- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Electrical circuits презентация
Содержание
- 1. Electrical circuits
- 2. Sources of Voltage (Energy) solar geothermal wind
- 3. Electrical Current Current is the rate of
- 4. Electrical Current Moving electrons collide with vibrating
- 5. Electrical Resistance Resistance is a measurement of
- 6. Alternating versus Direct Current Alternating current (ac)
- 7. Electrical circuit versus a water circuit Ohm’s
- 8. Energy, Power, and Cost in Circuits POWER
- 9. Kirchoff’s Rules Rule #1 - The Loop
- 10. Series Circuits A series circuit has only
- 11. Series Christmas Tree Lights Series wiring was
- 12. Parallel Circuits A parallel circuit has multiple
- 13. Combination Circuits A combination circuit must be
- 14. Combination Circuits The total current in the
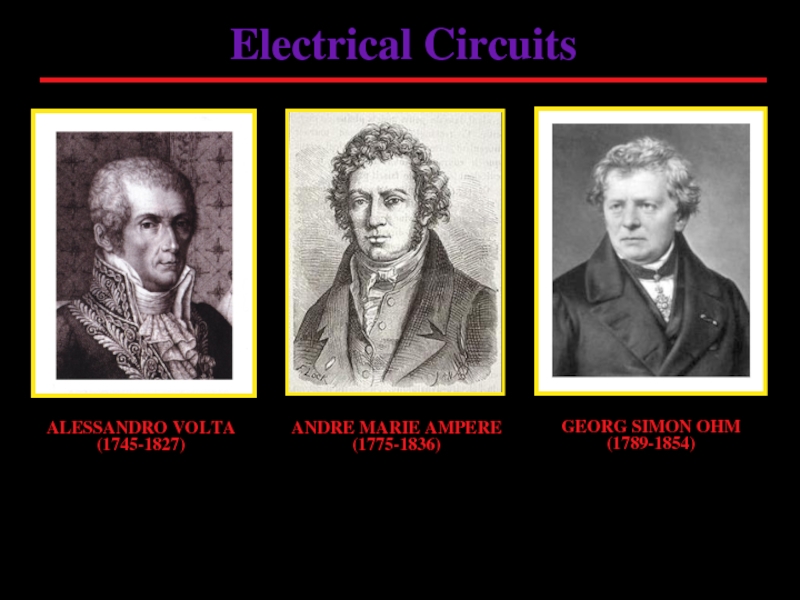
Слайд 1Electrical Circuits
ALESSANDRO VOLTA
(1745-1827)
GEORG SIMON OHM
(1789-1854)
ANDRE MARIE AMPERE
(1775-1836)
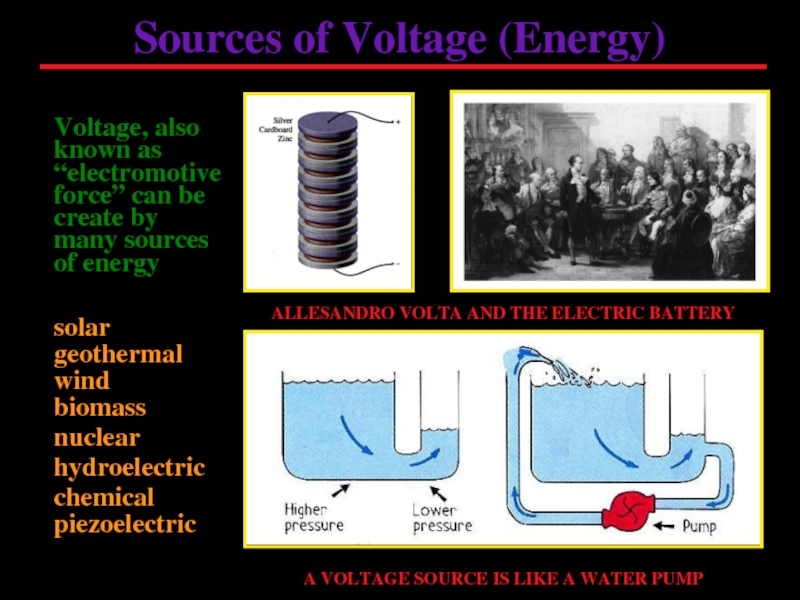
Слайд 2Sources of Voltage (Energy)
solar
geothermal
wind
hydroelectric
chemical
piezoelectric
nuclear
ALLESANDRO VOLTA AND THE ELECTRIC BATTERY
A VOLTAGE SOURCE
biomass
Voltage, also known as “electromotive force” can be create by many sources of energy
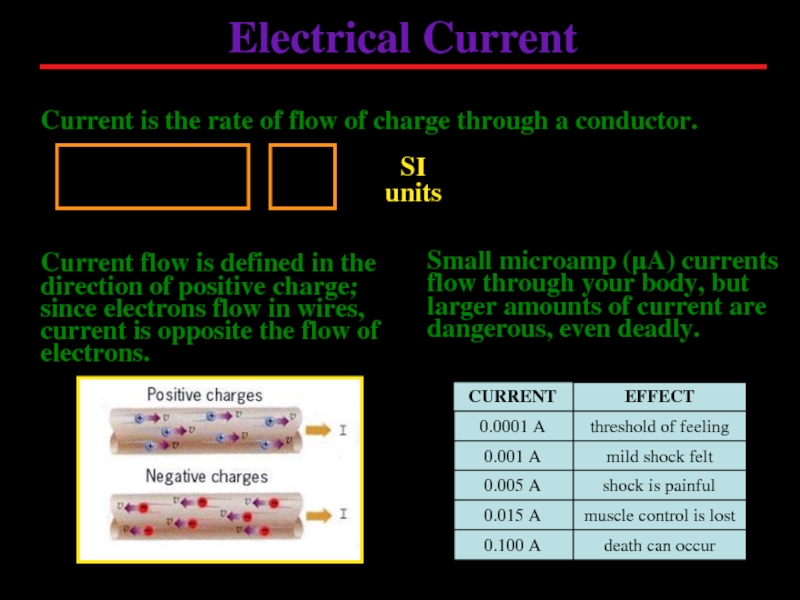
Слайд 3Electrical Current
Current is the rate of flow of charge through a
SI
units
Current flow is defined in the direction of positive charge; since electrons flow in wires, current is opposite the flow of electrons.
Small microamp (μA) currents flow through your body, but larger amounts of current are dangerous, even deadly.
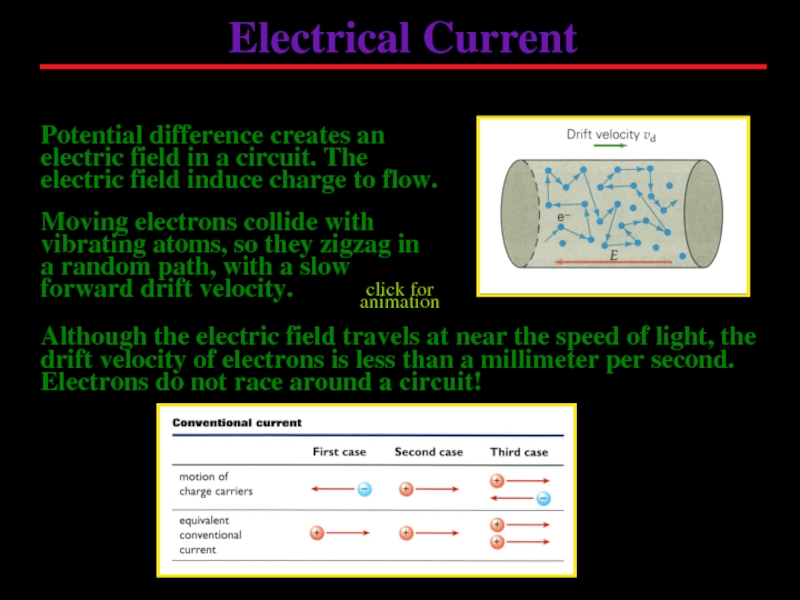
Слайд 4Electrical Current
Moving electrons collide with vibrating atoms, so they zigzag in
Potential difference creates an electric field in a circuit. The electric field induce charge to flow.
Although the electric field travels at near the speed of light, the drift velocity of electrons is less than a millimeter per second. Electrons do not race around a circuit!
click for animation
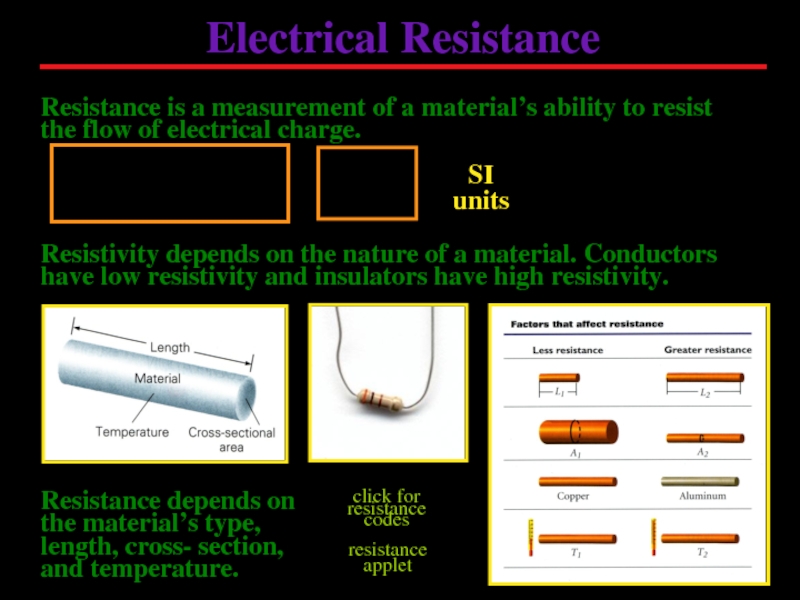
Слайд 5Electrical Resistance
Resistance is a measurement of a material’s ability to resist
Resistivity depends on the nature of a material. Conductors have low resistivity and insulators have high resistivity.
SI
units
Resistance depends on the material’s type, length, cross- section, and temperature.
click for resistance codes
resistance
applet
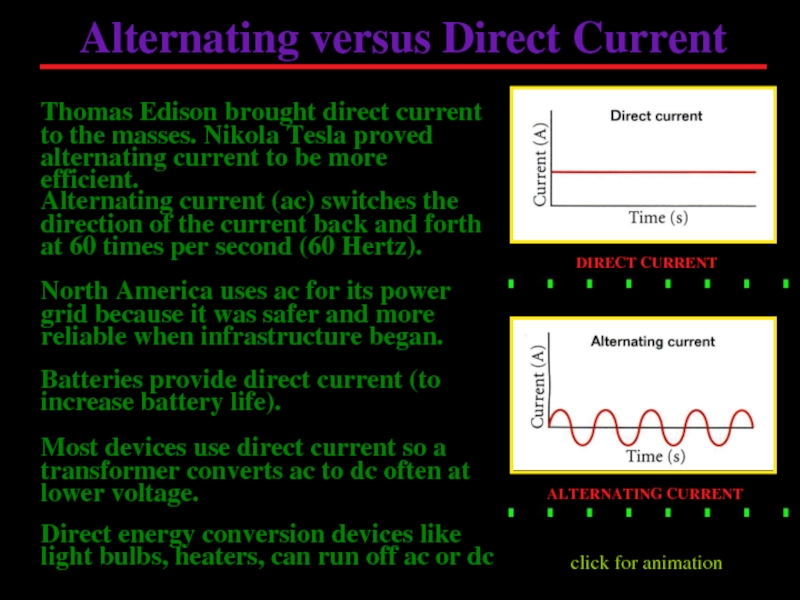
Слайд 6Alternating versus Direct Current
Alternating current (ac) switches the direction of the
North America uses ac for its power grid because it was safer and more reliable when infrastructure began.
Most devices use direct current so a transformer converts ac to dc often at lower voltage.
Direct energy conversion devices like light bulbs, heaters, can run off ac or dc
click for animation
ALTERNATING CURRENT
DIRECT CURRENT
Batteries provide direct current (to increase battery life).
Thomas Edison brought direct current to the masses. Nikola Tesla proved alternating current to be more efficient.
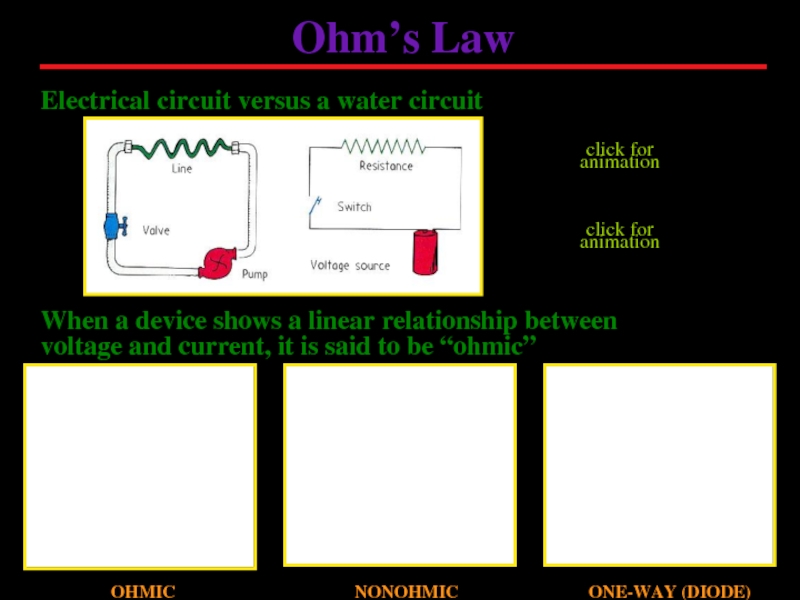
Слайд 7Electrical circuit versus a water circuit
Ohm’s Law
When a device shows a
OHMIC
NONOHMIC
click for animation
click for animation
ONE-WAY (DIODE)
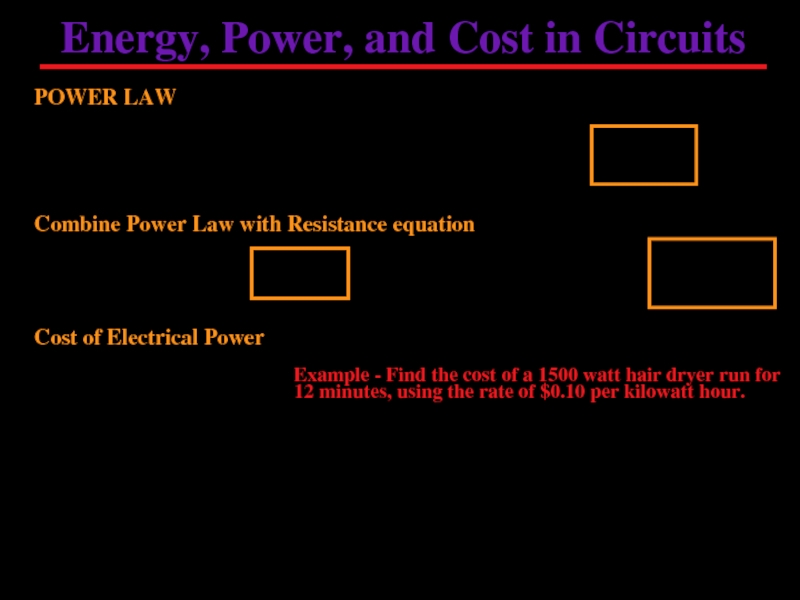
Слайд 8Energy, Power, and Cost in Circuits
POWER LAW
Combine Power Law with Resistance
Cost of Electrical Power
Example - Find the cost of a 1500 watt hair dryer run for 12 minutes, using the rate of $0.10 per kilowatt hour.
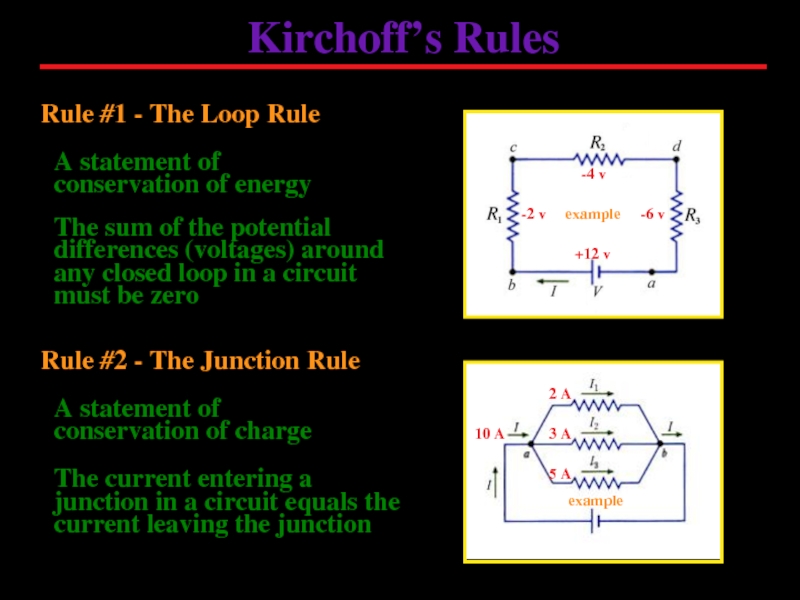
Слайд 9Kirchoff’s Rules
Rule #1 - The Loop Rule
Rule #2 - The Junction
The sum of the potential differences (voltages) around any closed loop in a circuit must be zero
The current entering a junction in a circuit equals the current leaving the junction
A statement of conservation of energy
A statement of conservation of charge
-6 v
-2 v
-4 v
+12 v
example
3 A
5 A
2 A
10 A
example
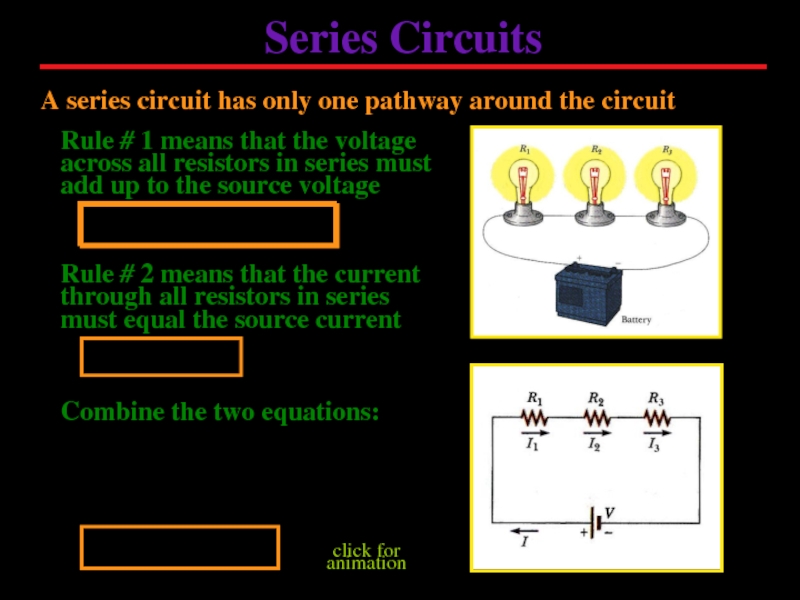
Слайд 10Series Circuits
A series circuit has only one pathway around the circuit
Rule
Rule # 2 means that the current through all resistors in series must equal the source current
Combine the two equations:
click for animation
Слайд 11Series Christmas Tree Lights
Series wiring was often used for Christmas tree
When the bulb burns out, the jumper now has 120 volts across it.
One bulb burns out, they all go out! Who’s to say which one burned out!
Modern bulbs use a “jumper” wire. This wire has insulation around it.
The voltage produces a spark, and the insulation burns off. The circuit is now complete, with the one bulb not lit but easily replaced.
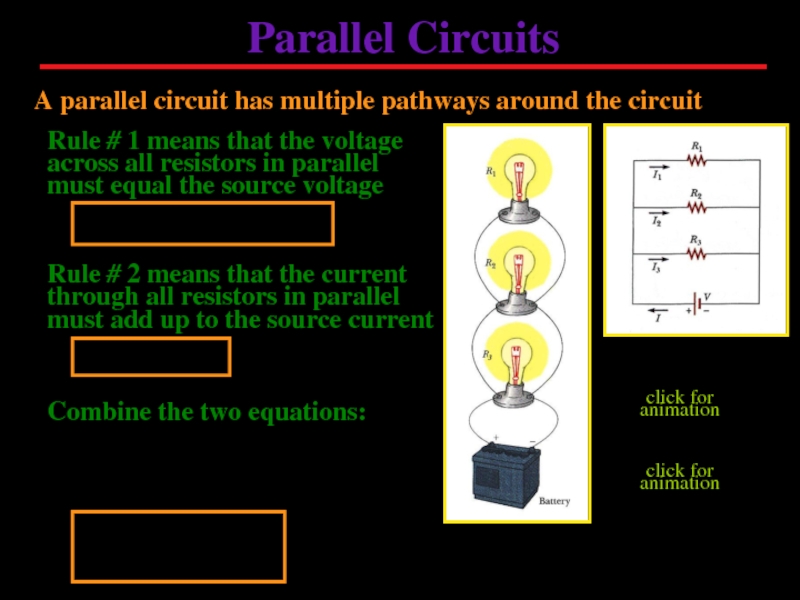
Слайд 12Parallel Circuits
A parallel circuit has multiple pathways around the circuit
Rule #
Rule # 2 means that the current through all resistors in parallel must add up to the source current
Combine the two equations:
click for animation
click for animation
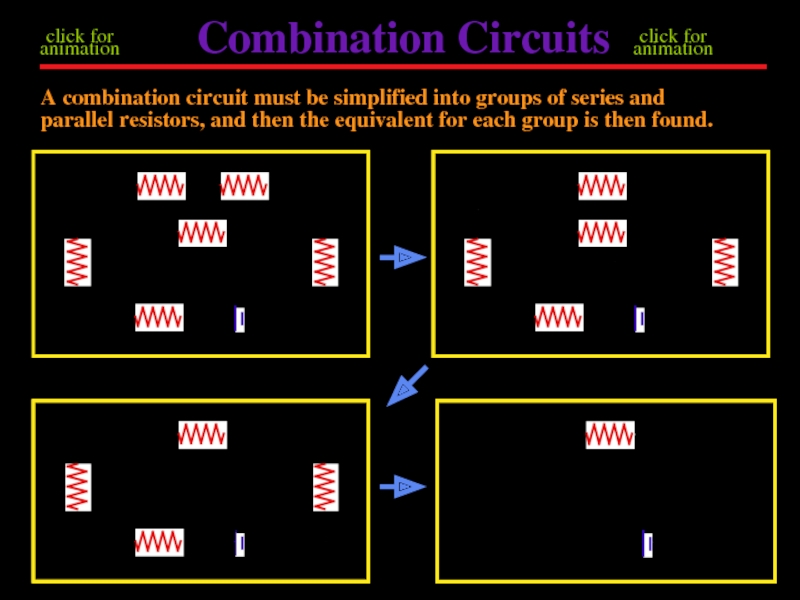
Слайд 13Combination Circuits
A combination circuit must be simplified into groups of series
click for animation
click for animation
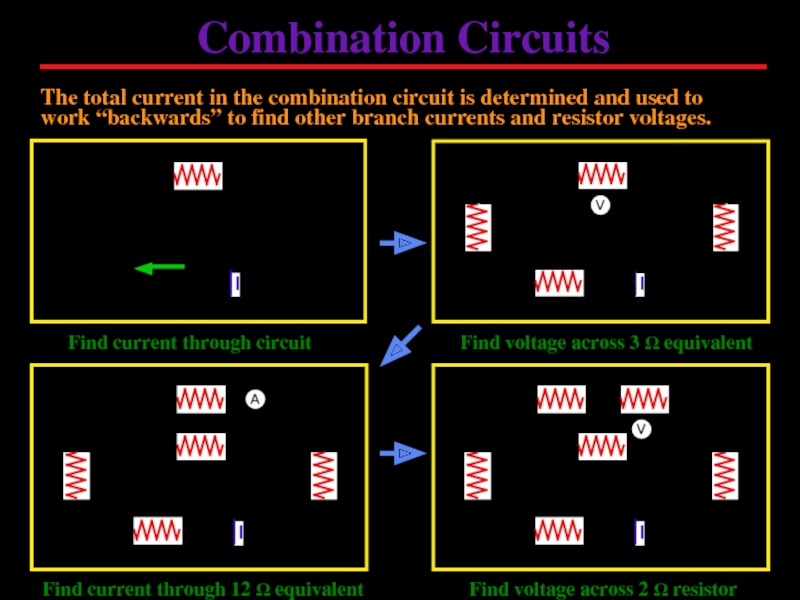
Слайд 14Combination Circuits
The total current in the combination circuit is determined and
Find current through circuit
Find voltage across 3 Ω equivalent
Find current through 12 Ω equivalent
Find voltage across 2 Ω resistor