- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Business Organization: Forms of Business Ownership презентация
Содержание
- 1. Business Organization: Forms of Business Ownership
- 2. After successful broadcasts Among CIFS students
- 3. Comes of one the most Expected lecture of season
- 4. Business Organization: Forms of Business Ownership Lecture 4
- 6. Selecting a Form of Business Ownership Sole
- 7. Concepts of Business Ownership Unlimited Liability –
- 8. Concepts of Business Ownership Continuity – death
- 9. Sole Proprietorship Owned by a single owner
- 10. Sole Proprietorship Advantages vs. Disadvantages “+” Easy
- 11. Partnership General Partnership Co-owned by two or
- 12. Partnership Limited Partnership Limited partner(s) + at
- 13. Partnership Advantages vs. Disadvantages “+” Additional capital
- 14. Limited Liability Company (LLC.) Similar to partnership
- 15. LLC “UNITEL” works under Beeline TM
- 16. Corporation A state-chartered entity that pays
- 17. Corporation Limited liability for owners Separate
- 18. Corporation Privately Held vs. Publicly Held Privately
- 19. Corporation Advantages vs. Disadvantages “+” Limited liability
- 21. Joint Venture Two businesses working together on
- 24. Franchise An arrangement whereby a business owner
- 26. Summary Sole Proprietorship Partnership General Partnership
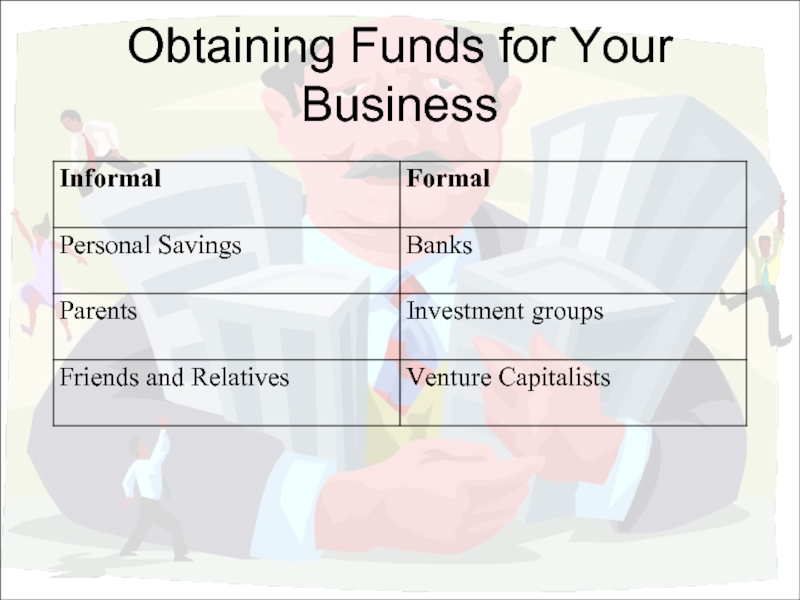
- 27. Obtaining Funds for Your Business
- 28. Sources Simpson, P. (2002) Business Studies AS
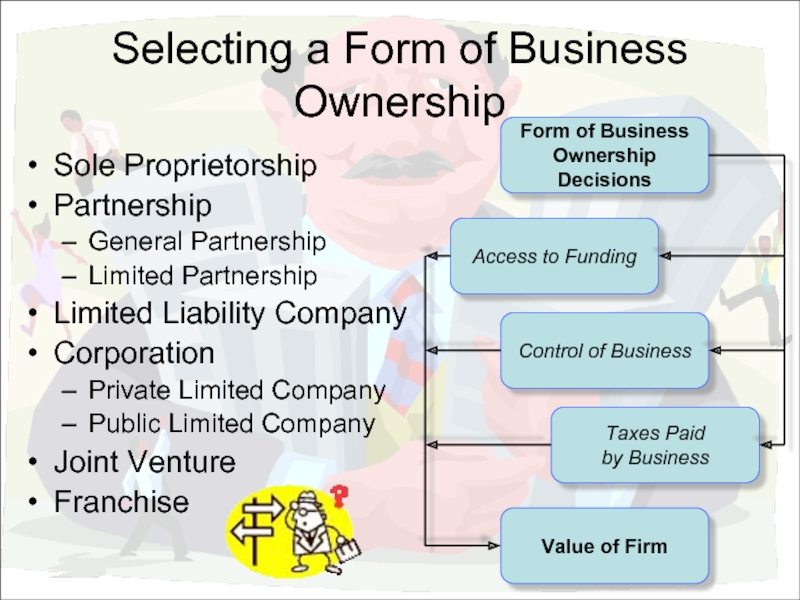
Слайд 6Selecting a Form of Business Ownership
Sole Proprietorship
Partnership
General Partnership
Limited Partnership
Limited Liability Company
Corporation
Private
Public Limited Company
Joint Venture
Franchise
Form of Business
Ownership Decisions
Access to Funding
Control of Business
Taxes Paid
by Business
Value of Firm
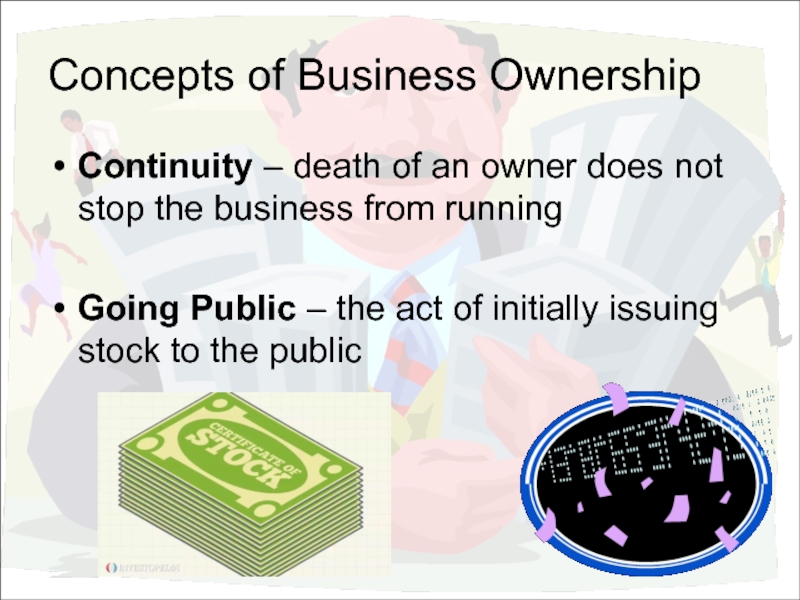
Слайд 7Concepts of Business Ownership
Unlimited Liability – no limit on the debts
Limited Liability – responsibility only for the amount of money invested into business
Legal Personality – legal identity separate from its owner
Слайд 8Concepts of Business Ownership
Continuity – death of an owner does not
Going Public – the act of initially issuing stock to the public
Слайд 9Sole Proprietorship
Owned by a single owner
The owner – sole proprietor, sole
Full control by the owner
Limited access to funds
The business is likely to remain very small
The owner has unlimited liability
Only Personal Income of the owner is taxed
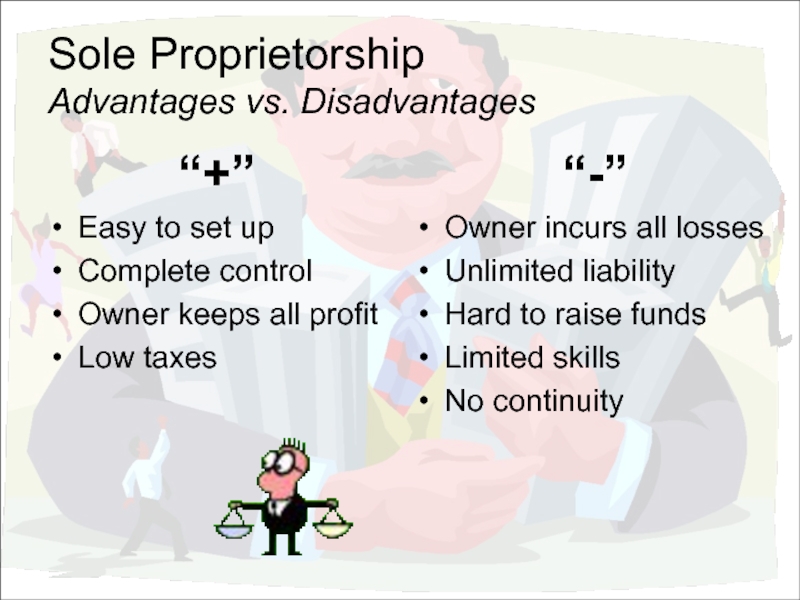
Слайд 10Sole Proprietorship
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
“+”
Easy to set up
Complete control
Owner keeps all profit
Low
“-”
Owner incurs all losses
Unlimited liability
Hard to raise funds
Limited skills
No continuity
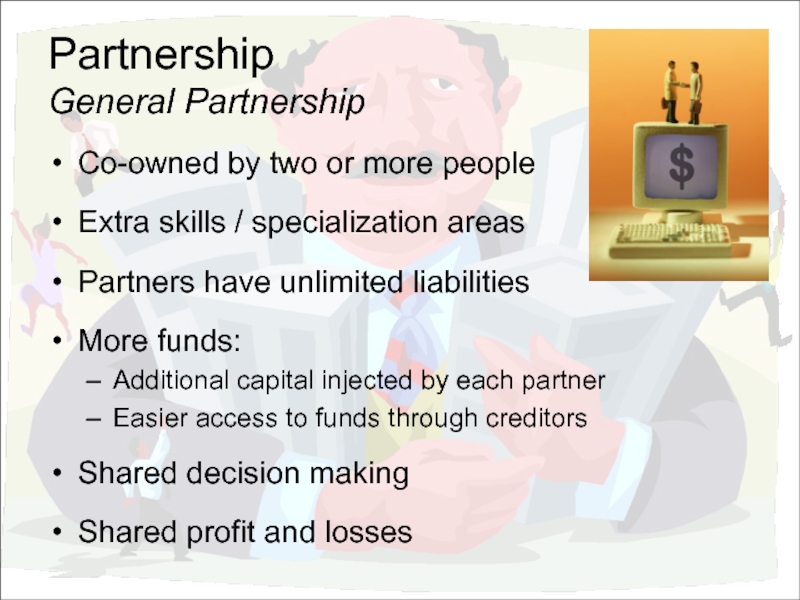
Слайд 11Partnership
General Partnership
Co-owned by two or more people
Extra skills / specialization areas
Partners
More funds:
Additional capital injected by each partner
Easier access to funds through creditors
Shared decision making
Shared profit and losses
Слайд 12Partnership
Limited Partnership
Limited partner(s) + at least one general partner
Limited partner
Liability is
Does not take part in decision making
General partner
Manages the business
Receives a salary
Shares the profits or losses of business
Has unlimited liability
Слайд 13Partnership
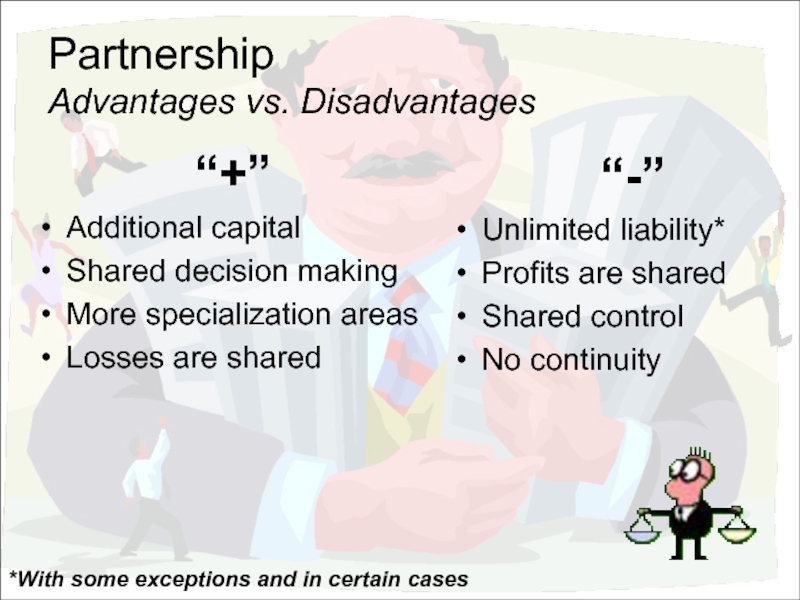
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
“+”
Additional capital
Shared decision making
More specialization areas
Losses are shared
“-”
Unlimited liability*
Profits
Shared control
No continuity
*With some exceptions and in certain cases
Слайд 14Limited Liability Company (LLC.)
Similar to partnership
Has all the advantages of partnership
All
Precise rules on liability protection vary from one region/state to another
Added complexity, compared to partnership
Have become popular in recent years
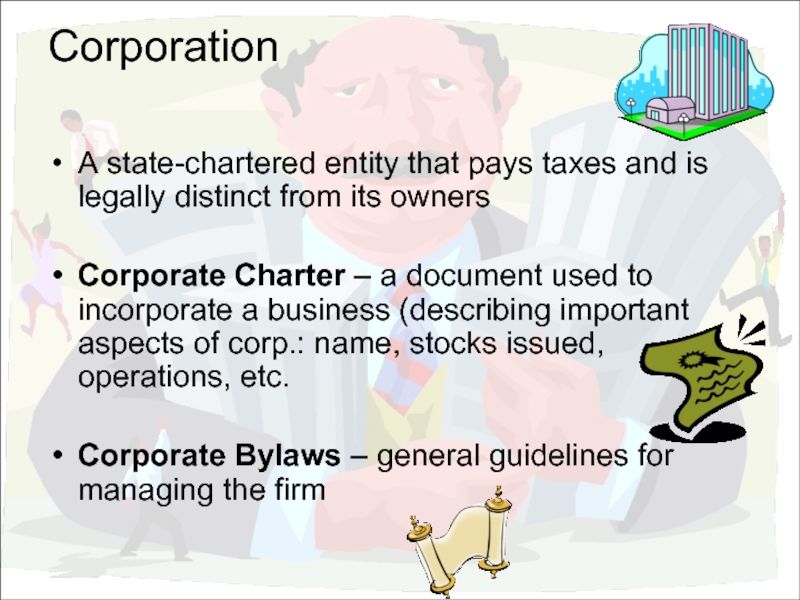
Слайд 16Corporation
A state-chartered entity that pays taxes and is legally distinct from
Corporate Charter – a document used to incorporate a business (describing important aspects of corp.: name, stocks issued, operations, etc.
Corporate Bylaws – general guidelines for managing the firm
Слайд 17Corporation
Limited liability for owners
Separate legal identity
This leads to double taxation (how?)
Shareholders
Board of Directors establish general policies, elect/replace Officers (CEO, CFO), etc.
Shareholders receive dividends
Слайд 18Corporation
Privately Held vs. Publicly Held
Privately Held Corporation (Ltd., Pte.) – restricted
Shares cannot be sold on the open market
Control often remains in hands of the original owner(s)
Publicly Held Corporation (Plc., Inc.) – shares can be easily purchased or sold by investors
Issue stock to public (go public)
Simplicity and flexibility in buying/selling stock
Higher degree of “divorce between ownership and control”
Agency problems and short-termism
Слайд 19Corporation
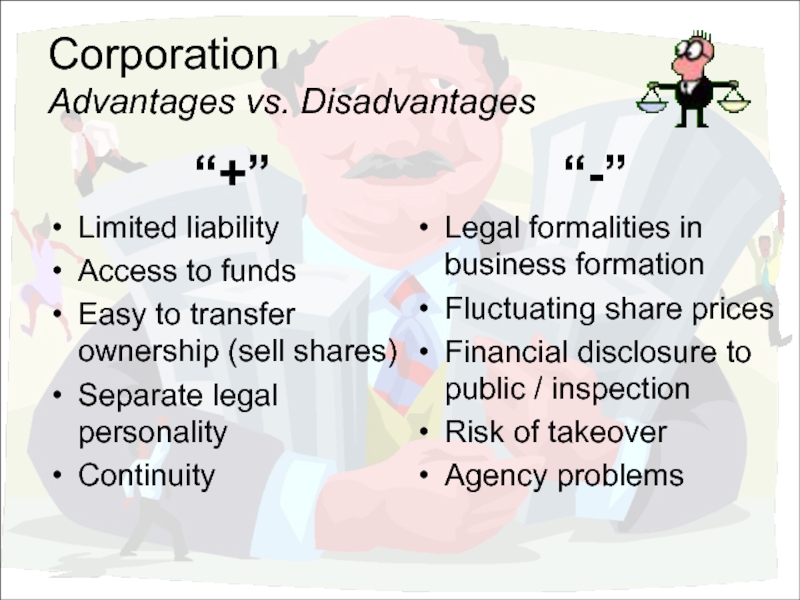
Advantages vs. Disadvantages
“+”
Limited liability
Access to funds
Easy to transfer ownership (sell shares)
Separate
Continuity
“-”
Legal formalities in business formation
Fluctuating share prices
Financial disclosure to public / inspection
Risk of takeover
Agency problems
Слайд 21Joint Venture
Two businesses working together on one project
Producing in one country
Producing different parts (automobile industry)
Not a merger, but can lead to one
Costs and risks are shared
Different strengths and experiences
Access to different markets whenever this is the case
Culture and management styles may be different
Potential conflicts over the errors
Failure of one business will put the joint venture at risk
Слайд 24Franchise
An arrangement whereby a business owner allows others to use its
E.g. McDonald’s, Body Shop, Pizza Hut, etc.
Styles of management and production provided by franchisor
Already recognized name
Some financial support
Profit is shared with franchisor
Less control
Слайд 26Summary
Sole Proprietorship
Partnership
General Partnership
Limited Partnership
Limited Liability Company
Corporation
Privately Limited Corporation
Publicly Limited Corporation
Joint Venture
Franchise
Which
Слайд 28Sources
Simpson, P. (2002) Business Studies AS level and A level, 3ed.,
Madura, J. (2001) Introduction to Business, 3ed., Thomson South-Western.
Kourilsky, M. (1995) “The New Youth Entrepreneur: Types of Business Ownership. Module 7.” Ewing Marion Kauffman Foundation, Kansas City, NJ
Jan Norman (2003) “For Small Businesses, LLC Option Offers Advantages, Disadvantages” Orange County Register, Santa Ana, CA.
Jan Norman (2005) “Liability, tax structure ownership”, OCRegister.com http://www.ocregister.com/ocregister/money/smallbusiness/qanda/article_466664.php
“Business Divorces and Who Gets Custody of Intellectual Property” (2002) Business North Carolina, 22(10), p.66
Lange, K (2002) “Spotlight on Limited Liability Companies” SCORE, www.score.org/leg_5