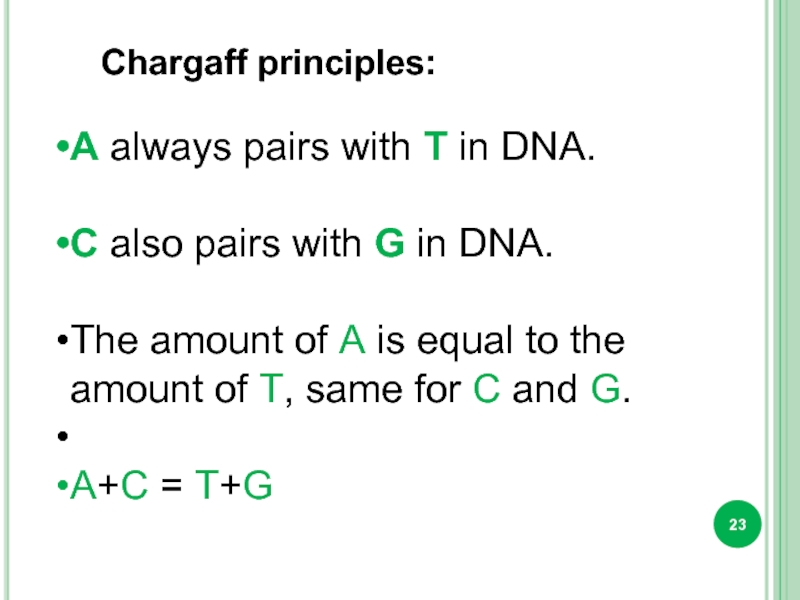Lecturer:
Assistant professor Antypenko Lyudmyla Mykolaivna
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Nucleic acids презентация
Содержание
- 1. Nucleic acids
- 2. Plan. First isolation of DNA (deoxyribonucleic
- 3. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) was firstly isolated by
- 4. The polymeric structure of DNA may be
- 9. Bases attached to a sugar is
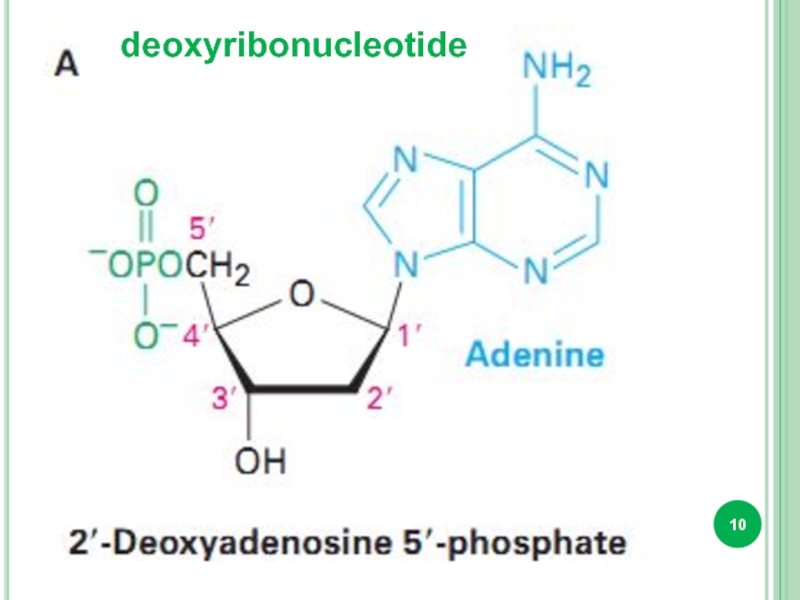
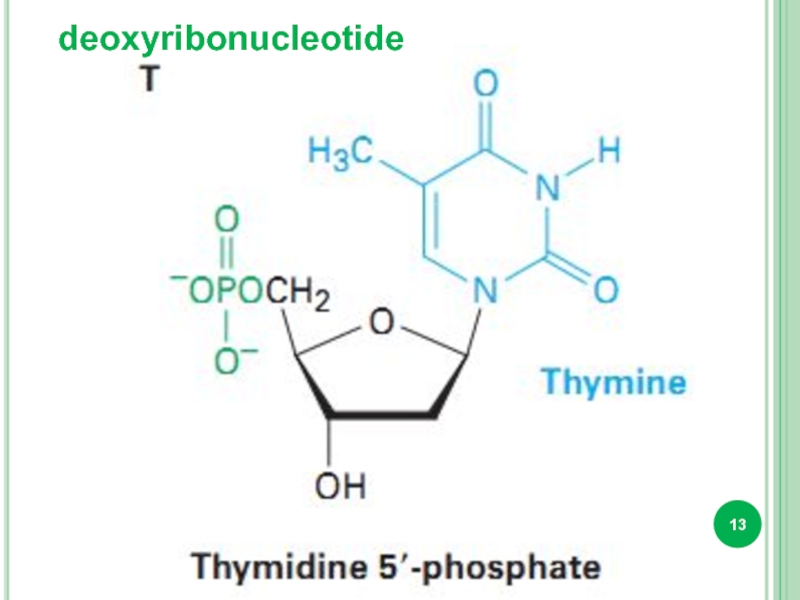
- 10. deoxyribonucleotide
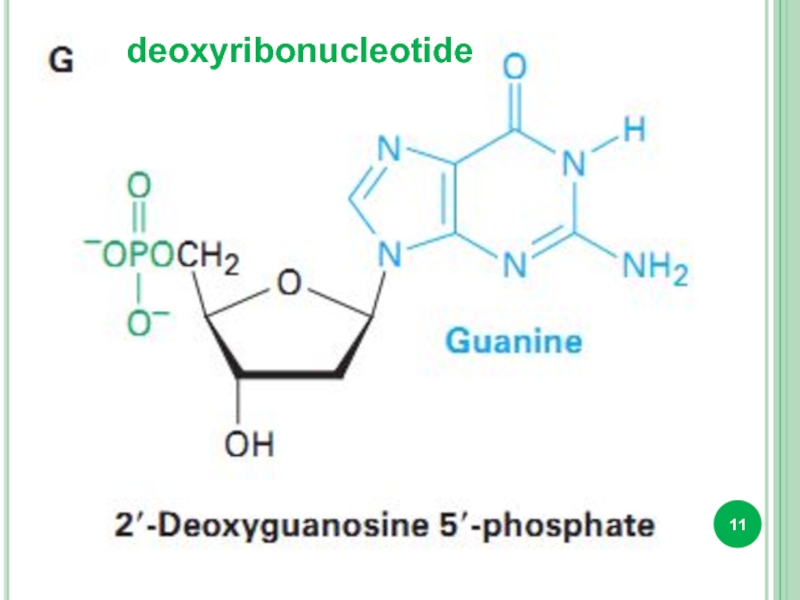
- 11. deoxyribonucleotide
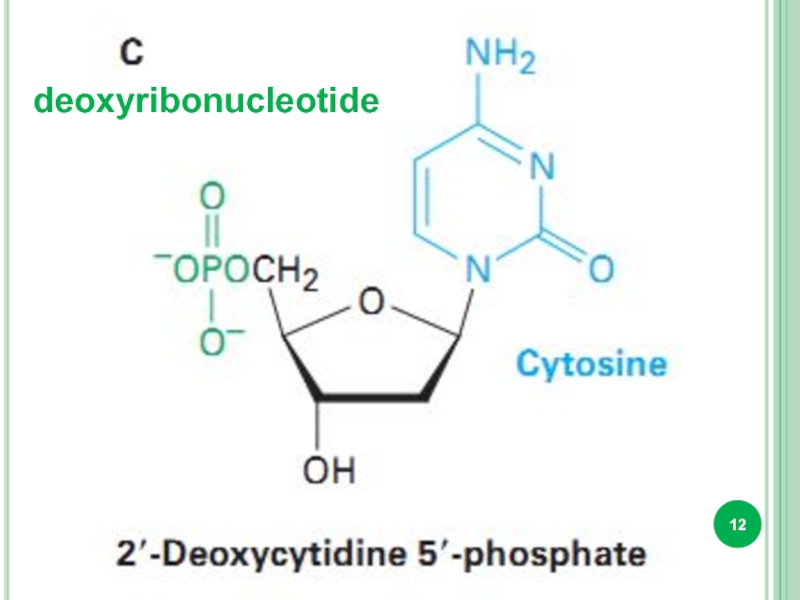
- 12. deoxyribonucleotide
- 13. deoxyribonucleotide
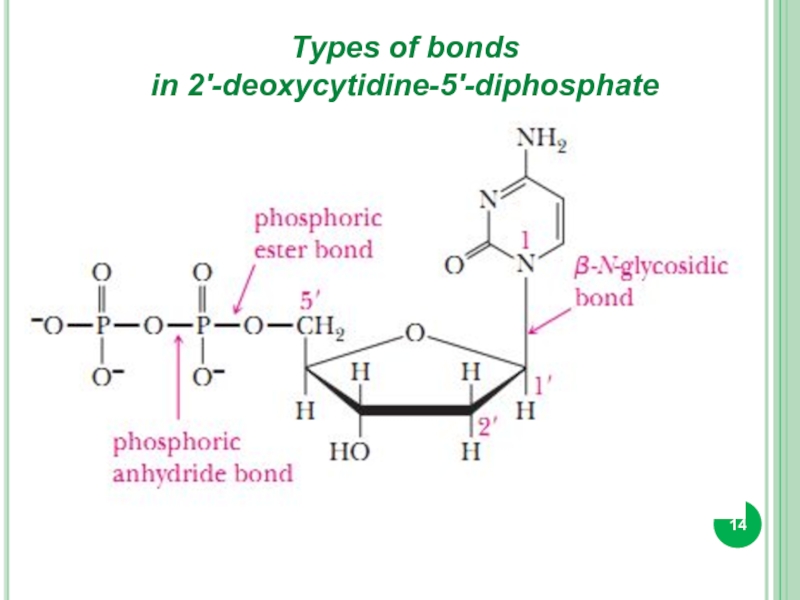
- 14. Types of bonds in 2'-deoxycytidine-5'-diphosphate
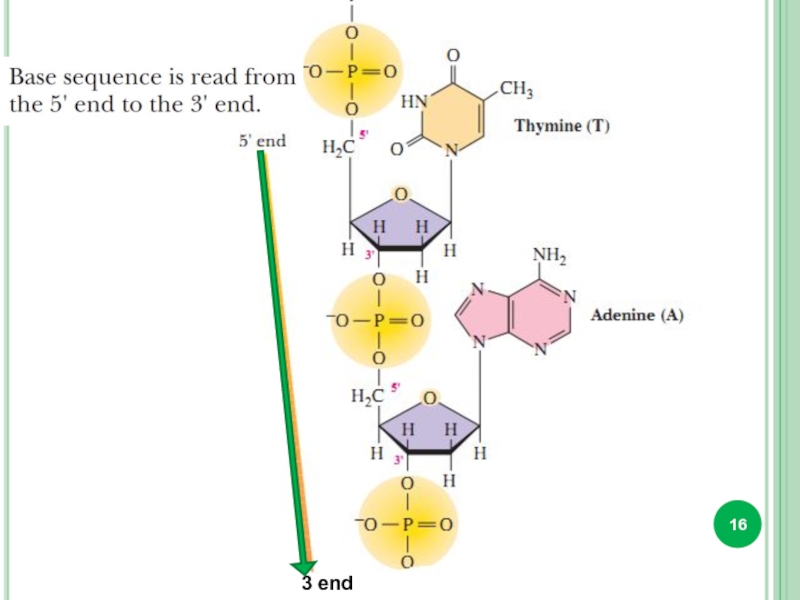
- 16. 3 end
- 17. RNA are easily hydrolyzed under mild alkaline
- 19. According to the Watson-Crick model of a
- 20. DNA double helix fragment in space-filling and wire-frame format
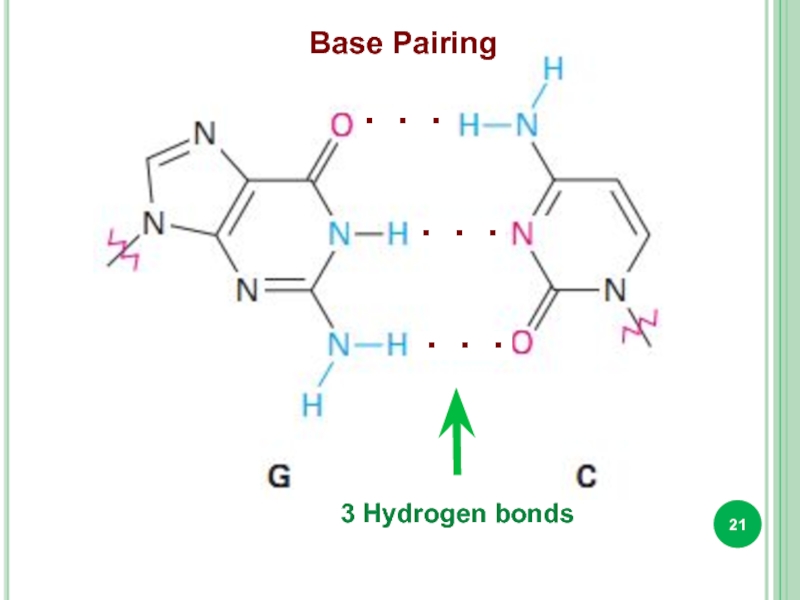
- 21. Base Pairing 3 Hydrogen bonds . . . . . . . . .
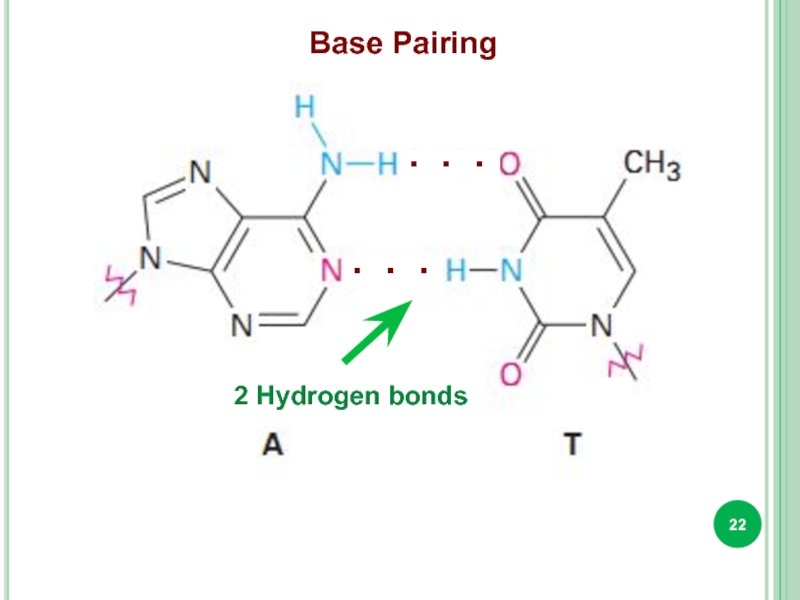
- 22. Base Pairing 2 Hydrogen bonds . . . . . .
- 23. A always pairs with T in
- 24. Different levels of DNA structure to fit
- 25. Replication — the process by which identical
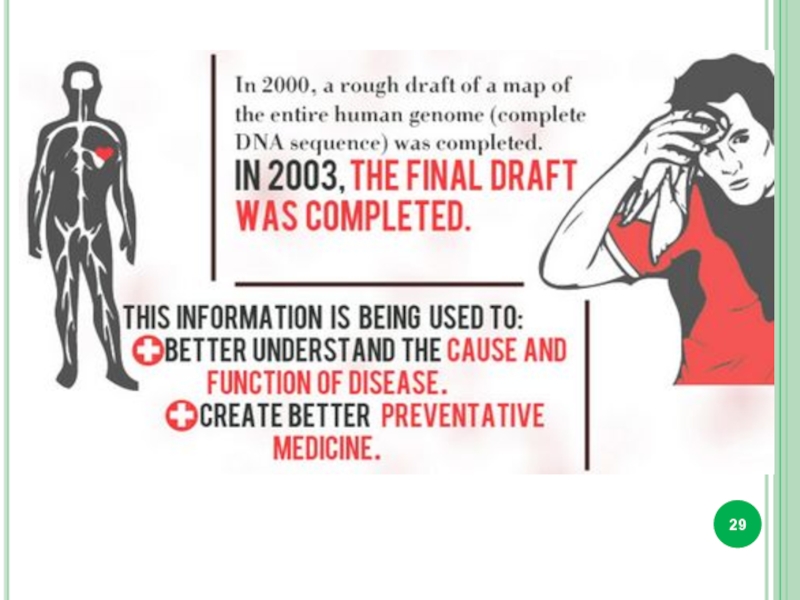
- 28. Almost all the cells in our body
- 30. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is one of the principal oxidation-reduction reagents in biological systems.
- 31. Bial’s test (pentose detection in products of
- 32. Bial’s test Also they gave red products of condensation with thymol (2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol).
- 33. A mutation is an error in the
- 34. Antiviral drugs DNA synthesis terminates whenever AZT
- 35. Thank You for Your attention!
Слайд 1LECTURE: NUCLEIC ACIDS.
MINISTRY OF PUBLIC HEALTH
ZAPOROZHYE STATE MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
DEPARTMENT OF
Слайд 2Plan.
First isolation of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid).
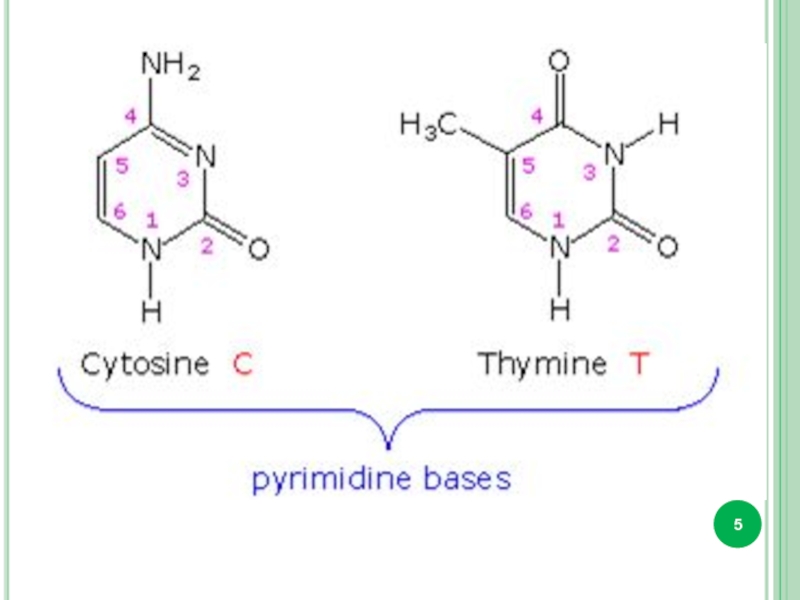
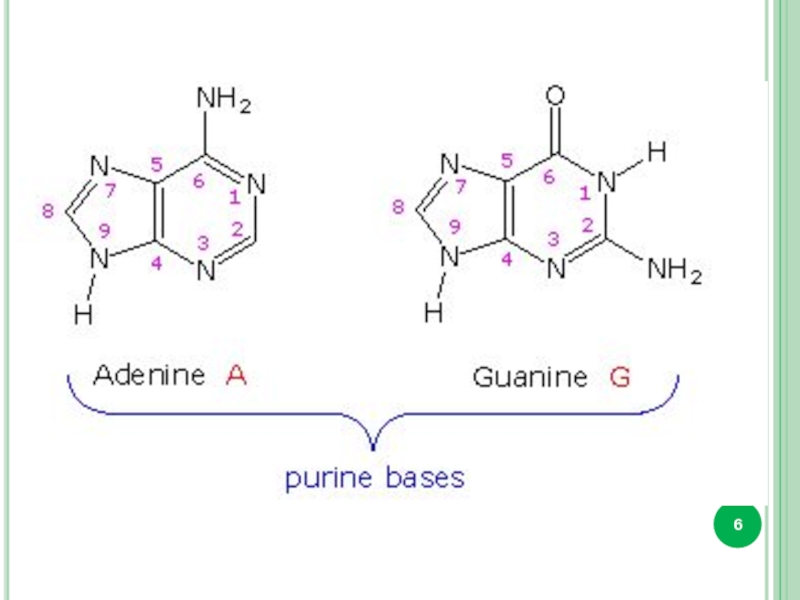
Pirimidine and purine bases.
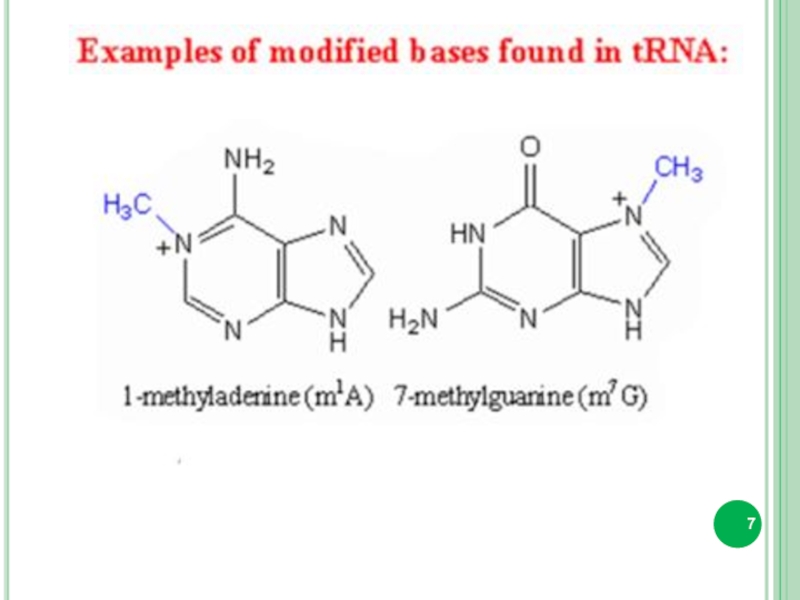
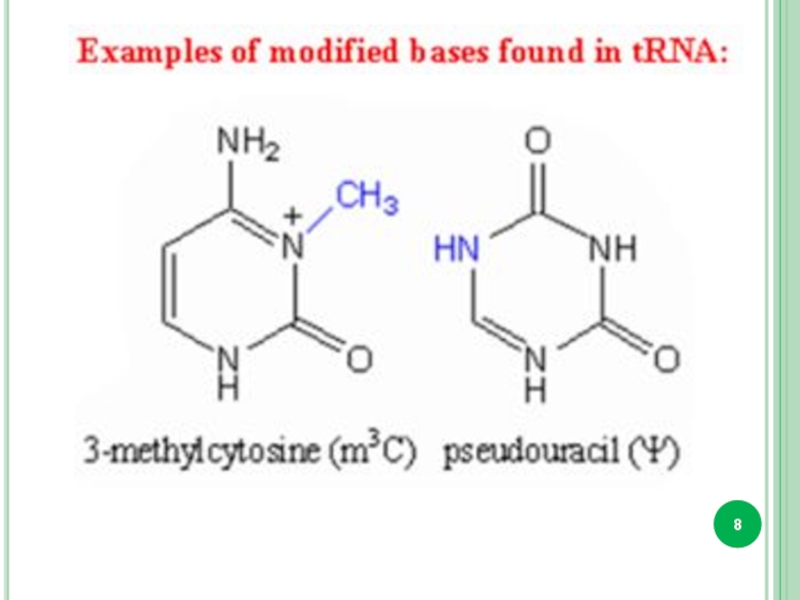
Minor bases.
Structure
Types of bonds in 2'-deoxycytidine-5'-diphosphate.
Watson-Crick model of a DNA.
Base pairing.
Chargaff principles.
Different levels of DNA structure.
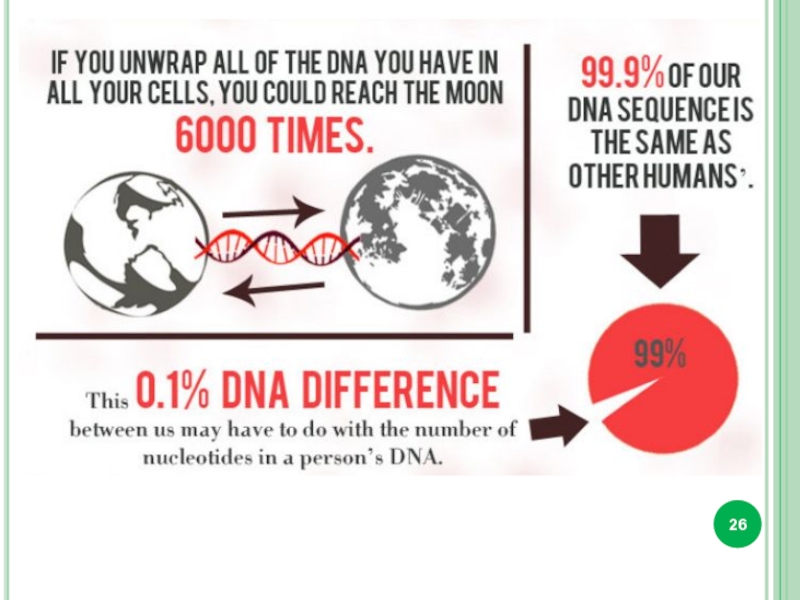
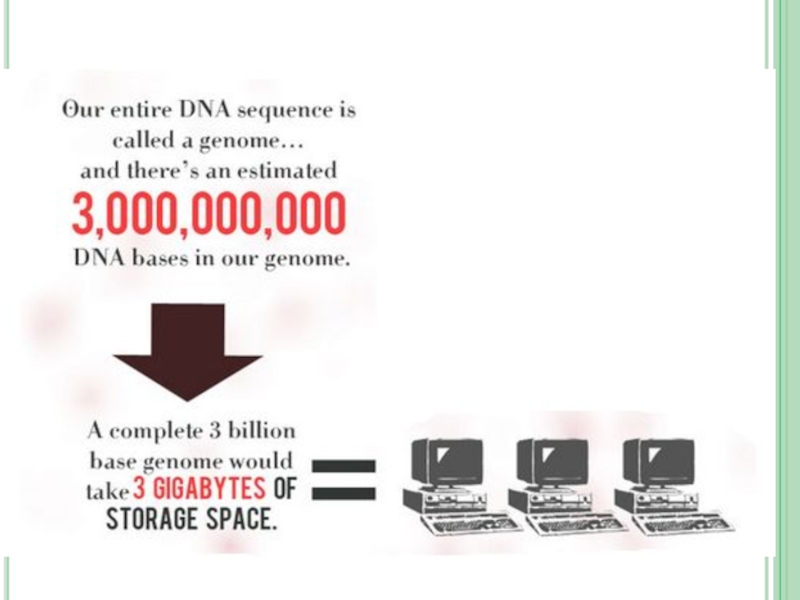
Interesting facts about DNA.
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide’s structure.
Bial’s test.
Mutations.
Antiviral drugs.
Слайд 3DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) was firstly isolated by the Swiss physician Friedrich
Actually it was Rosalind Franklin’s discovery (X-ray diffraction picture of structure of DNA) that led to Crick and Watson’s double helix model in 1953. She died from cancer at the age of 37 in 1958.
Professor Maurice Wilkins received the Nobel Prize with Crick and Watson for three-dimensional structure of DNA in 1962.
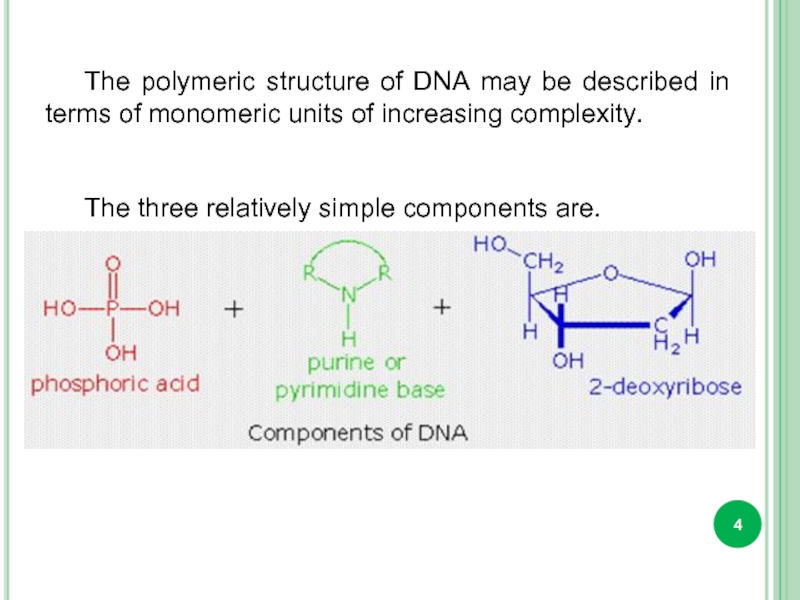
Слайд 4The polymeric structure of DNA may be described in terms of
The three relatively simple components are.
Слайд 9
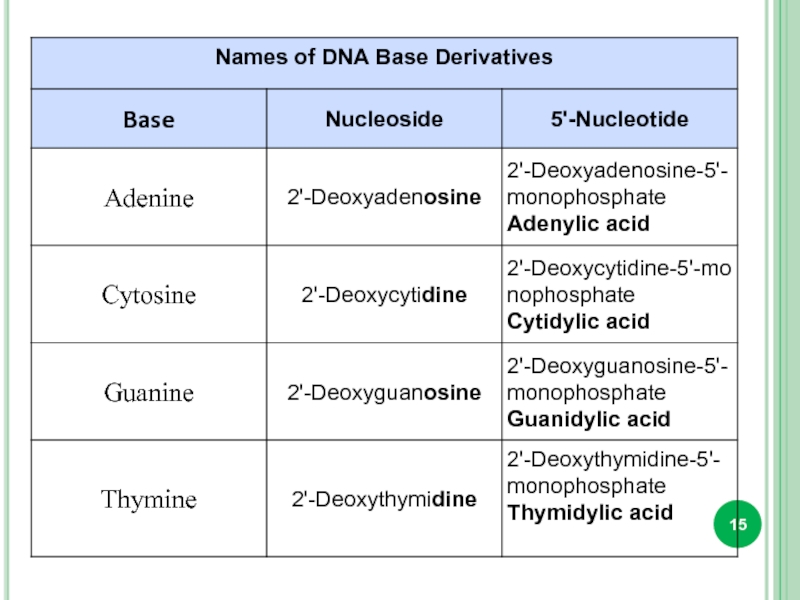
Bases attached to a sugar is called nucleoside.
Sugar + phosphate
nucleotide.
DNA only : Tymine, 2-deoxyribose
RNA only : Uracil, ribose
DNA and RNA : adenine, guanine, cytosine
Слайд 17RNA are easily hydrolyzed under mild alkaline conditions to nucleotides which
The secondary structure of DNA is determined by the spatial organization of the polynucleotide chain.
. The orientation of the heterocyclic base on each nucleotide residue is perpendicular to the axis of the double helix.
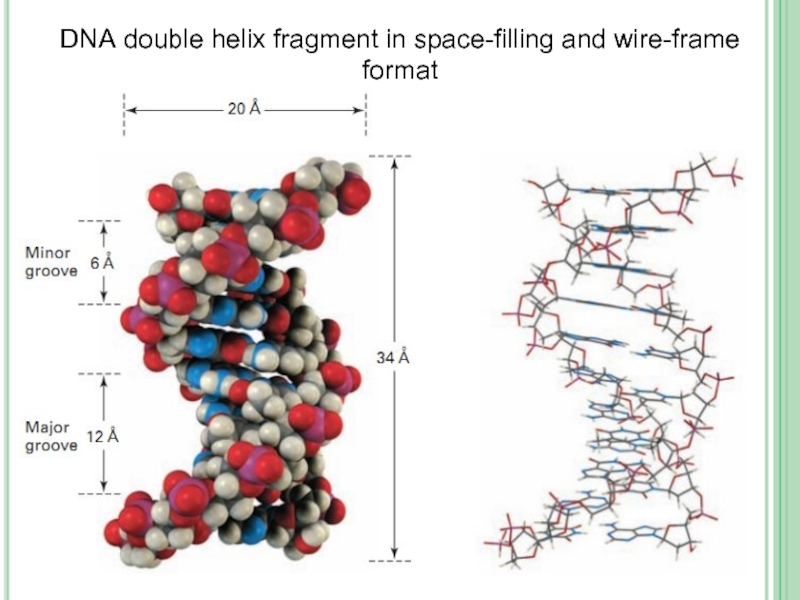
Слайд 19According to the Watson-Crick model of a DNA molecule consists of
The sugar– phosphate backbone runs along the outside of the helix, and the amine bases hydrogen bond to one another on the inside. Both major and minor grooves are visible.
Two polynucleotide strands are antiparallel to each other, so direction of phosphodiester formation is opposite: one chain is 5' - 3' end and the other of 3' – 5' end.
.
Слайд 23
A always pairs with T in DNA.
C also pairs with
The amount of A is equal to the amount of T, same for C and G.
A+C = T+G
Chargaff principles:
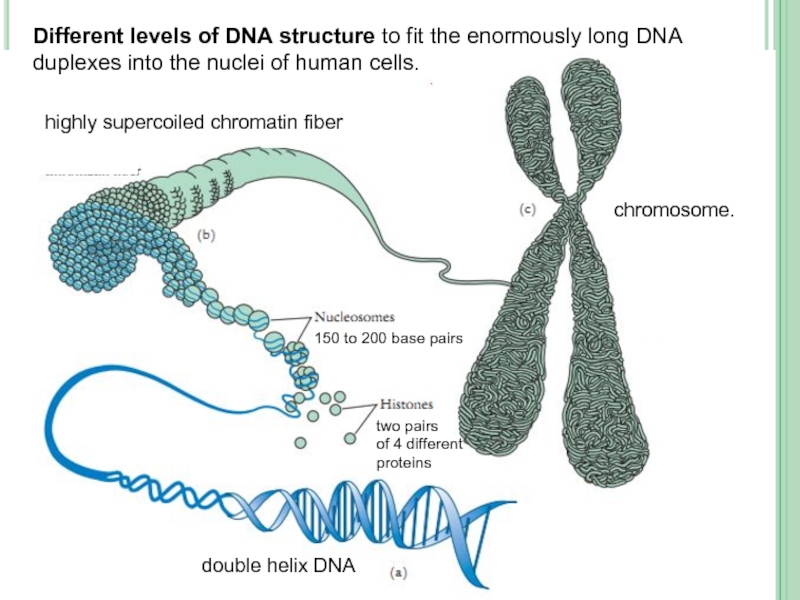
Слайд 24Different levels of DNA structure to fit the enormously long DNA
double helix DNA
highly supercoiled chromatin fiber
chromosome.
two pairs
of 4 different proteins
150 to 200 base pairs
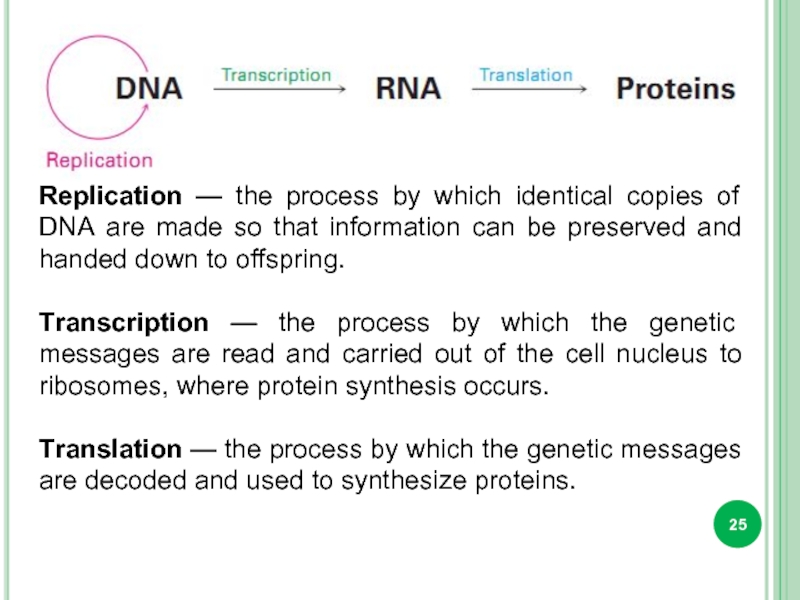
Слайд 25Replication — the process by which identical copies of DNA are
Transcription — the process by which the genetic messages are read and carried out of the cell nucleus to ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs.
Translation — the process by which the genetic messages are decoded and used to synthesize proteins.
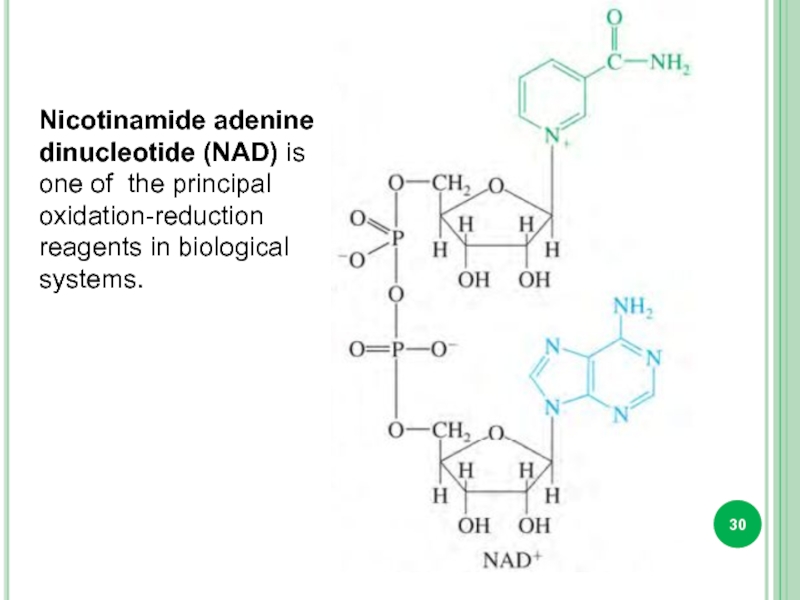
Слайд 30Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is one of the principal oxidation-reduction reagents
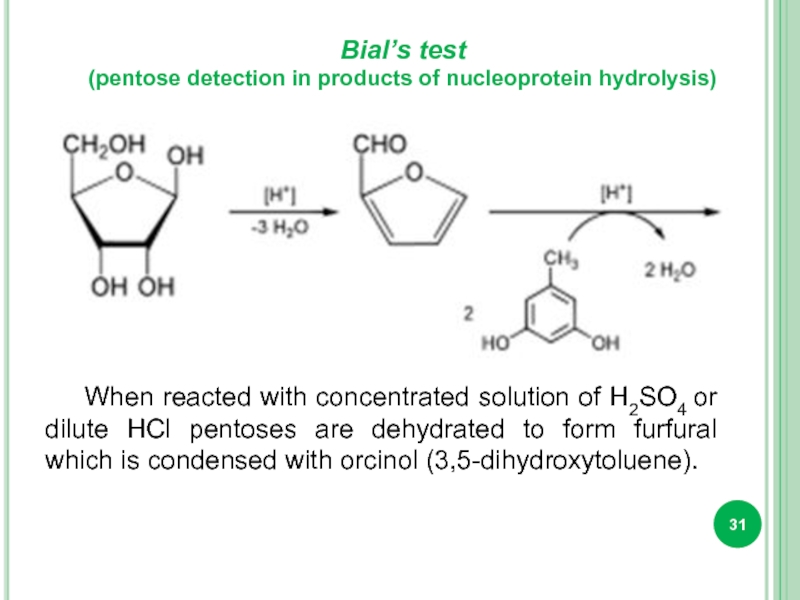
Слайд 31Bial’s test
(pentose detection in products of nucleoprotein hydrolysis)
When reacted with concentrated
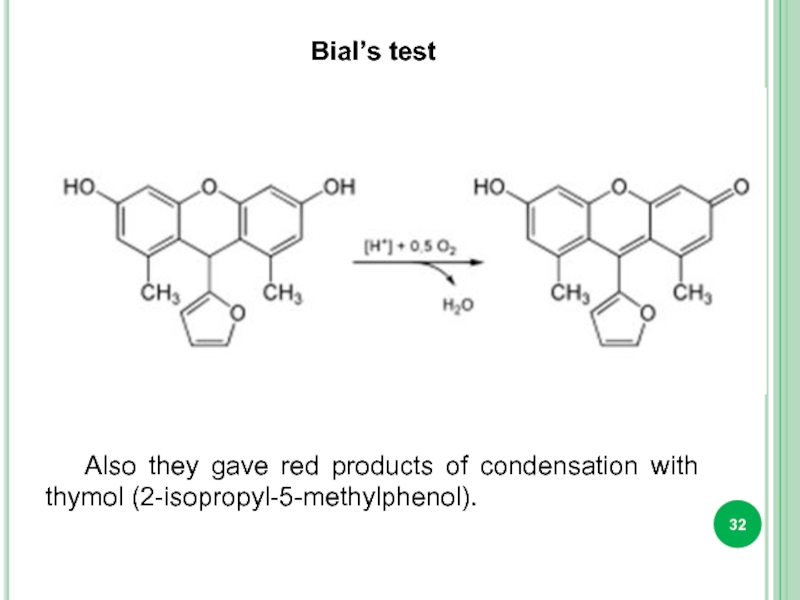
Слайд 32Bial’s test
Also they gave red products of condensation with thymol (2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol).
Слайд 33A mutation is an error in the base sequence of a
The end result can be the alteration or cessation of a polypeptide’s or protein’s functioning because of a change in its α-amino acid sequence.
There are two types of mutations:
• Substitution (point) mutations, in which one base substitutes for another in the normal base sequence: one purine for another, one pyrimidine for another, a purine for a pyrimidine, or a pyrimidine for a purine.
• Frameshift mutations, in which a base is inserted into the normal base sequence or is deleted from it.
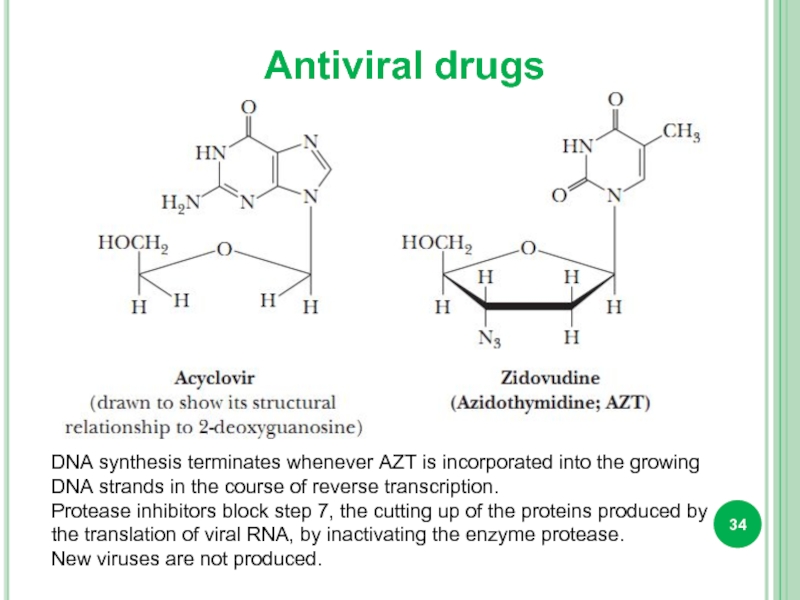
Слайд 34Antiviral drugs
DNA synthesis terminates whenever AZT is incorporated into the growing
Protease inhibitors block step 7, the cutting up of the proteins produced by the translation of viral RNA, by inactivating the enzyme protease.
New viruses are not produced.