- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture 8. Fundamentals of english lexicography презентация
Содержание
- 1. Lecture 8. Fundamentals of english lexicography
- 2. Plan: Encyclopedic and linguistic dictionaries. Classification of
- 3. Dictionaries are like watches: the worst
- 4. 1. Encyclopedic and linguistic dictionaries. Classification of linguistic dictionaries
- 5. Lexicography: the science of dictionary compiling
- 6. Lexicography is closely connected with Lexicology
- 7. Dictionary: a wordbook with lists
- 8. There are about 250 different
- 9. In Great Britain Oxford Cambridge dictionaries
- 10. In Great Britain Longman Collins dictionaries
- 11. In Great Britain Chambers’ dictionaries Penguin dictionaries
- 12. In the USA Merriam-Webster's Funk and Wagnalls Co.
- 13. In the USA Random house dictionaries
- 14. According to the choice of items included
- 15. Linguistic dictionaries are word-books.
- 16. Encyclopedic dictionaries are thing-books that give
- 17. INFLUENZA in a linguistic dictionary: spelling
- 18. The Encyclopedia Britannica (24 volumes)
- 19. The Encyclopedia Americana (30 volumes)
- 20. Collier’s Encyclopedia (24 volumes)
- 21. Chamber’s Encyclopedia (15 volumes)
- 22. Everyman’s Encyclopedia (12 volumes)
- 23. Reference books: books confined for definite fields of knowledge
- 24. The Oxford Companion to English Literature
- 25. CAMBRIDGE PAPERBACK GUIDE TO LITERATURE IN ENGLISH
- 26. The Oxford Companion to American Theatre
- 27. Encyclopedic and linguistic dictionaries often overlap.
- 28. Linguistic Dictionaries: 1. nature of the word-list:
- 29. 2. the information provided: explanatory –
- 30. 3. the language: monolingual (information is given in the same language); bilingual.
- 31. No dictionary can be a
- 32. Characterization of a Dictionary: the nature
- 33. Main types of linguistic dictionaries
- 34. Explanatory Dictionaries: provide information
- 35. Synchronic: deal
- 36. Diachronic: concerned with the
- 37. Translation Dictionaries: word-books containing
- 38. Phraseological Dictionaries: have vast
- 39. New Words Dictionaries: reflect the growth of neologisms in the English language.
- 40. Dictionaries of Neologisms: A Dictionary of
- 41. Dictionaries of Slang: contain
- 42. Usage Dictionaries: investigate usage
- 43. Dictionaries of Word-frequency:
- 44. Reverse Dictionary: a list
- 45. Pronouncing Dictionaries: record contemporary
- 46. Etymological Dictionaries: trace present-day
- 47. Ideographic Dictionaries: contain words grouped
- 48. Dictionaries of Synonyms: A Dictionary of
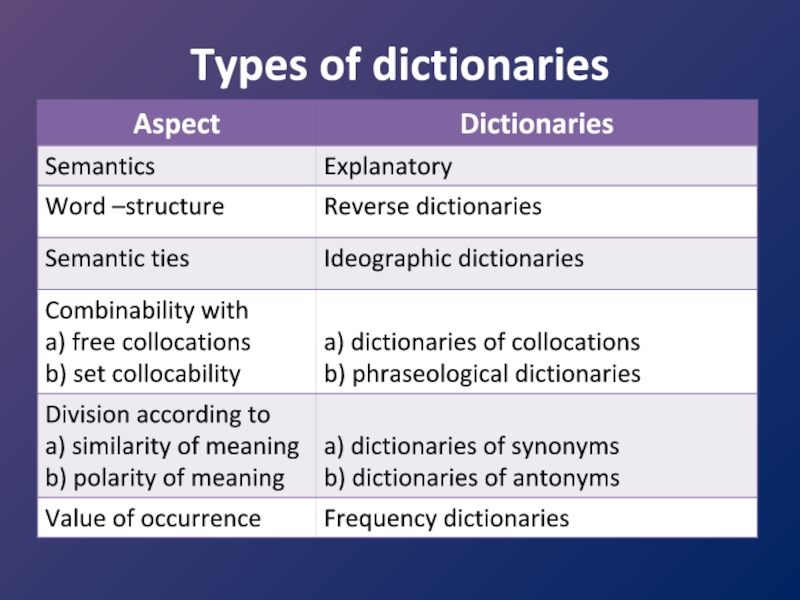
- 49. Types of dictionaries
- 50. 2. Basic problems of dictionary-compiling
- 51. Some basic problems of dictionary-compiling 1. Selection
- 52. 1. Selection of Lexical Units
- 53. No dictionary of any size can register all lexical units.
- 54. The Choice of Lexical Units Depends upon:
- 55. A Dictionary Compiler Chooses: the type of
- 56. 2. Arrangement of Entries
- 57. Types of Arrangement: 1) alphabetical: the basic
- 58. Run-outs – in the
- 59. Advantage: easy finding of any
- 60. Types of Arrangement: 2) cluster type: words
- 61. 3. Selection and Arrangement of Meanings
- 62. The number of meanings and their choice
- 63. Diachronic dictionaries list more meanings than synchronic dictionaries.
- 64. 3 ways of meaning arrangement:
- 65. 4. Definition of Meanings
- 66. Types of definitions: encyclopedic definition – determine
- 67. Types of definitions: synonymous words and expressions
- 68. 5. Illustrative Examples
- 69. Diachronic dictionaries: quotations
- 70. 6. Choice of Adequate Equivalents
- 71. It is one of the major problems in compiling translation dictionaries.
- 72. The dictionary-maker is
- 73. 7. Setting of the Entry
- 74. Explanatory Dictionaries of Synchronic Type Contain:
- 75. modern currency illustrative examples derivatives phraseology etymology synonyms and antonyms
- 76. Explanatory Dictionaries of Diachronic Type Include: chronological
- 77. 8. Structure of the Dictionary
- 78. Parts of a dictionary: introduction or preface
- 79. dictionary itself; addendum (usually contains a
- 80. 3. Learner’s dictionaries and some problems of their compilation
- 81. Learner’s Dictionaries: specially compiled dictionaries to meet
- 83. Features: a strictly limited word-list; a great
- 84. Problems of The Compilation the selection of
- 85. 2. the arrangement of meanings the actual
- 86. 3. the definition of meanings descriptive
- 87. 4. setting of the entry
- 88. 5. the supplementary lists of
- 89. List of Literature: Воробей, А. Н.
Слайд 2Plan:
Encyclopedic and linguistic dictionaries. Classification of linguistic dictionaries.
Basic problems of
Learner's dictionaries and some problems of their compilation.
Слайд 3
Dictionaries are like watches: the worst is better than none and
Samuel L. Johnson
Слайд 6Lexicography is closely connected with Lexicology The object of lexicography and lexicology:
The material collected in dictionaries is widely used by linguists in their research.
The principles of dictionary making are always based on linguistic fundamentals.
Слайд 7Dictionary:
a wordbook with lists of vocabulary units and their
Слайд 14According to the choice of items included and the sort of
Encyclopedic dictionaries
Linguistic dictionaries
Слайд 15
Linguistic dictionaries are word-books.
Subject matter: lexical units and
Слайд 16
Encyclopedic dictionaries are thing-books that give information about the extra-linguistic world.
Слайд 17INFLUENZA
in a linguistic dictionary:
spelling
pronunciation
grammar characteristics
synonyms, etc.
in an encyclopedic dictionary:
the causes
symptoms
characteristics and varieties of this disease
treatment, etc.
Слайд 28Linguistic Dictionaries:
1. nature of the word-list:
general – contain lexical units in
restricted – contain lexical units from a certain part of the word-stock (terminological, phraseological, dialectal, etc.).
Слайд 29
2. the information provided:
explanatory – present a wide range of data,
specialized – deal with lexical units only in relation to their etymology or frequency or pronunciation.
Слайд 31
No dictionary can be a general-purpose word-book. Each is designed
Слайд 32Characterization of a Dictionary:
the nature of the word-list;
the information supplied;
the
the prospective user.
Слайд 34Explanatory Dictionaries:
provide information on all aspects of the
Слайд 35
Synchronic: deal with the form, usage and
Concise Oxford Dictionary of Current English;
Universal Dictionary of the English Language.
Слайд 36
Diachronic: concerned with the development of words occurring within
New English Dictionary on Historical Principles;
The Shorter Oxford Dictionary on Historical Principles.
Слайд 37Translation Dictionaries:
word-books containing vocabulary items in one language
New E.-R. Dictionary by Prof. I.R. Galperin;
The E.-R. Dictionary by Prof. V.K. Muller;
The E.-R. Dictionary under Prof. A.I. Smirnitsky.
Слайд 38Phraseological Dictionaries:
have vast collections of idiomatic or colloquial
An E.-R. Phraseological Dictionary by A.V. Kunin
Слайд 40Dictionaries of Neologisms:
A Dictionary of new English. A Barnhart Dictionary
The Longman Register of New Words (1990);
Bloomsbury Dictionary of New Words (1996);
Beyond the Dictionary by Brian Locket (1998).
Слайд 41Dictionaries of Slang:
contain elements from areas of substandard
Dictionary of Slang and Unconventional English by E. Partridge;
The Dictionary of American Slang by H. Wentworth and S.B. Flexner.
Слайд 42Usage Dictionaries:
investigate usage problems of all kinds:
the
give the proper pronunciation of words;
give the plural forms.
Dictionary of Modern English Usage by N.W. Fowler.
Слайд 43Dictionaries of
Word-frequency:
inform the user about the frequency
Слайд 44Reverse Dictionary:
a list of words in which the
Rhyming Dictionary of the English Language by John Walker.
Слайд 45Pronouncing Dictionaries:
record contemporary pronunciation, indicate various pronunciations.
English Pronouncing
Слайд 46Etymological Dictionaries:
trace present-day words to the oldest forms
Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology by C.T. Onions
Слайд 47Ideographic Dictionaries:
contain words grouped by the concepts.
Thesaurus of English
Слайд 48Dictionaries of Synonyms:
A Dictionary of English Synonyms and Synonymous Expressions
Webster’s Dictionary of Synonyms;
The best known bilingual dictionary of synonyms is English Synonyms compiled by Y. Apresyan.
Слайд 51Some basic problems of dictionary-compiling
1. Selection of lexical units
2. Arrangement
3. Selection and arrangement of meanings
4. Definition of meanings
5. Illustrative examples
6. Choice of adequate equivalents
7. Setting of the entry
8. Structure of the dictionary
Слайд 54The Choice of Lexical Units Depends upon:
the type of the
the aim of the compiler;
the user of the dictionary.
Слайд 55A Dictionary Compiler Chooses:
the type of lexical units;
the number of items;
what
Слайд 57Types of Arrangement:
1) alphabetical: the basic units are given as main
Слайд 58
Run-outs – in the same entry
despicable, adj. Vile, contemptible
Subentry – includes definitions
despicable adj. that is or should be despised; contemptible. despicably, adv. in a despicable manner.
Слайд 60Types of Arrangement:
2) cluster type: words are arranged in nests, based
Advantage: it requires less space and presents a clear picture of the relations of this unit with other words.
Слайд 62The number of meanings and their choice depend on:
the aim of
their decisions about archaic, dialectical words, etc.
Слайд 643 ways of meaning arrangement:
in the sequence of
frequency of use (empirical or actual order);
logical connection (logical order).
Слайд 66Types of definitions:
encyclopedic definition – determine not only the word-meaning, but
descriptive definitions or paraphrases – determine only the word-meaning;
Слайд 67Types of definitions:
synonymous words and expressions – consist of words or
by means of cross-references.
decrescendo = diminuendo
waggle = wiggle
Слайд 69
Diachronic dictionaries: quotations are drawn from literary sources.
Synchronic: from classical or contemporary sources.
Слайд 72
The dictionary-maker is to give the most exact
When there is no equivalent
by means of a descriptive explanation or transliteration.
Слайд 74Explanatory Dictionaries of Synchronic Type Contain:
accepted spelling and pronunciation;
grammatical characteristics
definitions of meanings;
Слайд 76Explanatory Dictionaries of Diachronic Type Include:
chronological arrangement of entries
the etymology of
the dates which indicate the time of the 1st registration of the word or its last registration
Слайд 78Parts of a dictionary:
introduction or preface (some separate sections designed to
Слайд 79
dictionary itself;
addendum (usually contains a key to pronunciation, the list of
Слайд 81Learner’s Dictionaries:
specially compiled dictionaries to meet the demands of the learners
Слайд 83Features:
a strictly limited word-list;
a great attention to the functioning of lexical
a strong normative character of the lexical units included;
their compilation is focused on the native linguistic background of the user.
Слайд 84Problems of The Compilation
the selection of entry words
information of currently
no archaic, dialectal words;
only the most accepted pronunciation forms;
words are chosen on the frequency principle.
Слайд 852. the arrangement of meanings
the actual order (the main meanings before
literal uses before special,
easily understandable uses before difficult.
Слайд 863. the definition of meanings
descriptive definitions are mostly used;
encyclopedic
definitions are in simple terms.
Слайд 885. the supplementary
lists of irregular verbs, common abbreviations, geographical
common forenames,
numerical expressions,
the works of William Shakespeare, etc.
Слайд 89List of Literature:
Воробей, А. Н. Глоссарий лингвистических терминов / А.
Дубенец, Э. М. Современный английский язык. Лексикология : пособие для студ. гуманит. вузов / Э. М. Дубенец. – М. / СПб. : ГЛОССА / КАРО, 2004. – C. 179–184.
Лексикология английского языка : учебник для ин-тов и фак-тов иностр. яз. / Р. З. Гинзбург [и др.] ; под общ. ред. Р. З. Гинзбург. – 2-е изд., испр. и доп. – М. : Высш. школа, 1979. – C. 210–233.
Лещева, Л. М. Слова в английском языке. Курс лексикологии современного английского языка : учебник для студ. фак-в и отдел. английского языка (на англ. яз.) / Л. М. Лещева. – Минск : Академия управления при Президенте Республики Беларусь, 2001. – C. 136–153.