- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Passive transport презентация
Содержание
- 1. Passive transport
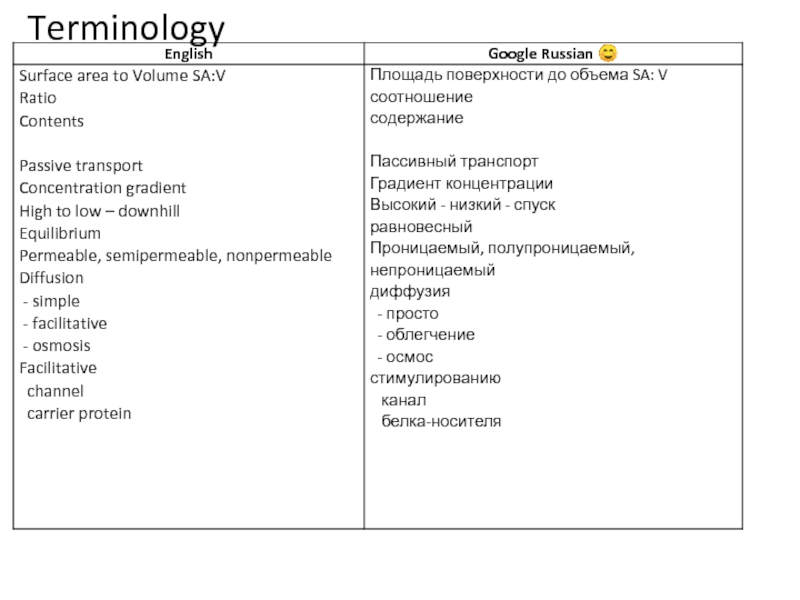
- 2. Terminology
- 3. Surface Area to Volume SA:V CIE Biology
- 6. Surface Area to Volume SA:V Surface Area Video Practical - (10 min) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CNkP4rycLbI
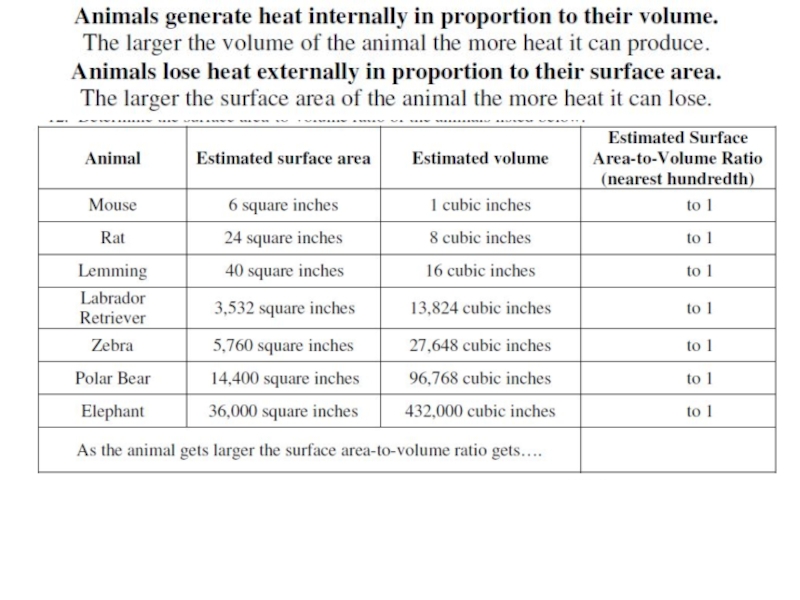
- 15. SA=6 Vol=1 SA/V=6 SA=24 Vol= 8 SA/Vol=3
- 16. To obtain sufficient oxygen for the demands
- 18. bronchiole alveoli Wall of alveolus
- 19. Summary: Why Surface Area to Volume is
- 20. Passive Transport CIE Biology Jones pp
- 21. Revise: Cell Membrane Cell membrane is semi-
- 22. Two types of transport
- 24. Diffusion moves substance [high] to [low] .
- 25. High Low
- 26. Passive transport uses a concentration gradient The
- 27. We will look at Passive Transport Only
- 28. Passive Transport Movement of molecules High High Low Low
- 29. Simple Diffusion across a Membrane -small molecules
- 30. Facilitated Diffusion Molecules move through proteins in
- 31. solute binds to protein protein changes shape
- 32. Osmosis Involves Water moving across a selectively
- 33. Look at the images and fill in
- 34. Respiration – Gas exchange Lung 1.
- 35. Dialysis – removal of wastes from blood
- 36. Kidney Filtration 3. H2O reabsorption is
- 37. Plant Cells 4. Movement of H2O
- 38. Erythrocytes RBC 5. Movement of H2O in a RBC is _____________
- 39. Placental Exchange of Nutrients, Wastes, Gases 6.
- 40. Gas exchange in Fish Exchange of gases
- 41. Root hair cells Absorb water and minerals
- 42. Glucose Absorption Glucose is a large
- 43. Absorption of Nutrients-Small Intestine 1. Digestion
- 44. Neural Transmission ________________ of neurotransmitter molecules from
- 45. Fill in the Blank Key
- 46. Respiration – Gas exchange Lung 1.
- 47. Dialysis – removal of wastes from blood
- 48. Kidney Filtration 3. H2O reabsorption is
- 49. Plant Cells 4. Movement of H2O
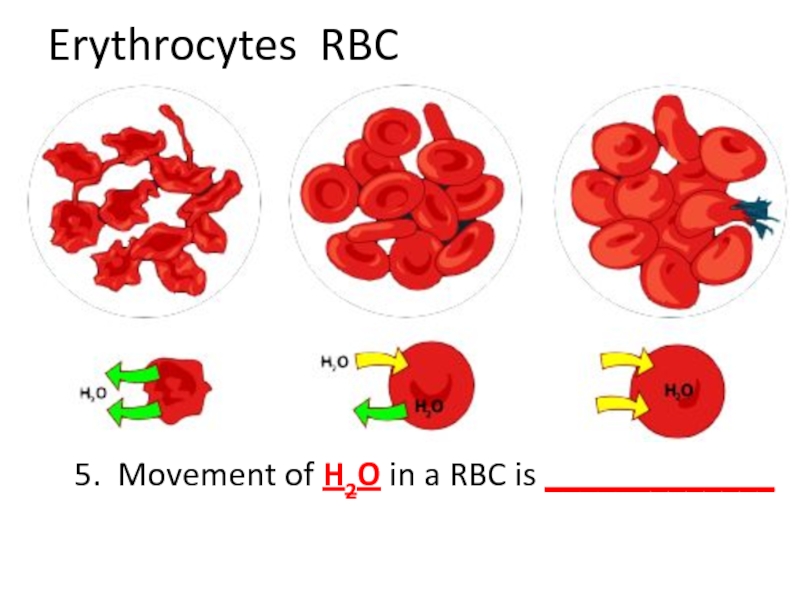
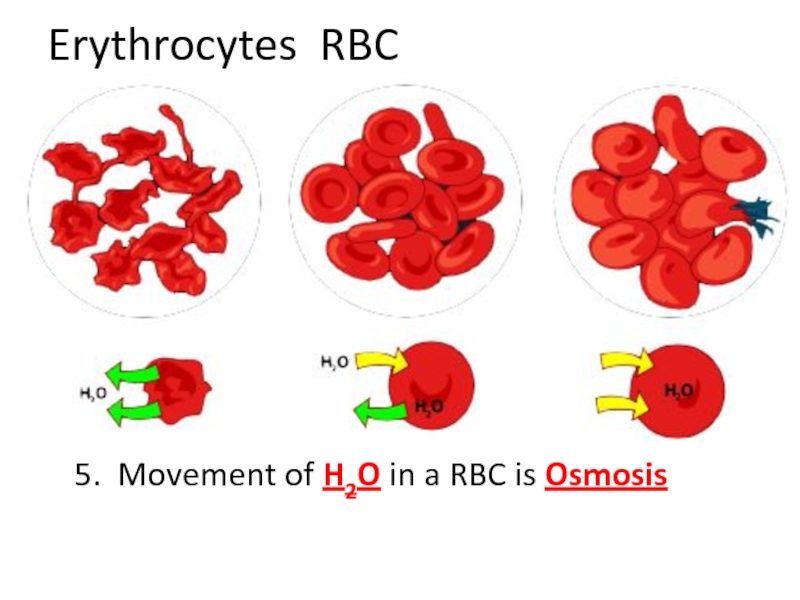
- 50. Erythrocytes RBC 5. Movement of H2O in a RBC is Osmosis
- 51. Placental Exchange of Nutrients, Wastes, Gases 6.
- 52. Gas exchange in Fish Exchange of gases
- 53. Root hair cells Absorb water and minerals
- 54. Glucose Absorption Glucose is a large
- 55. Absorption of Nutrients-Small Intestine 1. Digestion
- 56. Neural Transmission Diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules from
- 57. Video Passive (1min) and active transport
- 58. On back of paper make three columns
- 59. Paramecium Marine Sea Animal Freshwater fish
- 60. Normal state for animal cells Plant wilts
Слайд 1Passive Transport
CIE Biology Jones
pp 79-85
(Not water potential)
Learning Objective:
To explain the mechanism of passive transport
Calculate the ratio of the surface area to volume ratio and explain their meaning with respect to transport substances.
Success Criteria
Describe types of passive transport in oral or written form.
Explain passive transport mechanism
Calculate the value of SA/V ratio and explain its value regarding substance movement.
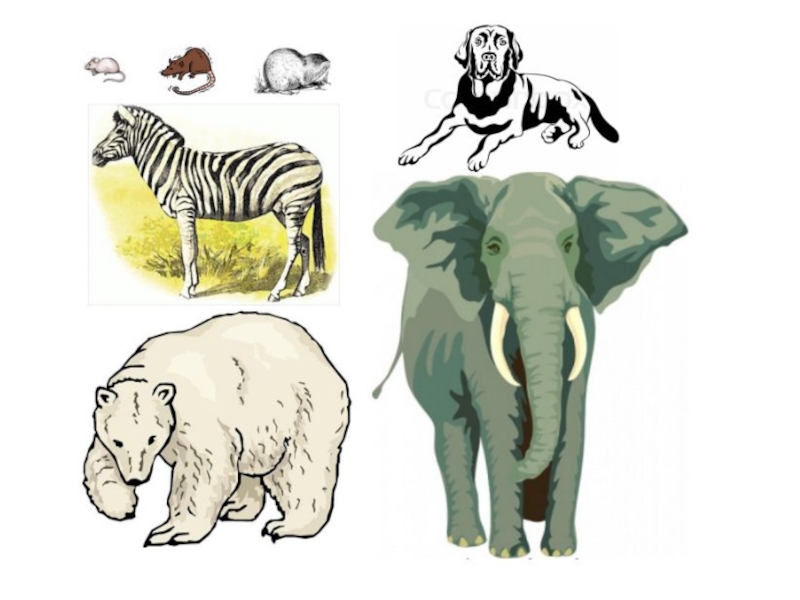
Correctly calculate two animals SA/V ratio.
Make right conclusion on movement of two mentioned animals (ex high SA/V ratio of amoeba says that oxygen can reach the center of amoeba, thus is does not require elements of transportation system.
Слайд 3Surface Area to Volume SA:V
CIE Biology Jones
pp 79-85
(Not water potential)
G11
Learning Objective:
Calculate the ratio of the surface area to volume ratio and explain their meaning with respect to transport substances.
Success Criteria
Calculate the value of SA/V ratio and explain its value regarding substance movement.
Correctly calculate two animals SA/V ratio.
Make right conclusion on movement of two mentioned animals (ex high SA/V ratio of amoeba says that oxygen can reach the center of amoeba, thus is does not require elements of transportation system.
Слайд 6Surface Area to Volume SA:V
Surface Area Video Practical - (10 min)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CNkP4rycLbI
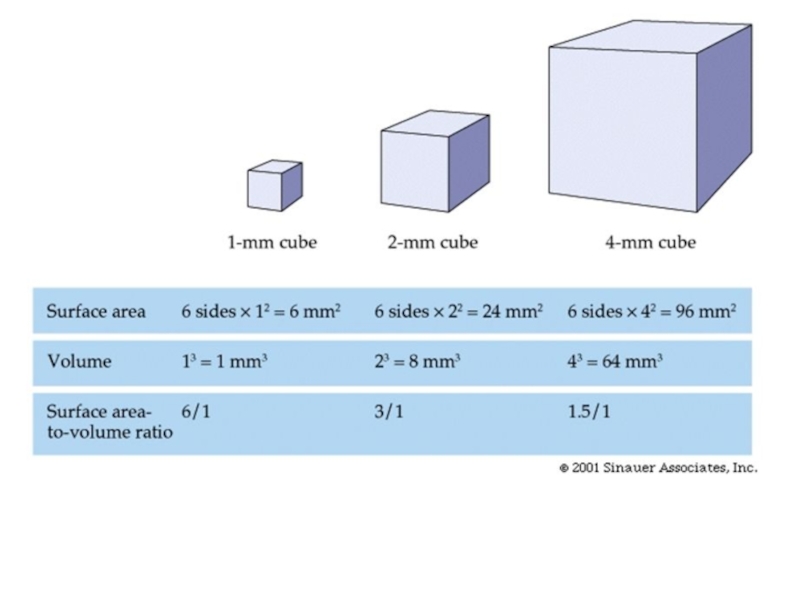
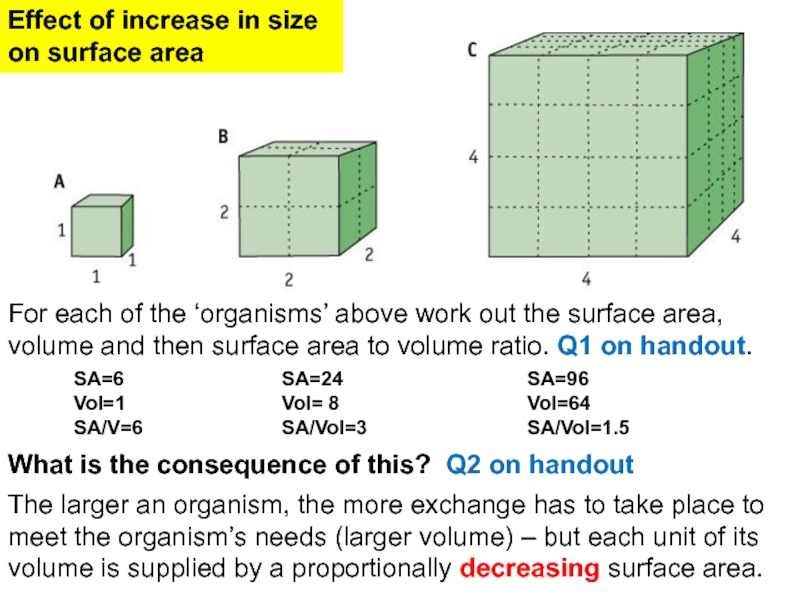
Слайд 15SA=6
Vol=1
SA/V=6
SA=24
Vol= 8
SA/Vol=3
SA=96
Vol=64
SA/Vol=1.5
What is the consequence of this? Q2 on handout
The larger
For each of the ‘organisms’ above work out the surface area, volume and then surface area to volume ratio. Q1 on handout.
Effect of increase in size
on surface area
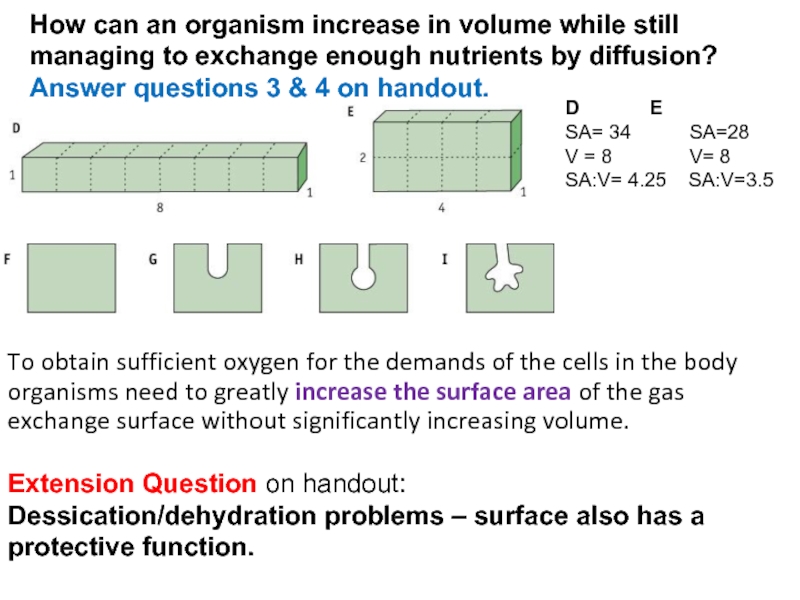
Слайд 16To obtain sufficient oxygen for the demands of the cells in
How can an organism increase in volume while still managing to exchange enough nutrients by diffusion?
Answer questions 3 & 4 on handout.
Extension Question on handout:
Dessication/dehydration problems – surface also has a protective function.
D E
SA= 34 SA=28
V = 8 V= 8
SA:V= 4.25 SA:V=3.5
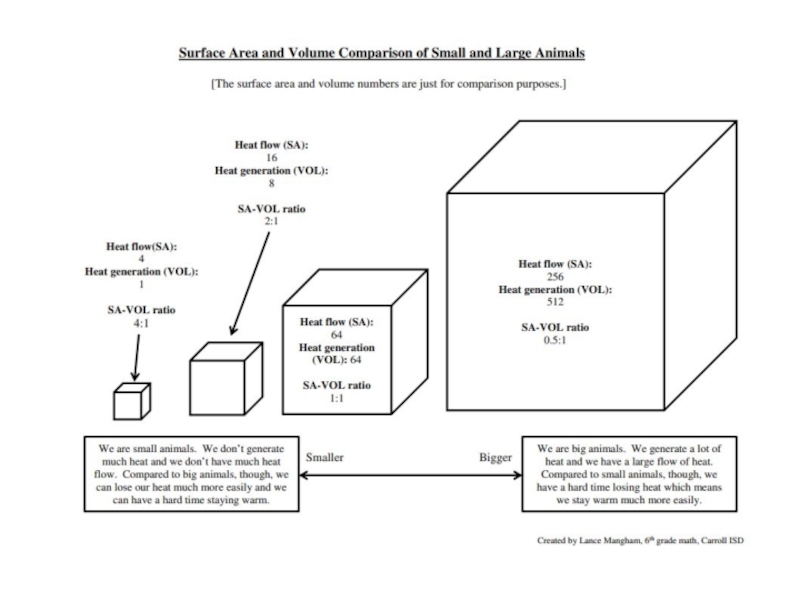
Слайд 19Summary: Why Surface Area to Volume is Important in Living Things.
-
Слайд 20Passive Transport
CIE Biology Jones
pp 79-85
(Not water potential)
Learning Objective:
To explain the mechanism of passive transport
Calculate the ratio of the surface area to volume ratio and explain their meaning with respect to transport substances.
Success Criteria
Describe types of passive transport in oral or written form.
Explain passive transport mechanism
Calculate the value of SA/V ratio and explain its value regarding substance movement.
Correctly calculate two animals SA/V ratio.
Make right conclusion on movement of two mentioned animals (ex high SA/V ratio of amoeba says that oxygen can reach the center of amoeba, thus is does not require elements of transportation system.
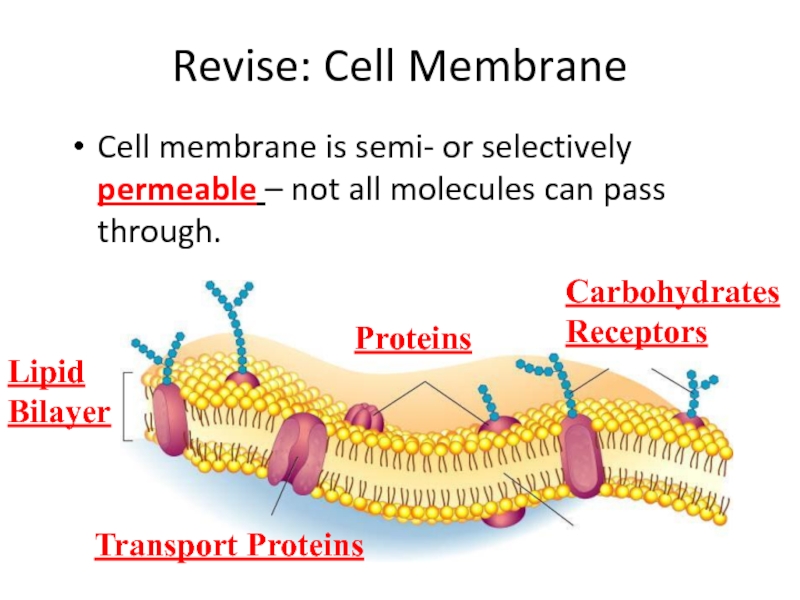
Слайд 21Revise: Cell Membrane
Cell membrane is semi- or selectively permeable – not
Carbohydrates
Receptors
Lipid
Bilayer
Proteins
Transport Proteins
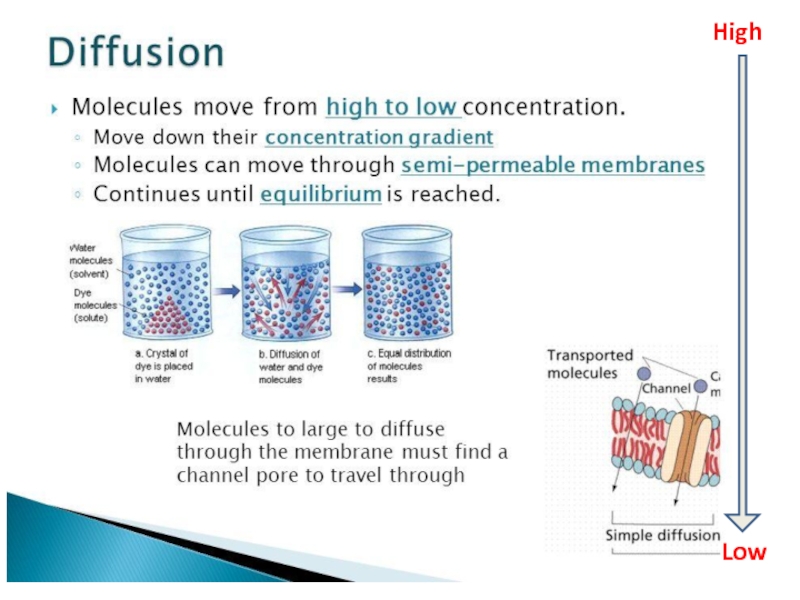
Слайд 24Diffusion
moves substance [high] to [low] .
Uses the kinetic energy – from
High
Low
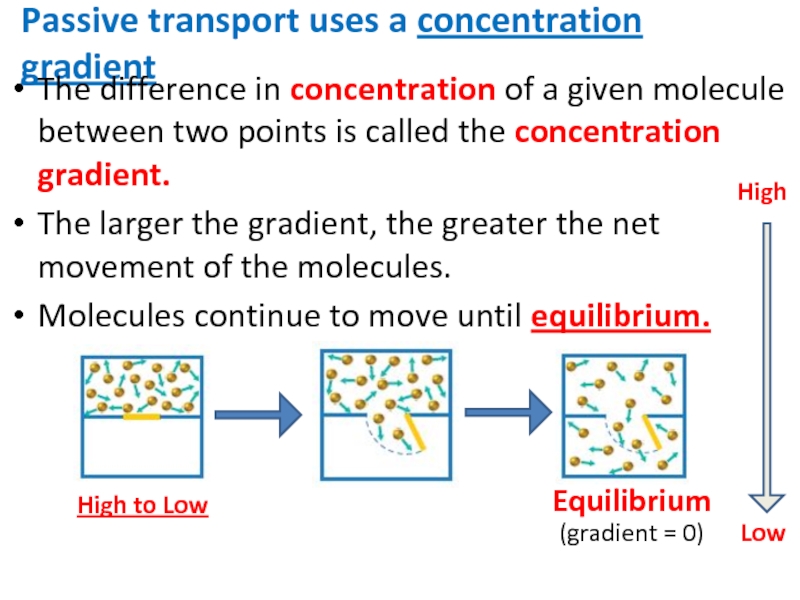
Слайд 26Passive transport uses a concentration gradient
The difference in concentration of a
The larger the gradient, the greater the net movement of the molecules.
Molecules continue to move until equilibrium.
Equilibrium
High to Low
(gradient = 0)
High
Low
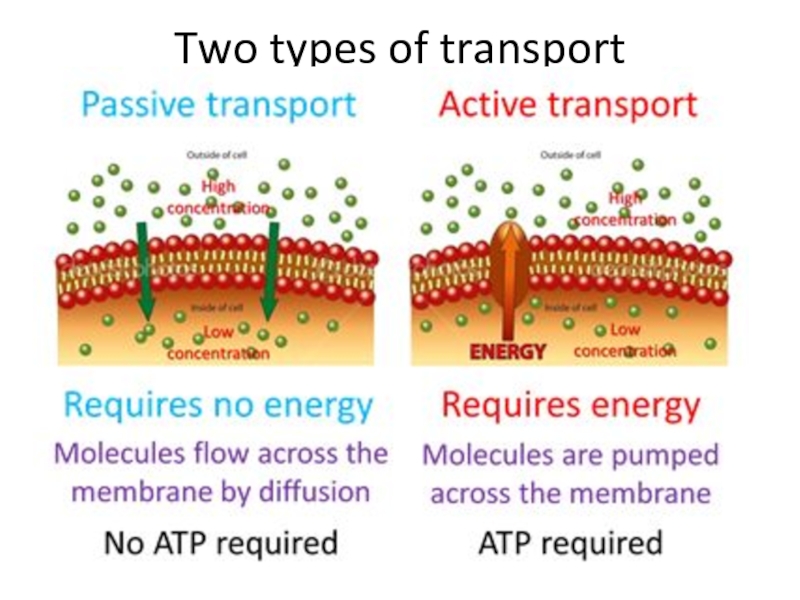
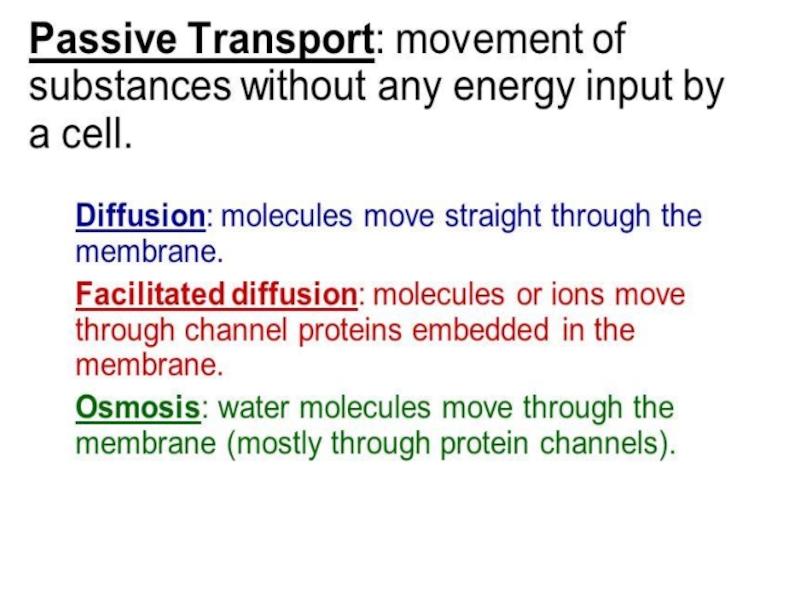
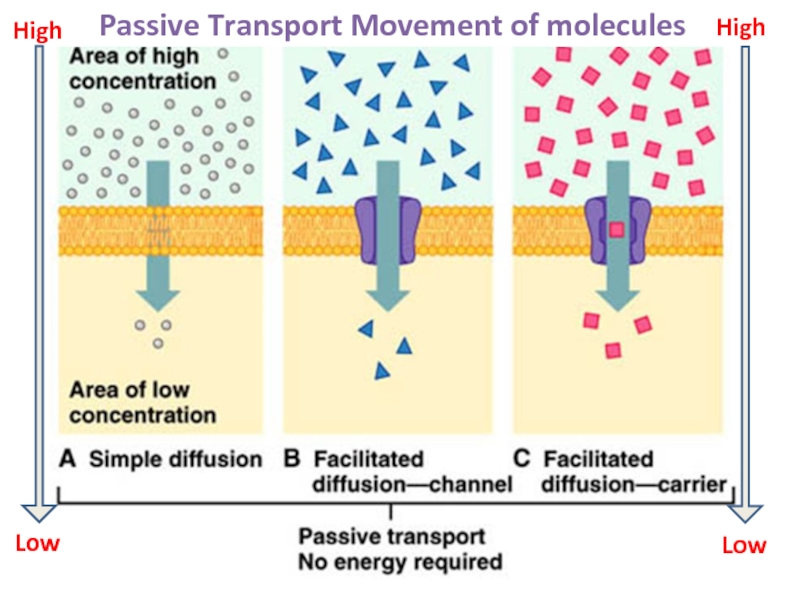
Слайд 27We will look at Passive Transport Only
Does not require energy
Molecules move [high] to [low].
Three major types:
Simple Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
High
Low
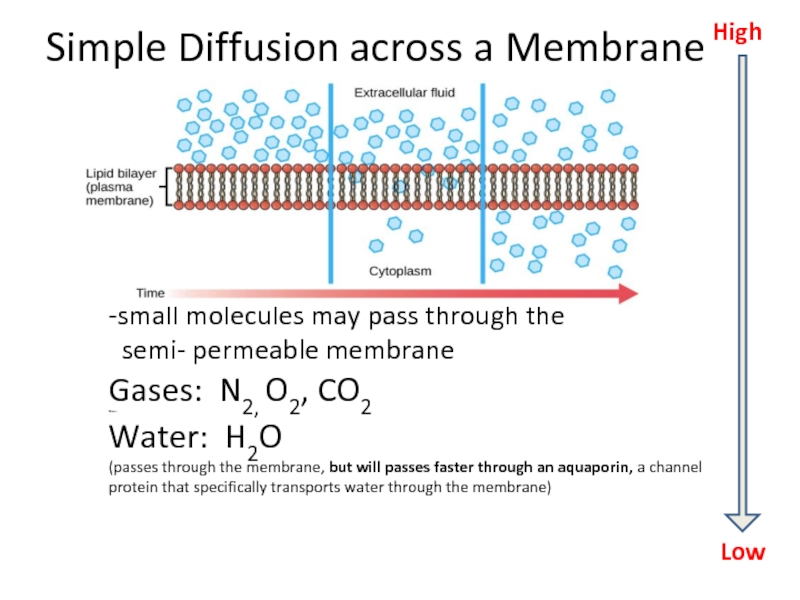
Слайд 29Simple Diffusion across a Membrane
-small molecules may pass through the
Gases: N2, O2, CO2
Water
Water: H2O
(passes through the membrane, but will passes faster through an aquaporin, a channel protein that specifically transports water through the membrane)
High
Low
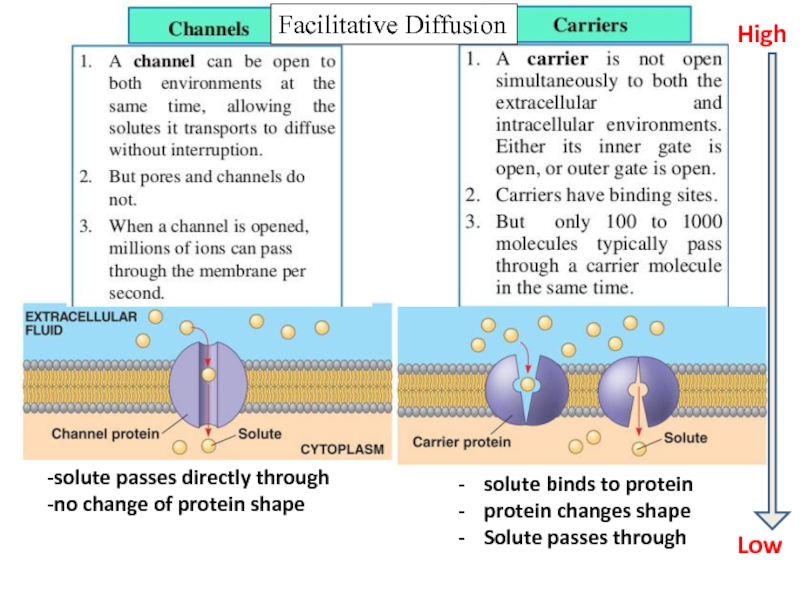
Слайд 30Facilitated Diffusion
Molecules move through proteins in the membrane by the concentration
[high] to [low]
No ENERGY (ATP)
High
Low
Слайд 31solute binds to protein
protein changes shape
Solute passes through
-solute passes directly through
-no
Facilitative Diffusion
High
Low
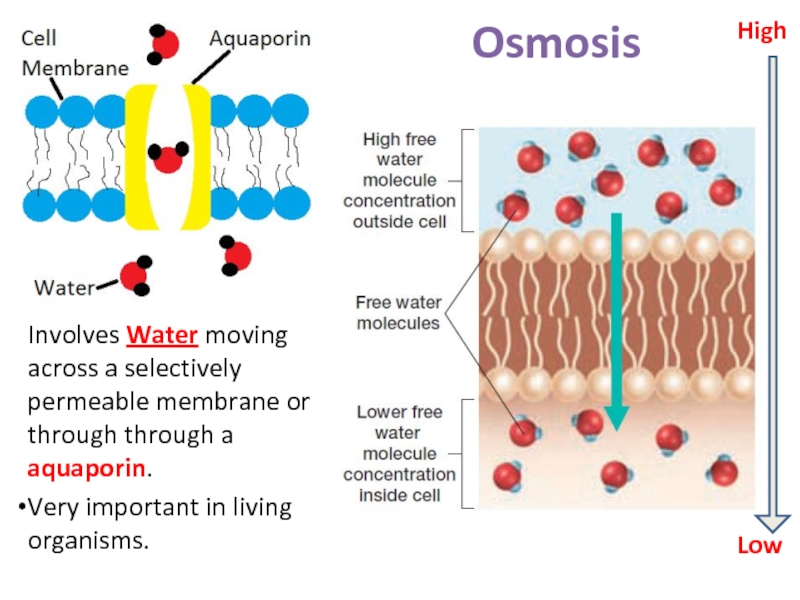
Слайд 32Osmosis
Involves Water moving across a selectively permeable membrane or through through
Very important in living organisms.
High
Low
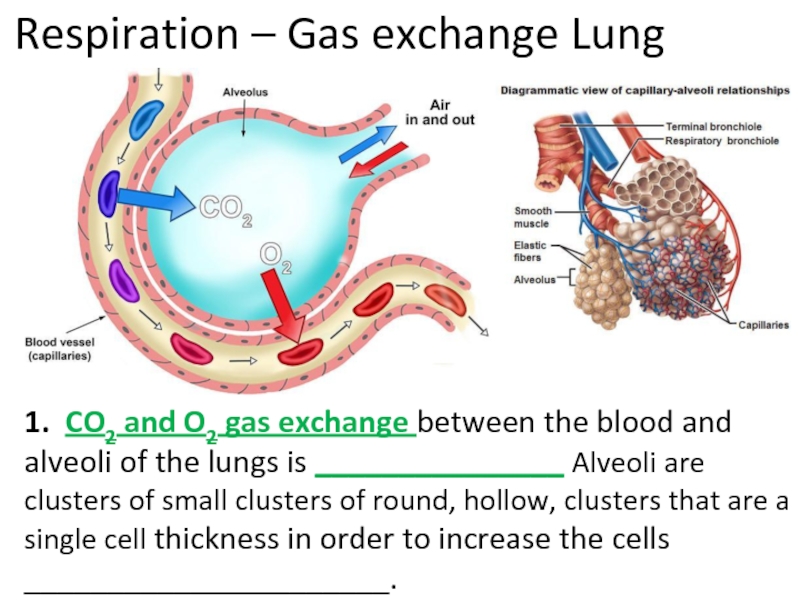
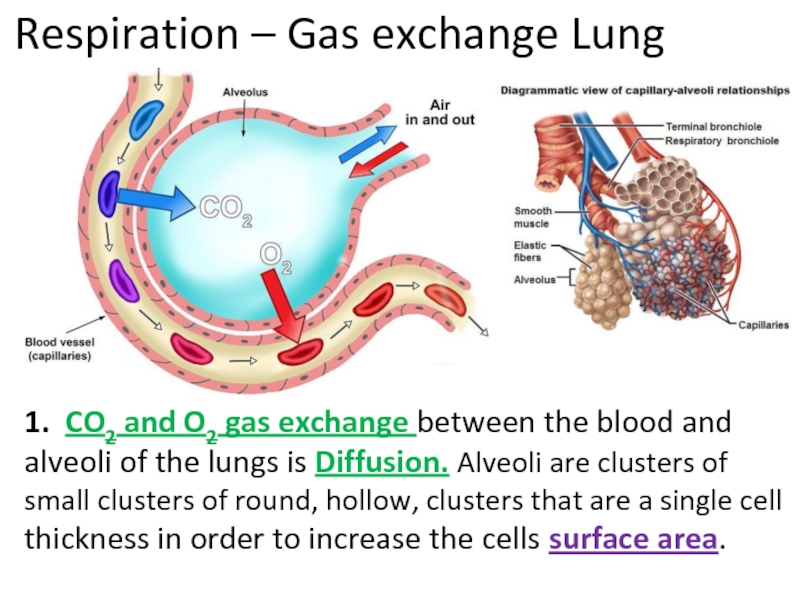
Слайд 34Respiration – Gas exchange Lung
1. CO2 and O2 gas exchange between
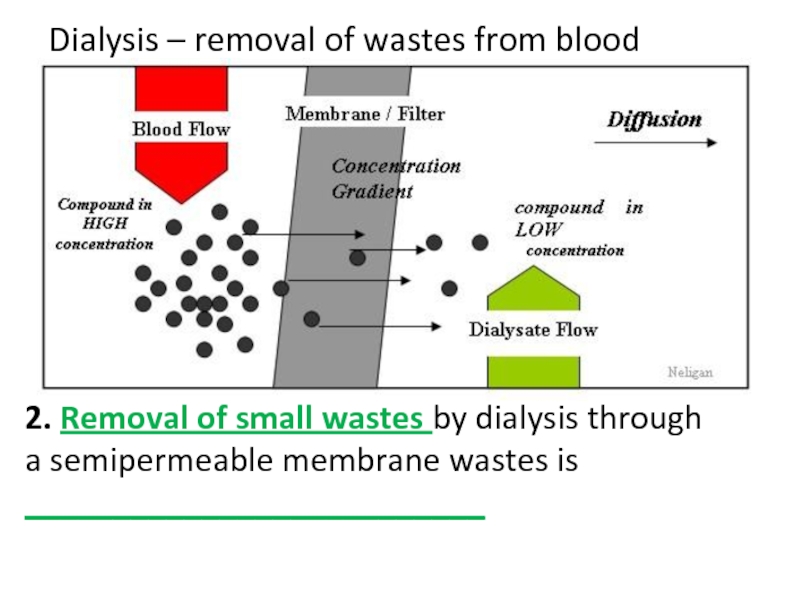
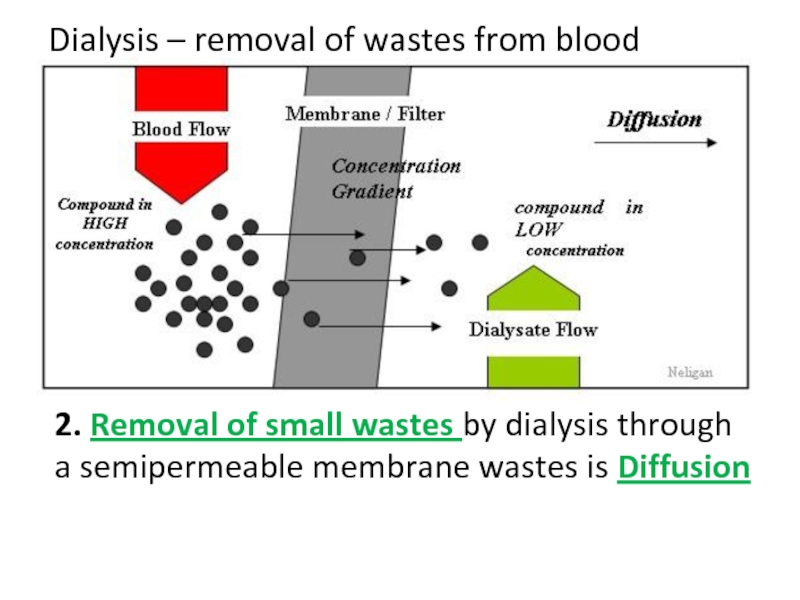
Слайд 35Dialysis – removal of wastes from blood
2. Removal of small wastes
a semipermeable membrane wastes is __________________________
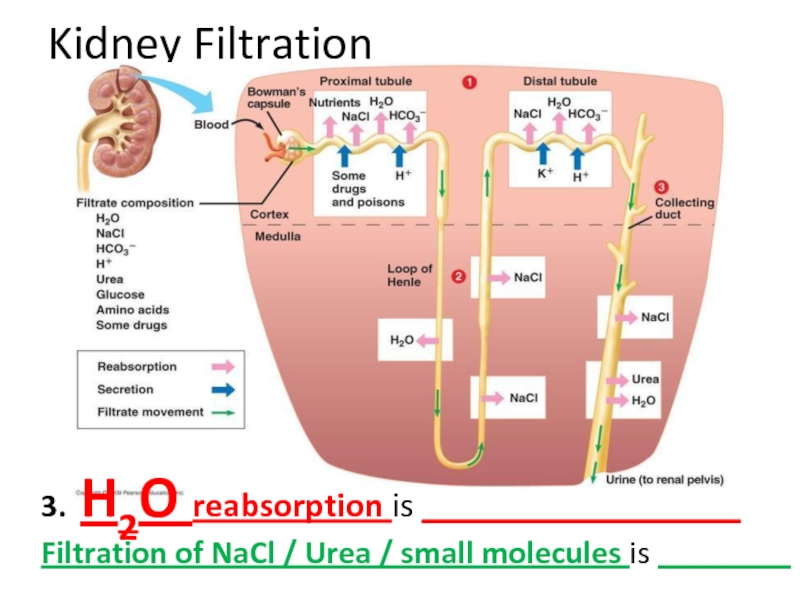
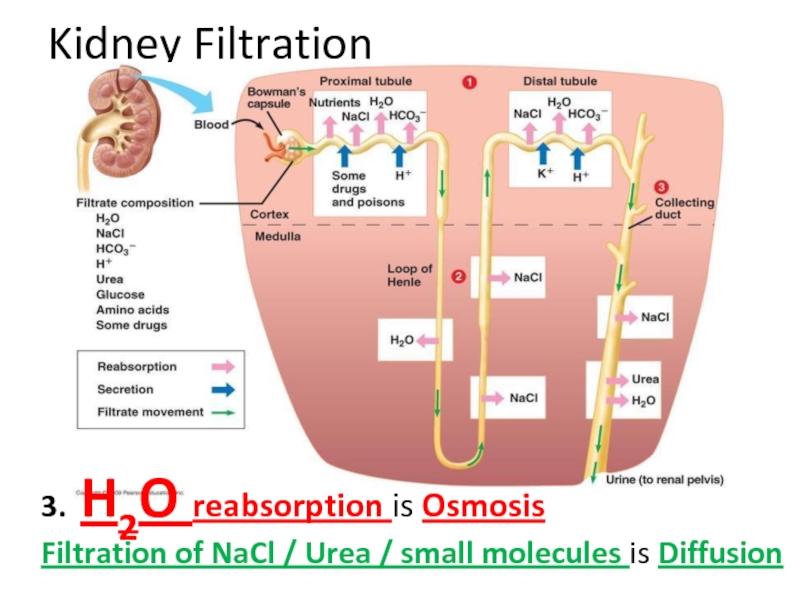
Слайд 36Kidney Filtration
3. H2O reabsorption is __________________
Filtration of NaCl / Urea /
Слайд 37
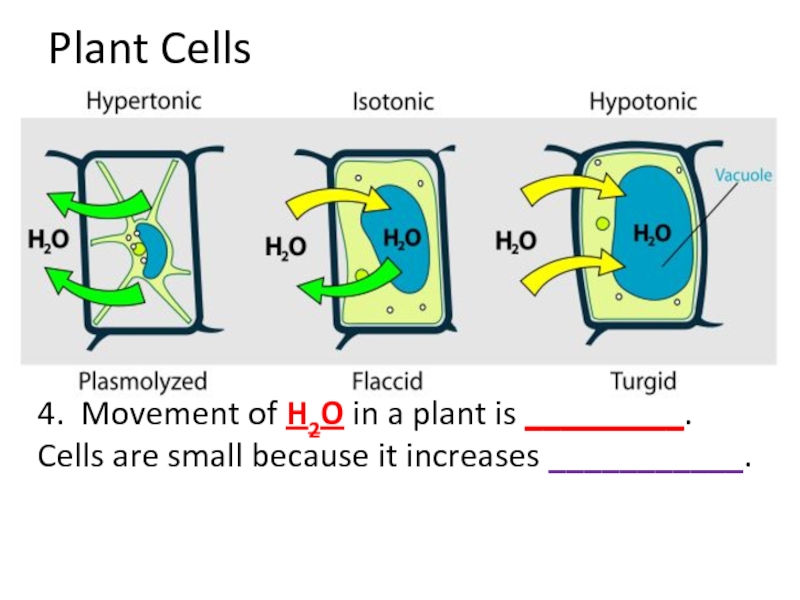
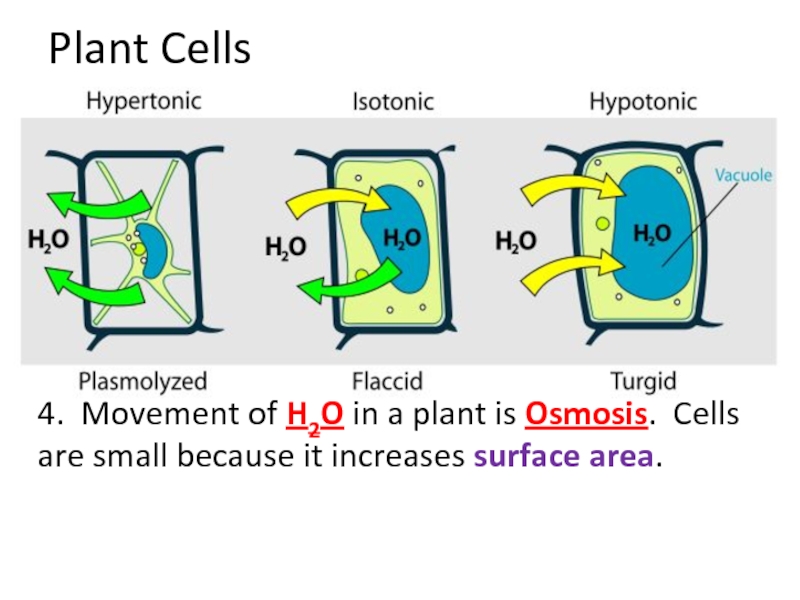
Plant Cells
4. Movement of H2O in a plant is _________. Cells
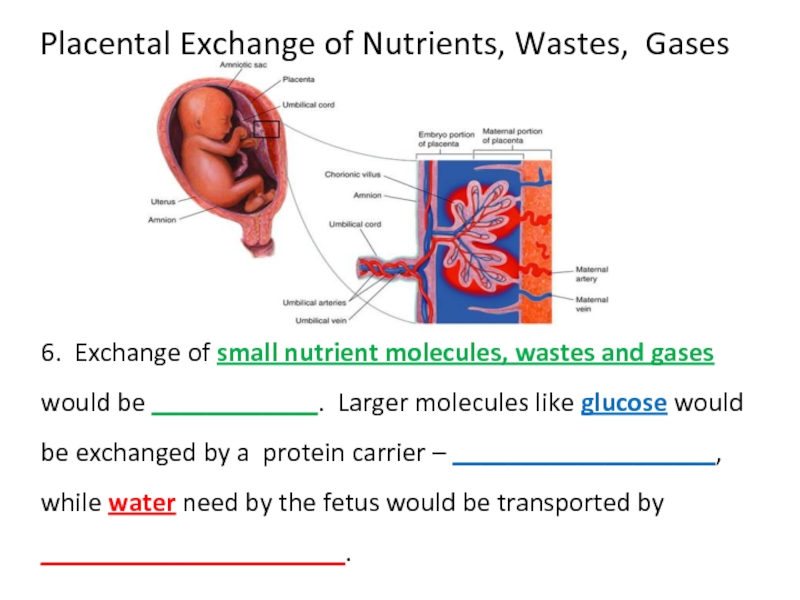
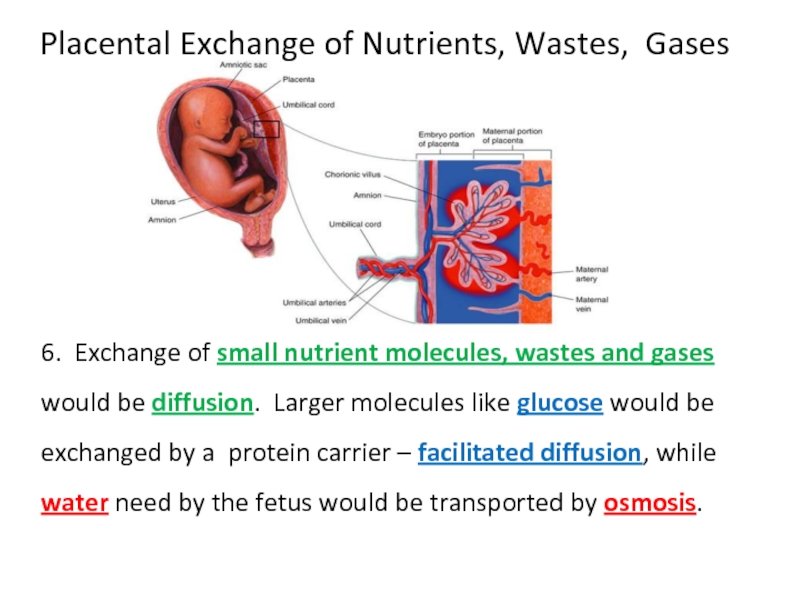
Слайд 39Placental Exchange of Nutrients, Wastes, Gases
6. Exchange of small nutrient molecules,
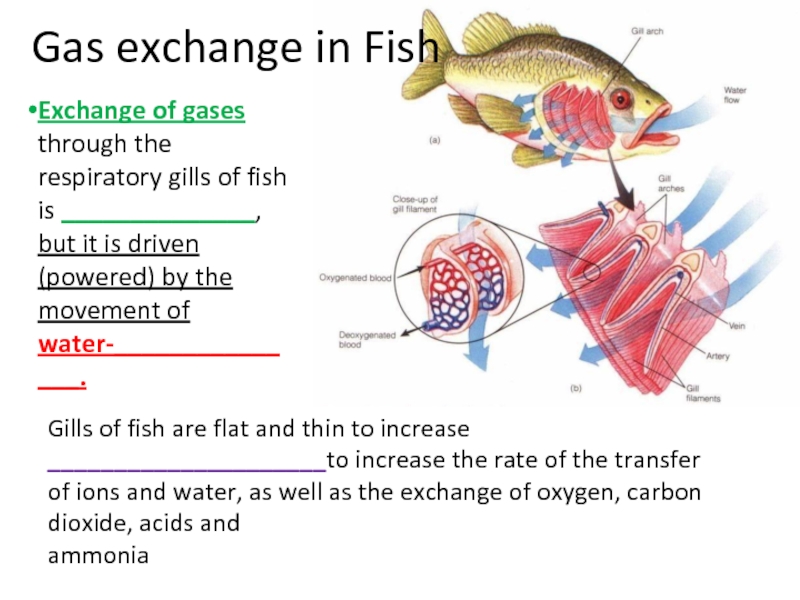
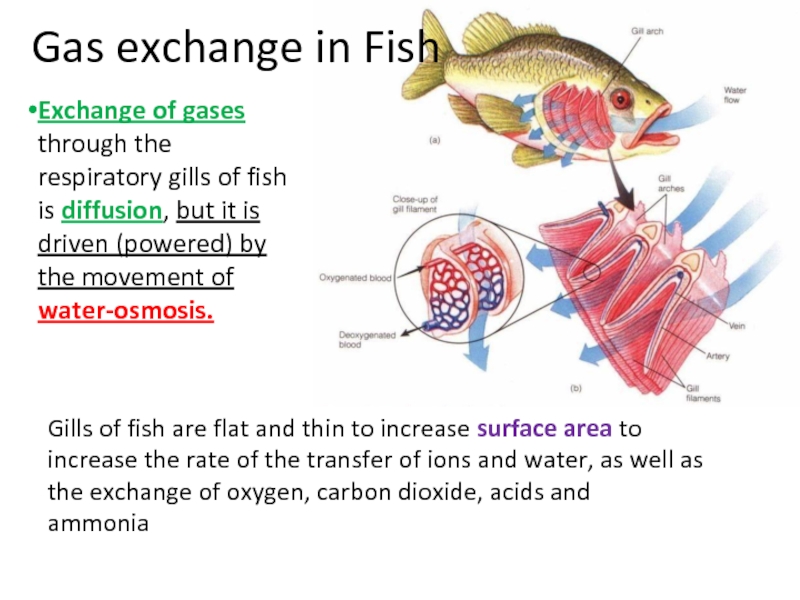
Слайд 40Gas exchange in Fish
Exchange of gases through the respiratory gills of
Gills of fish are flat and thin to increase _____________________to increase the rate of the transfer of ions and water, as well as the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, acids and
ammonia
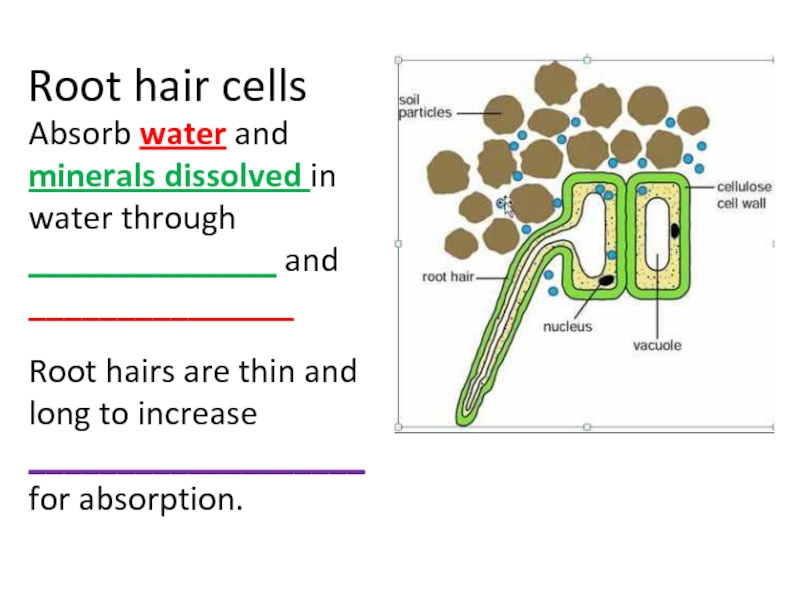
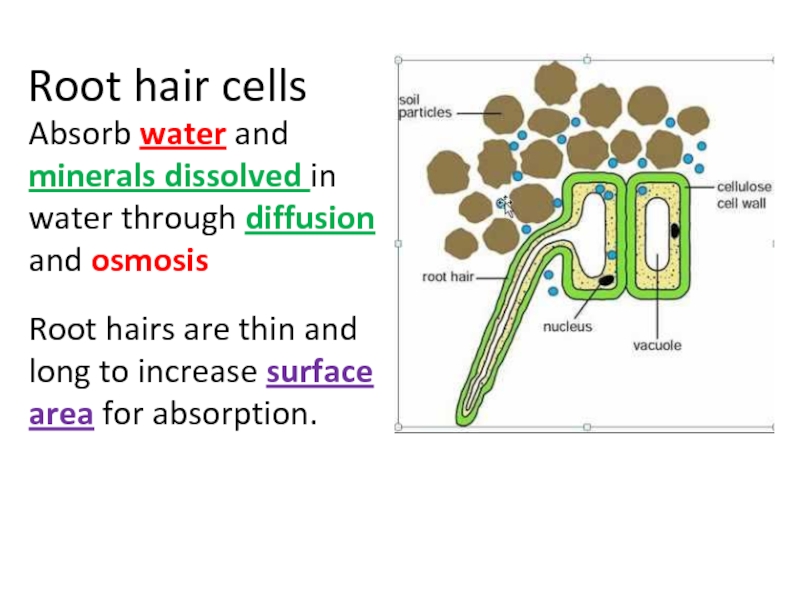
Слайд 41Root hair cells
Absorb water and minerals dissolved in water through ______________
Root hairs are thin and long to increase ___________________ for absorption.
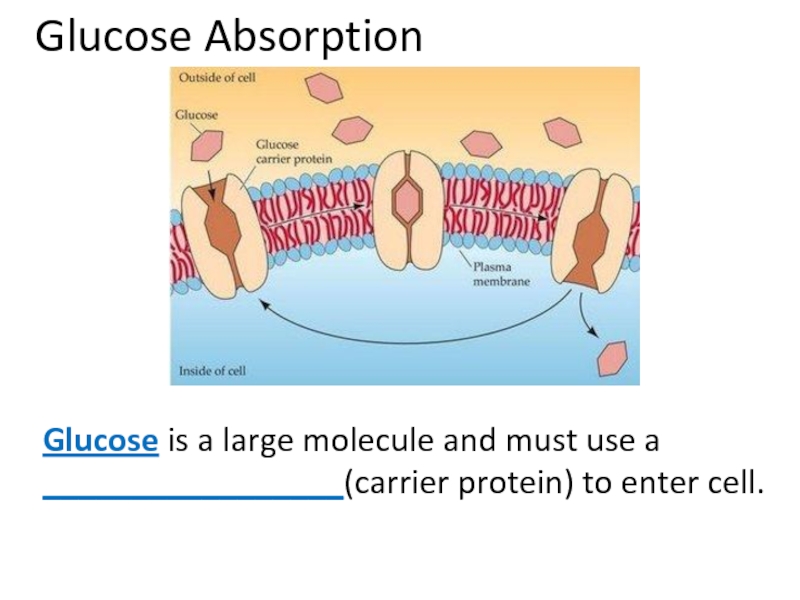
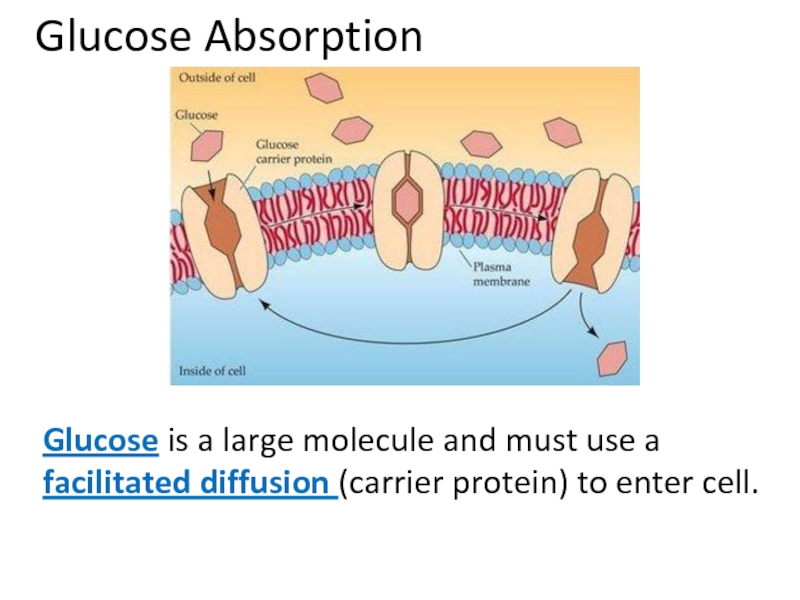
Слайд 42Glucose Absorption
Glucose is a large molecule and must use a _________________(carrier
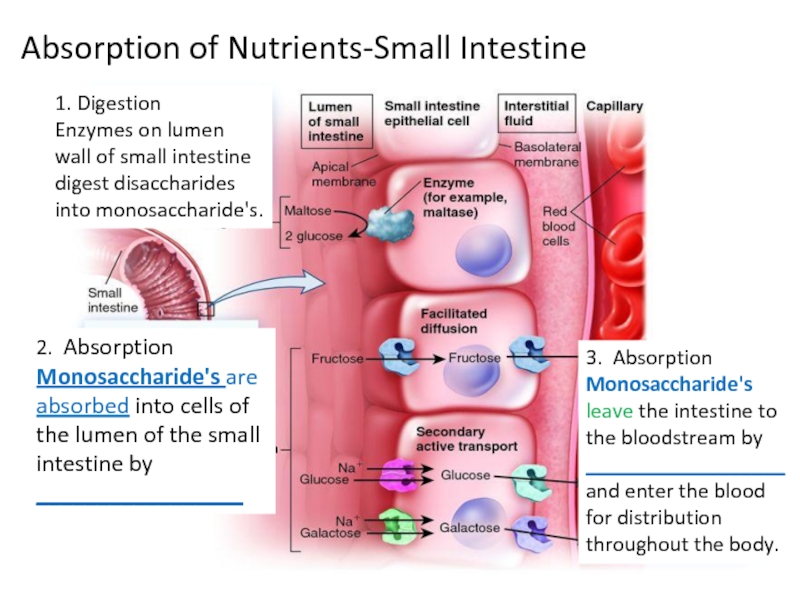
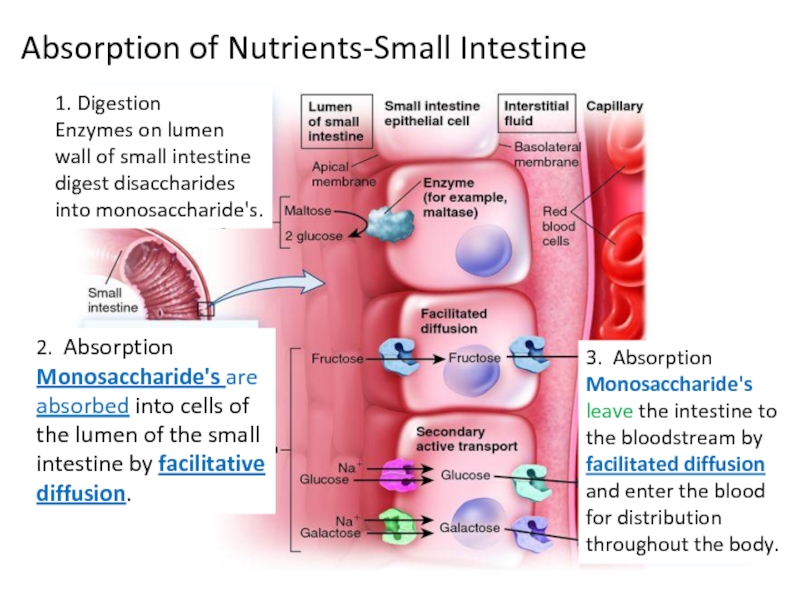
Слайд 43Absorption of Nutrients-Small Intestine
1. Digestion
Enzymes on lumen wall of small
2. Absorption
Monosaccharide's are absorbed into cells of the lumen of the small intestine by _________________
3. Absorption Monosaccharide's leave the intestine to the bloodstream by __________________and enter the blood for distribution throughout the body.
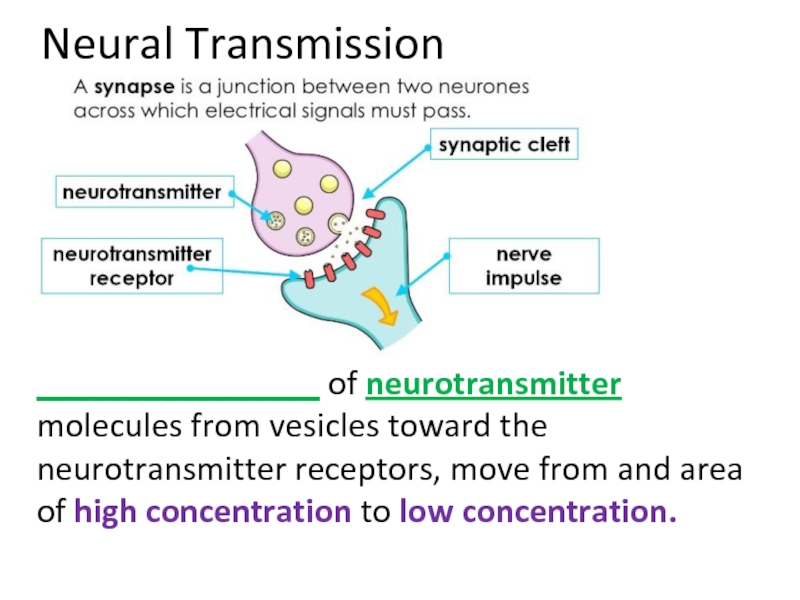
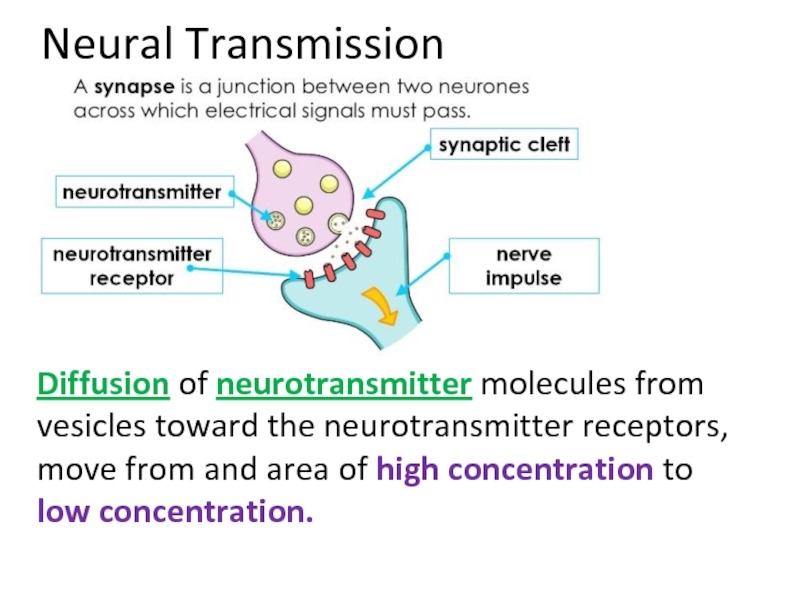
Слайд 44Neural Transmission
________________ of neurotransmitter molecules from vesicles toward the neurotransmitter receptors,
Слайд 46Respiration – Gas exchange Lung
1. CO2 and O2 gas exchange between
Слайд 47Dialysis – removal of wastes from blood
2. Removal of small wastes
a semipermeable membrane wastes is Diffusion
Слайд 48Kidney Filtration
3. H2O reabsorption is Osmosis
Filtration of NaCl / Urea
Слайд 49
Plant Cells
4. Movement of H2O in a plant is Osmosis. Cells
Слайд 51Placental Exchange of Nutrients, Wastes, Gases
6. Exchange of small nutrient molecules,
Слайд 52Gas exchange in Fish
Exchange of gases through the respiratory gills of
Gills of fish are flat and thin to increase surface area to increase the rate of the transfer of ions and water, as well as the exchange of oxygen, carbon dioxide, acids and
ammonia
Слайд 53Root hair cells
Absorb water and minerals dissolved in water through diffusion
Root hairs are thin and long to increase surface area for absorption.
Слайд 54Glucose Absorption
Glucose is a large molecule and must use a facilitated
Слайд 55Absorption of Nutrients-Small Intestine
1. Digestion
Enzymes on lumen wall of small
2. Absorption
Monosaccharide's are absorbed into cells of the lumen of the small intestine by facilitative diffusion.
3. Absorption Monosaccharide's leave the intestine to the bloodstream by facilitated diffusion and enter the blood for distribution throughout the body.
Слайд 56Neural Transmission
Diffusion of neurotransmitter molecules from vesicles toward the neurotransmitter receptors,
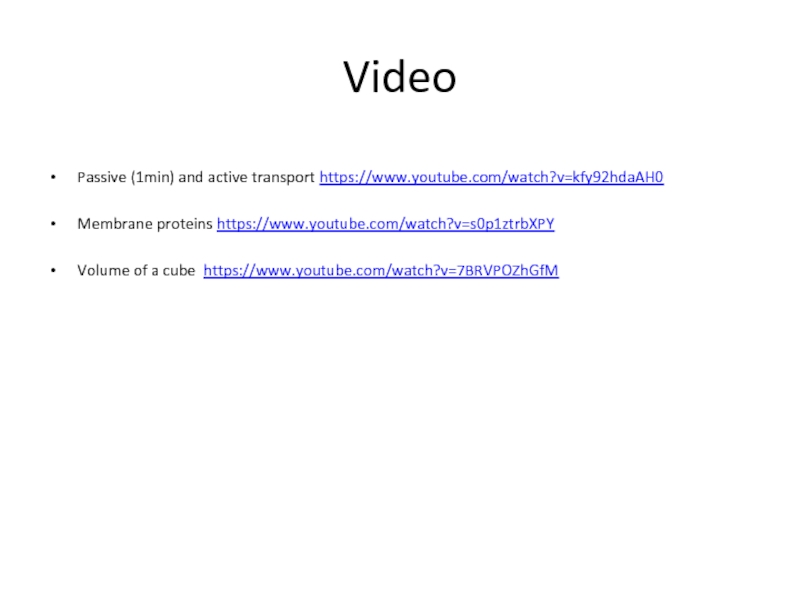
Слайд 57Video
Passive (1min) and active transport https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kfy92hdaAH0
Membrane proteins https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=s0p1ztrbXPY
Volume of a cube
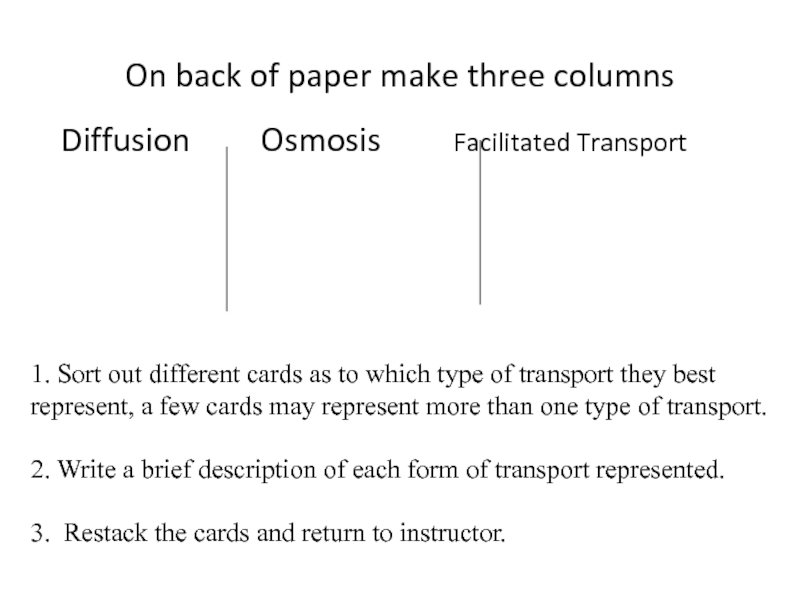
Слайд 58On back of paper make three columns
Diffusion Osmosis
1. Sort out different cards as to which type of transport they best
represent, a few cards may represent more than one type of transport.
2. Write a brief description of each form of transport represented.
3. Restack the cards and return to instructor.
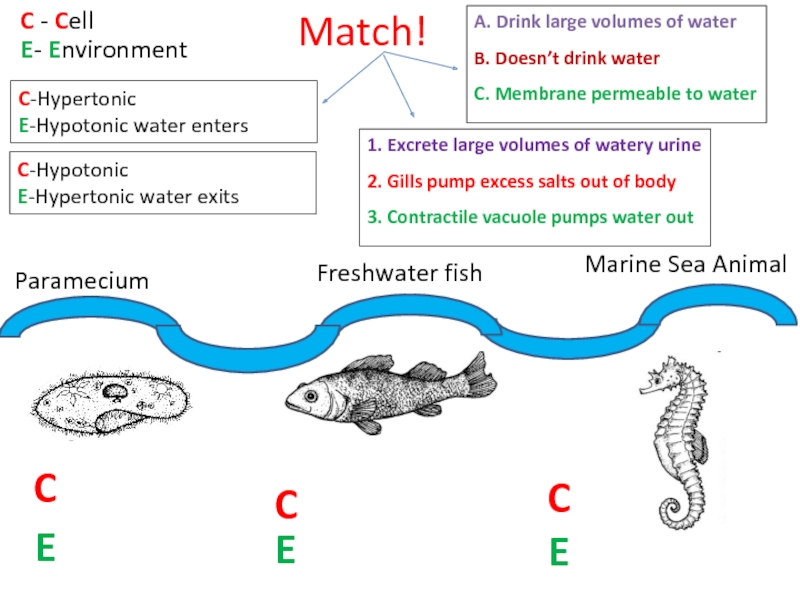
Слайд 59Paramecium
Marine Sea Animal
Freshwater fish
E- Environment
C - Cell
E
C
E
E
C
C
C-Hypertonic
E-Hypotonic water enters
C-Hypotonic
E-Hypertonic water
A. Drink large volumes of water
B. Doesn’t drink water
C. Membrane permeable to water
1. Excrete large volumes of watery urine
2. Gills pump excess salts out of body
3. Contractile vacuole pumps water out
Match!
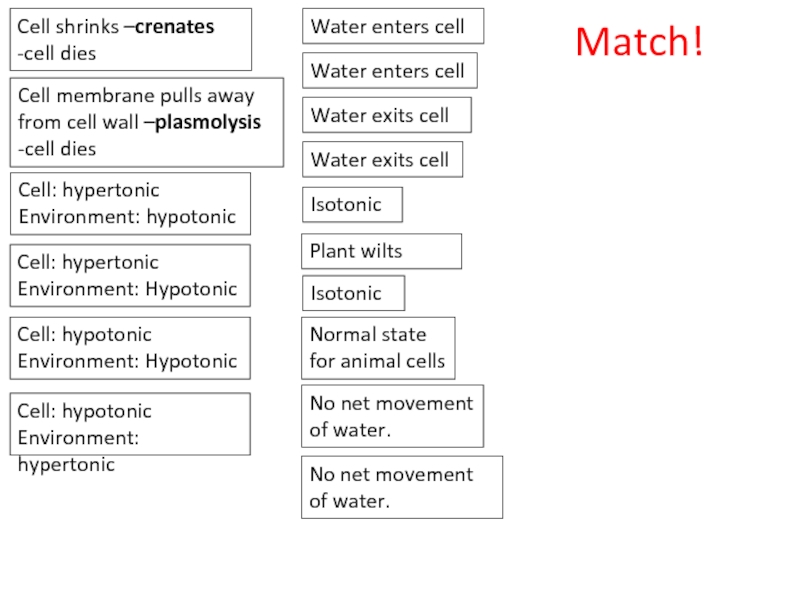
Слайд 60Normal state for animal cells
Plant wilts
Cell membrane pulls away from cell
-cell dies
Cell: hypotonic
Environment: hypertonic
Cell shrinks –crenates
-cell dies
Water exits cell
Water exits cell
Cell: hypotonic
Environment: Hypotonic
Cell: hypertonic
Environment: Hypotonic
Cell: hypertonic
Environment: hypotonic
Water enters cell
Water enters cell
No net movement of water.
Isotonic
Isotonic
No net movement of water.
Match!









![Diffusionmoves substance [high] to [low] .Uses the kinetic energy – from movement, NO ATP energy.HighLow](/img/tmb/5/459551/6bf551a29cf42d8c2ea090747db6ac33-800x.jpg)
![We will look at Passive Transport Only Does not require energy (ATP).Molecules move [high] to](/img/tmb/5/459551/4701d40b89a234dd4021be60691e9632-800x.jpg)
![Facilitated DiffusionMolecules move through proteins in the membrane by the concentration gradient. [high] to [low]No](/img/tmb/5/459551/2bb504d8438ce2d41386e3712f7a85b7-800x.jpg)