- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Specimen Preparation for SEM investigation презентация
Содержание
- 1. Specimen Preparation for SEM investigation
- 2. Presentation program Aim of SEM investigation
- 3. Aim of SEM investigation Materials are investigated
- 4. Analytical SEM JEOL JSM-6610A
- 5. Low vacuum SEM JSM- 5800LV
- 6. Types of specimens for SEM investigation
- 7. Metalic specimens For current conductive metalic specimens
- 8. Specimens from polymers and composites Polymer
- 9. Biological specimens Living cells, biological tissue, and
- 10. Biological specimens Biological specimens must be:
- 11. Flower petals sprinkled by gold
- 12. Samples of powder sputerred by gold
- 13. Biological specimens covered by gold
- 14. Specimen size Specime sizes are limited by
- 15. Specimens embeding Specimens are embeded at epoxy
- 16. Specimen embeding „Cold embeding” is suitable for
- 17. Electrical current conductivity Specimens analyzed by
- 18. Specimen preparation Cutting, to obtain dimensions limited
- 19. Specimen preparation Grinding, by using special waterproof fine grain grinding papers.
- 20. Specimen preparation Mechanical polishing by using special
- 21. Specimen preparation Etching is the last operation
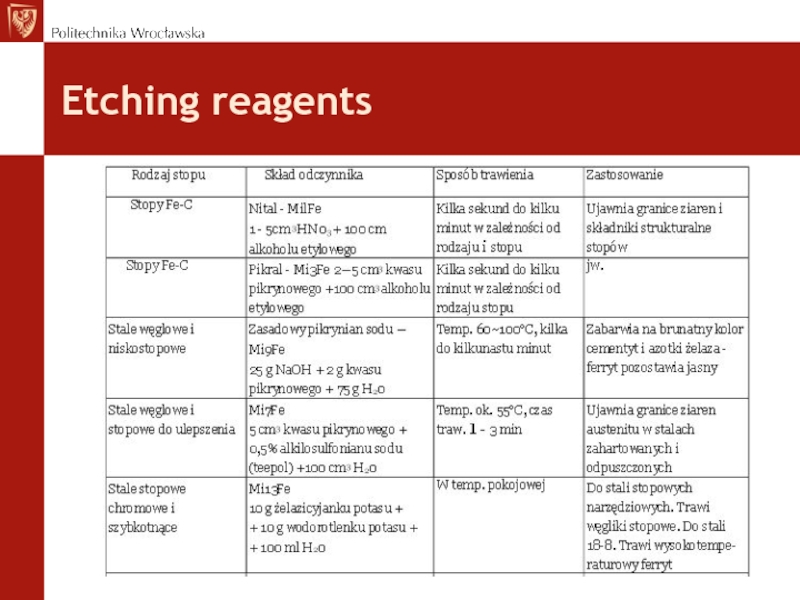
- 22. Etching reagents
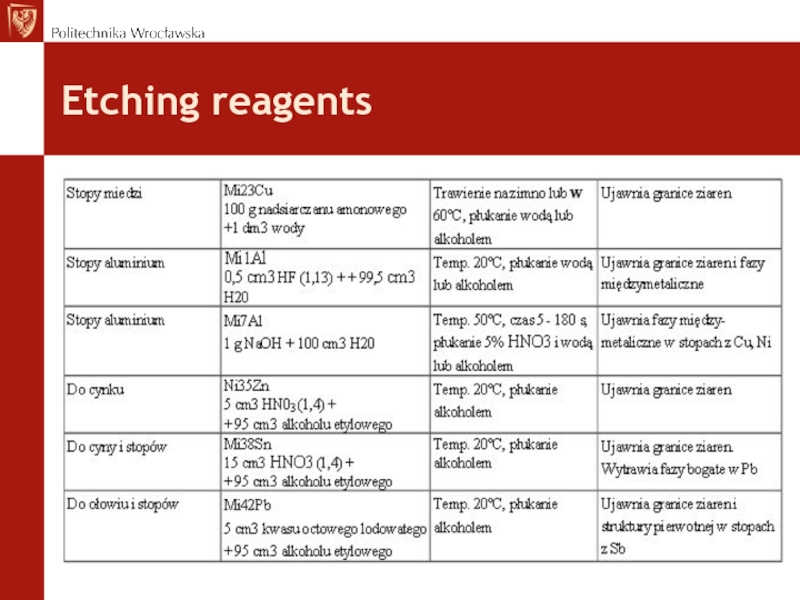
- 23. Etching reagents
- 24. Cross Section Polisher SM-09010 Cross Section
- 25. Cross Section Polisher SM-09010 Principle of operation .
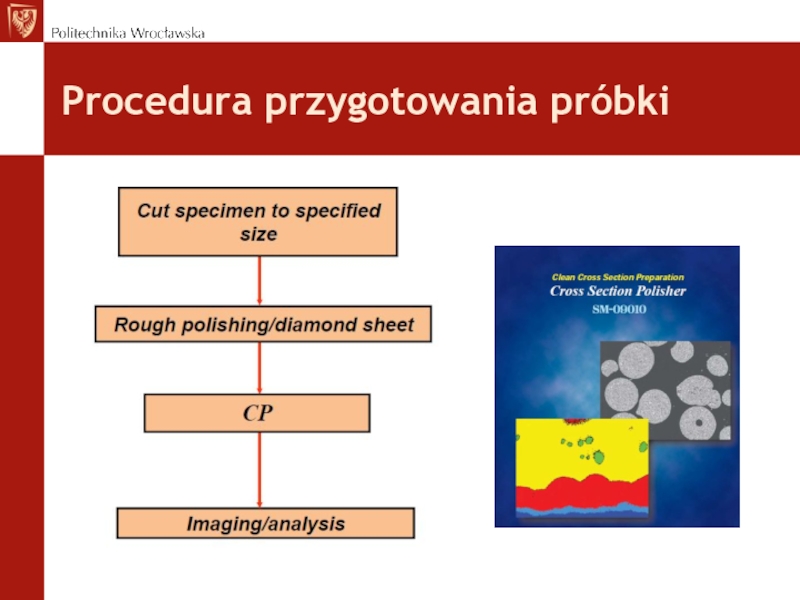
- 26. Procedura przygotowania próbki
- 27. Specimens cutting Saw equipment for sample precission cutting
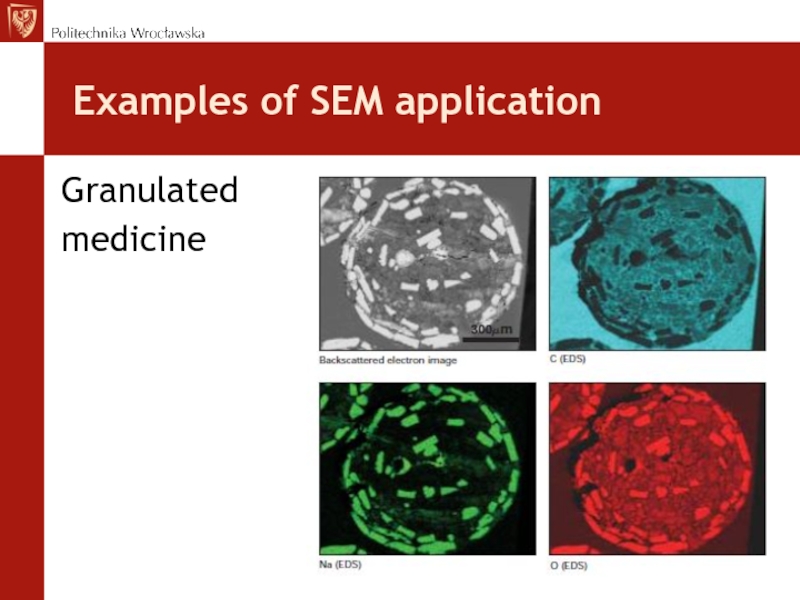
- 28. Examples of SEM application Granulated medicine
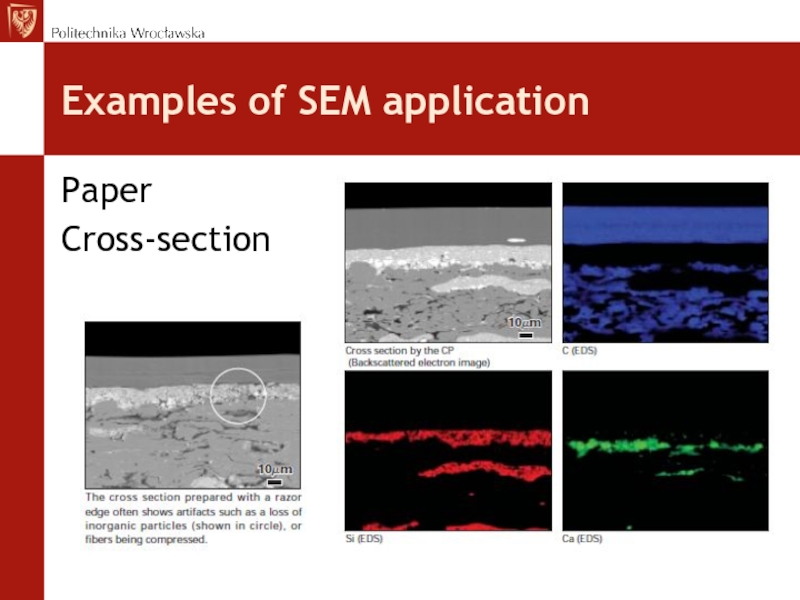
- 29. Examples of SEM application Paper Cross-section
- 30. Evaporisation / sputerring Is realised for covering
- 31. Evaporation
- 32. Cathode sputtering
- 33. Specimen fixation
- 34. Specimen fixation
- 35. Specimen fixed to the holder
- 36. Specimens inside the holder
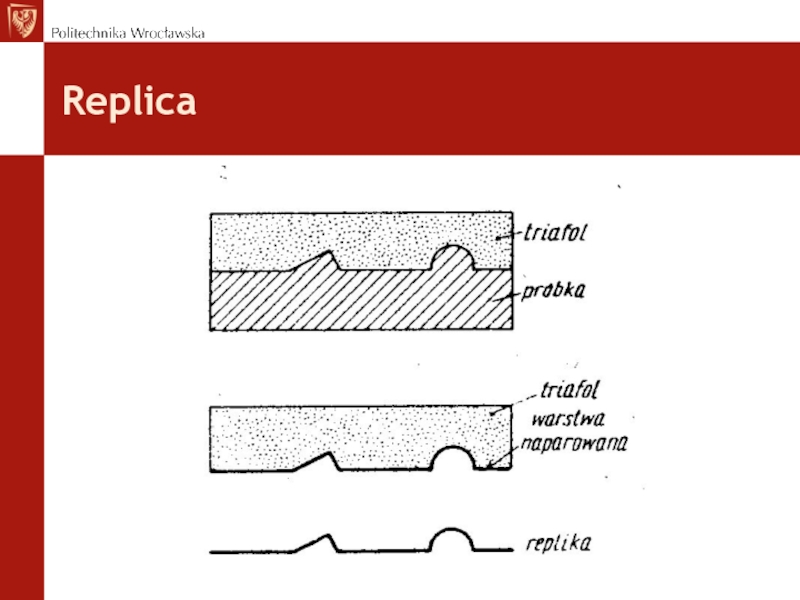
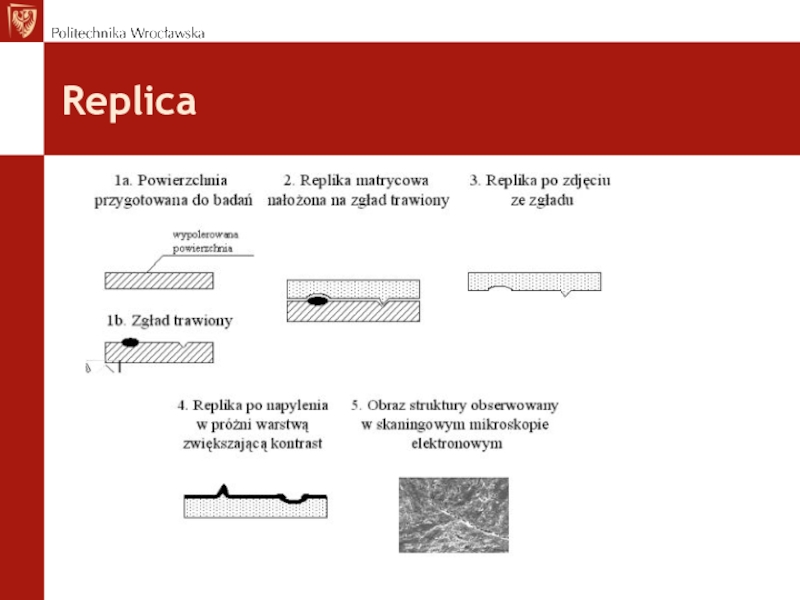
- 37. Replica The aim is to obtain direct
- 38. Replica
- 39. Replica
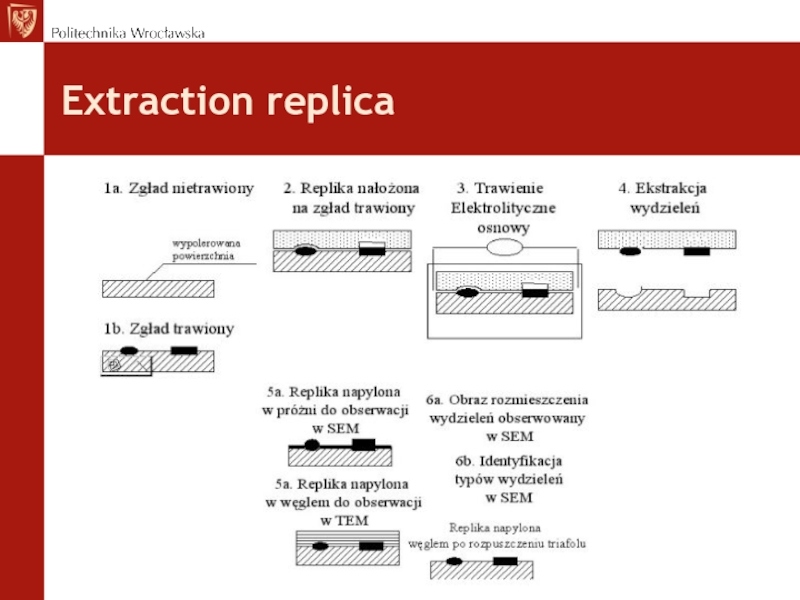
- 40. Extraction replica
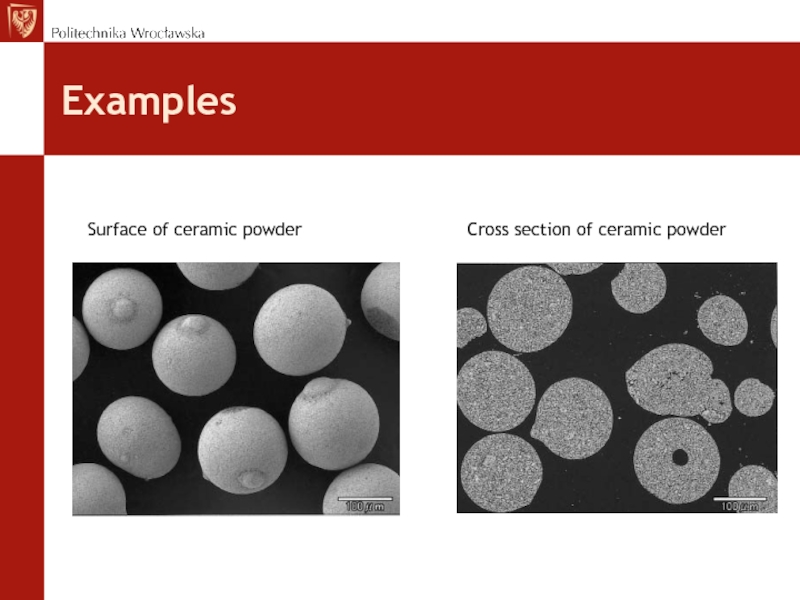
- 41. Examples Surface
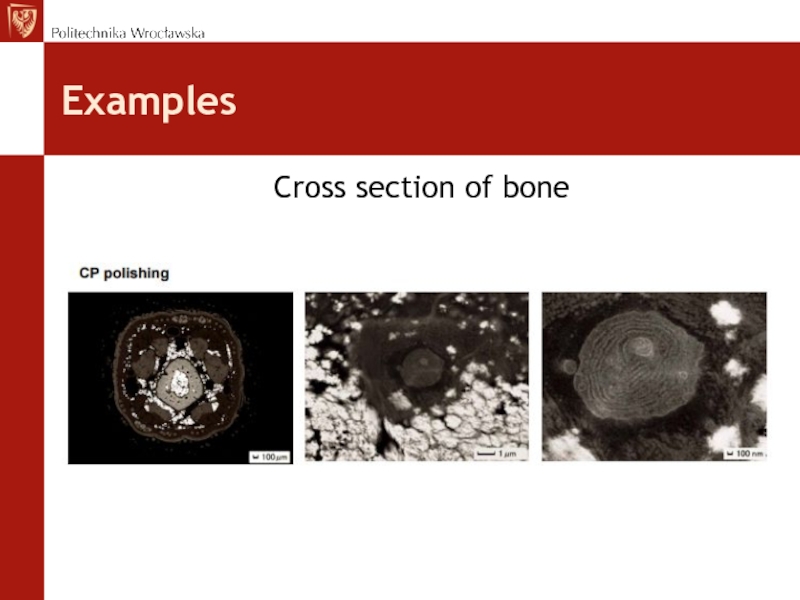
- 42. Examples Cross section of bone
- 43. Pollen of flowers
- 44. Part of insect head
- 45. Brittle fracture
- 46. Composite
Слайд 2Presentation program
Aim of SEM investigation
Investigated materials
Condition for specimens
Preparation
Specimen fixation
Replica
Examples
Слайд 3Aim of SEM investigation
Materials are investigated for:
Mikrostructure determination (SE, BSE, AE,
EBSD – Electron Beam Selected Diffraction)
Chemical composition: (EDS, BSE,AE)
Chemical composition: (EDS, BSE,AE)
Слайд 6Types of specimens for SEM investigation
Four types of specimens:
1. Metalic
2. Polymer
3.
Biological
4. Geological
4. Geological
Слайд 7Metalic specimens
For current conductive metalic specimens any additional preparation is not
necessary.
They can be investigated like specimens for macro or metallography research.
Specimen can be at polished or tobe at etched state.
It is only necessary to fix
the specimen with appropriate
holder.
They can be investigated like specimens for macro or metallography research.
Specimen can be at polished or tobe at etched state.
It is only necessary to fix
the specimen with appropriate
holder.
Слайд 8Specimens from polymers and composites
Polymer specimens must be sputtered by the
layer of current conductive elements like: C, Au, Pt, Cu.
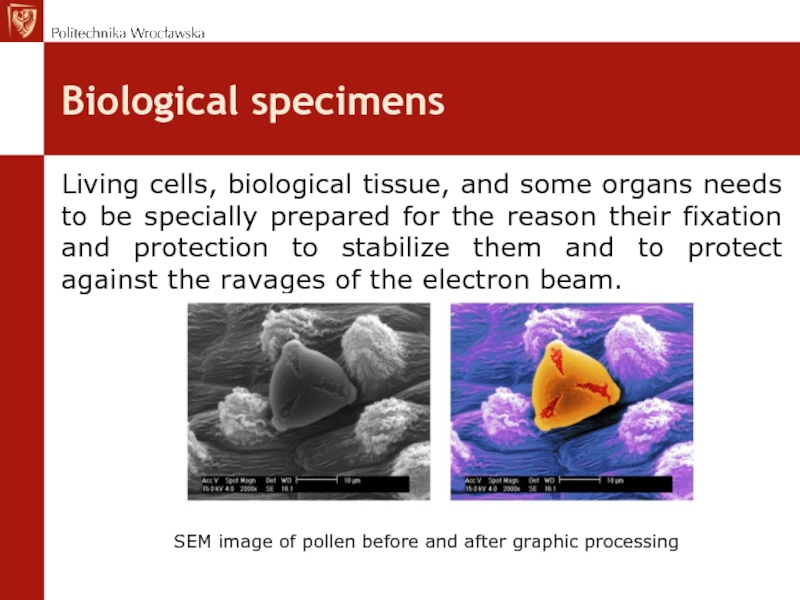
Слайд 9Biological specimens
Living cells, biological tissue, and some organs needs to be
specially prepared for the reason their fixation and protection to stabilize them and to protect against the ravages of the electron beam.
SEM image of pollen before and after graphic processing
Слайд 10Biological specimens
Biological specimens must be:
Dried, because inside the SEM chamber the
material will be in the vacuum and therefore can not be inserted preparations hydrated.
Sputered by current conductive material. Carbon is the best.
Sputered by current conductive material. Carbon is the best.
Слайд 14Specimen size
Specime sizes are limited by dimensions of SEM support table.
Typical values are:
- Diameter below 5cm,
- Highest below 2,5cm.
Typical dimensions are: 10 x 10 x 5 mm.
- Diameter below 5cm,
- Highest below 2,5cm.
Typical dimensions are: 10 x 10 x 5 mm.
Слайд 15Specimens embeding
Specimens are embeded at epoxy resin for the reason of
better mounting and correction of specimen quality.
Before mounting specimens must be cleaned, free of dust, grease and any impurities.
Two techniques can be applied:
Hot embeding under the pressure,
Cold embeding.
Before mounting specimens must be cleaned, free of dust, grease and any impurities.
Two techniques can be applied:
Hot embeding under the pressure,
Cold embeding.
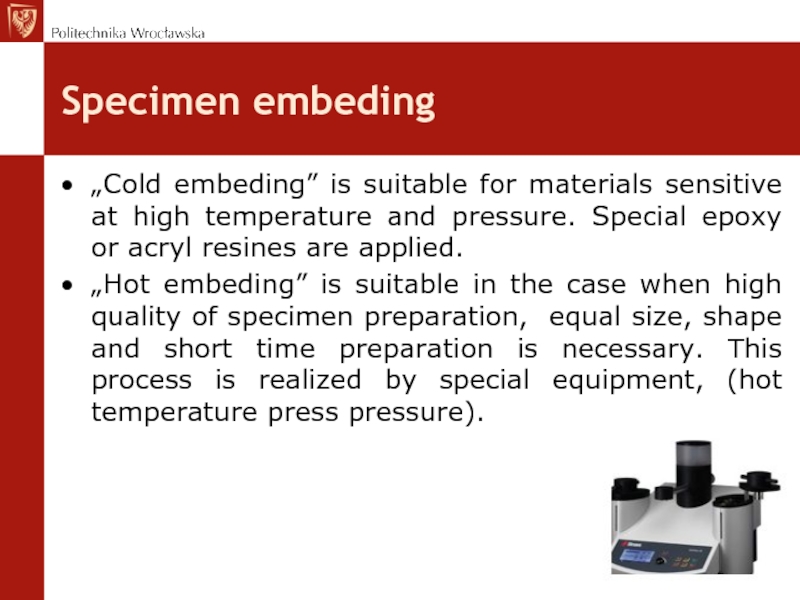
Слайд 16Specimen embeding
„Cold embeding” is suitable for materials sensitive at high temperature
and pressure. Special epoxy or acryl resines are applied.
„Hot embeding” is suitable in the case when high quality of specimen preparation, equal size, shape and short time preparation is necessary. This process is realized by special equipment, (hot temperature press pressure).
„Hot embeding” is suitable in the case when high quality of specimen preparation, equal size, shape and short time preparation is necessary. This process is realized by special equipment, (hot temperature press pressure).
Слайд 17Electrical current conductivity
Specimens analyzed by SEM methods must conduct electrical current.
If specimen doesn’t conduct electrical current, then must be covered by the layer of Au, Pt, C or Cu.
Such prepared specimens can be investigated at high or low vacuum.
Слайд 18Specimen preparation
Cutting, to obtain dimensions limited by support table disposed inside
specimen chamber
Cleaning and degreasing of specimen surfaces
Grinding
Polishing
Etching
Cleaning and degreasing of specimen surfaces
Grinding
Polishing
Etching
Слайд 20Specimen preparation
Mechanical polishing by using special velvet tissue immersed by diamant
paste or water suspension of Al2O3. Any traces of scratches must be eliminated. Specimen surface must be brillant.
Слайд 21Specimen preparation
Etching is the last operation necessary for microstructure visualisation. It
is realised by application chemical reagent on the surface of polished specimen.
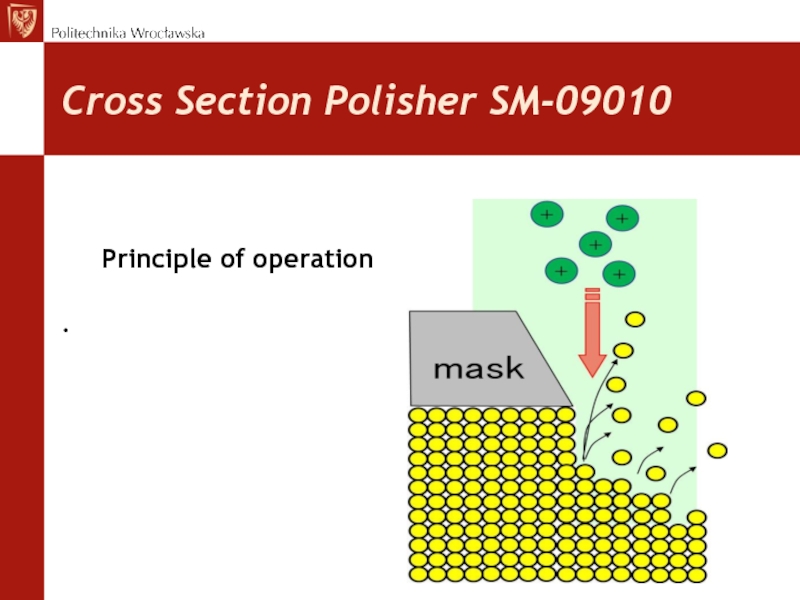
Слайд 24Cross Section Polisher SM-09010
Cross Section Polisher,
makes cross section
perpendicullar to
the
specimen surface. It is suitable for investigation
of multilayer structures.
specimen surface. It is suitable for investigation
of multilayer structures.
Слайд 30Evaporisation / sputerring
Is realised for covering
the surface specimen
by C, Au, Pt
or Cu
at high vacuum
using special equipment.
at high vacuum
using special equipment.
Слайд 37Replica
The aim is to obtain direct microstructure of construction elements without
their cutting or destruction.
Advantages:
Non destructive method (without decrising the strength of investigated elements).
Disadvantages:
The abbility to study only the outer surface layer (cannot be representative for whole volume / thickness of investigated material).
Advantages:
Non destructive method (without decrising the strength of investigated elements).
Disadvantages:
The abbility to study only the outer surface layer (cannot be representative for whole volume / thickness of investigated material).