- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Forms of business. Ownership презентация
Содержание
- 1. Forms of business. Ownership
- 2. Introduction A business is always owned
- 3. Key Learning Points What are
- 4. Main types of business organisation
- 5. Sole Trader A sole trader is a
- 6. Examples of sole traders Small shops Small
- 7. Advantages of a Sole Trader Cheap and
- 8. Disadvantages of a Sole Trader Unlimited
- 9. Partnership Business where there are two or
- 10. Advantages of a Partnership Spreads
- 11. Disadvantages of a Partnership Have
- 12. Limited Company Business owned
- 13. Private Limited Company (Ltd.) A private limited
- 14. Advantages of a Private Limited Company Shareholders
- 15. Disadvantages of a Private Limited Company
- 16. Public Limited Company (Plc) Business owned by
- 17. Advantages of a Public Limited Company The
- 18. Disadvantages of a Public Limited Company Costly
Слайд 2
Introduction
A business is always owned by someone. This can just be
one person, or thousands. So a business can have a number of different types of ownership depending on the aims and objectives of the owners.
Most businesses aim to make profit for their owners. Profits may not be the major objective, but in order to survive a business will need make a profit in the long term.
Some organisations however will be ‘not-for-profit’, such as charities or government-run corporations.
Most businesses aim to make profit for their owners. Profits may not be the major objective, but in order to survive a business will need make a profit in the long term.
Some organisations however will be ‘not-for-profit’, such as charities or government-run corporations.
Слайд 3
Key Learning Points
What are the different types of business organisation?
What are
the advantages and disadvantages of each type?
What are the implications of the choice of business organisation on key issues such as:
Ability to raise finance
Control of the business
Business aims and objectives
What are the implications of the choice of business organisation on key issues such as:
Ability to raise finance
Control of the business
Business aims and objectives
Слайд 4
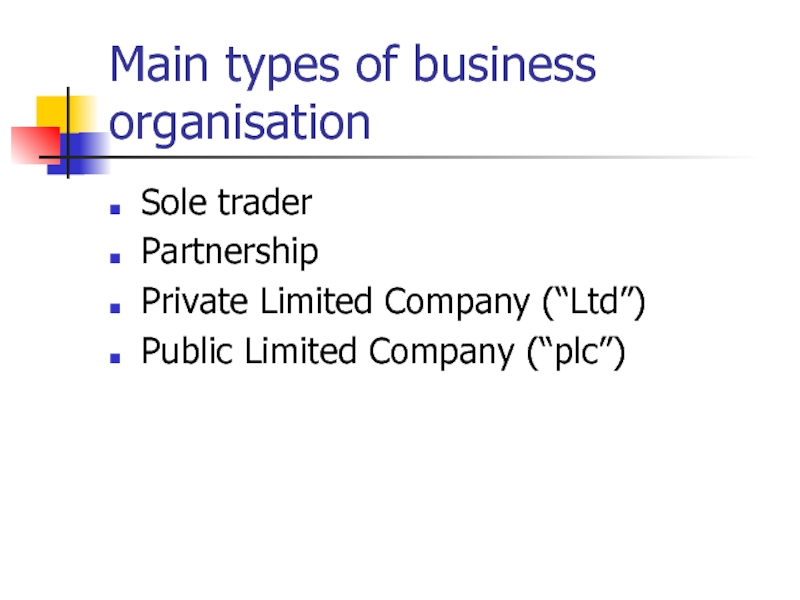
Main types of business organisation
Sole trader
Partnership
Private Limited Company (“Ltd”)
Public Limited Company
(“plc”)
Слайд 5Sole Trader
A sole trader is a business owned by one person
The
owner makes all the decisions about how the business is run
The owner keeps all the profit, but also suffers all the losses of the business
The owner keeps all the profit, but also suffers all the losses of the business
Слайд 7Advantages of a Sole Trader
Cheap and easy to set up
Keep
all the profits
Make all the decisions
Personal contact with customers
Make all the decisions
Personal contact with customers
Слайд 8Disadvantages of a
Sole Trader
Unlimited liability (this means that the owner
is responsible for all of the debts of the business)
Lack of capital can prevent expansion
Suffer all losses yourself
Business ends when the owner dies
Lack of capital can prevent expansion
Suffer all losses yourself
Business ends when the owner dies
Слайд 9Partnership
Business where there are two or more owners of the enterprise
Most
partnerships have between two and twenty members though there are examples like the major accountancy firms where there are hundreds of partners
Слайд 10
Advantages of a Partnership
Spreads the risk across more people, so if
the business gets into difficulty then the are more people to share the burden of debt
Partner may bring money and resources to the business
Partner may bring other skills and ideas to the business, complementing the work already done by the original partner
Partner may bring money and resources to the business
Partner may bring other skills and ideas to the business, complementing the work already done by the original partner
Слайд 11
Disadvantages of a Partnership
Have to share profits
Less control of business for
individual
Disputes over workload
Problems if partners disagree over of direction of business
Disputes over workload
Problems if partners disagree over of direction of business
Слайд 12
Limited Company
Business owned by shareholders
Run by directors (who may also be
shareholders)
Liability is limited (important)
Liability is limited (important)
Слайд 13Private Limited Company (Ltd.)
A private limited company is where between one
and ninety nine people come together and form a business
The owners are called shareholders and they invest money in the company
The profit is divided up among the shareholders and distributed in the form of dividends
“Ltd.” is written after the name of the company
The annual accounts are sent to the Registrar of Companies - they are not published
The owners are called shareholders and they invest money in the company
The profit is divided up among the shareholders and distributed in the form of dividends
“Ltd.” is written after the name of the company
The annual accounts are sent to the Registrar of Companies - they are not published
Слайд 14Advantages of a Private Limited Company
Shareholders have limited liability: If the
business fails you can only lose the money that you invested in the company. Your own personal wealth cannot be touched.
Easier to raise finance
Business continues to exist even when an owner dies
Easier to raise finance
Business continues to exist even when an owner dies
Слайд 15Disadvantages of a Private Limited Company
Costly to set up
A lot
of legal requirements when forming a company
Shares cannot be transferred to the general public
Shares cannot be transferred to the general public
Слайд 16Public Limited Company (Plc)
Business owned by shareholders
Run by directors (who may
also be shareholders)
Liability is limited
Liability is limited
Слайд 17Advantages of a Public Limited Company
The ability to raise larger capital
Widening
the shareholder base and spreading risk
More growth and expansion opportunities
Shares are more easily transferable
Going public can enhance the options for the founders to exit the business at some point in the future, if they wish to do so
More growth and expansion opportunities
Shares are more easily transferable
Going public can enhance the options for the founders to exit the business at some point in the future, if they wish to do so
Слайд 18Disadvantages of a Public Limited Company
Costly and complicated to set up
as a plc
Certain financial information must be made available for public (higher transparency)
Shareholders expect a steady stream of income from dividends
Increased threat of a takeover
Certain financial information must be made available for public (higher transparency)
Shareholders expect a steady stream of income from dividends
Increased threat of a takeover