- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Enterobacteriaceae (Gram negative rods enteric tract) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Enterobacteriaceae (Gram negative rods enteric tract)
- 2. Key Words Opportunistic diseases Shigella
- 3. septicemia, pneumonia, meningitis urinary tract
- 4. Enterobacteriaceae gastrointestinal diseases Escherichia coli
- 5. Histocompatibility antigen (HLA) B27
- 6. community acquired otherwise healthy
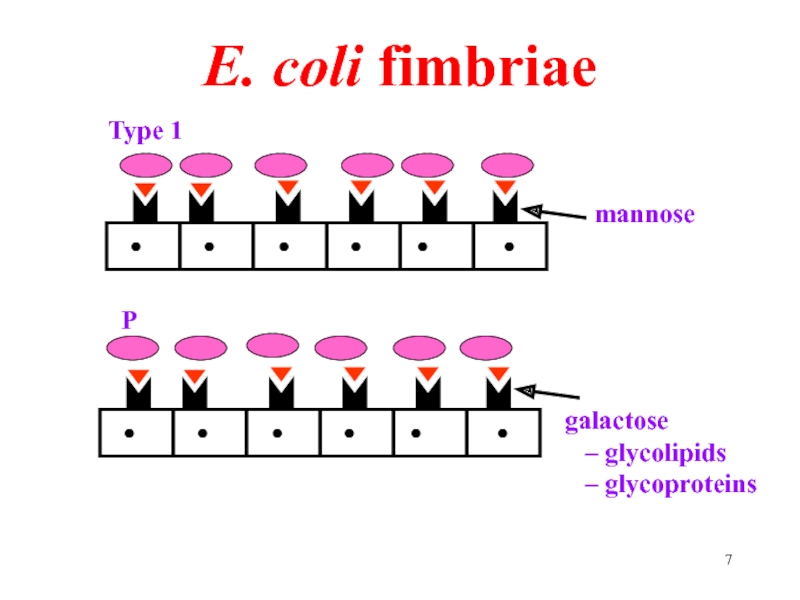
- 7. E. coli fimbriae mannose
- 8. Enterobacteriaceae gram negative facultative anaerobic rods – oxidase negative (no cytochrome oxidase)
- 9. E. coli lactose positive
- 10. other sites identified biochemically Enterobacteriaceae
- 11. Serotypes reference laboratory antigens O
- 12. Diarrhea (watery feces) and Dysentery (blood in stools)
- 13. Caption: E. coli Escherichia coli
- 14. E. coli and Shigella genetically very
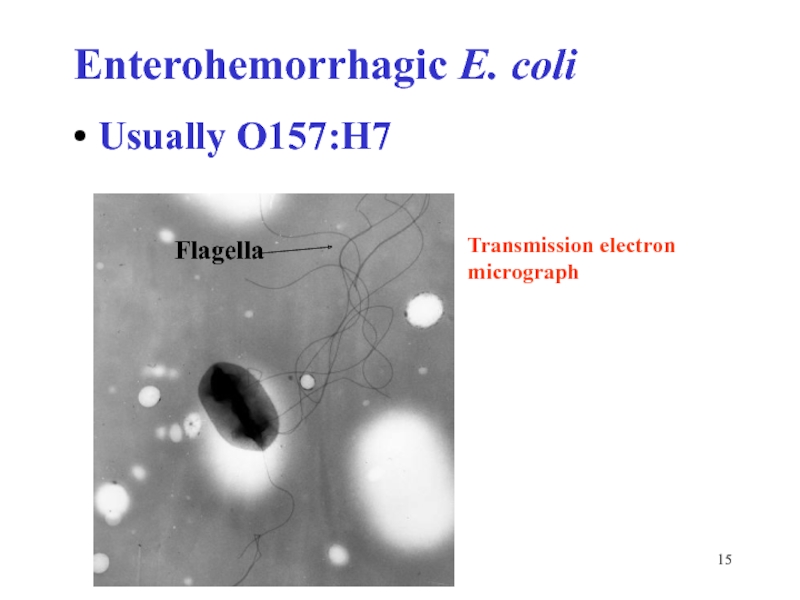
- 15. Enterohemorrhagic E. coli Usually O157:H7 Flagella
- 16. Transmission – meat products or sewage-contaminated vegetables
- 17. Vero toxin “shiga-like toxin” Hemolysins Enterohemorrhagic E. coli
- 18. Enterotoxigenic E. coli diarrhea
- 19. Enterotoxigenic E. coli Heat labile
- 20. Enteropathogenic E. coli destruction
- 21. Enteroaggregative Brick-like bacterial aggregates - cell
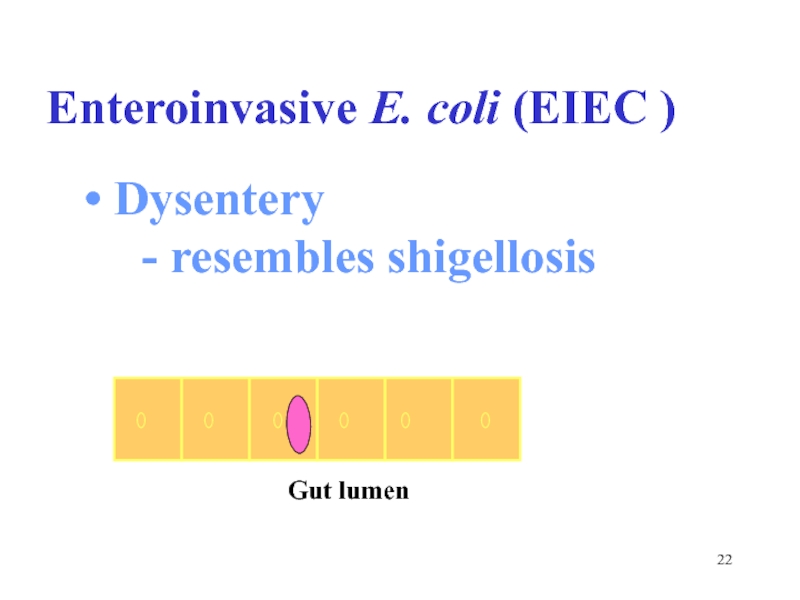
- 22. Dysentery - resembles shigellosis Enteroinvasive E. coli (EIEC ) Gut lumen
- 23. Treatment -gastrointestinal disease fluid replacement antibiotics
- 24. Shigella Modified from Fig, Dennis Kunkel
- 25. Shigella S. flexneri, S. boydii, S. sonnei,
- 26. Shigellosis within 2-3 days epithelial cell damage Gut lumen
- 27. Shiga toxin enterotoxic cytotoxic inhibits protein synthesis lysing 28S rRNA
- 28. Shigellosis man only "reservoir" mostly young children
- 29. Treating shigellosis manage dehydration patients respond to antibiotics disease duration diminished
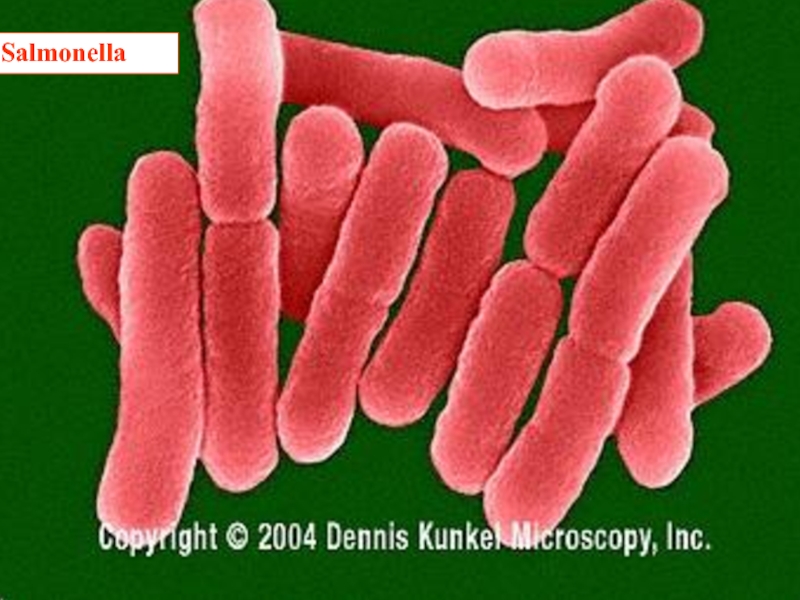
- 30. Salmonella
- 31. Salmonella 2000 antigenic "types” genetically single species
- 32. Salmonellosis S. enteritidis the common salmonella infection
- 33. Control of salmonellosis Monitoring of food in
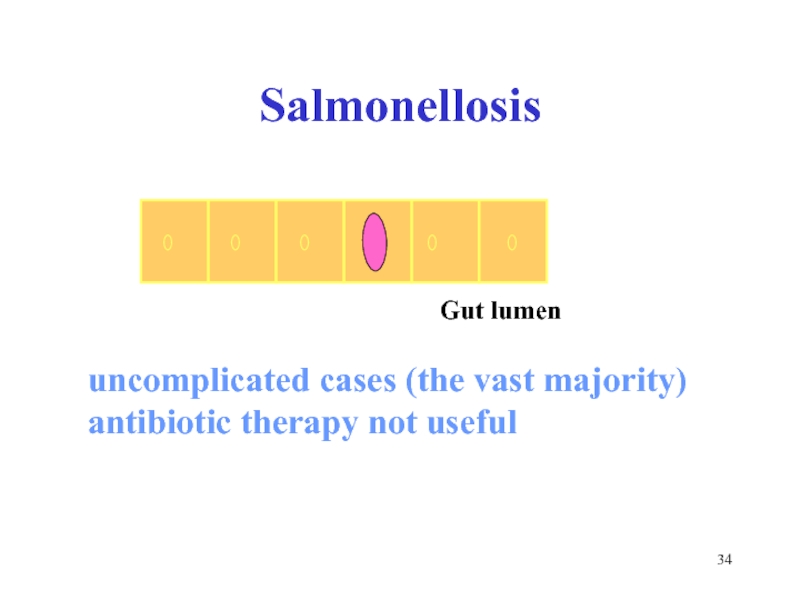
- 34. Salmonellosis uncomplicated cases (the
- 35. S. cholerae-suis much less common septicemia antibiotic therapy essential
Слайд 2Key Words
Opportunistic diseases Shigella
Diarrhea - Bacillary dysentery
Dysentery
- Shiga toxin
Urinary tract infections Salmonella enteritidis
Pili Salmonellosis
Lactose positive/negative Salmonella cholerae-suis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli Salmonella typhi
- Vero toxin (Shiga-like) - Typhoid
- Hemolysin - Vi
Enterotoxigenic E. coli Yersinia entercolitica
- Heat stable toxin Vibrio cholerae
- Heat labile toxin Choleragen (cholera toxin)
Enteropathogenic E. coli Campylobacter jejuni
Enteroaggregative E. coli Helicobacter pylori
Enteroinvasive E. coli
Urinary tract infections Salmonella enteritidis
Pili Salmonellosis
Lactose positive/negative Salmonella cholerae-suis
Enterohemorrhagic E. coli Salmonella typhi
- Vero toxin (Shiga-like) - Typhoid
- Hemolysin - Vi
Enterotoxigenic E. coli Yersinia entercolitica
- Heat stable toxin Vibrio cholerae
- Heat labile toxin Choleragen (cholera toxin)
Enteropathogenic E. coli Campylobacter jejuni
Enteroaggregative E. coli Helicobacter pylori
Enteroinvasive E. coli
Слайд 3septicemia,
pneumonia,
meningitis
urinary tract infections
Citrobacter Enterobacter
Escherichia
Hafnia
Morganella
Providencia
Serratia
Opportunistic diseases
-Enterobacteriaceae
Слайд 4Enterobacteriaceae
gastrointestinal diseases
Escherichia coli
Salmonella
Shigella
Yersinia entercolitica
Слайд 5
Histocompatibility antigen (HLA) B27
Enterobacteriaceae
Salmonella
Shigella
Yersinia
Non-Enterobacteriaceae
Campylobacter
Chlamydia
Reiter's syndrome
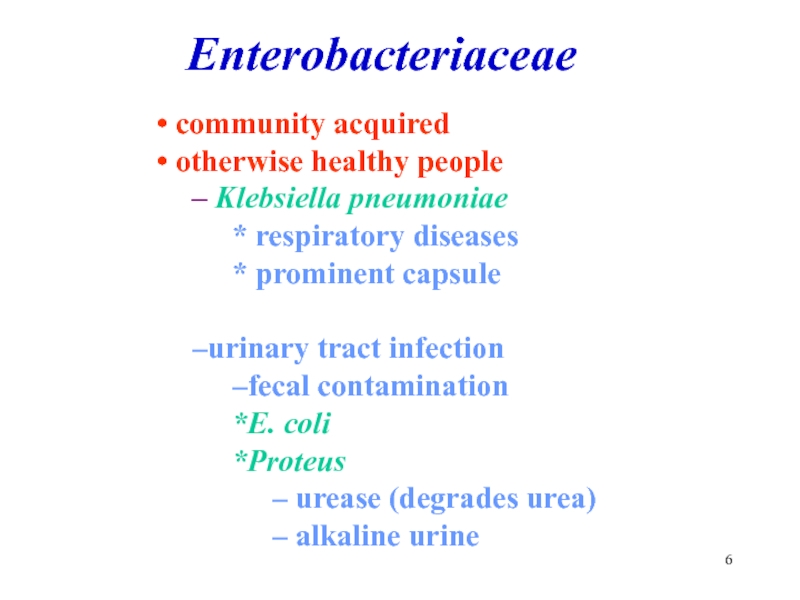
Слайд 6 community acquired
otherwise healthy people
Klebsiella pneumoniae
respiratory
diseases
prominent capsule
urinary tract infection
fecal contamination
E. coli
Proteus
urease (degrades urea)
alkaline urine
prominent capsule
urinary tract infection
fecal contamination
E. coli
Proteus
urease (degrades urea)
alkaline urine
Enterobacteriaceae
Слайд 8Enterobacteriaceae
gram negative facultative anaerobic rods
– oxidase negative (no cytochrome oxidase)
Слайд 9 E. coli
lactose positive
not usually identified
lactose
positive sp. common, healthy intestine
Shigella, Salmonella,Yersinia
lactose negative
identified
Shigella, Salmonella,Yersinia
lactose negative
identified
Feces
Слайд 14
E. coli and Shigella
genetically very similar
separated for historical reasons
overlap in
pathogenesis
Escherichia coli
Слайд 16Transmission – meat products or sewage-contaminated vegetables
Hemorrhagic
Bloody dysentery
copious
diarrhea
few leukocytes
afebrile
hemolytic-uremic syndrome
hemolytic anemia
thrombocytopenia (low platelets)
kidney failure
few leukocytes
afebrile
hemolytic-uremic syndrome
hemolytic anemia
thrombocytopenia (low platelets)
kidney failure
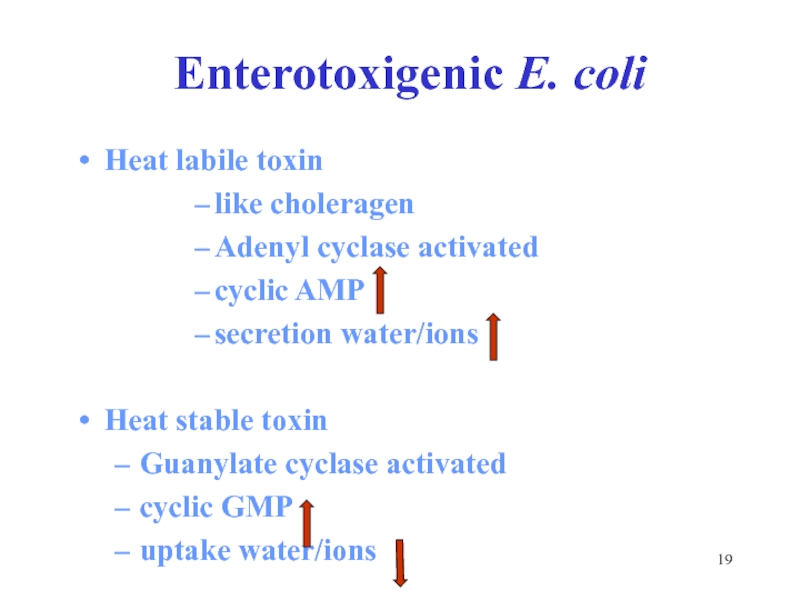
Слайд 19Enterotoxigenic E. coli
Heat labile toxin
like choleragen
Adenyl cyclase activated
cyclic AMP
secretion water/ions
Heat stable toxin
Guanylate cyclase activated
cyclic GMP
uptake water/ions
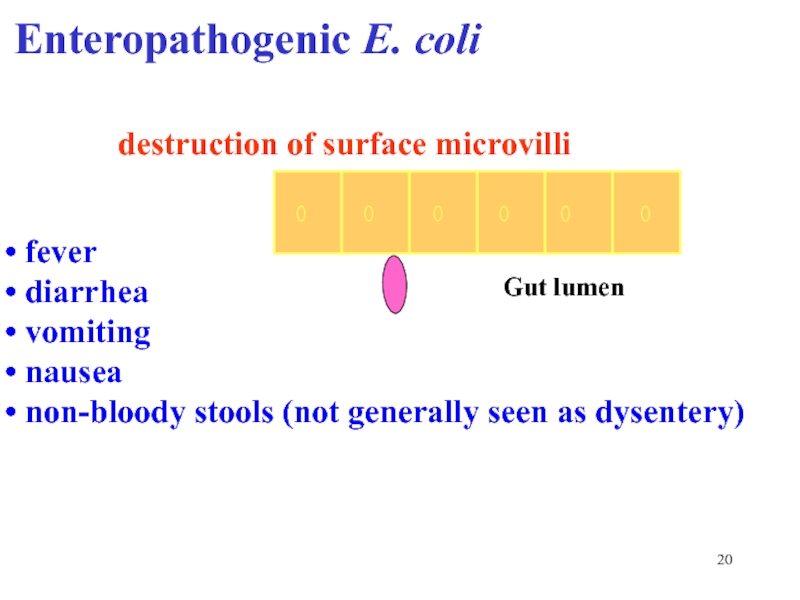
Слайд 20Enteropathogenic E. coli
destruction of surface microvilli
fever
diarrhea
vomiting
nausea
non-bloody stools (not generally seen as dysentery)
nausea
non-bloody stools (not generally seen as dysentery)
Gut lumen
Слайд 21Enteroaggregative
Brick-like bacterial aggregates - cell surfaces
Mucus biofilm inhibits fluid
absorption
Diarrhea
Diarrhea
Слайд 23Treatment -gastrointestinal disease
fluid replacement
antibiotics
not used usually unless systemic
e.g. hemolytic-uremia
syndrome
Слайд 25Shigella
S. flexneri, S. boydii, S. sonnei, S. dysenteriae
bacillary dysentery
shigellosis
bloody feces
intestinal
pain
pus
pus
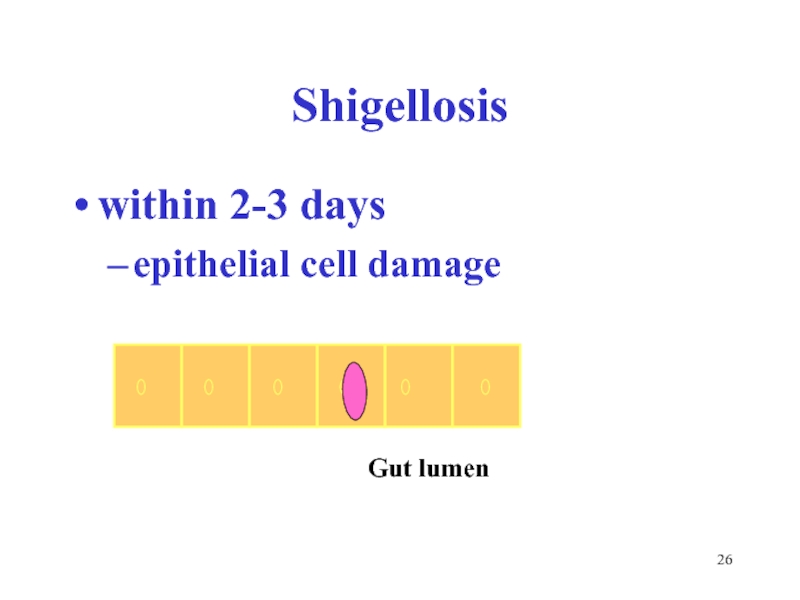
Слайд 28Shigellosis
man only "reservoir"
mostly young children
fecal to oral contact
children to adults
transmitted
by adult food handlers
unwashed hands
unwashed hands
Слайд 29Treating shigellosis
manage dehydration
patients respond to antibiotics
disease duration diminished
Слайд 31Salmonella
2000 antigenic "types”
genetically single species
S. enterica
disease category
S. enteritidis
many serotypes
S.
cholerae-suis
S. typhi
S. typhi
Слайд 32Salmonellosis
S. enteritidis
the common salmonella infection
poultry, eggs
no human reservoir
Gastroenteritis
nausea
vomiting
non-bloody
stool
self-limiting (2 - 5 days)
self-limiting (2 - 5 days)
Слайд 33Control of salmonellosis
Monitoring of food in the US is limited
microbiology is
difficult
Regulation is not optimal
Chickens are not vaccinated in US
UK, salmonellosis largely erradicated
Regulation is not optimal
Chickens are not vaccinated in US
UK, salmonellosis largely erradicated