- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The World Economy презентация
Содержание
- 1. The World Economy
- 2. Lecture 4 Overview of the World Economy
- 3. The World Economy “Globalization” Means different things
- 4. Lecture 1: Overview The World Economy “Globalization”
- 5. The World Economy International Economics Is NOT about countries It IS about interactions among countries
- 6. Lecture 4 Overview of the World Economy
- 7. The World Economy World Economy consists of
- 8. (Aside, on getting information) An excellent source
- 9. The World Economy World Economy consists of
- 10. The World Economy Implication US is very
- 11. Lecture 4 Overview of the World Economy
- 12. The World Economy Ways that countries interact
- 14. The World Economy See tables below
- 15. Who Trades the Most? ($ b. &
- 16. Who Trades the Most? Developed countries are
- 17. Who Trades the Most? See Economist from
- 18. Who Trades the Most? “Emerging Markets” in
- 19. Lecture 1: Overview
- 21. Who Trades with Whom? ($ b., 2013,
- 22. North America, Europe, and Asia trade mostly
- 23. What Does the World Trade? ($ b.
- 24. Lecture 1: Overview What Does the World
- 25. Lecture 1: Overview What Does the World
- 26. Lecture 1: Overview What Does the World
- 27. What Does the US Trade? ($ b.
- 28. Lecture 1: Overview What Does the US
- 29. Importance of Trade for Countries? (GDP in
- 30. Importance of Trade for Countries? Even though
- 31. Importance of Trade for Countries? A Few
- 32. Lecture 4 Overview of the World Economy
- 33. The World Economy Ways that countries interact
- 34. Lecture 1: Overview The World Economy Ways
- 35. The World Economy Ways that countries interact
- 36. US Investment Position ($ trillion at market
- 37. US Investment Position (Qualification: “Owe” isn’t quite
- 38. Lecture 4 Overview of the World Economy
- 39. The World Economy Other ways that countries
- 40. Lecture 4 Overview of the World Economy
- 41. The World Economy Other ways that countries
- 42. The World Economy Other ways that countries
- 43. The World Economy Aside on Tariffs We
- 44. The World Economy Aside on Tariffs Tariffs
- 45. The World Economy Aside on Tariffs 45%
- 46. The World Economy Other ways that countries
- 47. Next Time Institutions of the International Economy
Слайд 2Lecture 4
Overview of the World Economy
“Globalization”
Elements of the World Economy
Ways that
Trade
Capital Flows
Migration
Policies that Affect Others
Слайд 3The World Economy
“Globalization”
Means different things to different people
My definitions (see my
1. The increasing world-wide integration of markets for goods, services and capital.
2. Also the role of MNCs, IMF, WTO, World Bank.
3. Elsewhere: domination by United States.
Some see good, others bad
Bad: reading by powell
Good: reading by Bhagwati
Both make valid points. Read to see what they are.
Слайд 4Lecture 1: Overview
The World Economy
“Globalization”
Some aspects of globalization declined with the
The Economist, on Nov 15, 2014, reported “Signs of Life”:
Globalization is back
Various measures of globalization (though not all) have risen past their previous peaks
The “depth” of trade (its volume) has increased
The “breadth” of trade (number of borders crossed) has not fully recovered
Слайд 5The World Economy
International Economics
Is NOT about countries
It IS about interactions among
Слайд 6Lecture 4
Overview of the World Economy
“Globalization”
Elements of the World Economy
Ways that
Trade
Capital Flows
Migration
Policies that Affect Others
Слайд 7The World Economy
World Economy consists of
Countries: a few hundred
(CIA lists about
(WTO has 160 members)
People: over 7 billion
(7.216 b. 1/5/15, compare 320 m. US)
Land: about 15 times the US
Слайд 8(Aside, on getting information)
An excellent source of information about countries is
(Just Google “fact book”)
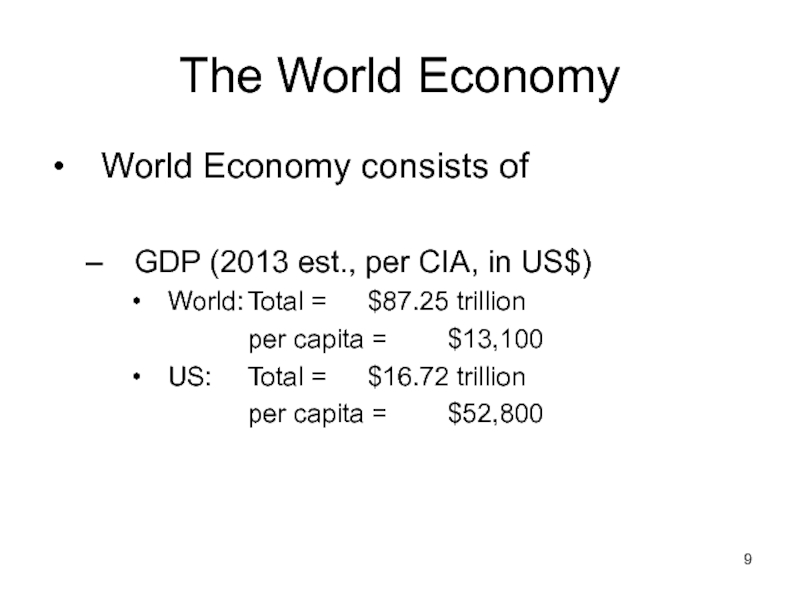
Слайд 9The World Economy
World Economy consists of
GDP (2013 est., per CIA, in
World: Total = $87.25 trillion
per capita = $13,100
US: Total = $16.72 trillion
per capita = $52,800
Слайд 10The World Economy
Implication
US is very unusual
Very rich
US has less than
Слайд 11Lecture 4
Overview of the World Economy
“Globalization”
Elements of the World Economy
Ways that
Trade
Capital Flows
Migration
Policies that Affect Others
Слайд 12The World Economy
Ways that countries interact economically
Trade (per CIA, 2013 est.)
World
(compare world GDP of $87 trillion)
World trade has grown faster than world GDP most years
But not during 2008-9, due to world recession
Слайд 14The World Economy
See tables below for
Who trades most?
Who trades with whom?
Share
US:
What do we export/import?
To/from whom?
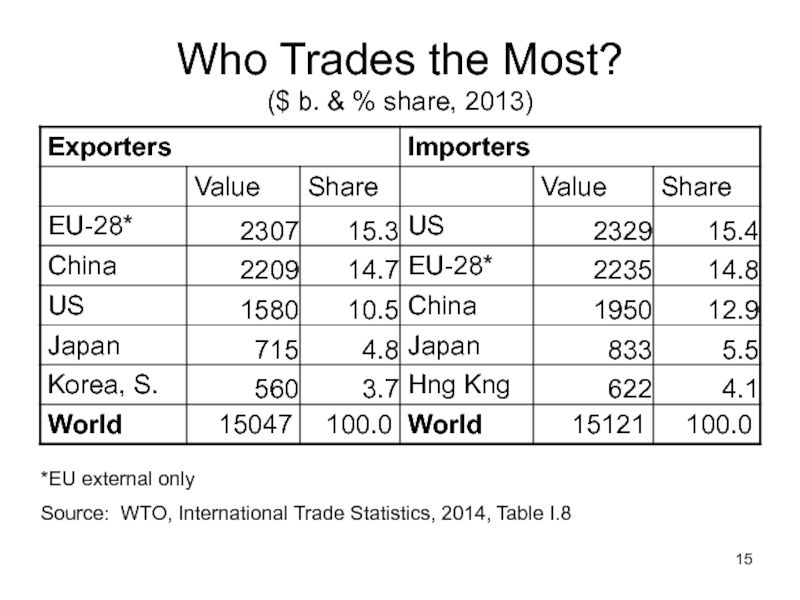
Слайд 15Who Trades the Most?
($ b. & % share, 2013)
*EU external only
Source:
Слайд 16Who Trades the Most?
Developed countries are the biggest traders
China is catching
It was the #3 exporter six years ago when I taught the course; now it’s #2 and closing in on EU.
Others are gaining as well: Four years ago Canada was #5 exporter. Three years ago that was S Korea
Слайд 17Who Trades the Most?
See Economist from about a year ago: “Trading
China claimed to have surpassed US. True only for goods, not goods + services
But with time China will pass US in both
China’s trade per GDP is much larger than the US, but below world average
Much of the value in China’s exports is imported inputs, thus low “value added.”
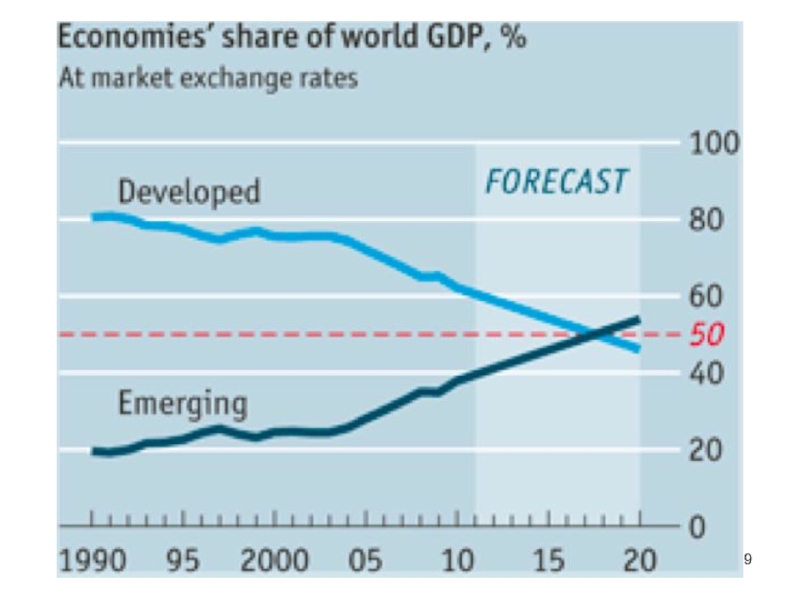
Слайд 18Who Trades the Most?
“Emerging Markets” in general are catching up to,
In GDP, trade, and more
See Economics Focus from The Economist, “Why the Tail Wags the Dog”
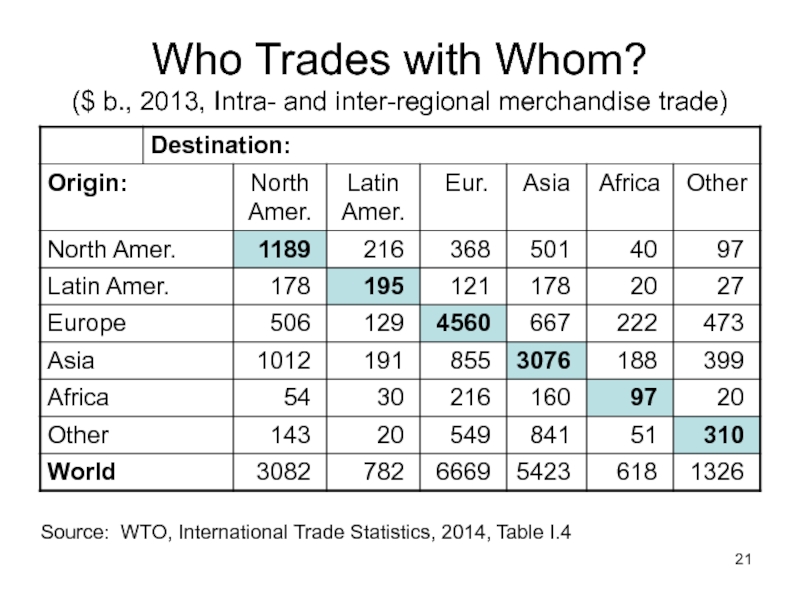
Слайд 21Who Trades with Whom?
($ b., 2013, Intra- and inter-regional merchandise trade)
Source:
Слайд 22North America, Europe, and Asia trade mostly within their group
Poorer regions
This reflects what is not so clear in the table:
Rich countries trade most with each other
Poor countries trade most with rich countries
But their trade with each other is growing
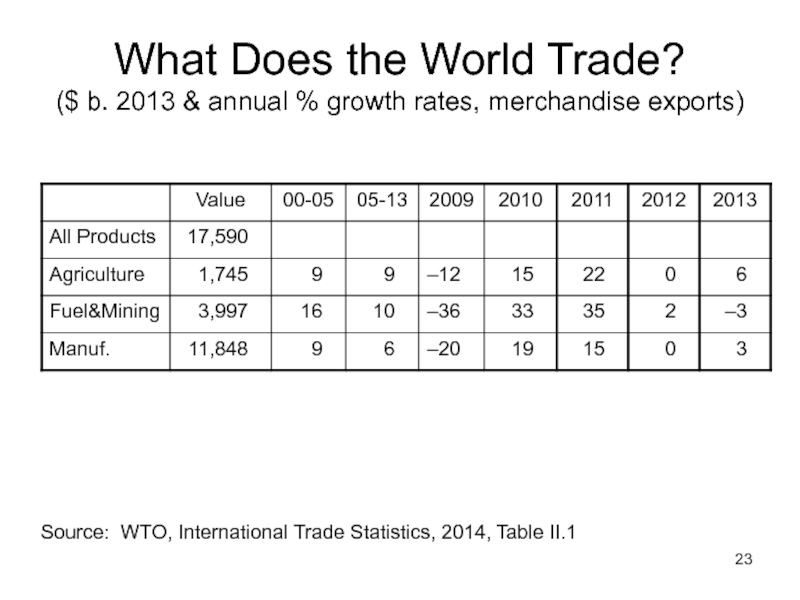
Слайд 23What Does the World Trade? ($ b. 2013 & annual % growth
Source: WTO, International Trade Statistics, 2014, Table II.1
Слайд 24Lecture 1: Overview
What Does the World Trade?
Biggest traded category: manufactures
Fastest growing,
Why?
Because this is the value of trade, and prices of oil and other raw materials were rising, and then falling.
But within Manufactures, Iron & Steel is even more volatile:
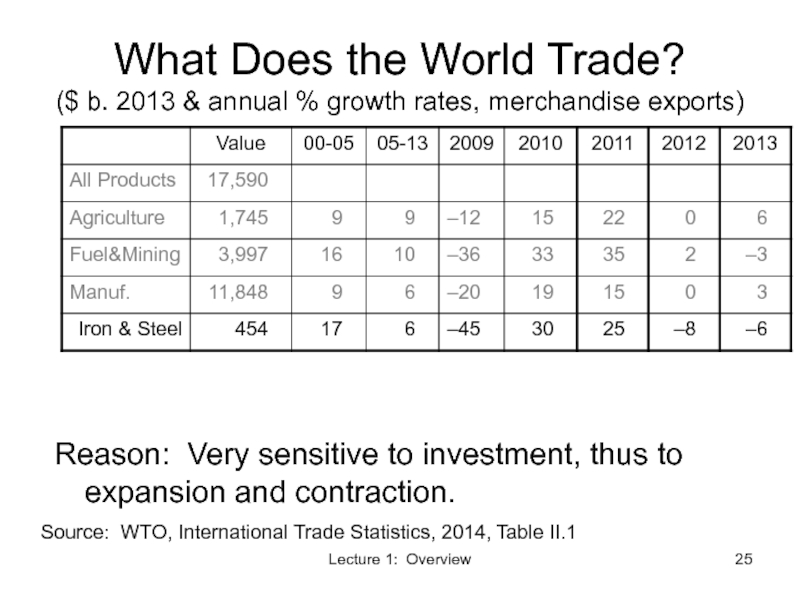
Слайд 25Lecture 1: Overview
What Does the World Trade?
($ b. 2013 & annual
Source: WTO, International Trade Statistics, 2014, Table II.1
Reason: Very sensitive to investment, thus to expansion and contraction.
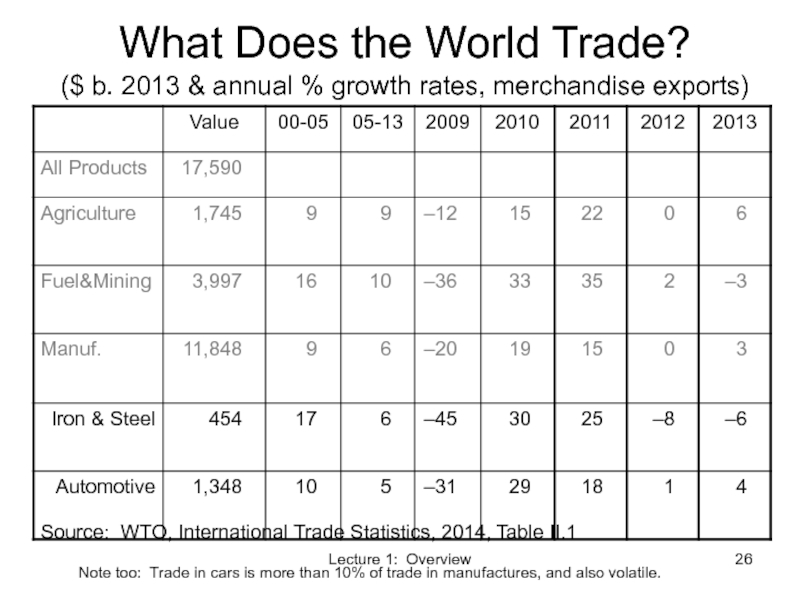
Слайд 26Lecture 1: Overview
What Does the World Trade?
($ b. 2013 & annual
Source: WTO, International Trade Statistics, 2014, Table II.1
Note too: Trade in cars is more than 10% of trade in manufactures, and also volatile.
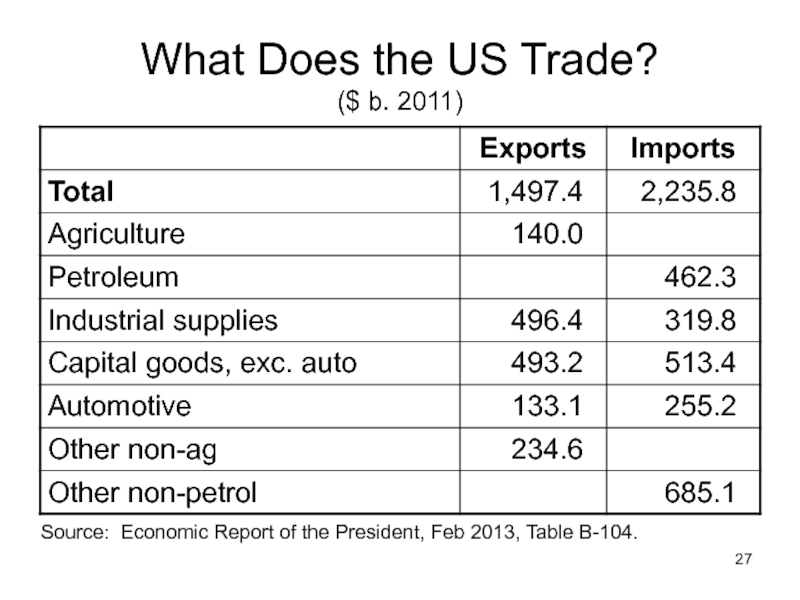
Слайд 27What Does the US Trade?
($ b. 2011)
Source: Economic Report of the
Слайд 28Lecture 1: Overview
What Does the US Trade?
US imports are much larger
(We’ll see what that means later in the course.)
US is a big…
Exporter of agricultural products
Importer of oil
Exporter and importer of capital goods (i.e., machines for making things)
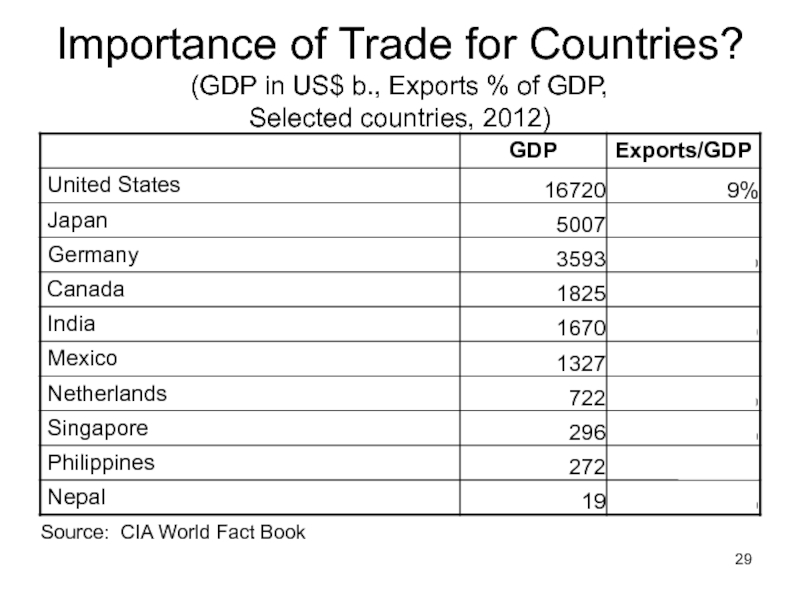
Слайд 29Importance of Trade for Countries? (GDP in US$ b., Exports % of
Source: CIA World Fact Book
Слайд 30Importance of Trade for Countries?
Even though we trade more than most,
Others that are low: Japan, Nepal (even lower than US)
Note Singapore: Exports can be more than GDP.
Reason: Exports are made using imported inputs, so value of exports includes imports.
Слайд 32Lecture 4
Overview of the World Economy
“Globalization”
Elements of the World Economy
Ways that
Trade
Capital Flows
Migration
Policies that Affect Others
Слайд 33The World Economy
Ways that countries interact economically
Capital Flows
Financial (holdings of financial
Real (international ownership of real assets)
Слайд 34Lecture 1: Overview
The World Economy
Ways that countries interact economically
Capital Flows
Financial (holdings
Currency
Bank deposits
Bonds – private and government
Stocks
Bank loans
Real (international ownership of real assets)
Слайд 35The World Economy
Ways that countries interact economically
Capital Flows
Financial (holdings of financial
Real (international ownership of real assets)
Real estate
Capital assets (plant and equipment)
Stocks (equities) if ownership share is large
Other
Data, below, are stocks (i.e, amounts at a point in time)
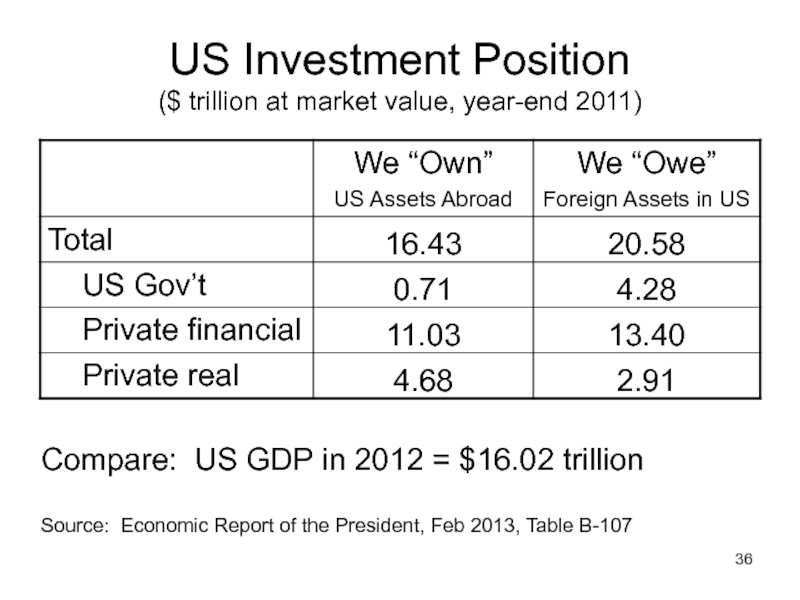
Слайд 36US Investment Position
($ trillion at market value, year-end 2011)
Source: Economic Report
Compare: US GDP in 2012 = $16.02 trillion
Слайд 37US Investment Position
(Qualification: “Owe” isn’t quite right. This includes all assets
Lessons:
US is a large net “debtor” (result of our spending more than we earn)
Most of this today is government, but some is private
Слайд 38Lecture 4
Overview of the World Economy
“Globalization”
Elements of the World Economy
Ways that
Trade
Capital Flows
Migration
Policies that Affect Others
Слайд 39The World Economy
Other ways that countries interact economically
Migration
Temporary
Guest workers
Day workers
Permanent
In practice,
Слайд 40Lecture 4
Overview of the World Economy
“Globalization”
Elements of the World Economy
Ways that
Trade
Capital Flows
Migration
Policies that Affect Others
Слайд 41The World Economy
Other ways that countries interact economically
Policies that affect other
Direct
Indirect
Слайд 42The World Economy
Other ways that countries interact economically
Policies that affect other
Direct
Trade policies (tariffs, quotas)
Foreign aid
Capital controls
Exchange rate management
Immigration restrictions
Indirect
Слайд 43The World Economy
Aside on Tariffs
We will be dealing a lot with
See reading by Hufbauer and Grieco:
US tariffs are much lower than they used to be (average 4% now, vs. 40% in 1946)
US has gained a great deal from lowering tariffs
US still has much to gain from further lowering
But there are also severe costs for some people and firms who compete with imports
Слайд 44The World Economy
Aside on Tariffs
Tariffs could go up:
WTO enforces only upper
Actual tariffs in many countries are below these limits, and could legally rise
There was danger that the recent world recession would push countries to do that.
They didn’t – at least not much.
Слайд 45The World Economy
Aside on Tariffs
45% of US exports go to developing
US tariffs are much higher against developing countries than against developed countries
Слайд 46The World Economy
Other ways that countries interact economically
Policies that affect other
Indirect
Subsidies (esp. agriculture)
US farm subsidies > foreign aid (see CGD reading)
Macro policies (monetary, fiscal)
Exchange-rate policies
Environmental policies
Standards
Labor
Health & safety
Norms
Слайд 47Next Time
Institutions of the International Economy
What are they?
The WTO
The IMF
The World
The OECD
What’s happening (or not happening) now?