- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Кср 2. Methods of lexicological analysis презентация
Содержание
- 1. Кср 2. Methods of lexicological analysis
- 2. Plan: Contrastive Analysis. Statistical Analysis. Immediate Constituents
- 3. List of Terms: contrastive analysis statistical analysis
- 4. The process of scientific investigation may be
- 5. Example: English nouns -er is added
- 6. 3. generalisation (the formulation of a hypothesis, rule, or law)
- 7. Example: The rule:
- 8. 4. verification (to seek evidence of
- 9. Various methods of lexicological research are used
- 10. The selection of this
- 11. Contrastive analysis
- 12. Comparative linguistics investigates those elements and
- 13. The aim of the contrastive analysis:
- 14. Contrastive analysis can be carried out at
- 15. Contrastive analysis is the
- 16. новости, деньги, волосы
- 17. Contrastive analysis is
- 18. Watch, clock and часы Head: the
- 19. Statistical methods of analysis
- 20. The aim of the statistical analysis: the
- 21. Statistical regularities can be
- 22. Immediate Constituents analysis
- 23. The theory of Immediate
- 24. The aim of the Immediate Constituents analysis:
- 25. Friendliness: 1. is divided into the component
- 26. The aim of the Immediate Constituents analysis:
- 27. a black dress in severe style
- 28. Immediate Constituents analysis depends on the
- 29. Distributional Analysis
- 30. Distribution: the position which linguistic units may
- 31. The aim of the distributional analysis: the
- 32. The word has different meanings
- 33. The boy__________ home. the missing
- 34. Transformational Analysis
- 35. Transformational analysis: repatterning (reorganization) of identical
- 36. Example of transformation: his work is excellent
- 37. The aim of the transformational analysis: to
- 38. Componential Analysis
- 39. In the componential analysis
- 40. man can be described as [+HUMAN]
- 41. It helps to find
- 42. List of Literature: Воробей, А. Н.
Слайд 2Plan:
Contrastive Analysis.
Statistical Analysis.
Immediate Constituents Analysis.
Distributional Analysis.
Transformational Analysis.
Componential Analysis.
Слайд 3List of Terms:
contrastive analysis
statistical analysis
immediate constituents analysis
distributional analysis
transformational analysis
componential
Слайд 4The process of scientific investigation may be subdivided into several stages:
1.
2. classification (orderly arrangement of the data obtained through observation)
Слайд 5Example:
English nouns
-er is added to verbal stems (speak + -er),
the same morpheme in mother, father. But they haven’t a suffix
-er can be found in derived and non-derived words
Слайд 7Example:
The rule:
derived nouns in -er may
The suffix -er in combination with adjectival or adverbial stems cannot form nouns (bigger, longer are not nouns).
Слайд 8
4. verification (to seek evidence of the correctness of the generalizations
Слайд 9Various methods of lexicological research are used for classification, generalization and
1. Contrastive analysis.
2. Statistical methods of analysis.
3. Immediate Constituents analysis.
4. Distributional analysis.
5. Transformational analysis.
6. Componential analysis.
Слайд 10
The selection of this or that particular method largely
Слайд 12
Comparative linguistics investigates those elements and processes despite their surface diversity
Contrastive linguistics attempts to find out similarities and differences in both related and non-related languages.
Слайд 13The aim of the contrastive analysis:
a detailed comparison of the
Слайд 14Contrastive analysis can be carried out at three linguistic levels:
phonology
grammar (morphology and syntax)
lexis (vocabulary)
Слайд 15
Contrastive analysis is the basis of teaching foreign languages:
Слайд 17
Contrastive analysis is generally applied to reveal the
Слайд 18
Watch, clock and часы
Head: the head of a person, bed or
Слайд 20The aim of the statistical analysis:
the quantitative evaluation of the material
the selection of vocabulary items of a foreign language for teaching purposes
Слайд 21
Statistical regularities can be observed only if the phenomena
Слайд 23
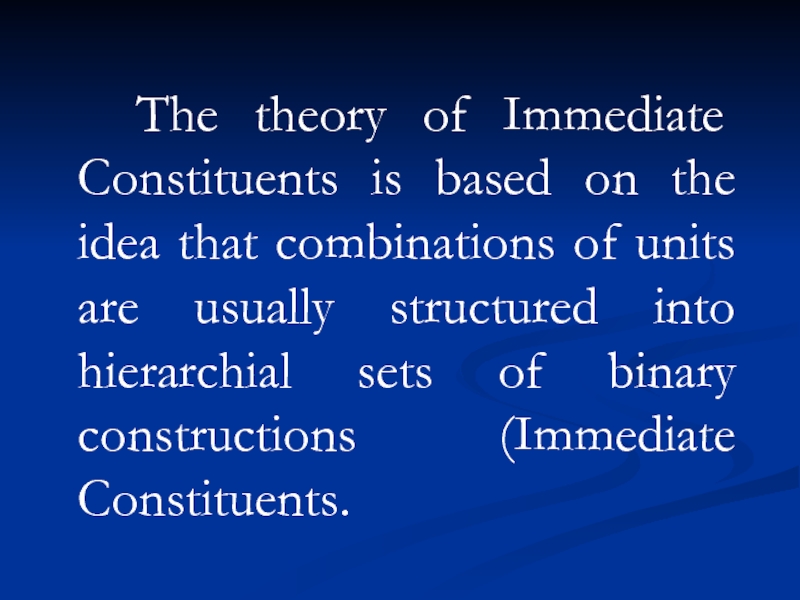
The theory of Immediate Constituents is based on the
Слайд 24The aim of the Immediate Constituents analysis:
1. to find out the
Слайд 25Friendliness:
1. is divided into the component friendly-, occurring in such words
2. is divided into friend- and -ly which are ultimate constituents (cannot be divided into smaller meaningful units).
Слайд 26The aim of the Immediate Constituents analysis:
2. to determine the ways
Слайд 27a black dress in severe style
a black
a + black + dress|in + severe + style
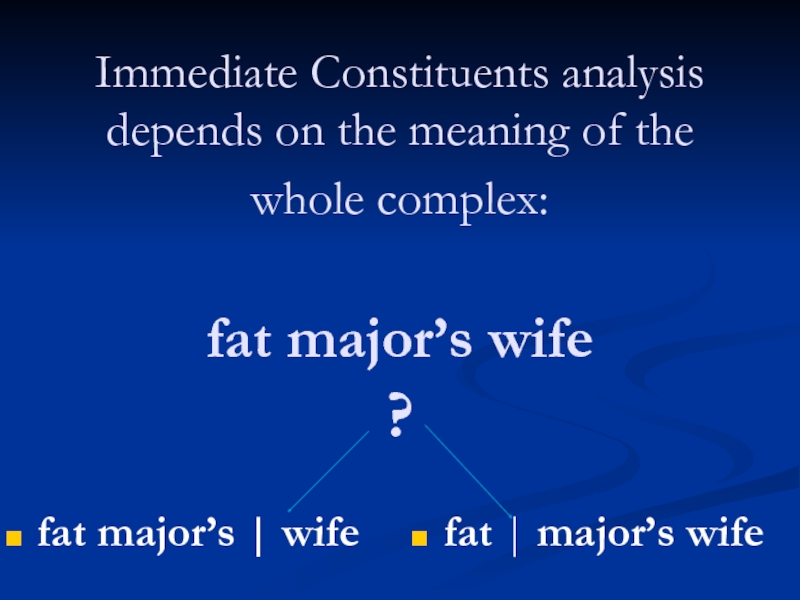
Слайд 28 Immediate Constituents analysis depends on the meaning of the whole complex:
fat major’s | wife
fat | major’s wife
Слайд 30Distribution:
the position which linguistic units may occupy in the flow of
Слайд 31The aim of the distributional analysis:
the investigation of sameness / difference
the analysis of word-formation.
Слайд 32
The word has different meanings in different patterns:
to treat
to treat smb to ice-cream (treat + N + to + N) – to supply with smth at one’s own expense.
Слайд 33The boy__________ home.
the missing word is easily identified as
Слайд 35Transformational analysis:
repatterning (reorganization) of identical distributional structures in order to
Слайд 36Example of transformation:
his work is excellent –
his excellent work –
the excellence of his work –
he works excellently
Слайд 37The aim of the transformational analysis:
to investigate polysemantic patterns (e.g. compounds
Слайд 39
In the componential analysis linguists proceed from the assumption
Слайд 40
man can be described as [+HUMAN] [+ADULT] [+MALE]
boy as [+HUMAN] [–ADULT]
woman as [+HUMAN] [+ADULT] and
[–MALE]
girl as [+HUMAN] [–ADULT] and
[– MALE].
Слайд 41
It helps to find out which of the meanings
Слайд 42List of Literature:
Воробей, А. Н. Глоссарий лингвистических терминов / А.
Лексикология английского языка : учебник для ин-тов и фак-тов иностр. яз. / Р. З. Гинзбург [и др.] ; под общ. ред. Р. З. Гинзбург. – 2-е изд., испр. и доп. – М. : Высш. школа, 1979. – С. 234–261.
Лещева, Л. М. Слова в английском языке. Курс лексикологии современного английского языка : учебник для студ. фак-в и отдел. английского языка (на англ. яз.) / Л. М. Лещева. – Минск : Академия управления при Президенте Республики Беларусь, 2001. – С. 42–44, 64.





































![man can be described as [+HUMAN] [+ADULT] [+MALE]boy as [+HUMAN] [–ADULT] [+MALE]woman as [+HUMAN] [+ADULT]](/img/tmb/4/369959/ce49b10e74e4e61831702b1199577ac8-800x.jpg)