- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Representing waves презентация
Содержание
- 1. Representing waves
- 2. Representing waves There are two ways we can represent a wave in a graph;
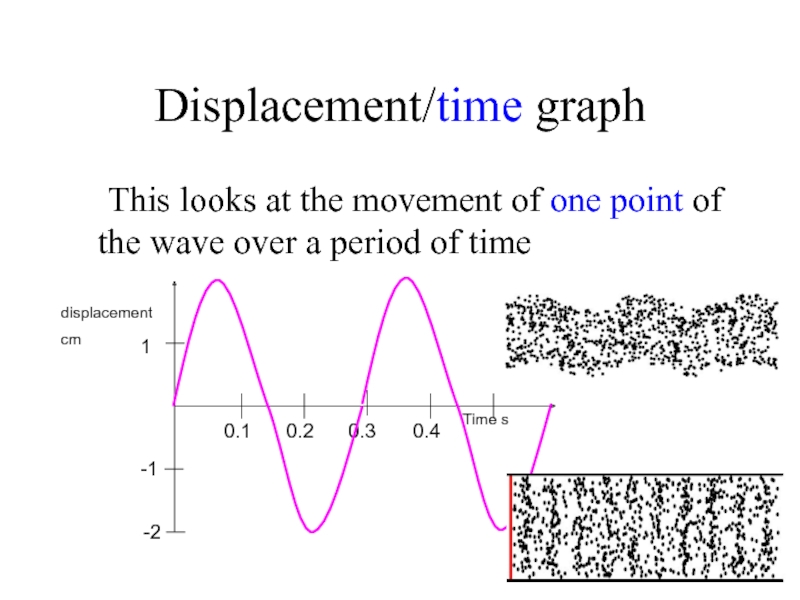
- 3. Displacement/time graph This looks at the movement
- 4. Displacement/time graph This looks at the movement
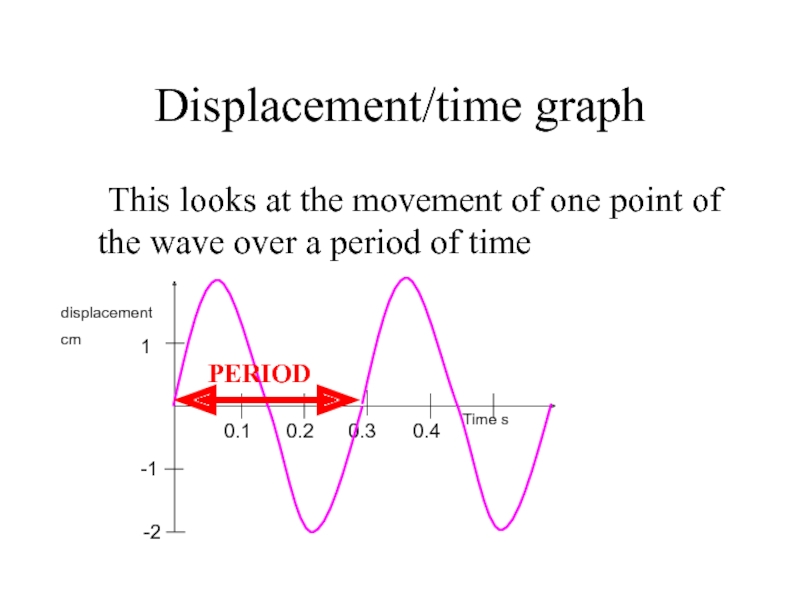
- 5. Displacement/time graph This looks at the movement
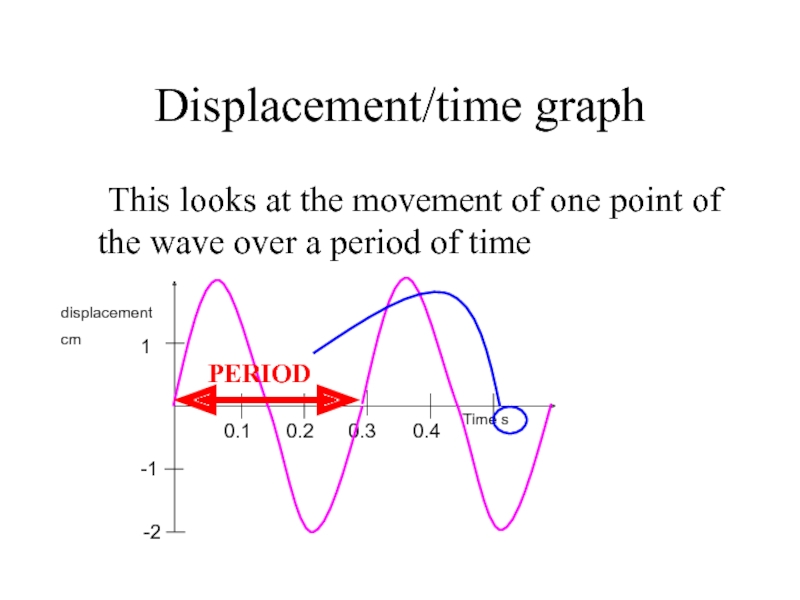
- 6. Displacement/time graph This looks at the movement
- 7. Displacement/distance graph This is a “snapshot” of
- 8. Displacement/distance graph This is a “snapshot” of
- 9. Displacement/distance graph This is a “snapshot” of
- 10. Displacement/distance graph This is a “snapshot” of
- 11. Wave intensity
- 12. Wave intensity This is defined as the
- 13. Wave intensity For example, imagine a window
- 14. Intensity at a distance from a light
- 15. Intensity at a distance from a light source I = P/4πd2 d
- 16. Sound intensity The lowest intensity that can
- 17. Intensity and amplitude
- 18. Intensity and amplitude The intensity of a
- 19. Intensity and amplitude This means if you
- 20. Surfers know this!
- 21. Let’s try some more questions!
Слайд 3Displacement/time graph
This looks at the movement of one point of the
1
Слайд 4Displacement/time graph
This looks at the movement of one point of the
1
PERIOD
Слайд 5Displacement/time graph
This looks at the movement of one point of the
1
PERIOD
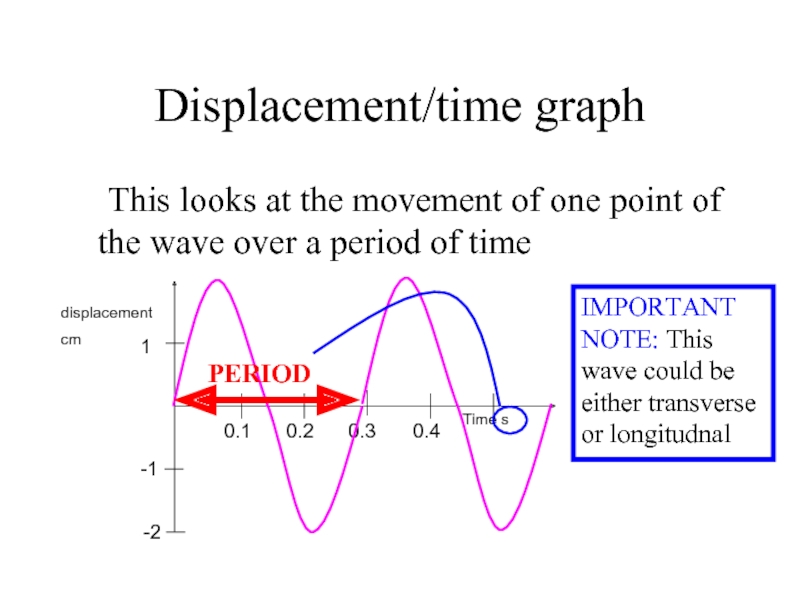
Слайд 6Displacement/time graph
This looks at the movement of one point of the
1
PERIOD
IMPORTANT NOTE: This wave could be either transverse or longitudnal
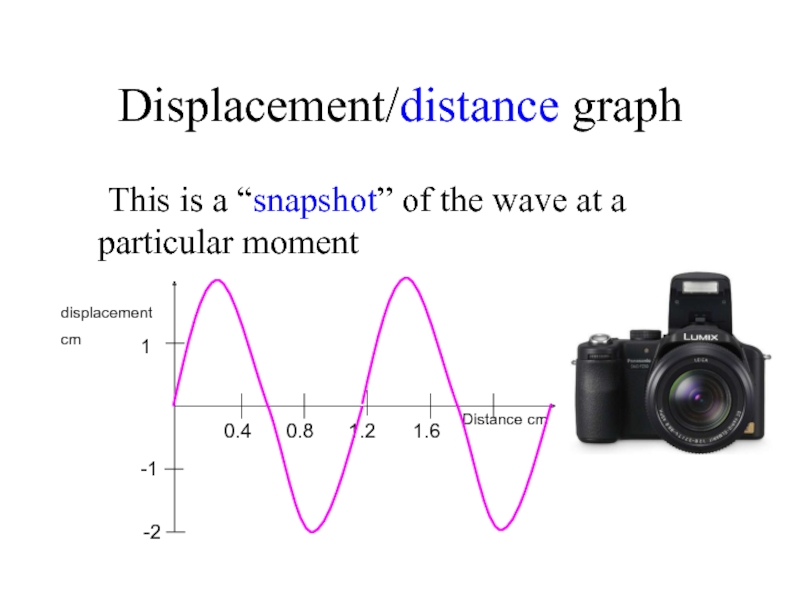
Слайд 7Displacement/distance graph
This is a “snapshot” of the wave at a particular
1
Distance cm
-1
-2
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
displacement
cm
Слайд 8Displacement/distance graph
This is a “snapshot” of the wave at a particular
1
Distance cm
-1
-2
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
displacement
cm
WAVELENGTH
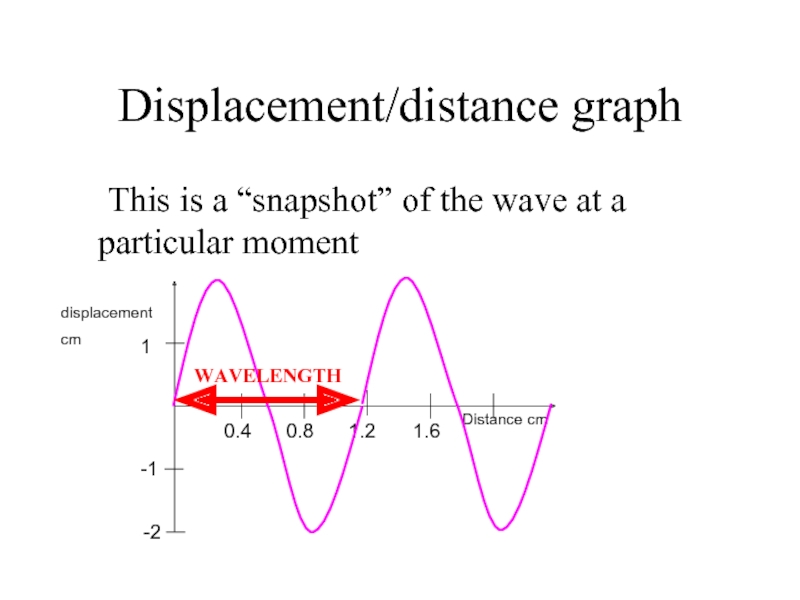
Слайд 9Displacement/distance graph
This is a “snapshot” of the wave at a particular
1
Distance cm
-1
-2
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
displacement
cm
WAVELENGTH
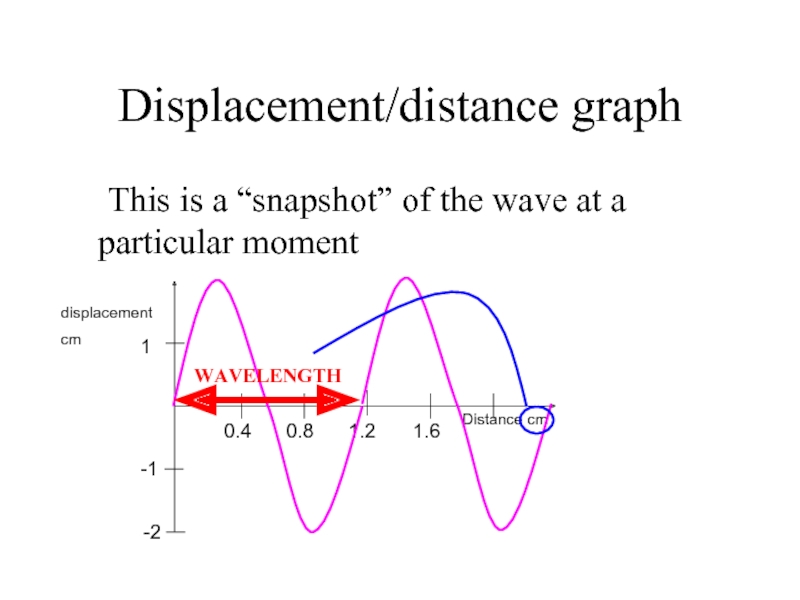
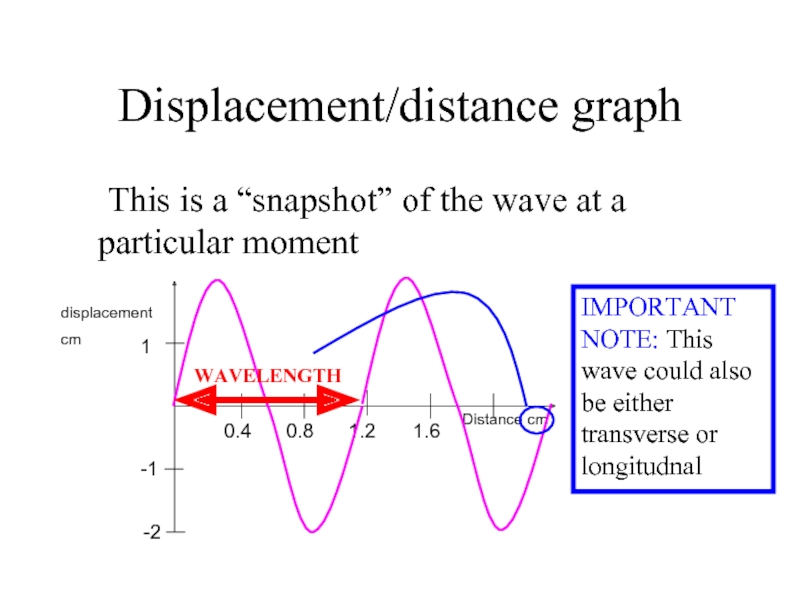
Слайд 10Displacement/distance graph
This is a “snapshot” of the wave at a particular
1
Distance cm
-1
-2
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
displacement
cm
WAVELENGTH
IMPORTANT NOTE: This wave could also be either transverse or longitudnal
Слайд 12Wave intensity
This is defined as the amount of energy per unit
It is normally measured in W.m-2
Слайд 13Wave intensity
For example, imagine a window with an area of 1m2.
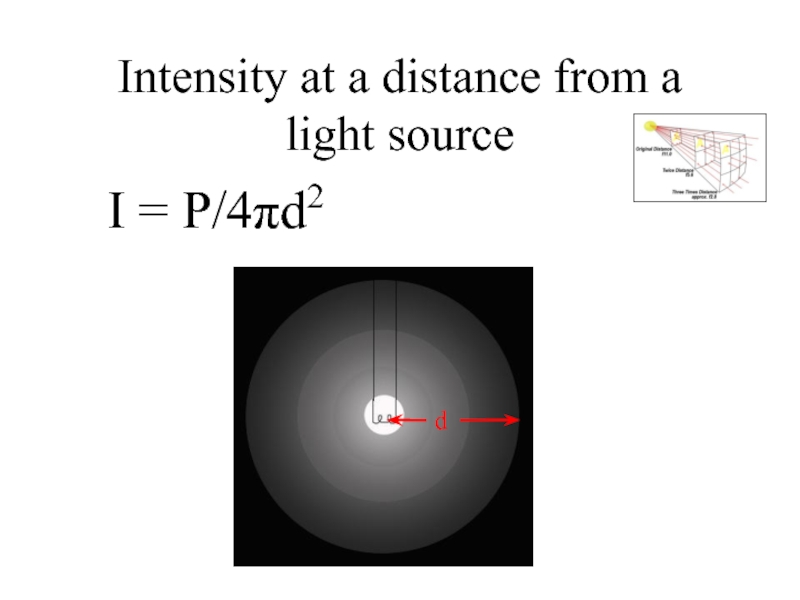
Слайд 14Intensity at a distance from a light source
I = P/4πd2
where d
Слайд 16Sound intensity
The lowest intensity that can normally be heard by a
This is a sound intensity level of 0 dB
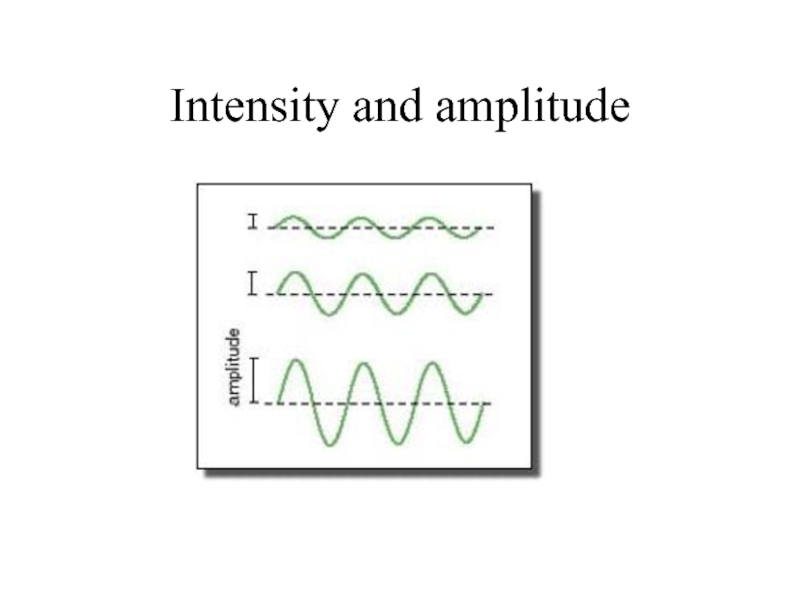
Слайд 18Intensity and amplitude
The intensity of a wave is proportional to the
I α a2
(or I = ka2)
Слайд 19Intensity and amplitude
This means if you double the amplitude of a
I = ka2
If amplitude = 2a,
new intensity = k(2a)2
new intensity = 4ka2