- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Interpersonal Behavior презентация
Содержание
- 1. Interpersonal Behavior
- 2. Lecture structure Acquaintance (Let’s meet) & mutual
- 5. Synonyms Social behavior Interpersonal interaction Social connectedness Social interaction Prosocial behavior Co-existence …
- 6. Course topics need to belong exclusion and
- 7. Class structure Short quiz (3-4 Qs) Discussion, debates, tasks, etc. Individual presentation(s) (hw 1)
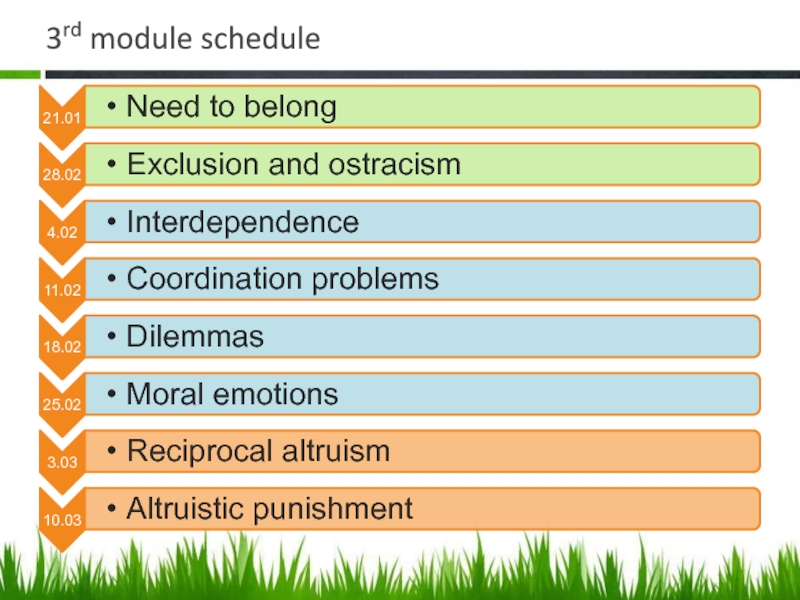
- 8. 3rd module schedule
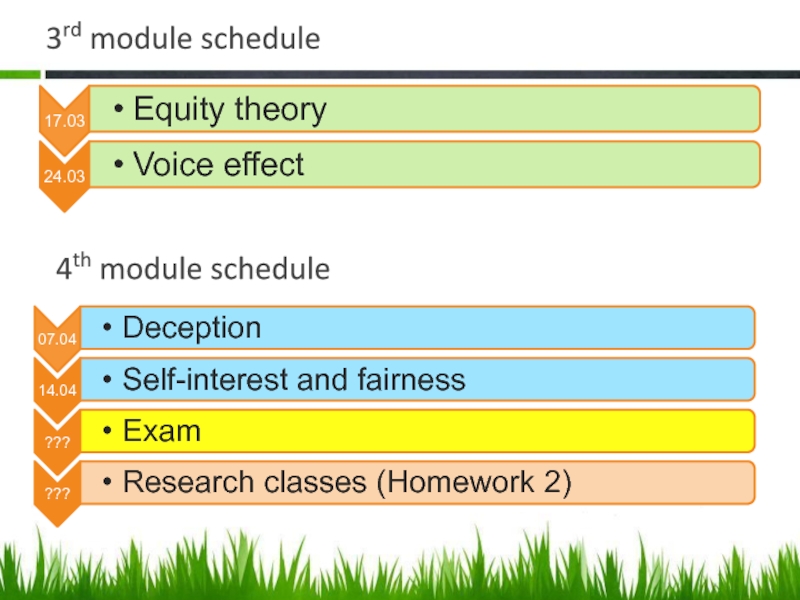
- 9. 3rd module schedule 4th module schedule
- 10. Assessment Home reading – short quizzes Participation
- 11. Grading Total = 0.2*Оexam+0.8*Оaccumulated mark 0.5*Ohw
- 12. Supporting material and services LMS: General info
- 13. Next time Reading and discussion: Topic 1. Need to belong Short quiz Presentation(s) ?
- 14. Horowitz, L.M., Wilson, K.R., Turan,
- 15. Short history interpersonal theories and interpersonal models
- 16. Interpersonal models affiliation friendly behavior hostile behavior submissive behavior dominating behavior dominance
- 17. Problems the principle does not work
- 18. Revised Circumplex Model. Basic postulates (27) Interpersonal
- 19. Conclusions The negative pole of communion is
- 20. Handouts
- 21. Social exclusion and need to belong
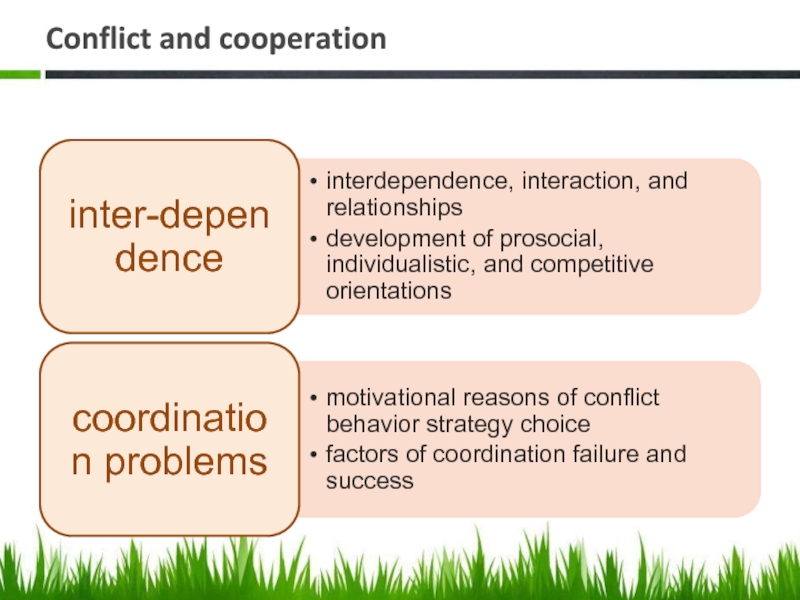
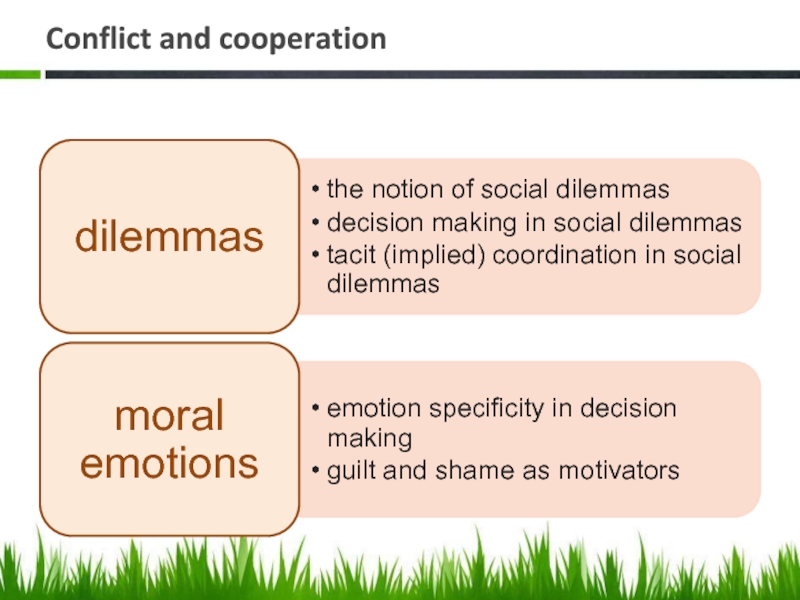
- 22. Conflict and cooperation
- 23. Conflict and cooperation
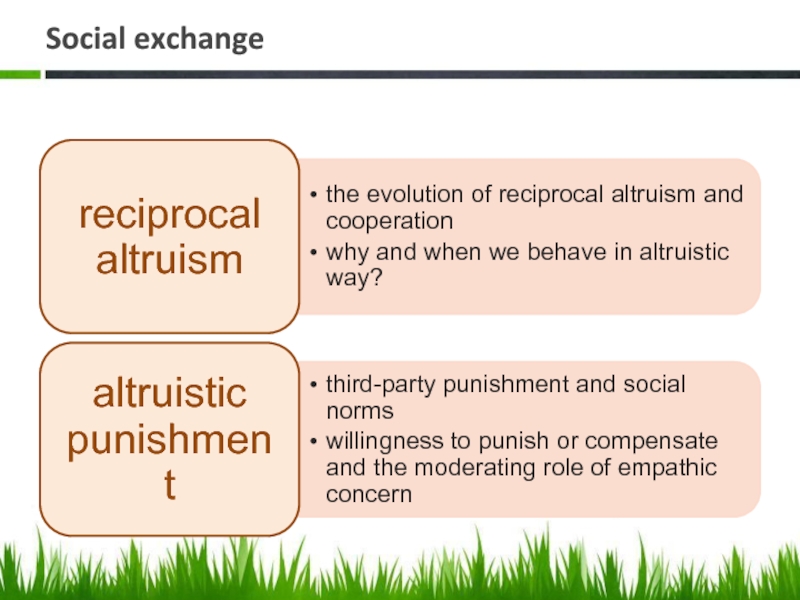
- 24. Social exchange
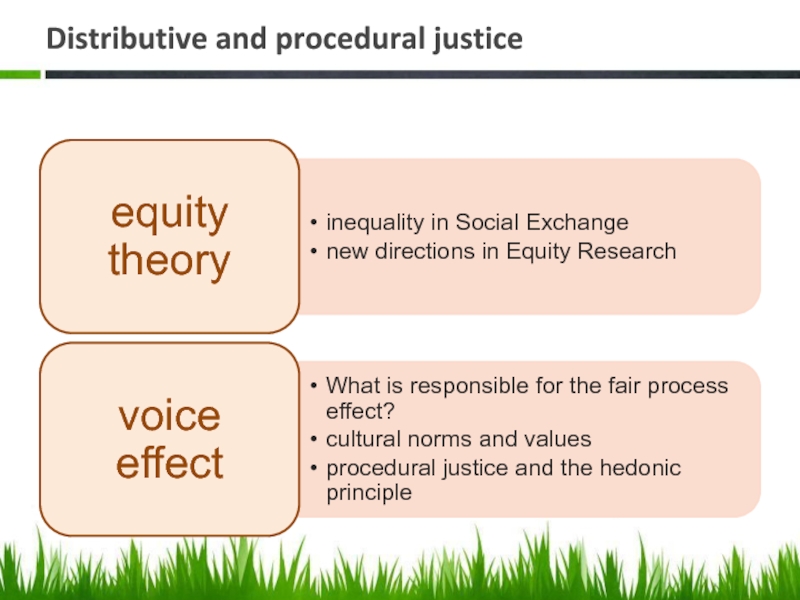
- 25. Distributive and procedural justice
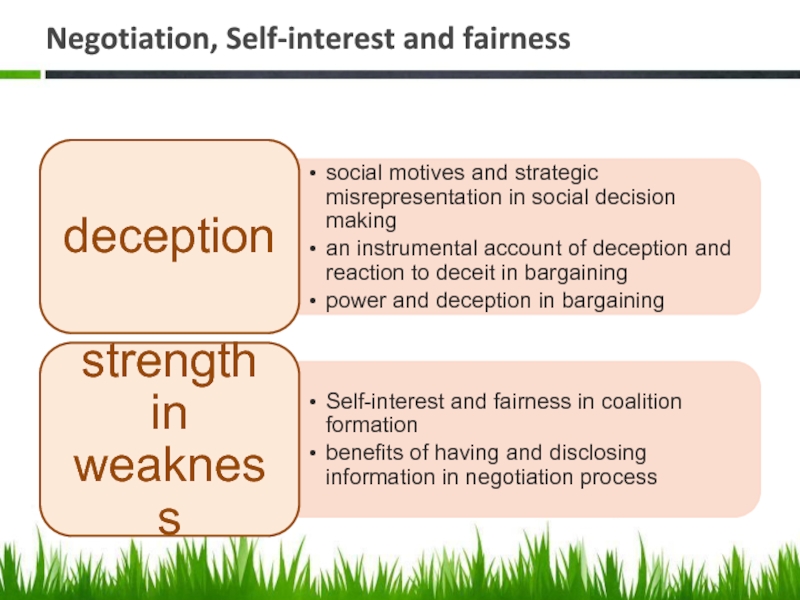
- 26. Negotiation, Self-interest and fairness
Слайд 2Lecture structure
Acquaintance (Let’s meet) & mutual expectations
What does the term “IB”
Course structure and schedule
Assessment and grading
Defining areas of interests
Слайд 3
Acquaintance (Let’s meet)
Teachers’ ideas and
students’ growth
new knowledge
interesting discussions
Students’ ideas and expectations
?
Слайд 4
Interpersonal behavior
What does the term
?
IB is an aggregated notion → different areas of research
IB is behavior that is driven by interpersonal motivation
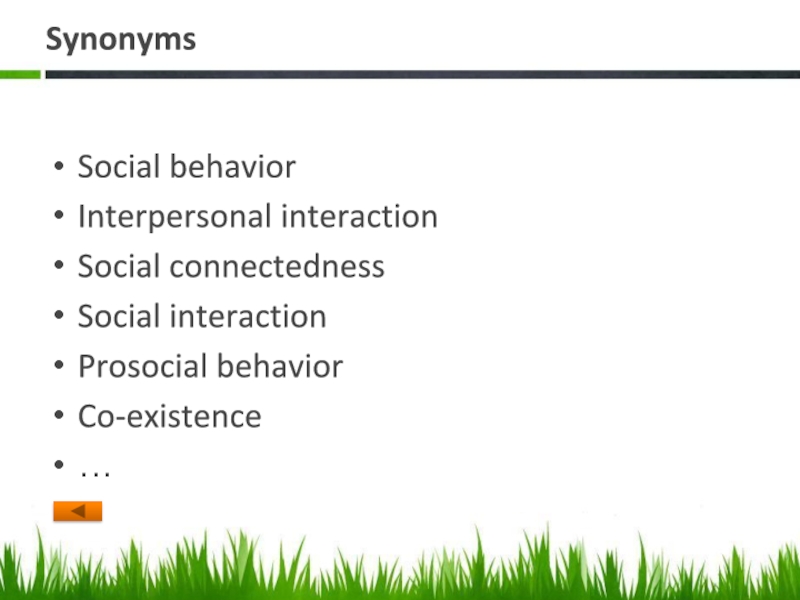
Слайд 5Synonyms
Social behavior
Interpersonal interaction
Social connectedness
Social interaction
Prosocial behavior
Co-existence
…
Слайд 6Course topics
need to belong
exclusion and
ostracism
interdependence
dilemmas
coordination problems
moral emotions
reciprocal altruism
alt. punishment
equity theory
voice
deception
fairness
Слайд 7Class structure
Short quiz (3-4 Qs)
Discussion, debates, tasks, etc.
Individual presentation(s) (hw 1)
Слайд 10Assessment
Home reading – short quizzes
Participation
Homework (1) – presentation and post hoc
Homework (2) – research based on course materials (mini-groups; deadline – June …)
Exam – final test (April-May, appr.)
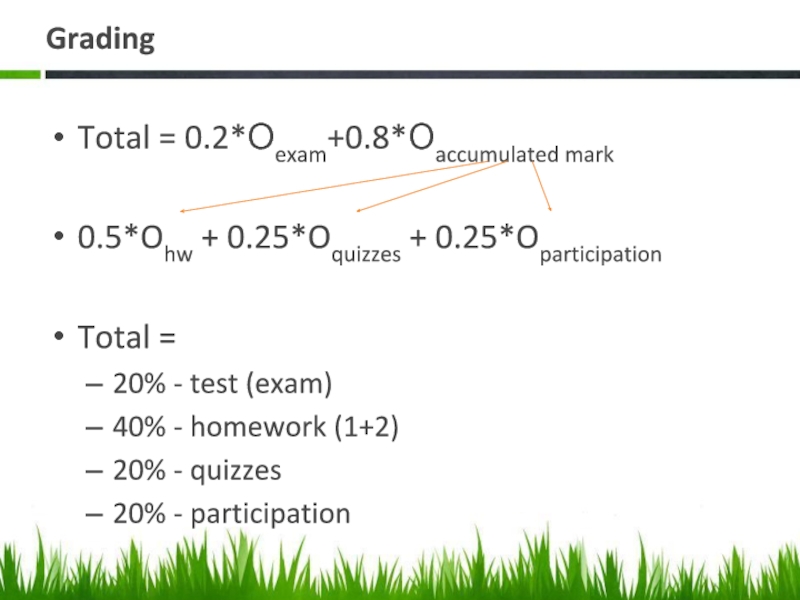
Слайд 11Grading
Total = 0.2*Оexam+0.8*Оaccumulated mark
0.5*Ohw + 0.25*Oquizzes + 0.25*Oparticipation
Total =
20% - test
40% - homework (1+2)
20% - quizzes
20% - participation
Слайд 12Supporting material and services
LMS:
General info
Core reading
Articles for individual presentations + online
Course presentations (teachers’)
Assignments + projects
Слайд 14
Horowitz, L.M., Wilson, K.R.,
Turan, B., Zolotsev, P.,
Constantino, M.J., Henderson,
How interpersonal motives clarify the meaning of interpersonal behavior: A revised circumplex model
Personality and Social Psychology Review, 2006, 10, 67-86.
Слайд 15Short history
interpersonal theories and interpersonal models (Kiesler, 1983; Leary, 1957; Sullivan
“theorem of reciprocal emotion” – reciprocity (or complementarity) in human interaction (Sullivan, 1953)
the principle of complementarity – “A person’s interpersonal actions tend (with a probability significantly greater than chance) to initiate, invite, or evoke from a interactant complementary responses” (Kiesler, 1983, pp.200-201)
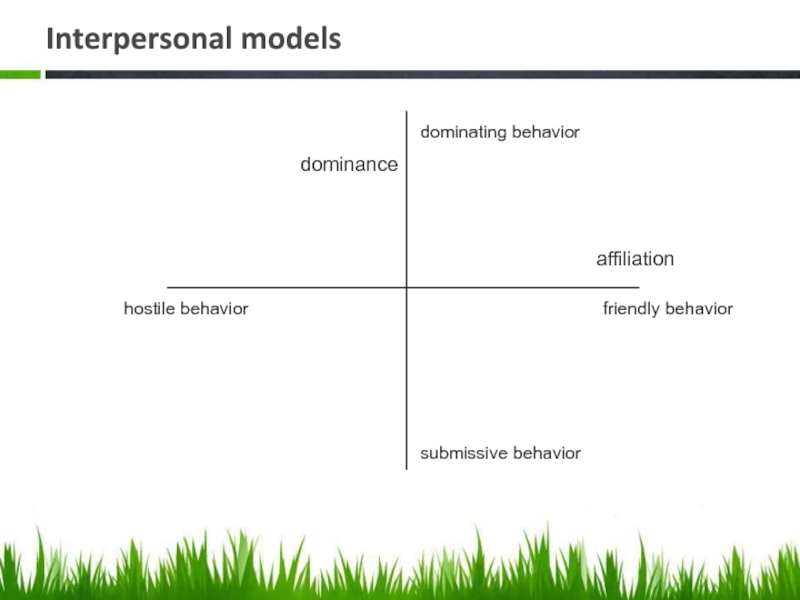
Слайд 16Interpersonal models
affiliation
friendly behavior
hostile behavior
submissive behavior
dominating behavior
dominance
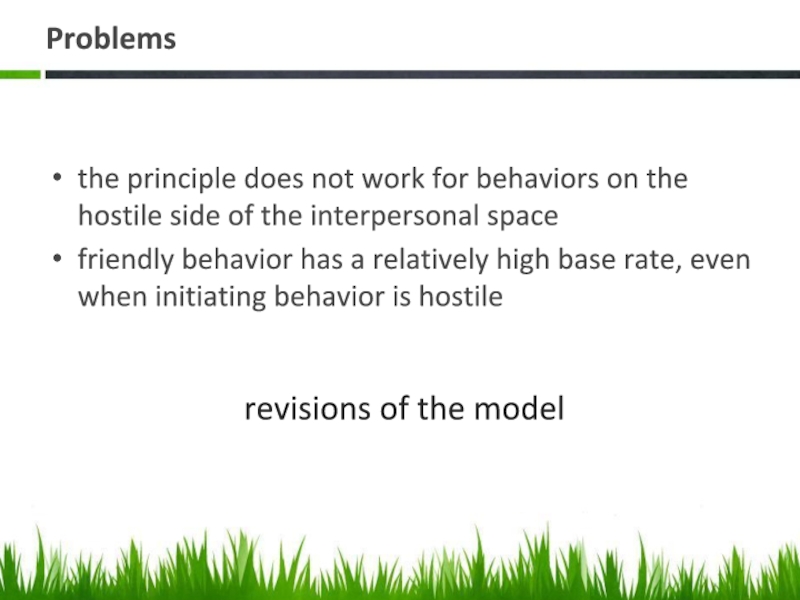
Слайд 17Problems
the principle does not work for behaviors on the hostile side
friendly behavior has a relatively high base rate, even when initiating behavior is hostile
revisions of the model
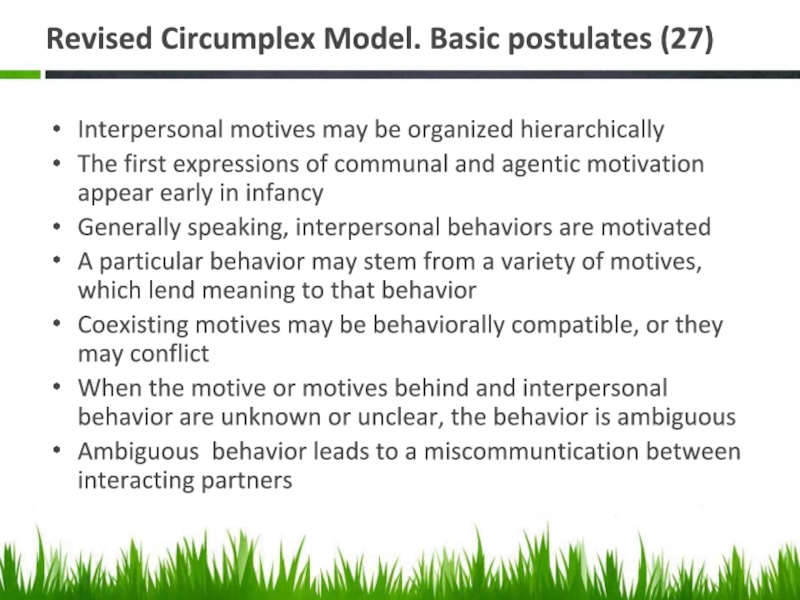
Слайд 18Revised Circumplex Model. Basic postulates (27)
Interpersonal motives may be organized hierarchically
The
Generally speaking, interpersonal behaviors are motivated
A particular behavior may stem from a variety of motives, which lend meaning to that behavior
Coexisting motives may be behaviorally compatible, or they may conflict
When the motive or motives behind and interpersonal behavior are unknown or unclear, the behavior is ambiguous
Ambiguous behavior leads to a miscommuntication between interacting partners
Слайд 19Conclusions
The negative pole of communion is taken to be indifference, not
A given behavior invites (rather than evokes) a particular reaction, which the partner may choose not to satisfy
The complement of a behavior is the reaction that would satisfy the motive behind it
Noncomplementary reactions induce negative affect