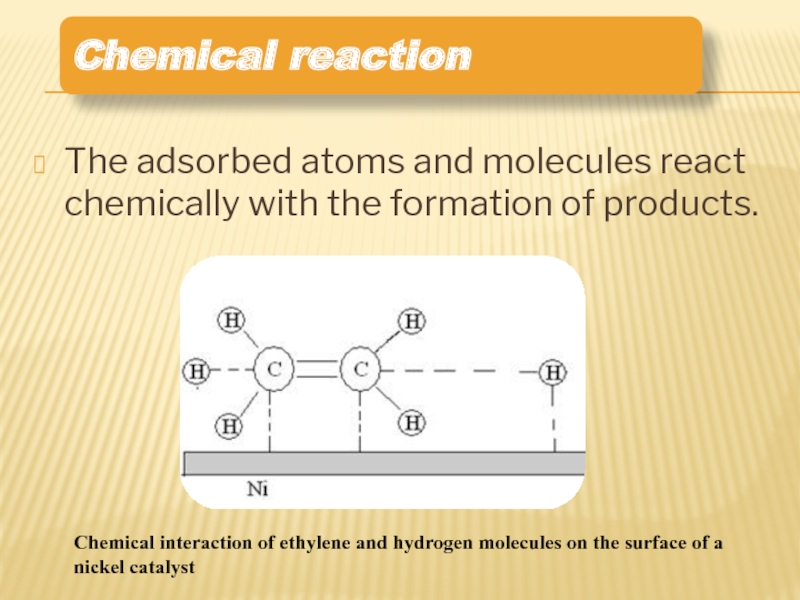
- 11. The adsorbed atoms and molecules react chemically
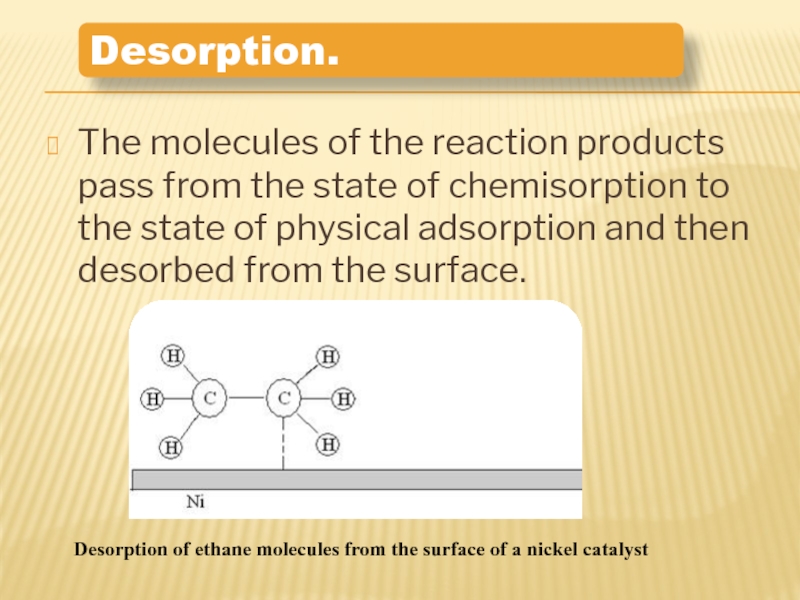
- 12. The molecules of the reaction products pass
- 13. The molecules of the reaction products diffuse
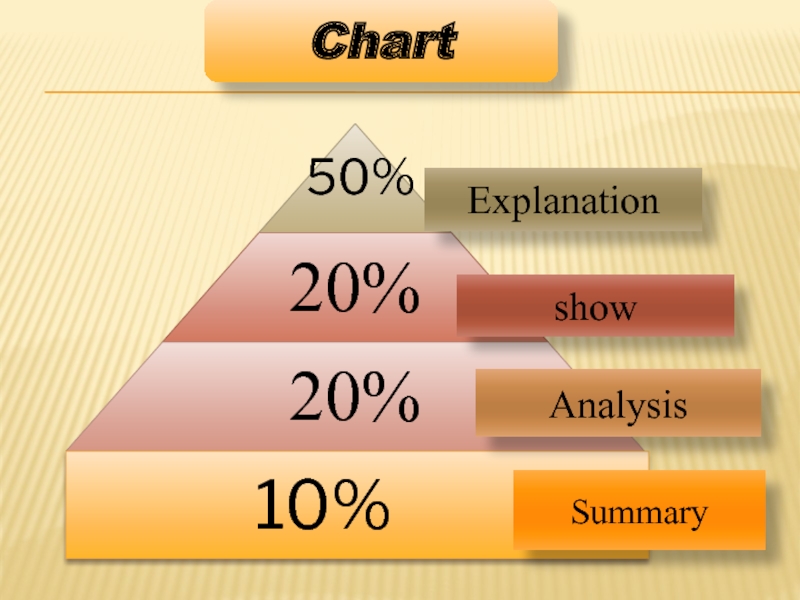
- 15. 10% Explanation show Analysis Summary Chart
- 16. CONCEPTS In heterogeneous catalysis, the reactants diffuse
- 17. REFERENCES Gadi Rothenberg, Catalysis: Concepts and green
Слайд 1 ҚАЗАҚСТАН РЕСПУБЛИКАСЫ БІЛІМ ЖӘНЕ ҒЫЛЫМ МИНИСТРЛІГІ ПОРТФОЛИО ПӘНІ: ФИЗИКАЛЫҚ ХИМИЯ Қ.А.ЯСАУИ АТЫНДАҒЫ
Слайд 2SIW plan :
Smart-мақсат
Lecture :Heterogeneous catalysis
The basic concept of heterogeneous catalysis
Adsorption
Stages of heterogeneous catalysis
Concepts
Слайд 3Интерактивті тақта арқылы студенттерге гетерогенді катализ және оның механизмі мен себептері
Слайд 4PLAN:
The basic concept of heterogeneous catalysis
Adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis
Stages
Concepts
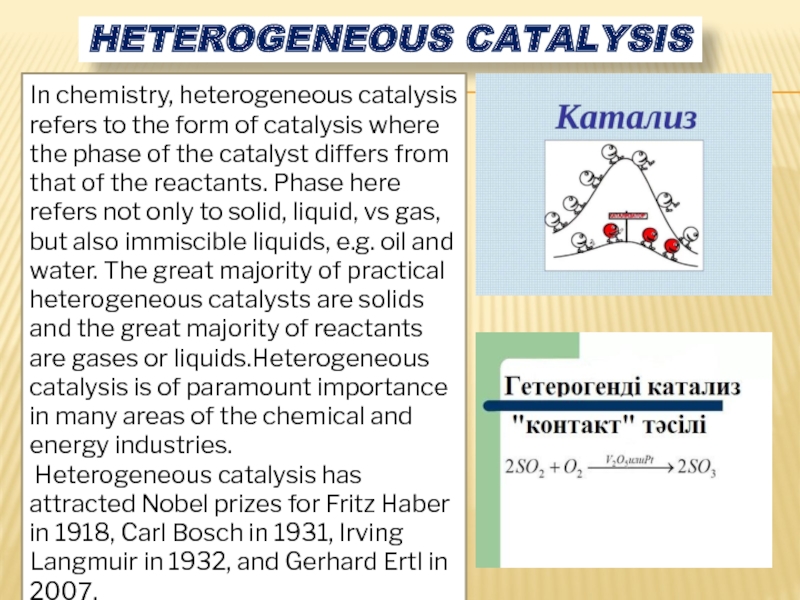
Слайд 6HETEROGENEOUS CATALYSIS
In chemistry, heterogeneous catalysis refers to the form of catalysis
Heterogeneous catalysis has attracted Nobel prizes for Fritz Haber in 1918, Carl Bosch in 1931, Irving Langmuir in 1932, and Gerhard Ertl in 2007.
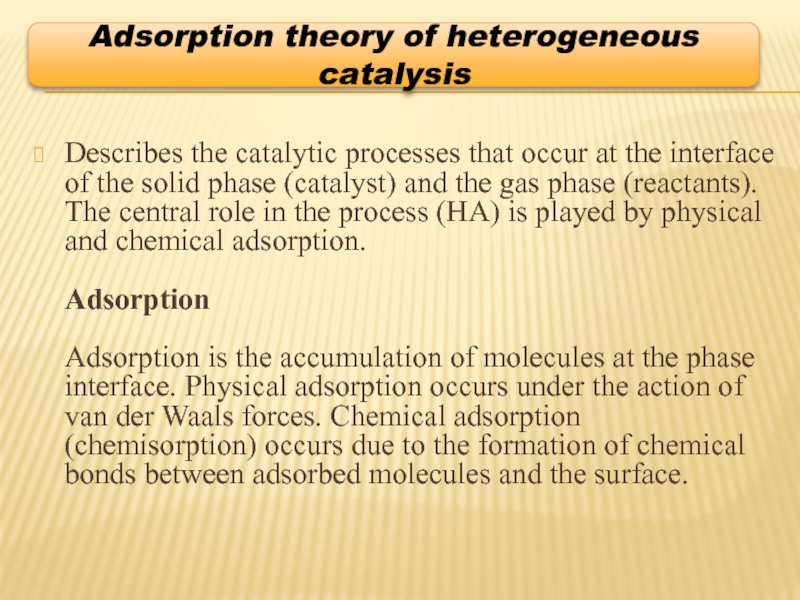
Слайд 7Describes the catalytic processes that occur at the interface of the
Adsorption theory of heterogeneous catalysis
Слайд 9Reactive molecules diffuse to the surface of a solid.
Diffusion
Diffusion of ethylene
Слайд 10The reacting molecules are first adsorbed physically, then enter into chemical
Adsorption of ethylene and hydrogen molecules on the surface of a nickel catalyst
Adsorption
Слайд 11The adsorbed atoms and molecules react chemically with the formation of
Chemical reaction
Chemical interaction of ethylene and hydrogen molecules on the surface of a nickel catalyst
Слайд 12The molecules of the reaction products pass from the state of
Desorption.
Desorption of ethane molecules from the surface of a nickel catalyst
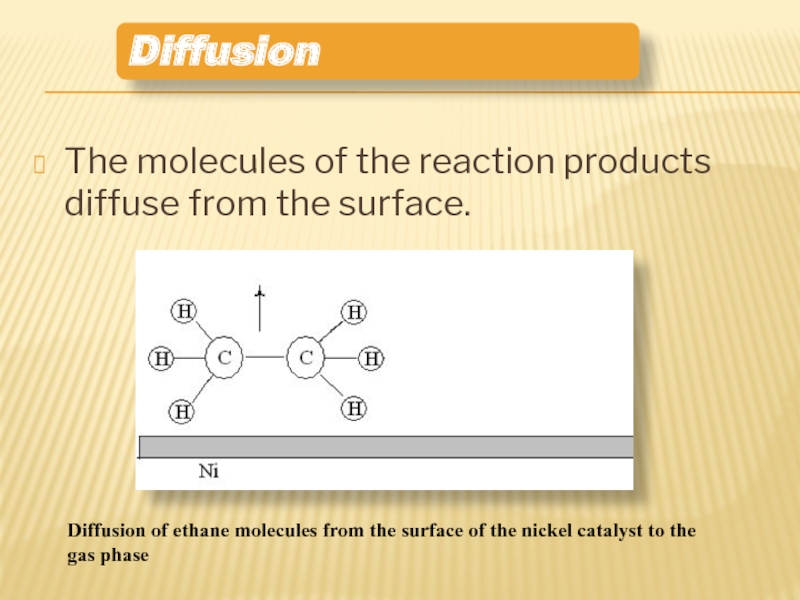
Слайд 13The molecules of the reaction products diffuse from the surface.
Diffusion
Diffusion of
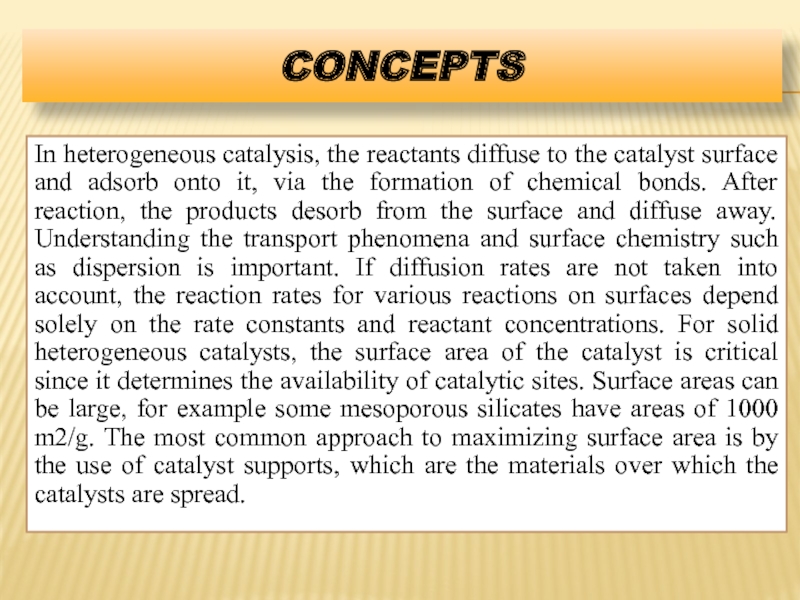
Слайд 16CONCEPTS
In heterogeneous catalysis, the reactants diffuse to the catalyst surface and
Слайд 17REFERENCES
Gadi Rothenberg, Catalysis: Concepts and green applications, Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, ISBN 978-3-527-31824-7 Swathi,
Molecular mechanism of heterogeneous catalysis. Resonance Vol. 13 Issue 6 (2008) p. 548-560.
Frank, B.; Blume, R.; Rinaldi, A.; Trunschke, A.; Schlögl, R. (2011). "Oxygen Insertion Catalysis by sp2 Carbon". Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50 (43): 10226–10230. doi:10.1002/anie.201103340.
Sheehan, D.P., Nonequilibrium heterogeneous catalysis in the long mean-free-path regime, Phys. Rev. E 88 032125 (2013).