- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
What is RNA splicing презентация
Содержание
- 1. What is RNA splicing
- 2. Genetic information is transferred from genes to
- 3. Most genes have their protein-coding information interrupted
- 4. The intron is also present in the
- 5. Splicing a pre-mRNA involves two reactions pre-mRNA intron branchpoint A
- 6. Splicing occurs in a “spliceosome” an
- 7. RNA is produced in the nucleus of
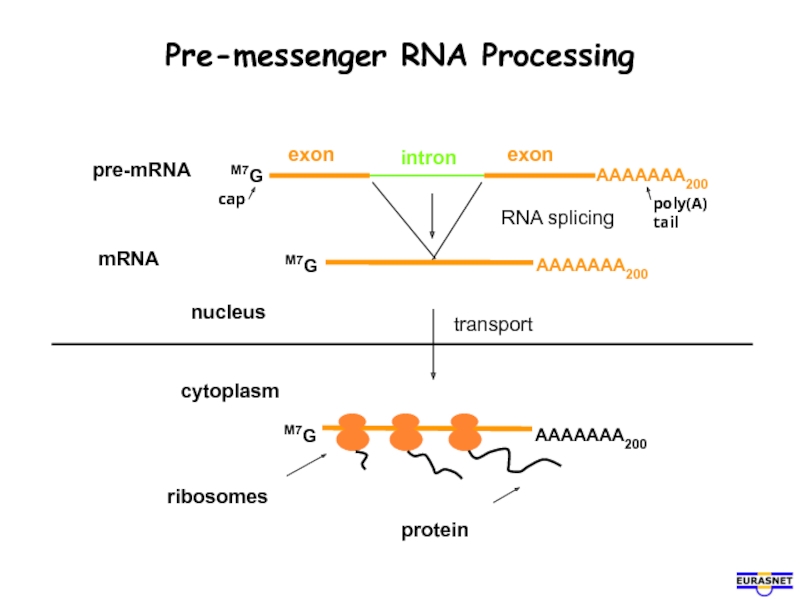
- 8. Pre-messenger RNA Processing cytoplasm nucleus cap poly(A) tail
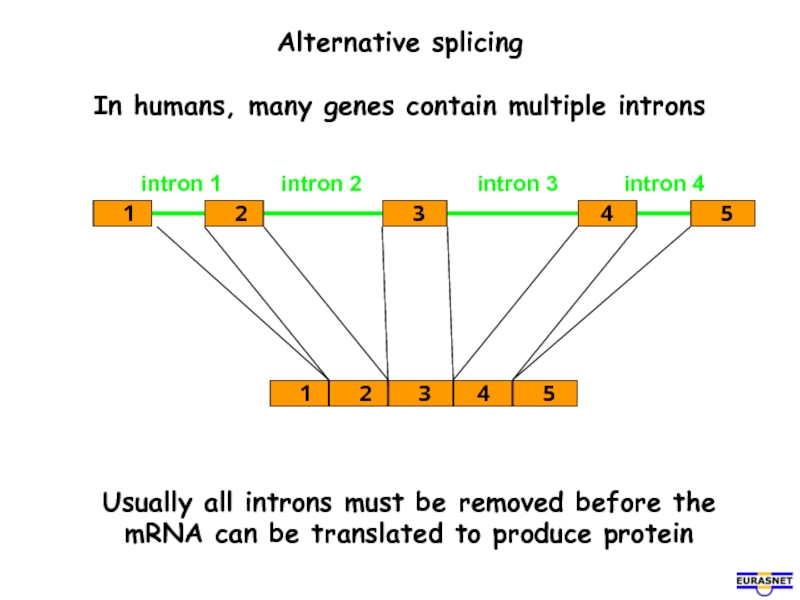
- 9. Alternative splicing In humans, many genes
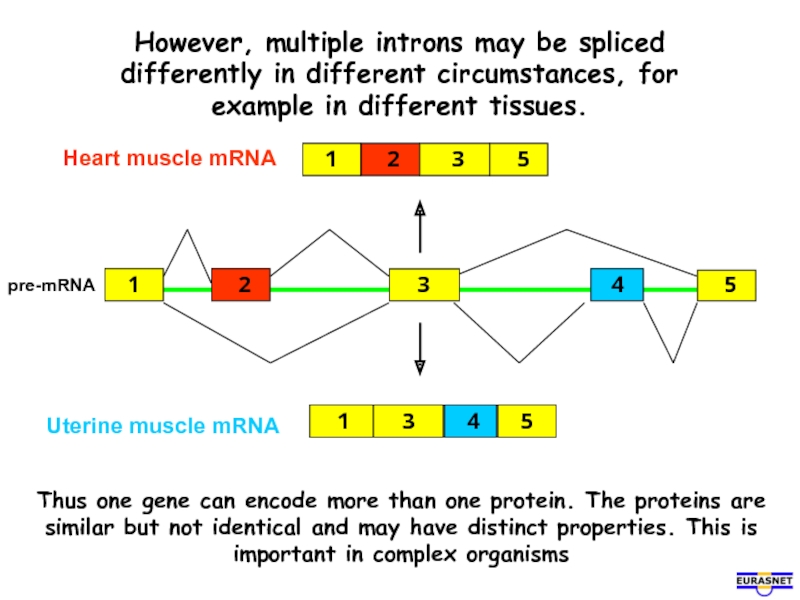
- 10. However, multiple introns may be spliced differently
- 11. Different signals in the pre-mRNA and different
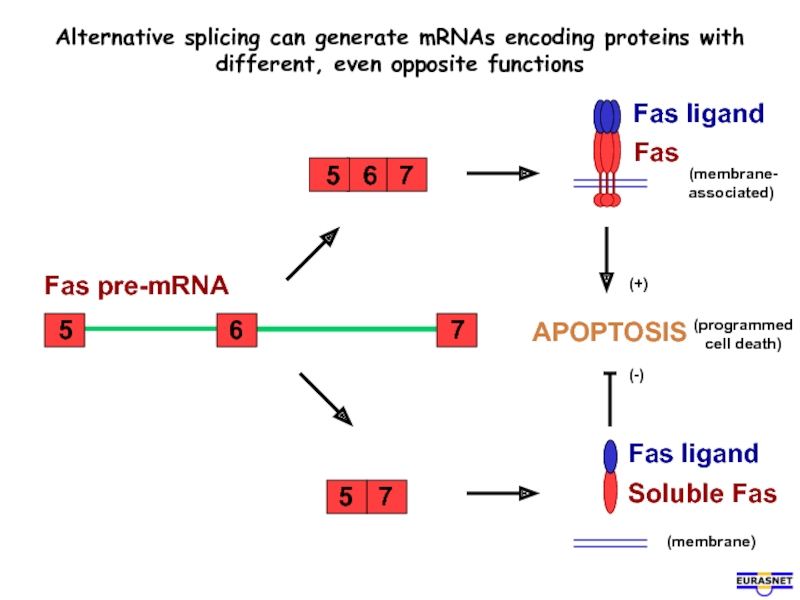
- 12. APOPTOSIS Alternative splicing can generate mRNAs
- 13. Alternative splicing can generate tens of thousands
- 14. Examples of the potential consequences of mutations
- 15. Pathologies resulting from aberrant splicing can be
- 16. Therefore, understanding the mechanism of RNA splicing
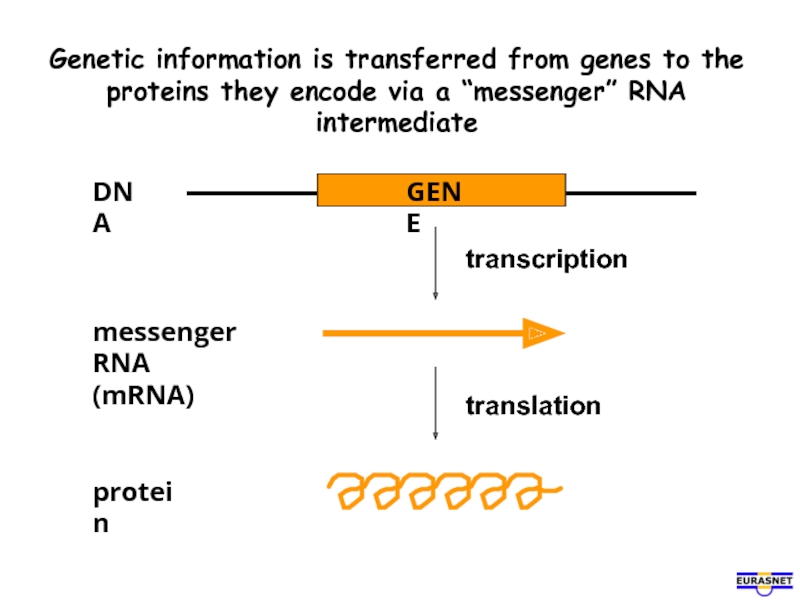
Слайд 2Genetic information is transferred from genes to the proteins they encode
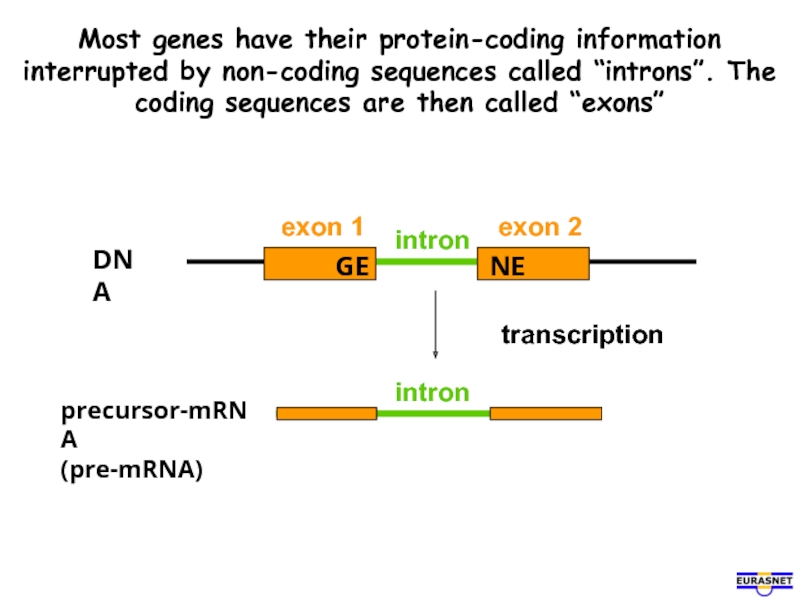
Слайд 3Most genes have their protein-coding information interrupted by non-coding sequences called
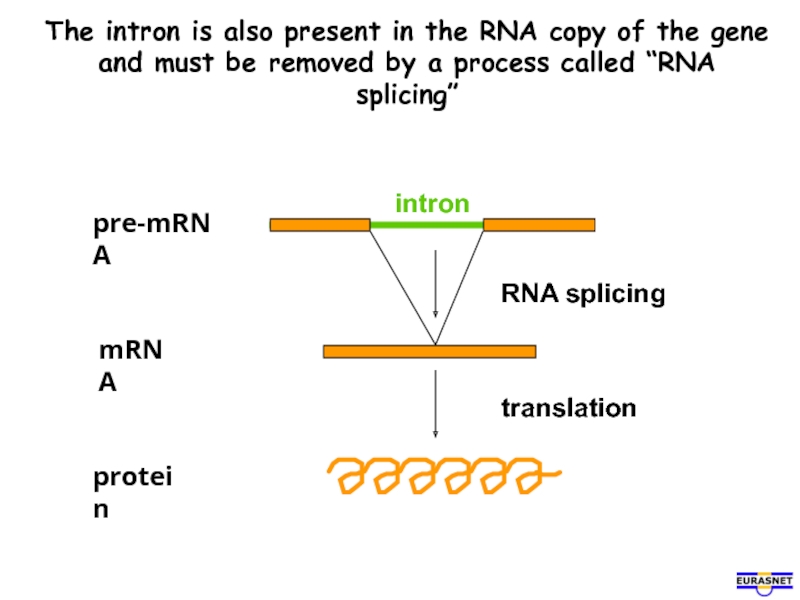
Слайд 4The intron is also present in the RNA copy of the
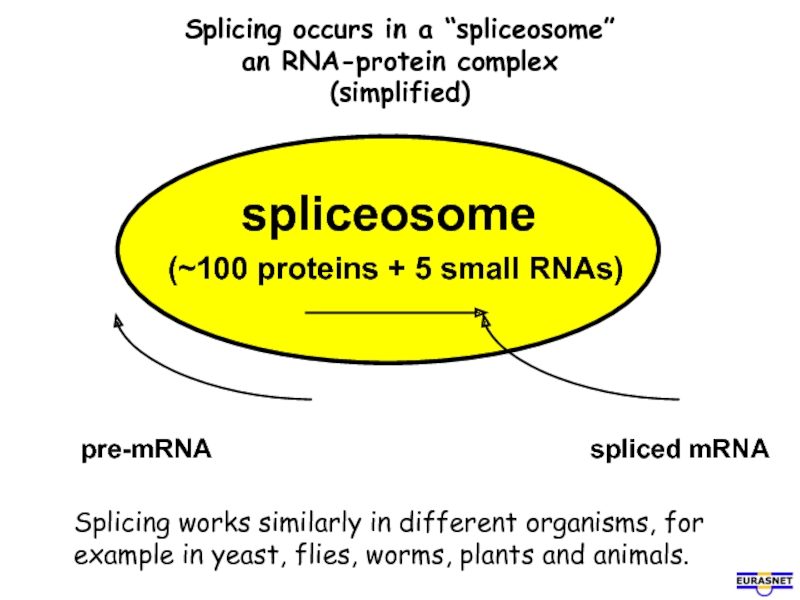
Слайд 6Splicing occurs in a “spliceosome”
an RNA-protein complex
(simplified)
spliceosome
(~100 proteins + 5
Splicing works similarly in different organisms, for example in yeast, flies, worms, plants and animals.
Слайд 7RNA is produced in the nucleus of the cell. The mRNA
Ribosomes are RNA-protein machines that make proteins, translating the coding information in the mRNA
Слайд 9Alternative splicing
In humans, many genes contain multiple introns
Usually all introns must
Слайд 10However, multiple introns may be spliced differently in different circumstances, for
Thus one gene can encode more than one protein. The proteins are similar but not identical and may have distinct properties. This is important in complex organisms
pre-mRNA
Слайд 11Different signals in the pre-mRNA and different proteins cause spliceosomes to
We are studying how mRNAs and proteins interact in order to understand how these machines work in general and, in particular, how RNA splicing is regulated as it affects which proteins are produced in each cell and tissue in the body.
Слайд 12APOPTOSIS
Alternative splicing can generate mRNAs encoding proteins with
different, even opposite functions
(programmed
cell
(+)
(-)
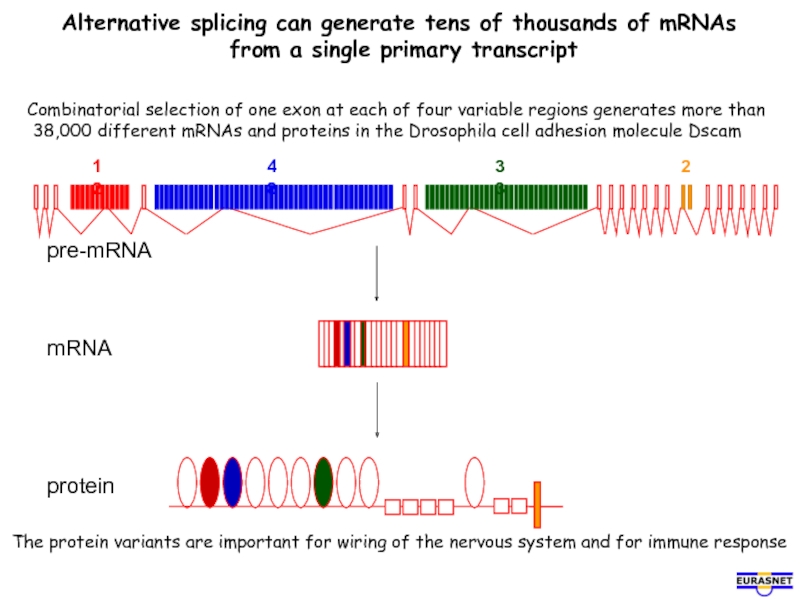
Слайд 13Alternative splicing can generate tens of thousands of mRNAs
from a
Combinatorial selection of one exon at each of four variable regions generates more than
38,000 different mRNAs and proteins in the Drosophila cell adhesion molecule Dscam
The protein variants are important for wiring of the nervous system and for immune response
protein
mRNA
pre-mRNA
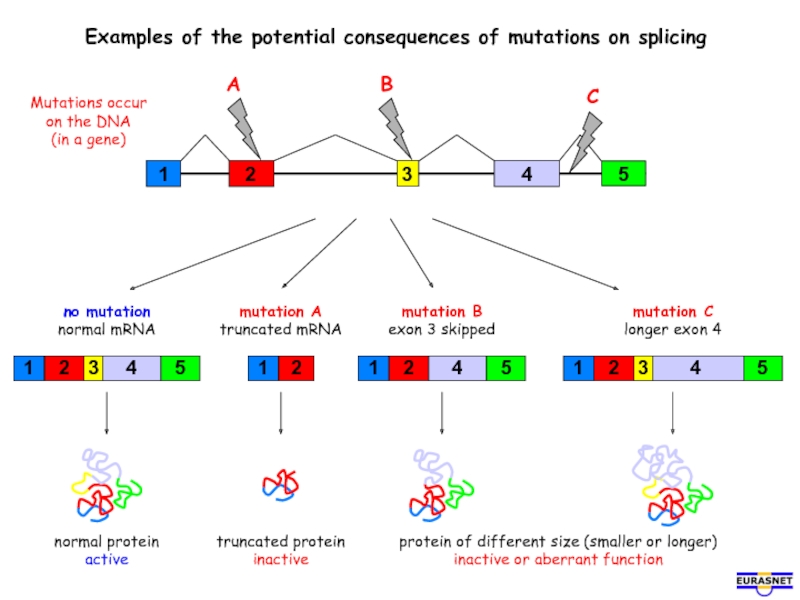
Слайд 14Examples of the potential consequences of mutations on splicing
Mutations occur
on
(in a gene)
mutation A
truncated mRNA
mutation B
exon 3 skipped
mutation C
longer exon 4
no mutation
normal mRNA
normal protein
active
truncated protein
inactive
protein of different size (smaller or longer)
inactive or aberrant function
Слайд 15Pathologies resulting from aberrant splicing can be grouped in two major
Mutations affecting proteins that are involved in splicing
Examples: Spinal Muscular Atrophy
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Myotonic Dystrophy
Mutations affecting a specific messenger RNA and disturbing its normal splicing pattern
Examples: ß-Thalassemia
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Cystic Fibrosis
Frasier Syndrome
Frontotemporal Dementia and Parkinsonism