- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
The First Three Weeks of Human Embryogenesis презентация
Содержание
- 1. The First Three Weeks of Human Embryogenesis
- 2. Week 1 1. Fertilization – is the
- 3. Week 1 Zygote – 1 cell embryo
- 4. zygote Fertilization zygote
- 5. At the end of cleavage blastula is
- 6. Embryoblast At the 7-th day
- 7. Week 2: Beginning of 3.
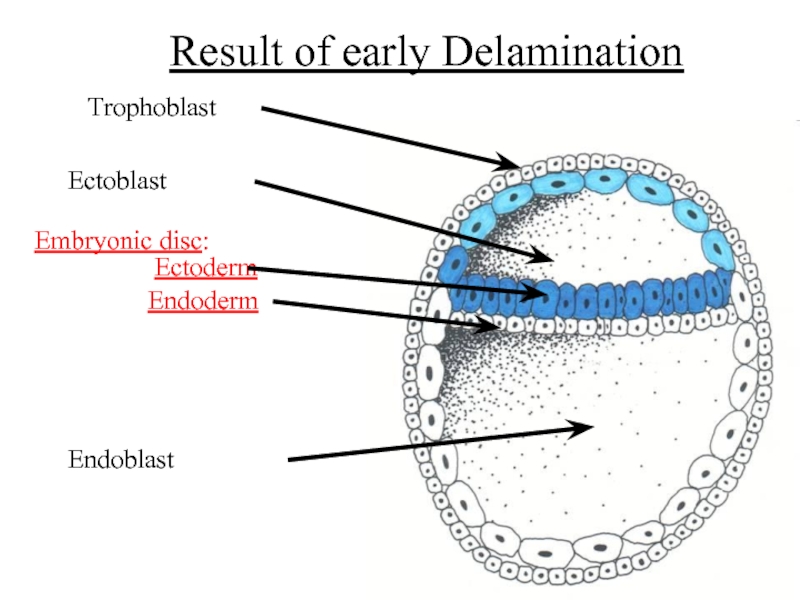
- 8. Result of early Delamination Embryonic disc:
- 9. Late gastrulation – formation of mesoderm –
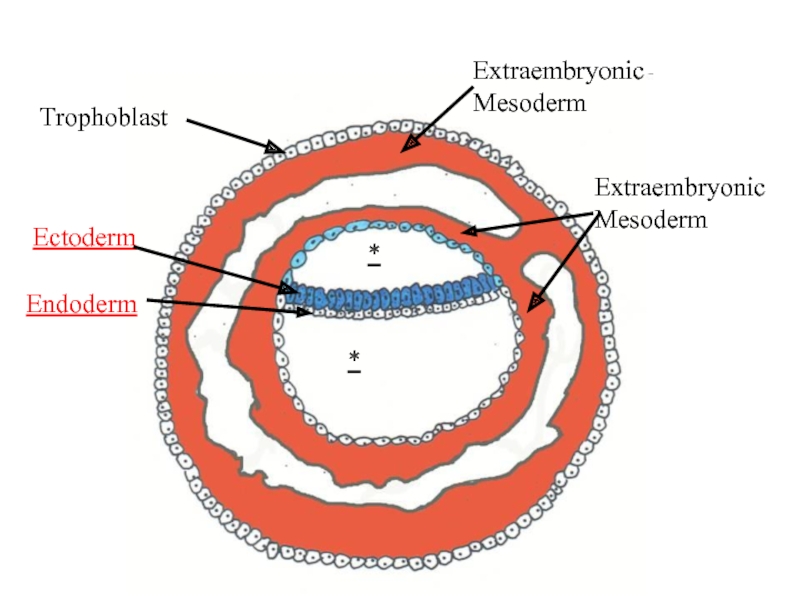
- 10. 1-st appear extraembryonic mesoderm: it
- 11. Trophoblast Extraembryonic Mesoderm * Ectoderm Endoderm Extraembryonic Mesoderm *
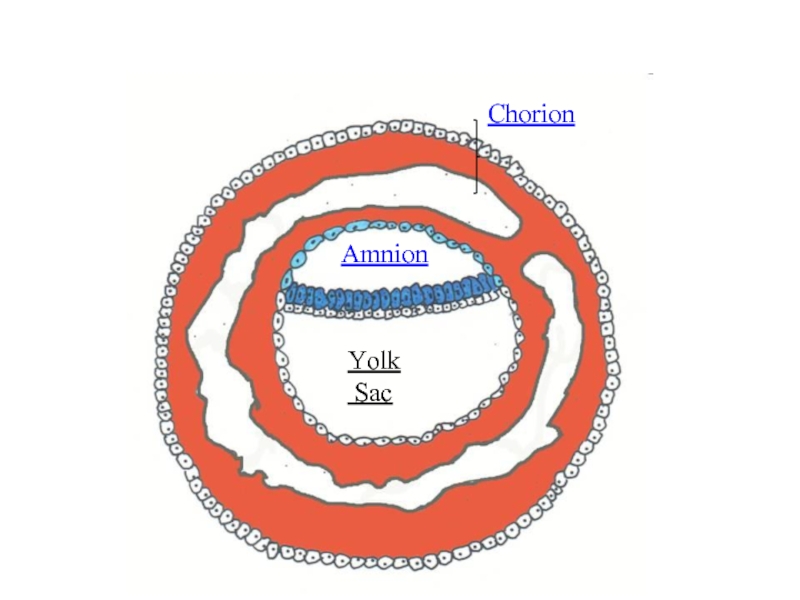
- 12. As a result appear so-called extraembryonic organs - amnion, yolk sac and chorion
- 13. Chorion Amnion Yolk Sac
- 14. Migration of cells within the
- 15. Migration of cells within embryonic disc leads
- 16. Transverse section Ectoderm Endoderm Amniotic Cavity
- 17. In front of primitive
- 18. ectoderm endoderm mesoderm Notochord appears by the
- 19. 3-2.(next step): Development of the Neural
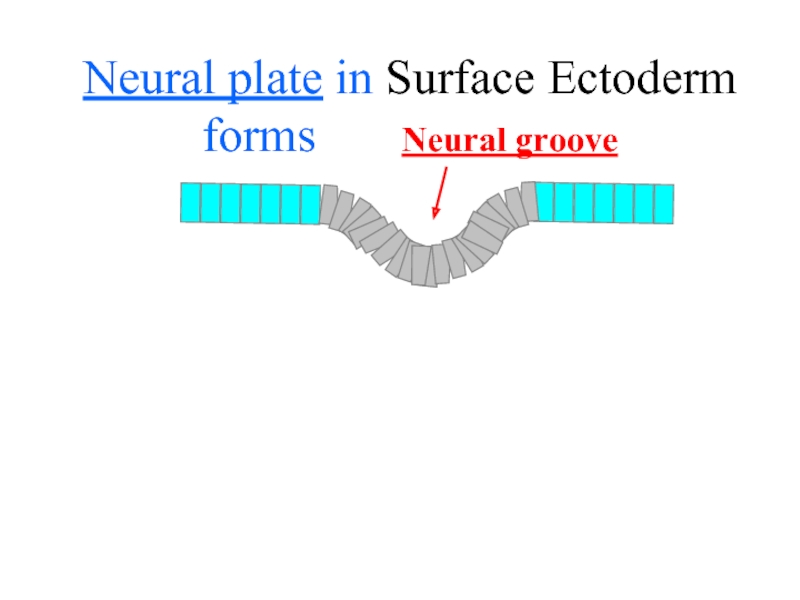
- 20. Neural plate in Surface Ectoderm forms Neural groove
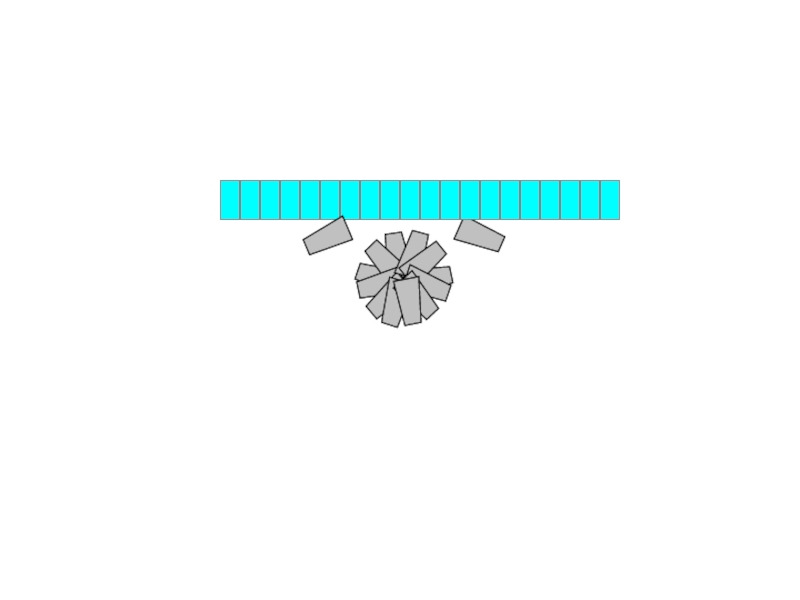
- 21. Then - Neural Tube
- 23. Development of the Neural Tube Surface Ectoderm Neural Crest Neural Tube
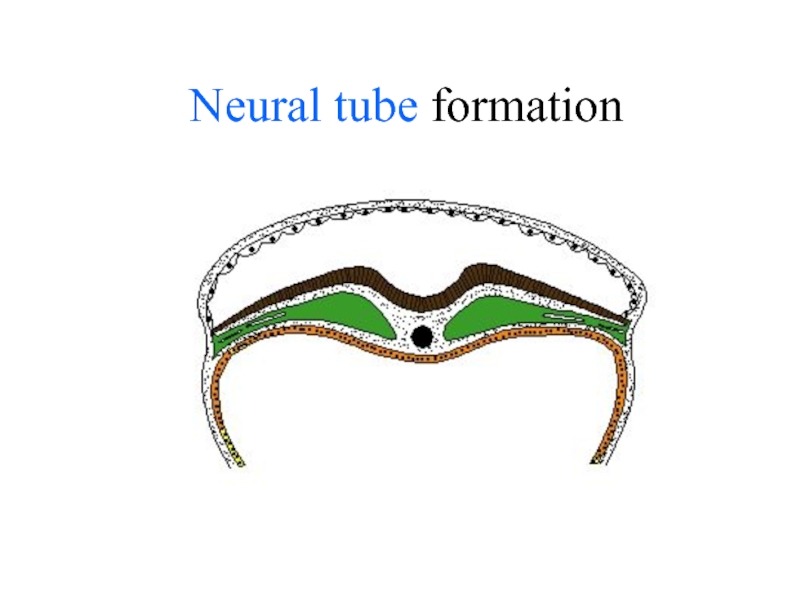
- 24. Neural tube formation
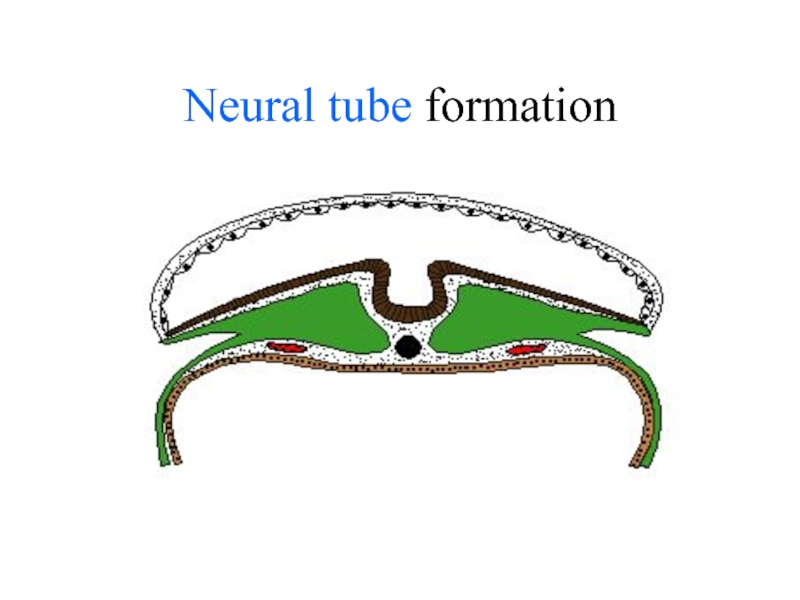
- 25. Neural tube formation
- 26. Gastrulation is finished with the formation
- 27. 4. Formation of the embryo
- 28. Body flexion
- 29. Differentiation of GERM LAYERS: 1.
- 30. Surface Ectoderm differentiates to epithelium of
- 31. Neural tube (neuroectoderm) --- brain, spinal cord,
- 32. Endoderm differentiates to epithelium of stomach, intestine, liver, pancreas, respiratory system
- 33. Mesoderm Notochord Endoderm Ectoderm Yolk Sac Amniotic
- 34. Mesoderm Nephrotome urogenital system including kydneys,
- 35. Late embryonic stages Histogenesis Organogenesis
- 36. Summary: Week 1-3: Early Stages: 1.
Слайд 2Week 1
1. Fertilization – is the fusion of the sperm and
(in the uterine tube) :
- distant phase – sperms find ovum;
- contact phase – 1 sperm fertilizes ovum.
Слайд 3Week 1
Zygote – 1 cell embryo – starts to divide:
2. Cleavage
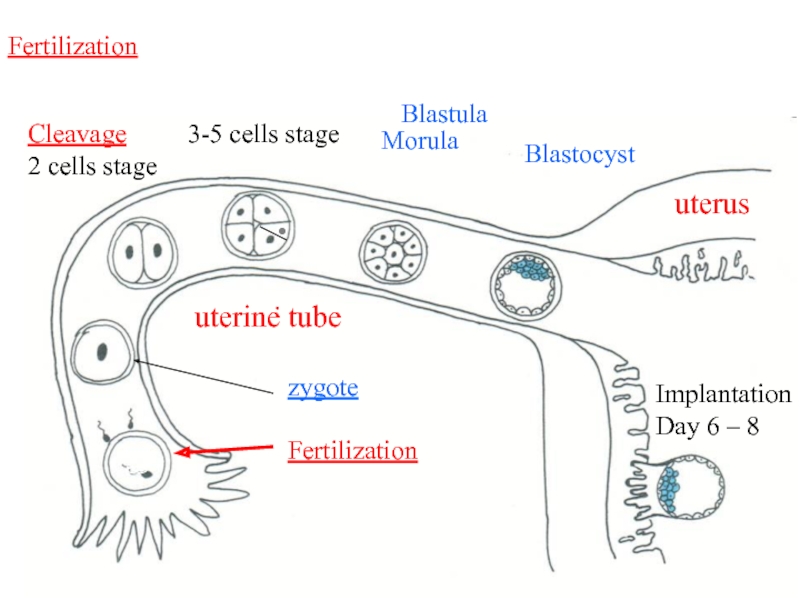
Слайд 4zygote
Fertilization
zygote
Fertilization
Cleavage
2 cells stage
3-5 cells stage
Morula
Blastocyst
Implantation
Day 6 – 8
uterus
uterine
.
.
Blastula
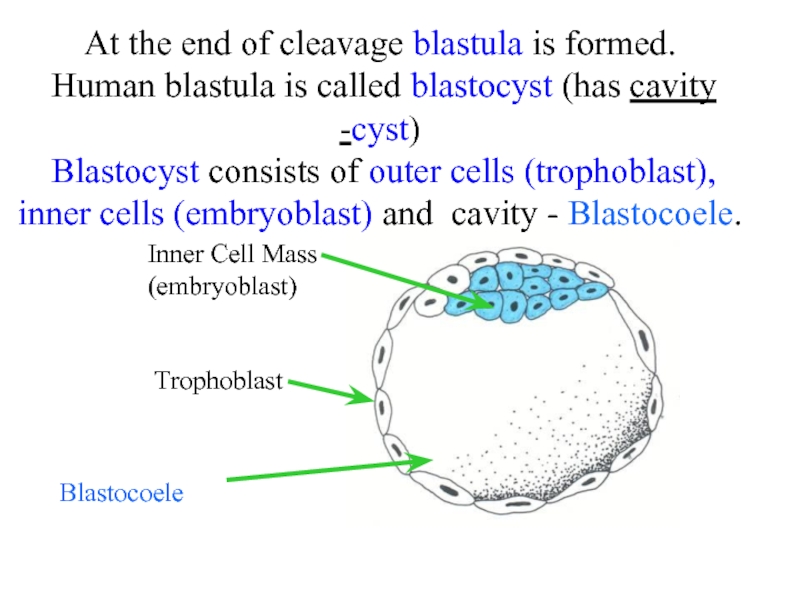
Слайд 5At the end of cleavage blastula is formed. Human blastula
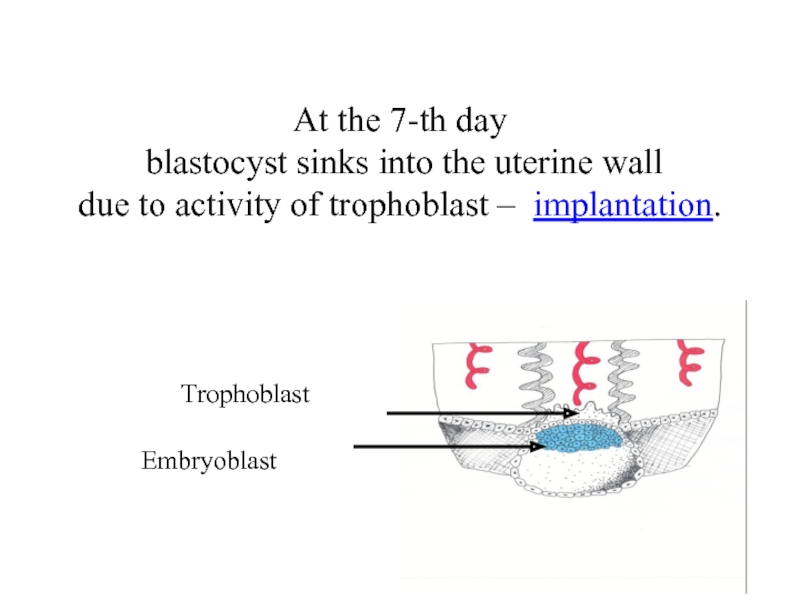
Слайд 6Embryoblast
At the 7-th day
blastocyst sinks into the uterine wall
Trophoblast
Слайд 7Week 2: Beginning of 3. Gastrulation – formation of 3 germ
Слайд 9Late gastrulation – formation of mesoderm – 3-d germ layer –
Слайд 101-st appear extraembryonic mesoderm: it surrounds upper and lower sacs, and underly
Слайд 14
Migration of cells within the embryonic disc leads to formation of
embryonic mesoderm
and axial organs
(neural tube, notochord and somites)
Слайд 15Migration of cells within embryonic disc leads to formation of temporal
It is a primitive streak.
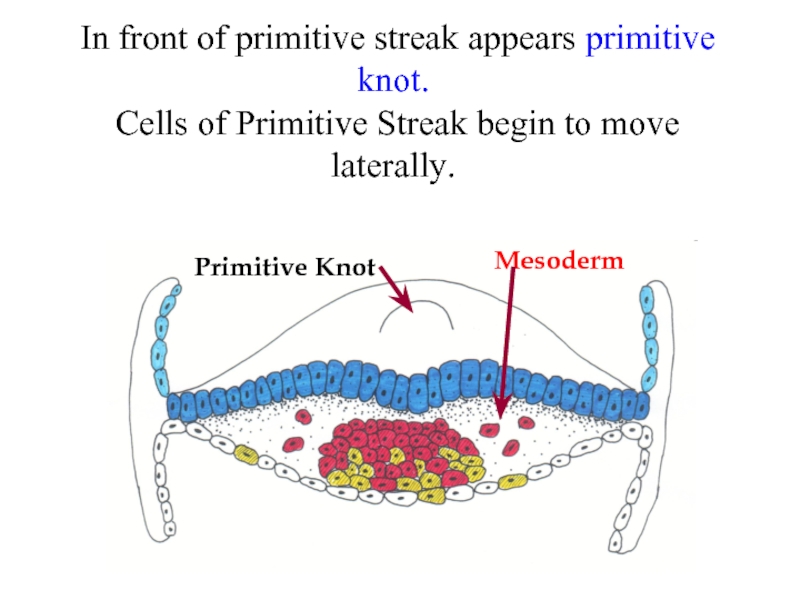
Слайд 17 In front of primitive streak appears primitive knot. Cells of
Primitive Knot
Mesoderm
Слайд 18ectoderm
endoderm
mesoderm
Notochord appears by the primitive knot invagination. Mesoderm appears by migration
notochord
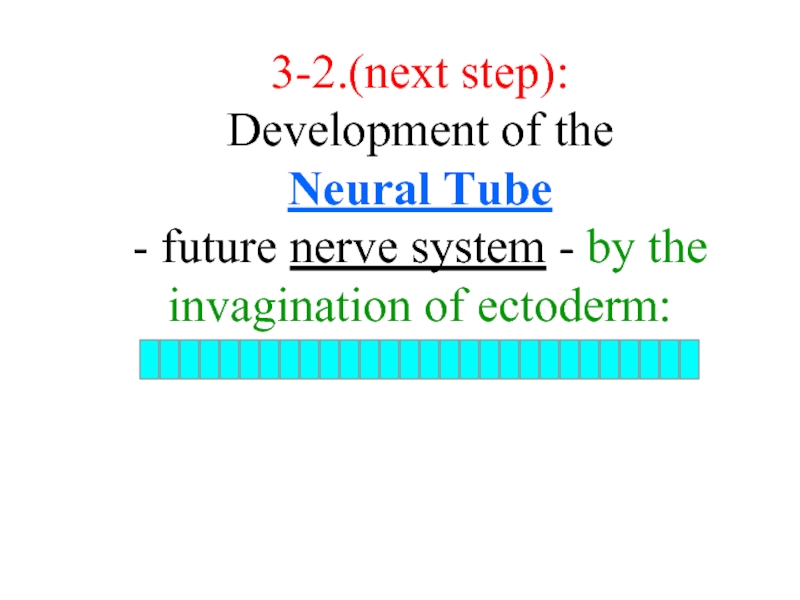
Слайд 193-2.(next step): Development of the Neural Tube - future nerve system - by
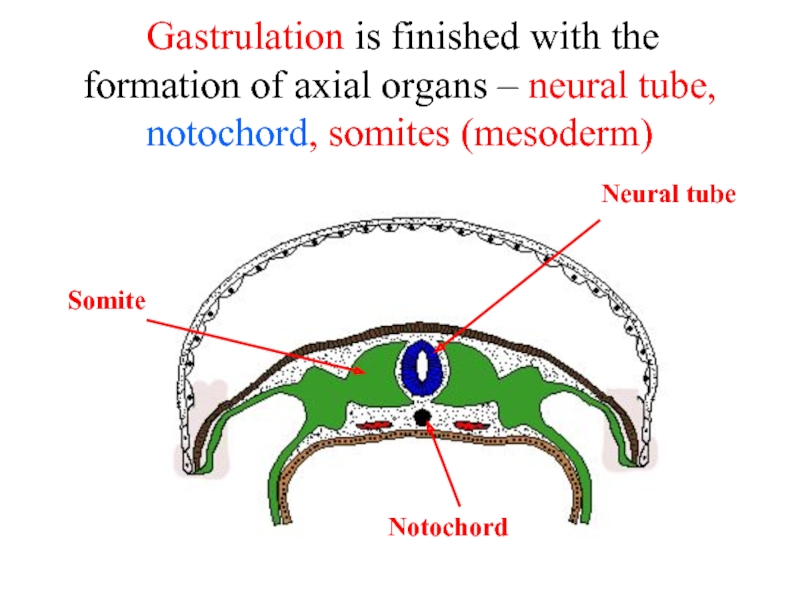
Слайд 26 Gastrulation is finished with the formation of axial organs –
Somite
Notochord
Neural tube
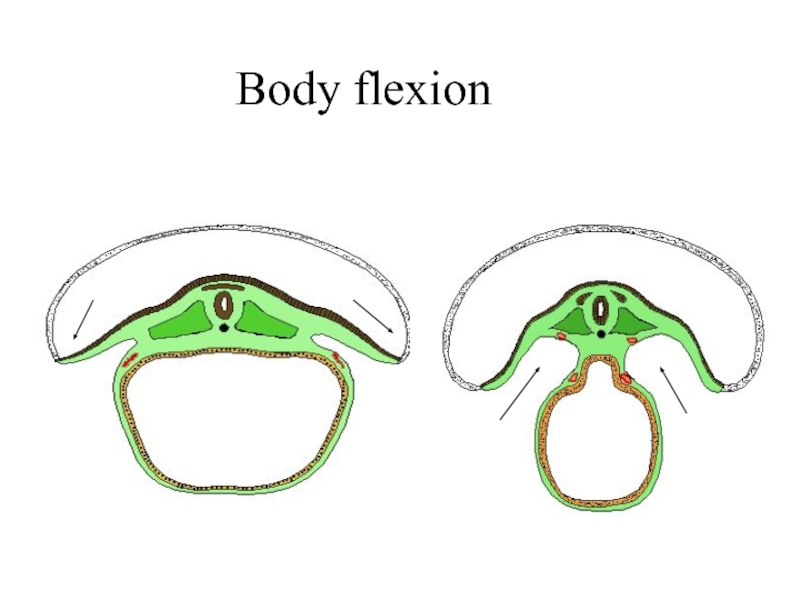
Слайд 27
4. Formation of the embryo body
(20-th day) by:
- body flexion,
- head and tail folds formation.
Result: separation of embryonic organs from extra-embryonic organs
Слайд 29Differentiation of GERM LAYERS:
1. Differentiation of Ectoderm
B. Neural Tube
2. Differentiation of Endoderm
A. G.I. Tract
B. Respiratory Tree
C. Endocrine glands
3. Differentiation of Mesoderm
A. Somites (have 3 part - dermatome, myotome, sclerotome)
B. Intermediate mesoderm - nephrotome
C. Lateral mesoderm -splanchnotome
D. Mesenchyme
Слайд 30Surface Ectoderm differentiates to
epithelium of skin, and its derivatives,
oral
rectal epithelium,
outer corneal epithelium, tooth enamel
Differentiation of GERM LAYERS:
Слайд 31Neural tube (neuroectoderm) --- brain, spinal cord, and the retina Neural crests ---
Слайд 32 Endoderm differentiates to epithelium of stomach, intestine, liver, pancreas, respiratory
Слайд 33Mesoderm
Notochord
Endoderm
Ectoderm
Yolk Sac
Amniotic Cavity
Somite
Intermediate mesoderm
(nephrotome)
Lateral plate mesoderm
(somatopleuric,
splanchnopleuric
mesoderm)
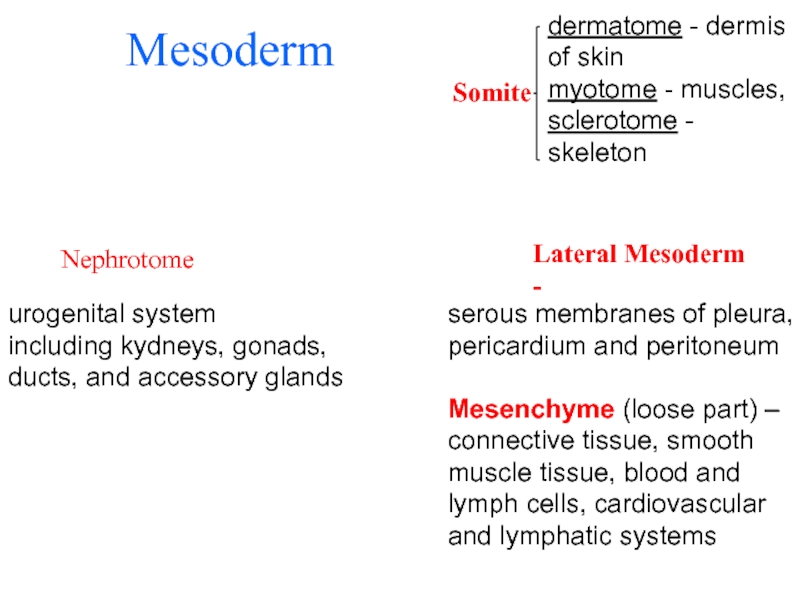
Слайд 34Mesoderm
Nephrotome
urogenital system
including kydneys, gonads,
ducts, and accessory glands
dermatome - dermis of skin
myotome - muscles,
sclerotome - skeleton
Lateral Mesoderm -
serous membranes of pleura, pericardium and peritoneum
Mesenchyme (loose part) –
connective tissue, smooth muscle tissue, blood and lymph cells, cardiovascular and lymphatic systems
Слайд 36Summary:
Week 1-3:
Early Stages:
1. Fertilization – Zygote formation
2. Cleavage – Blastocyst
3. Gastrulation – Germ layers formation
Axial organs formation
4. Formation of the embryo body
Late stages:
Histogenesis, Organogenesis – next lectures