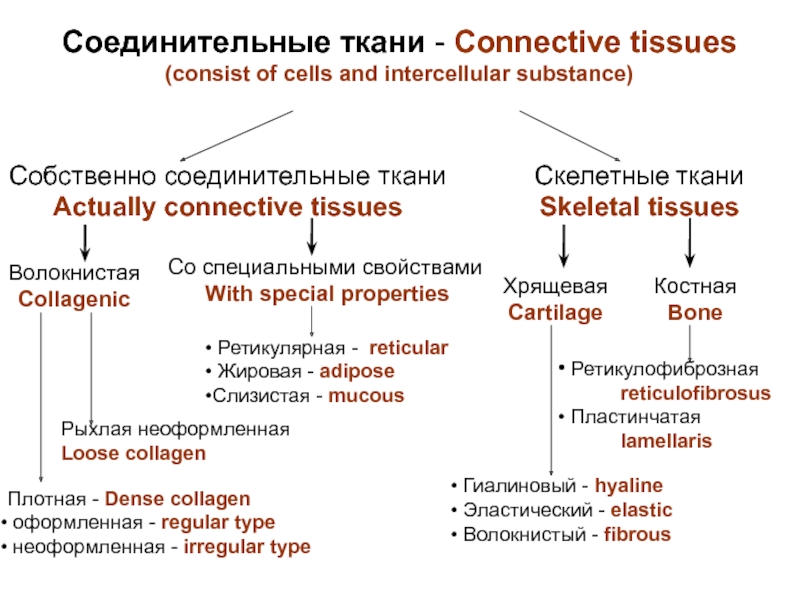
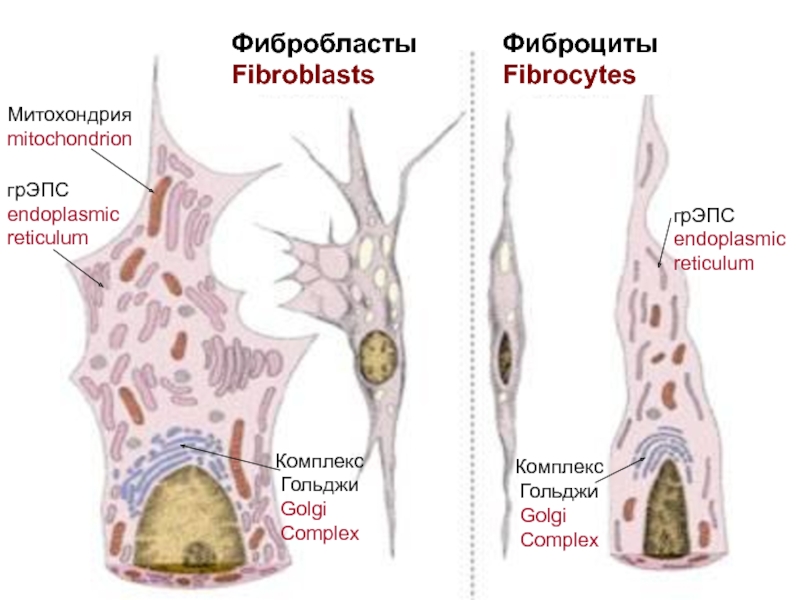
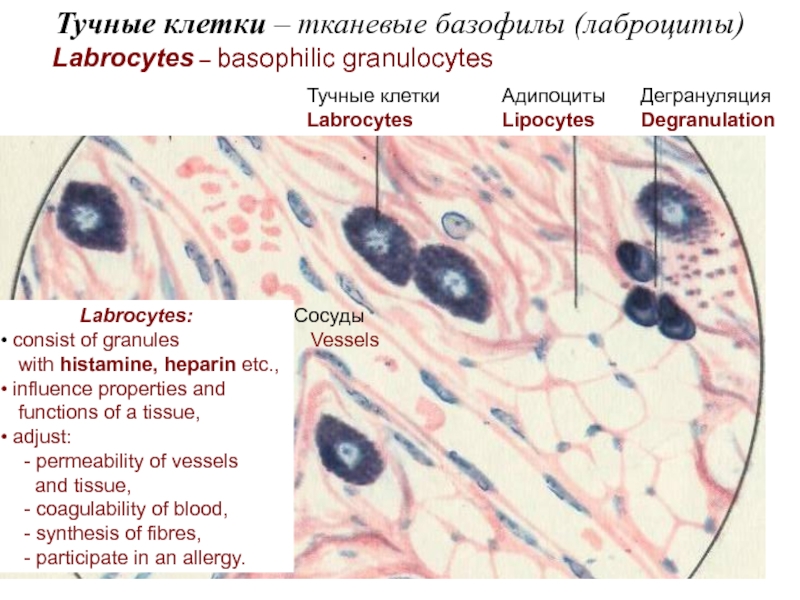
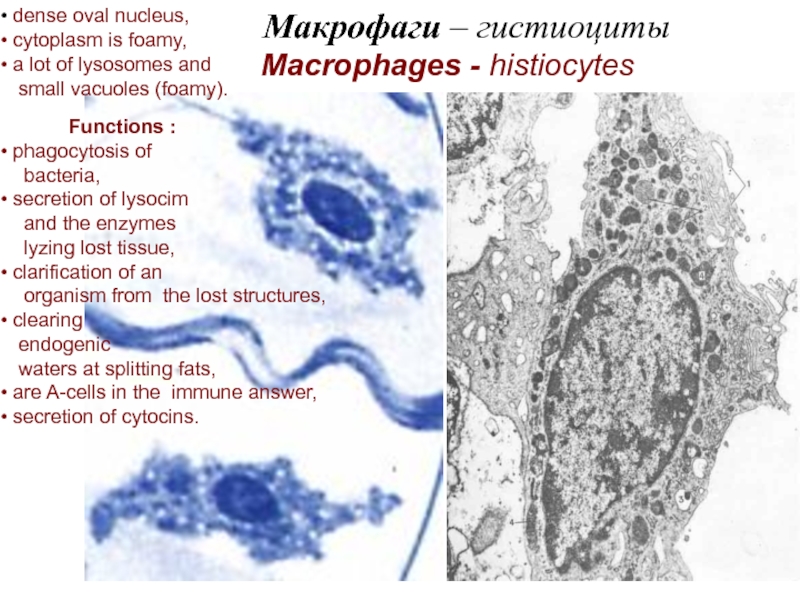
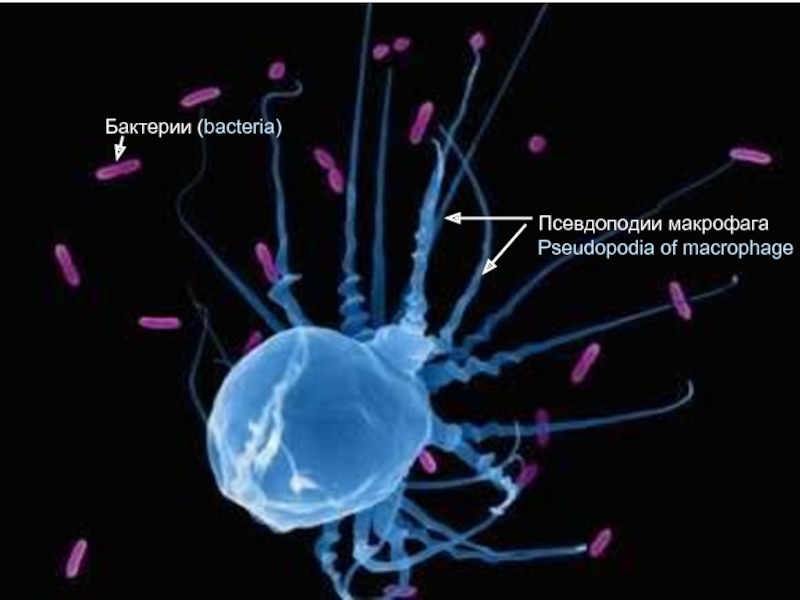
Actually connective tissues
Скелетные ткани
Skeletal tissues
Волокнистая
Collagenic
Со специальными свойствами
With special properties
Хрящевая
Cartilage
Костная
Bone
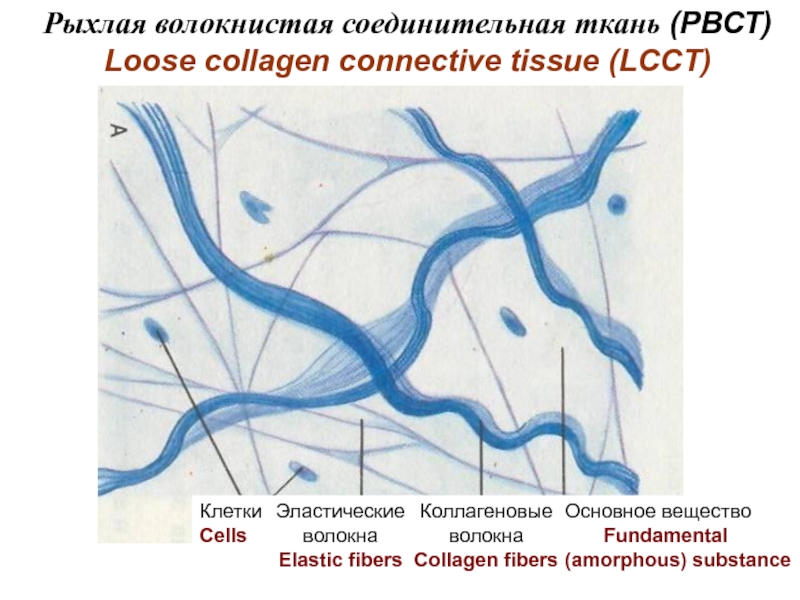
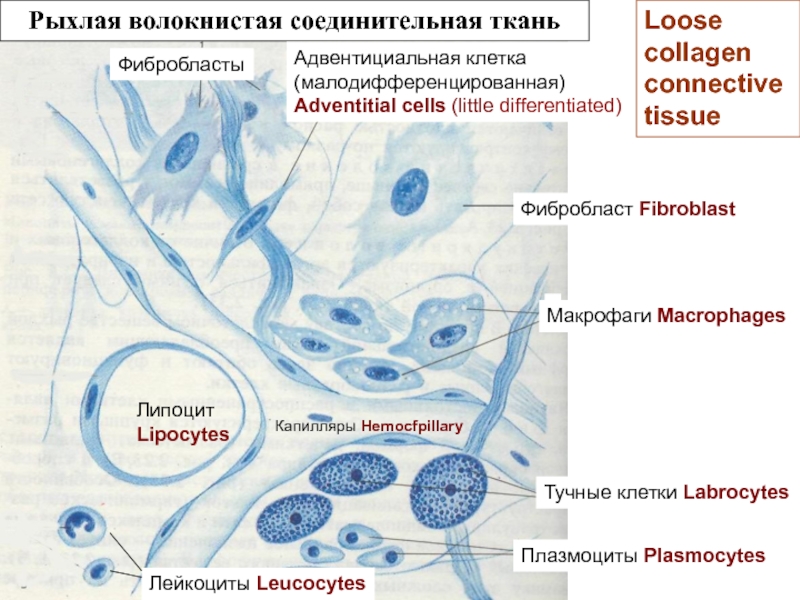
Рыхлая неоформленная
Loose collagen
Плотная - Dense collagen
оформленная - regular type
неоформленная - irregular type
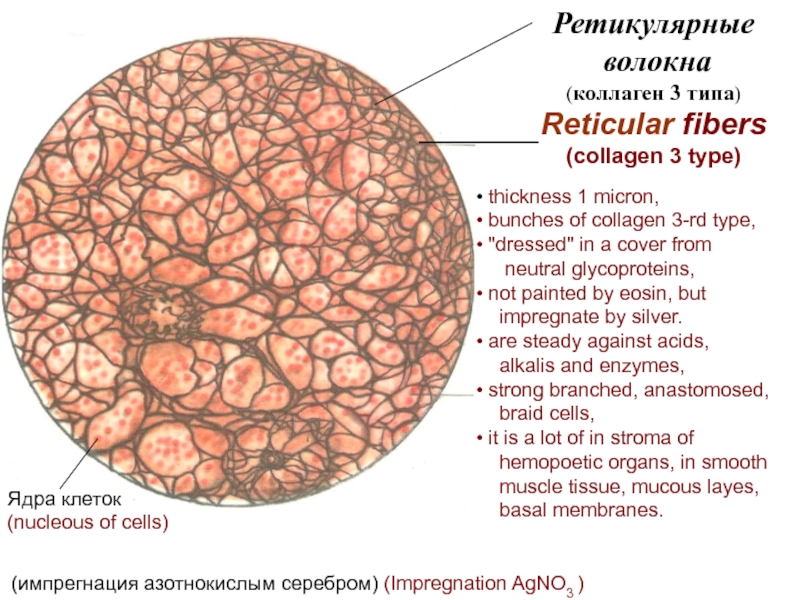
Ретикулярная - reticular
Жировая - adipose
Слизистая - mucous
Гиалиновый - hyaline
Эластический - elastic
Волокнистый - fibrous
Ретикулофиброзная
reticulofibrosus
Пластинчатая
lamellaris