- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Interest Rates and Monetary Policy презентация
Содержание
- 1. Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
- 2. Interest Rates The price paid for the
- 3. Demand for Money Why hold money? Transactions
- 4. Demand for Money Rate of interest, i
- 5. Assets Securities Loans to commercial banks Liabilities
- 6. Tools of Monetary Policy Open market operations
- 7. Tools of Monetary Policy Fed buys bonds
- 8. Tools of Monetary Policy Fed sells bonds
- 9. Tools of Monetary Policy The reserve ratio
- 10. Tools of Monetary Policy Open market operations
- 11. The Federal Funds Rate Rate charged by
- 12. Monetary Policy Expansionary monetary policy Economy faces
- 13. Monetary Policy Restrictive monetary policy Periods of
- 14. Taylor Rule Rule of thumb for tracking
- 15. Expansionary Monetary Policy Problem: Unemployment and Recession
- 16. Restrictive Monetary Policy Problem: Inflation Fed sells
- 17. Evaluation and Issues Advantages over fiscal policy
- 18. Problems and Complications Lags Recognition and operational Cyclical asymmetry Liquidity trap
Слайд 2Interest Rates
The price paid for the use of money
Many different interest
Speak as if only one interest rate
Determined by the money supply and money demand
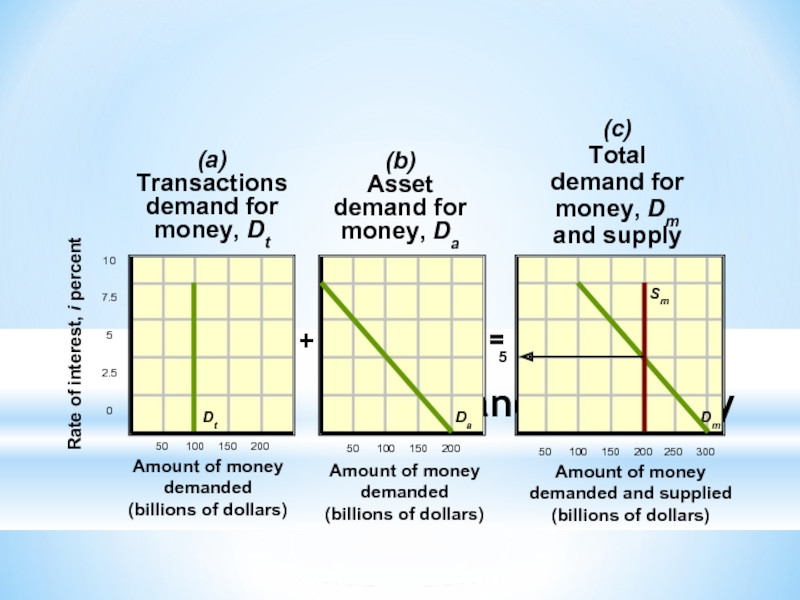
Слайд 3Demand for Money
Why hold money?
Transactions demand, Dt
Determined by nominal GDP
Independent of
Asset demand, Da
Money as a store of value
Varies inversely with the interest rate
Total money demand, Dm
Слайд 4Demand for Money
Rate of interest, i percent
10
7.5
5
2.5
0
Amount of money
demanded
(billions of dollars)
Amount
demanded
(billions of dollars)
Amount of money
demanded and supplied
(billions of dollars)
=
+
(a)
Transactions
demand for
money, Dt
(b)
Asset
demand for
money, Da
(c)
Total
demand for
money, Dm
and supply
Dt
Da
Dm
Sm
5
Слайд 5Assets
Securities
Loans to commercial banks
Liabilities
Reserves of commercial banks
Treasury deposits
Federal Reserve Notes outstanding
Federal
Слайд 6Tools of Monetary Policy
Open market operations
Buying and selling of government securities
Commercial banks and the general public
Used to influence the money supply
When the Fed sells securities, commercial bank reserves are reduced
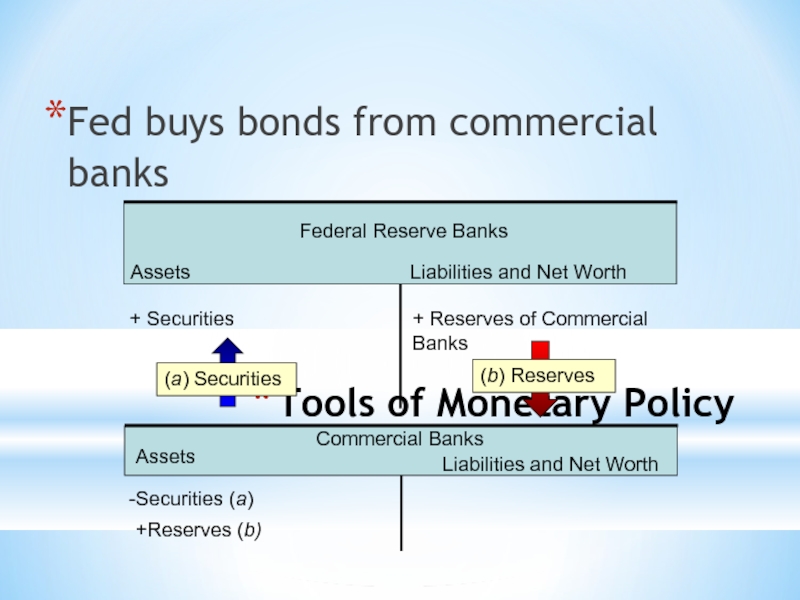
Слайд 7Tools of Monetary Policy
Fed buys bonds from commercial banks
Federal Reserve Banks
+
+ Reserves of Commercial Banks
(b) Reserves
Commercial Banks
Securities (a)
+Reserves (b)
Assets
Liabilities and Net Worth
(a) Securities
Слайд 8Tools of Monetary Policy
Fed sells bonds to commercial banks
Federal Reserve Banks
-
- Reserves of Commercial Banks
Commercial Banks
+ Securities (a)
- Reserves (b)
Assets
Liabilities and Net Worth
(a) Securities
(b) Reserves
Слайд 9Tools of Monetary Policy
The reserve ratio
Changes the money multiplier
The discount rate
The
Short term loans
Term auction facility
Introduced December 2007
Banks bid for the right to borrow reserves
Слайд 10Tools of Monetary Policy
Open market operations are the most important
Reserve ratio
Discount rate was a passive tool
Term auction facility is new
Guaranteed amount lent by the Fed
Anonymous
Слайд 11The Federal Funds Rate
Rate charged by banks on overnight loans
Targeted by
FOMC conducts open market operations to achieve the target
Demand curve for Federal funds
Supply curve for Federal funds
Слайд 12Monetary Policy
Expansionary monetary policy
Economy faces a recession
Lower target for Federal funds
Fed buys securities
Expanded money supply
Downward pressure on other interest rates
Слайд 13Monetary Policy
Restrictive monetary policy
Periods of rising inflation
Increases Federal funds rate
Increases money
Increases other interest rates
Слайд 14Taylor Rule
Rule of thumb for tracking actual monetary policy
Fed has 2%
If real GDP = potential GDP and inflation is 2%, then targeted Federal funds rate is 4%
Target varies as inflation and real GDP vary
Слайд 15Expansionary Monetary Policy
Problem: Unemployment and Recession
Fed buys bonds, lowers reserve ratio,
Excess reserves increase
Federal funds rate falls
Money supply rises
Interest rate falls
Investment spending increases
Aggregate demand increases
Real GDP rises
CAUSE-EFFECT CHAIN
Слайд 16Restrictive Monetary Policy
Problem: Inflation
Fed sells bonds, increases reserve ratio, increases the
Excess reserves decrease
Federal funds rate rises
Money supply falls
Interest rate rises
Investment spending decreases
Aggregate demand decreases
Inflation declines
CAUSE-EFFECT CHAIN