- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
What is the Present State of the Art Of In-Memory Analytics? презентация
Содержание
- 1. What is the Present State of the Art Of In-Memory Analytics?
- 2. Disclaimer “i think you’ll find it’s a bit more complicated than that.”
- 3. A Bit of History
- 4. LEO: Lyon’s Electronic Office, 1951 Sixty-four 5ft-long
- 5. 1980s – first in-memory BI tools Usefulness
- 6. 1995: Windows 95 & 32-bit Architectures Qlikview,
- 7. Complex Event Processing
- 8. Complex Event Processing
- 9. In-Memory and The Internet of Things
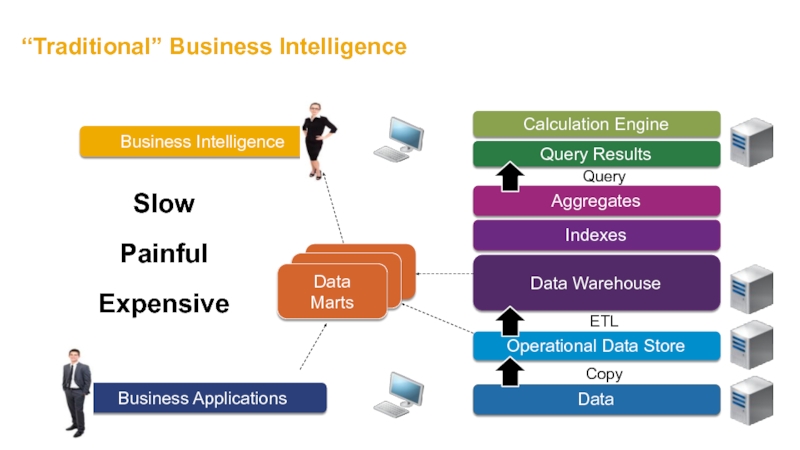
- 10. “Traditional” Business Intelligence Slow Painful Expensive Copy ETL
- 11. It’s Like An Onion… The more layers there are, the more it makes you cry…
- 12. What Was The Problem? Slow Disks &
- 13. Why Talk About In-Memory?
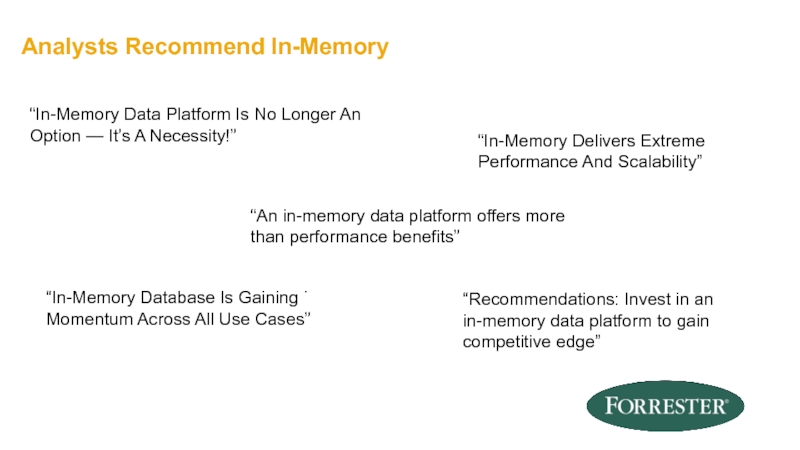
- 14. Analysts Recommend In-Memory . “An in-memory data
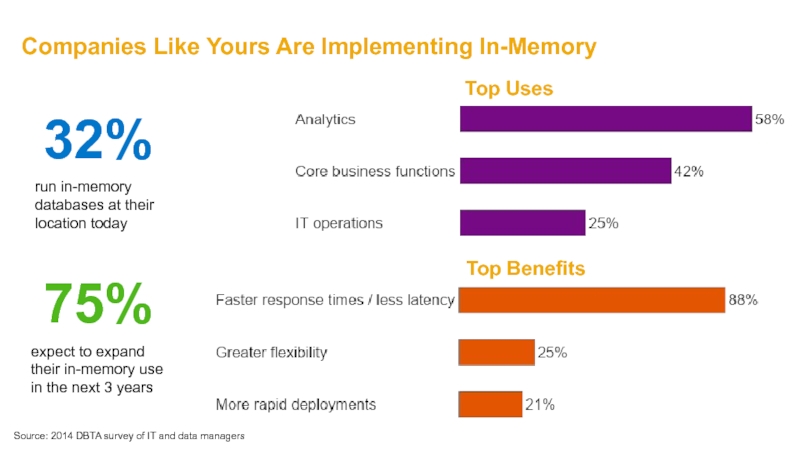
- 15. Companies Like Yours Are Implementing In-Memory 32%
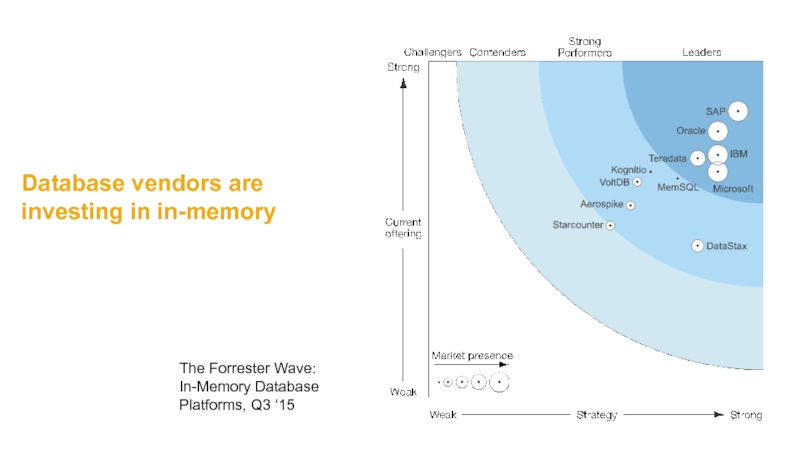
- 16. Database vendors are investing in in-memory The Forrester Wave: In-Memory Database Platforms, Q3 ‘15
- 17. All Analytics Vendors Now Support In-Memory To
- 18. What Is In-Memory? And why now?
- 19. What Is In-Memory? Data access times of
- 20. In-Memory Databases vs. Caching “Much of the
- 21. In-Memory Computing Costs have Plummeted Turning Torso:
- 22. In-Memory Computing Costs have Plummeted Cost of
- 23. Prices Continue to Slide DRAM production costs drop by 30% every 12 months
- 24. In-Memory Computing Copy ETL Up to 1,000x faster No optimizations required
- 25. Row vs. Column Databases My Filing System My Wife’s Filing System Row-based Column-based
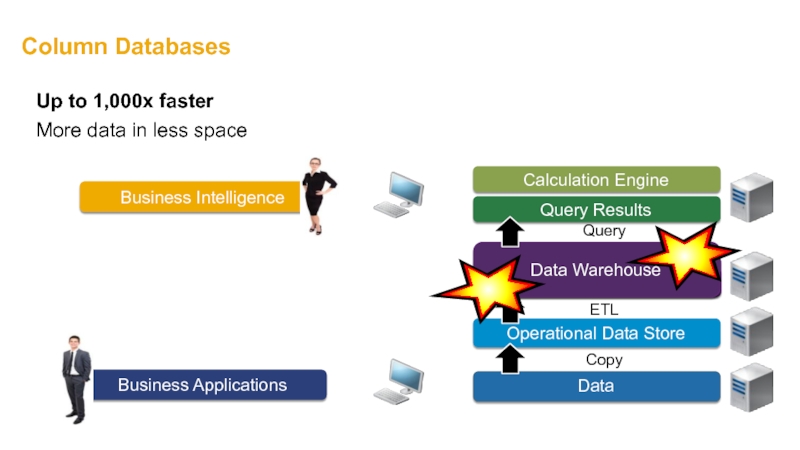
- 26. Column Databases Copy ETL Up to 1,000x faster More data in less space
- 27. Massively Parallel Systems E.g. Netezza technology now
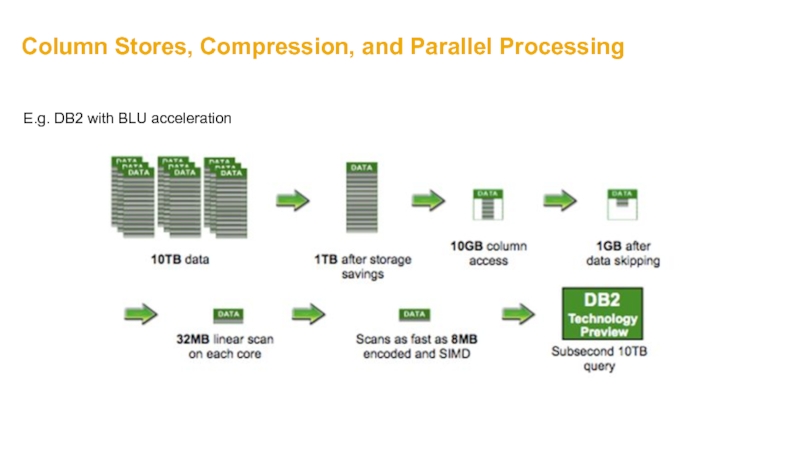
- 28. Column Stores, Compression, and Parallel Processing E.g. DB2 with BLU acceleration
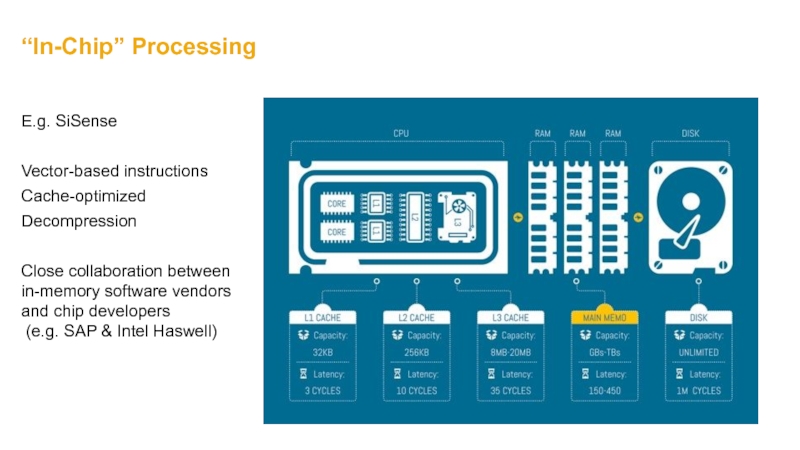
- 29. “In-Chip” Processing E.g. SiSense Vector-based instructions
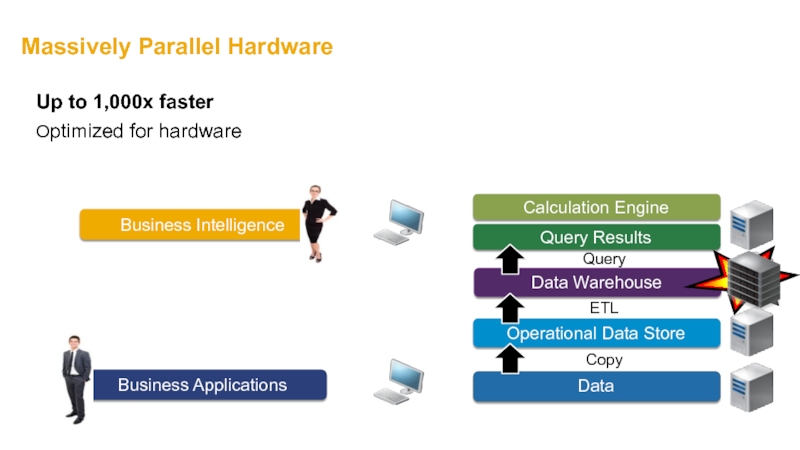
- 30. Massively Parallel Hardware Copy ETL Query
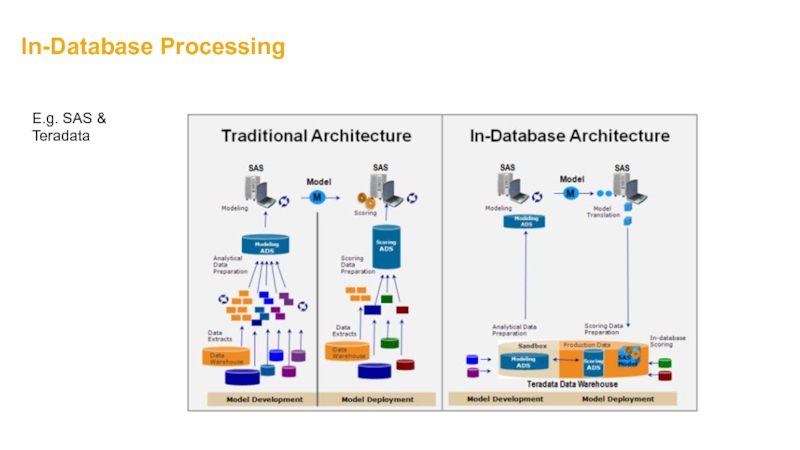
- 31. In-Database Processing E.g. SAS & Teradata
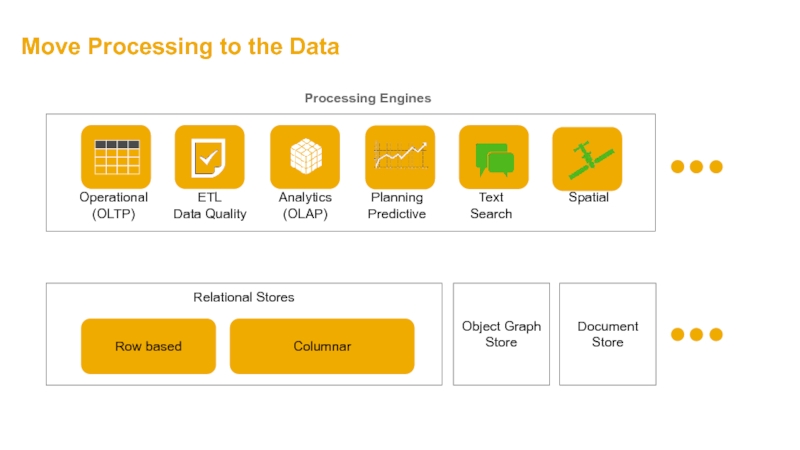
- 32. Move Processing to the Data Operational
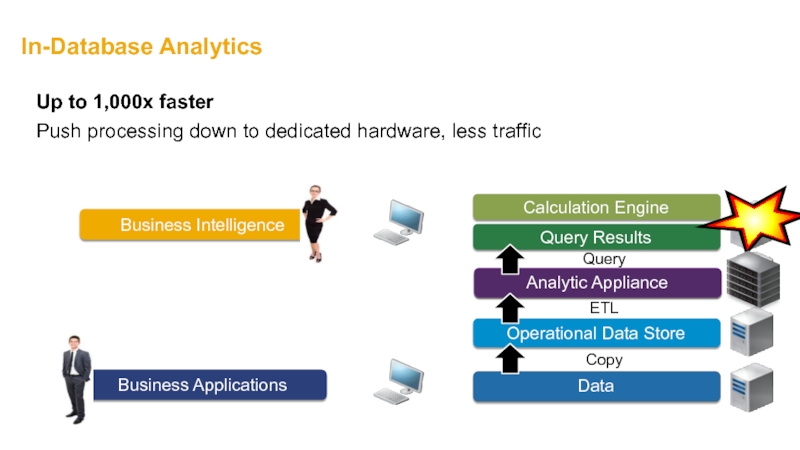
- 33. In-Database Analytics Copy ETL Query Up
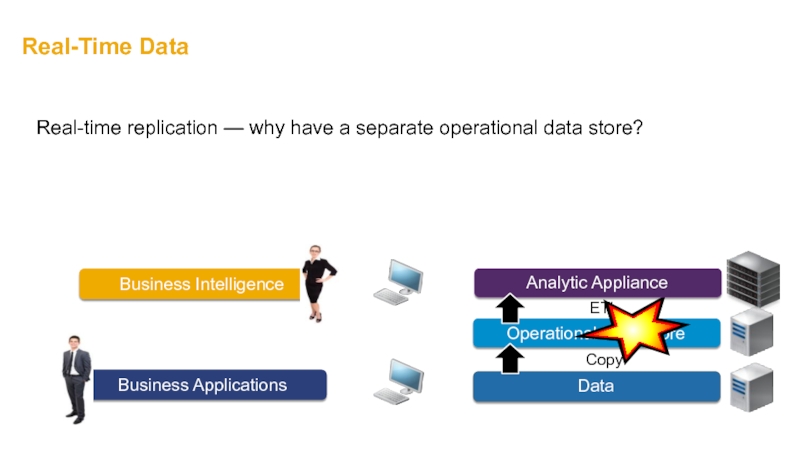
- 34. Real-Time Data Copy ETL Real-time replication —
- 35. Transactions ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) is
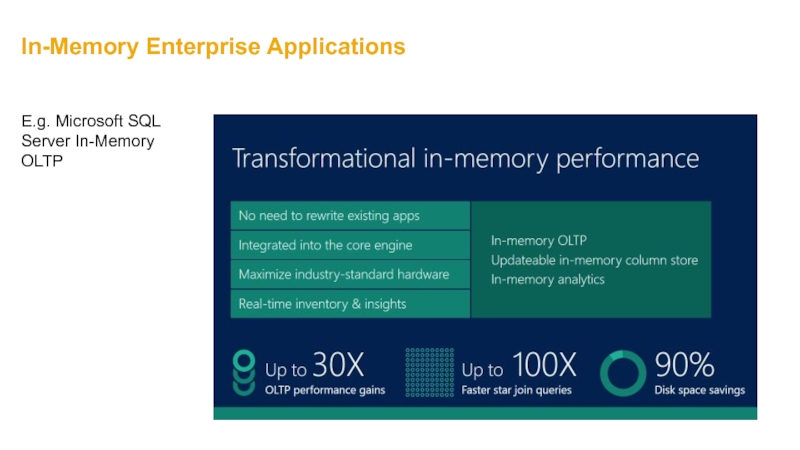
- 36. In-Memory Enterprise Applications E.g. Microsoft SQL Server In-Memory OLTP
- 37. In-Memory Enterprise Applications E.g. SAP S/4 HANA
- 38. Hybrid Transactional Analytical Processing Copy Use a single platform for both analytics and applications
- 39. Virtuous Circle of Technology In-Memory Columnar
- 40. Apache Spark MAP Reduce HDFS
- 41. Lots of Support for Spark
- 42. YARN HDFS HANA-Spark Adapter for improved
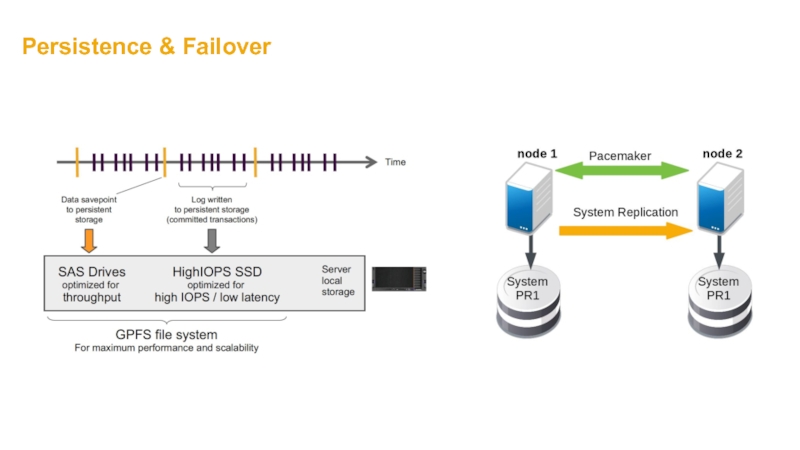
- 43. Persistence & Failover
- 44. Next-Generation Chips Are On Their Way NVM non-volatile memory
- 45. Scale Up 4,294,967,296x 256x 16 bit 32
- 46. What About Scale? There are now systems
- 47. Balancing Data Temperature and Costs Hot Warm
- 48. What Type of In-Memory Is The Right
- 49. Fast-Moving Market
- 50. Hybrid vs. Pure In-Memory Tradeoffs data duplication
- 51. Top Benefits
- 52. Speed “If things seem under control, you’re just not going fast enough.” Mario Andretti
- 53. Real-Time Operations Instead of analyzing the shards
- 54. Agility (Speed of Change)
- 55. Simplification = Lower Costs “In-memory changes the
- 56. Lower Costs “Don’t let somebody say to
- 57. The price of light… …is
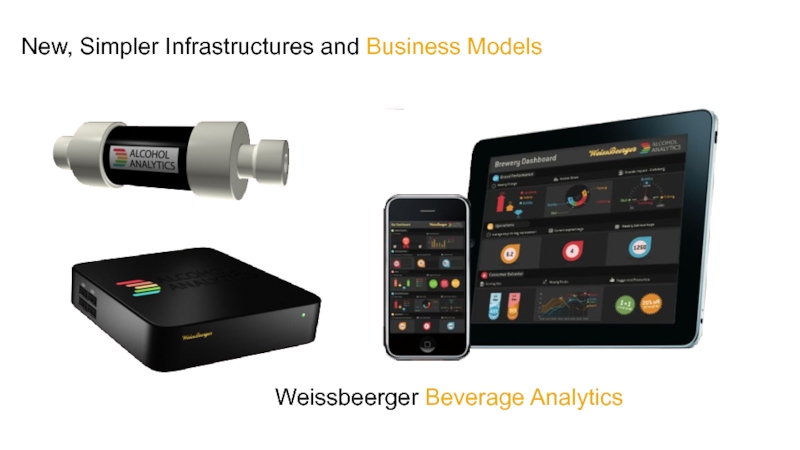
- 58. New, Simpler Infrastructures and Business Models Weissbeerger Beverage Analytics
- 59. Conclusion
- 60. Myths & Facts It’s a niche technology
- 61. Business Impact of In-Memory Computing Reducing
- 62. In-Memory Changes Everything “In-memory computing will have
- 63. Thank you!
Слайд 1
What is the Present State of the Art Of In-Memory Analytics?
Timo
Слайд 4LEO: Lyon’s Electronic Office, 1951
Sixty-four 5ft-long mercury tubes, each weighing half
Слайд 51980s – first in-memory BI tools
Usefulness limited by high cost of
640KB max memory
Слайд 61995: Windows 95 & 32-bit Architectures
Qlikview, TimesTen, and others take advantage
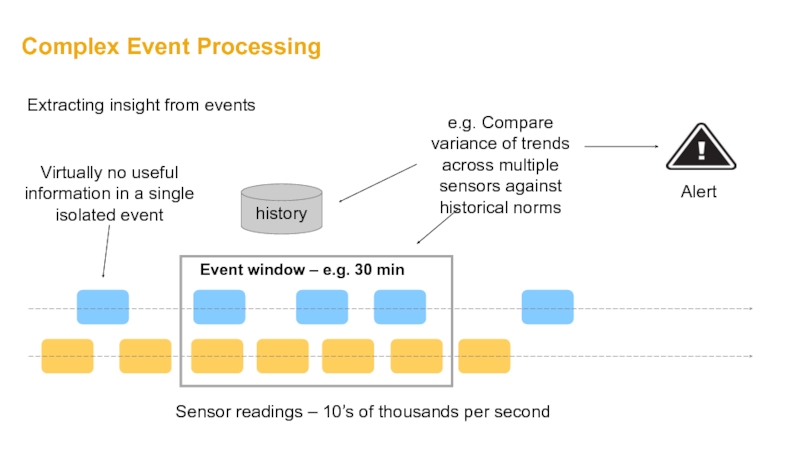
Слайд 7Complex Event Processing
Sensor readings – 10’s of thousands per second
Virtually no
history
e.g. Compare variance of trends across multiple sensors against historical norms
Event window – e.g. 30 min
Alert
Extracting insight from events
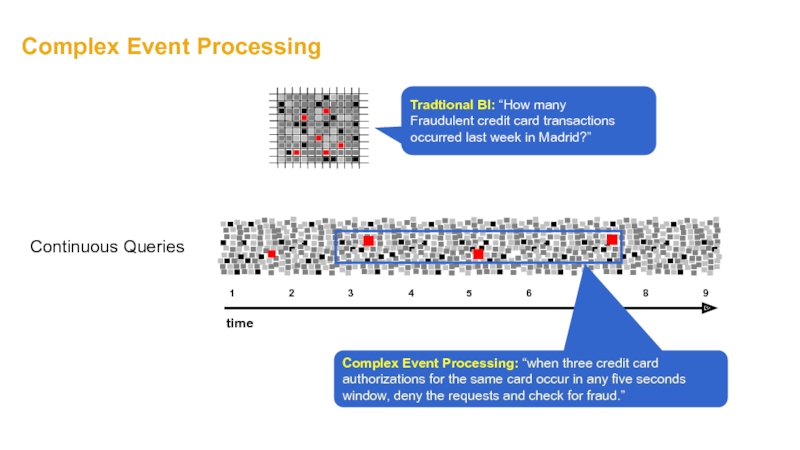
Слайд 8Complex Event Processing
Tradtional BI: “How many
Fraudulent credit card transactions
occurred last week
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
time
Complex Event Processing: “when three credit card authorizations for the same card occur in any five seconds
window, deny the requests and check for fraud.”
Continuous Queries
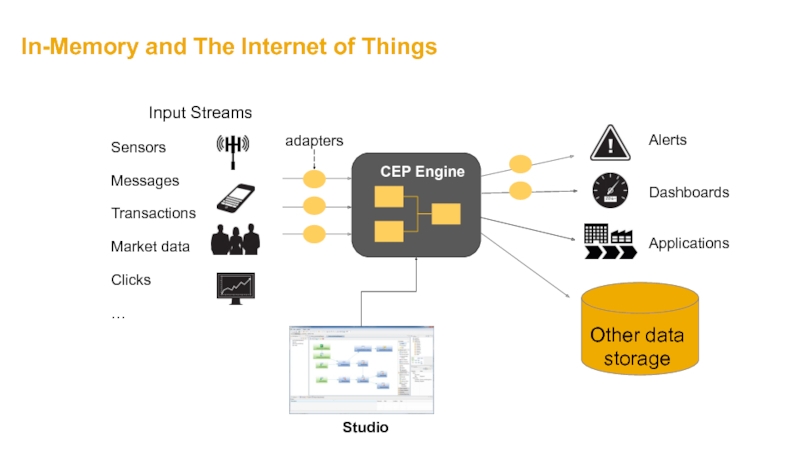
Слайд 9In-Memory and The Internet of Things
CEP Engine
Studio
Input Streams
Sensors
Messages
Transactions
Market data
Clicks
…
Alerts
Dashboards
Applications
adapters
Слайд 12What Was The Problem?
Slow Disks & CPUs
I/O Bottleneck
Expensive Memory
Optimized for Transactions
BI
30 Year-Old Database Design Principles
Слайд 14Analysts Recommend In-Memory
.
“An in-memory data platform offers more than performance benefits”
“Recommendations:
“In-Memory Database Is Gaining Momentum Across All Use Cases”
“In-Memory Delivers Extreme Performance And Scalability”
“In-Memory Data Platform Is No Longer An
Option — It’s A Necessity!”
Слайд 15Companies Like Yours Are Implementing In-Memory
32%
run in-memory databases at their location
75%
expect to expand their in-memory use in the next 3 years
Source: 2014 DBTA survey of IT and data managers
Top Uses
Top Benefits
Слайд 16Database vendors are investing in in-memory
The Forrester Wave: In-Memory Database Platforms,
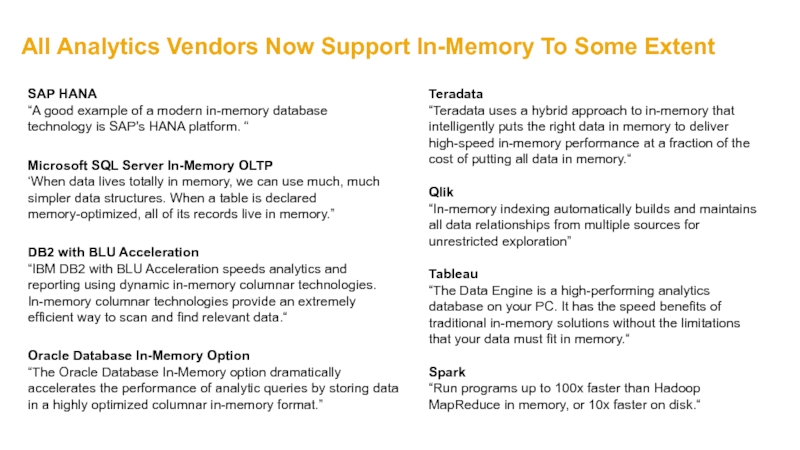
Слайд 17All Analytics Vendors Now Support In-Memory To Some Extent
Oracle Database In-Memory
“The Oracle Database In-Memory option dramatically accelerates the performance of analytic queries by storing data in a highly optimized columnar in-memory format.”
Microsoft SQL Server In-Memory OLTP
‘When data lives totally in memory, we can use much, much simpler data structures. When a table is declared memory-optimized, all of its records live in memory.”
DB2 with BLU Acceleration
“IBM DB2 with BLU Acceleration speeds analytics and reporting using dynamic in-memory columnar technologies. In-memory columnar technologies provide an extremely efficient way to scan and find relevant data.“
Qlik
“In-memory indexing automatically builds and maintains all data relationships from multiple sources for unrestricted exploration”
SAP HANA
“A good example of a modern in-memory database technology is SAP's HANA platform. “
Teradata
“Teradata uses a hybrid approach to in-memory that intelligently puts the right data in memory to deliver high-speed in-memory performance at a fraction of the cost of putting all data in memory.“
Tableau
“The Data Engine is a high-performing analytics database on your PC. It has the speed benefits of traditional in-memory solutions without the limitations that your data must fit in memory.“
Spark
“Run programs up to 100x faster than Hadoop MapReduce in memory, or 10x faster on disk.“
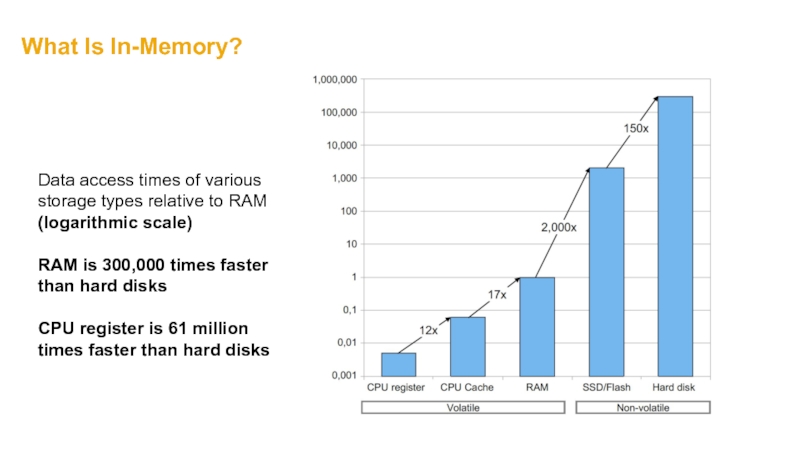
Слайд 19What Is In-Memory?
Data access times of various storage types relative to
RAM is 300,000 times faster than hard disks
CPU register is 61 million times faster than hard disks
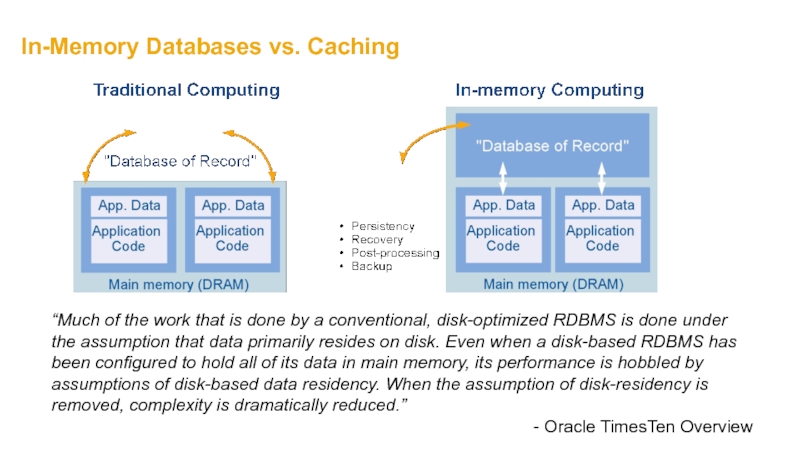
Слайд 20In-Memory Databases vs. Caching
“Much of the work that is done by
- Oracle TimesTen Overview
Слайд 21In-Memory Computing Costs have Plummeted
Turning Torso: 190m
Cost of 1 Mb of
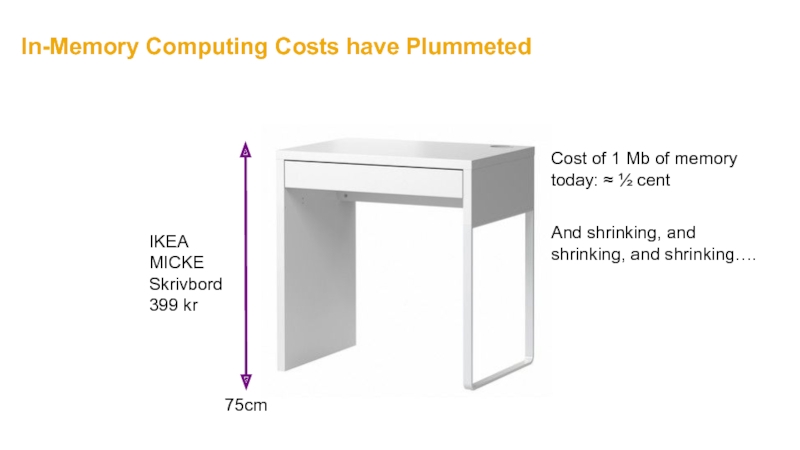
Слайд 22In-Memory Computing Costs have Plummeted
Cost of 1 Mb of memory today:
75cm
And shrinking, and shrinking, and shrinking….
IKEA
MICKE
Skrivbord
399 kr
Слайд 27Massively Parallel Systems
E.g. Netezza technology now part of IBM PureSystems
E.g. Greenplum,
Слайд 29“In-Chip” Processing
E.g. SiSense
Vector-based instructions
Cache-optimized
Decompression
Close collaboration between in-memory software vendors and chip
Слайд 32Move Processing to the Data
Operational (OLTP)
Analytics (OLAP)
Planning Predictive
Text
Search
Spatial
Processing Engines
Relational Stores
Row based
Columnar
ETL
Data
Document
Store
Object Graph Store
Слайд 33In-Database Analytics
Copy
ETL
Query
Up to 1,000x faster
Push processing down to dedicated hardware, less
Слайд 35Transactions
ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) is a set of properties that
ACID
ACID
compliance
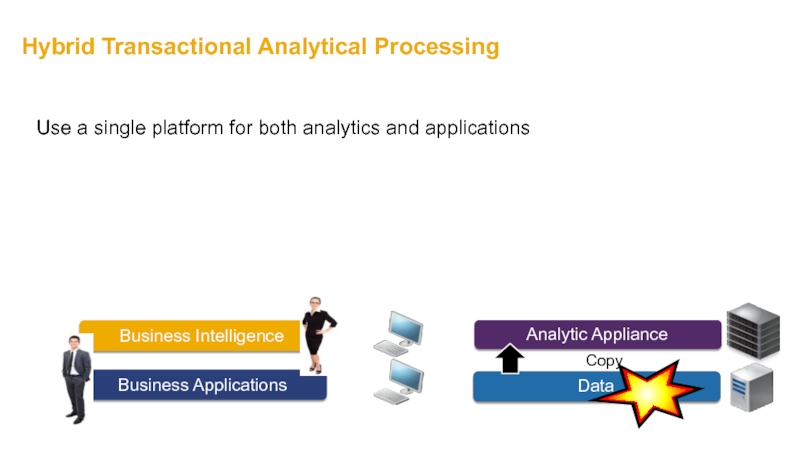
Слайд 38Hybrid Transactional Analytical Processing
Copy
Use a single platform for both analytics and
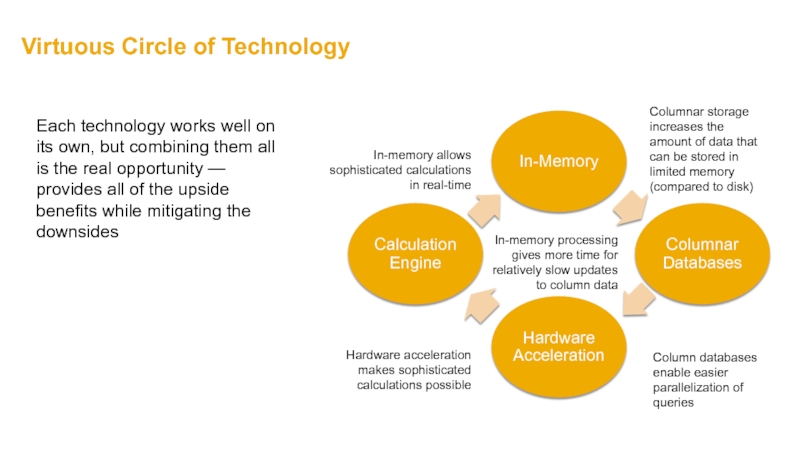
Слайд 39Virtuous Circle of Technology
In-Memory
Columnar Databases
Hardware Acceleration
Calculation Engine
Columnar storage increases the amount
Column databases enable easier parallelization of queries
In-memory processing gives more time for relatively slow updates to column data
In-memory allows sophisticated calculations in real-time
Hardware acceleration makes sophisticated calculations possible
Each technology works well on its own, but combining them all is the real opportunity — provides all of the upside benefits while mitigating the downsides
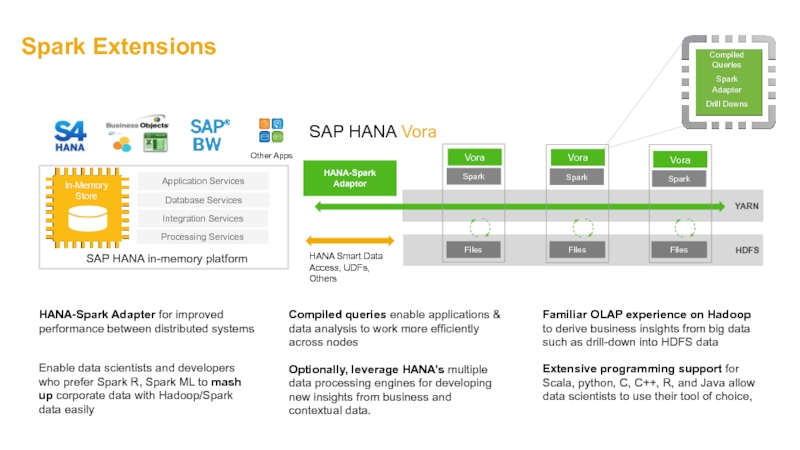
Слайд 42YARN
HDFS
HANA-Spark Adapter for improved performance between distributed systems
Compiled queries enable applications
Familiar OLAP experience on Hadoop to derive business insights from big data such as drill-down into HDFS data
Compiled Queries
Spark Adapter
Drill Downs
SAP HANA in-memory platform
Vora
Spark
Vora
Spark
Vora
Spark
HANA-Spark Adaptor
HANA Smart Data Access, UDFs, Others
Extensive programming support for Scala, python, C, C++, R, and Java allow data scientists to use their tool of choice,
Enable data scientists and developers who prefer Spark R, Spark ML to mash up corporate data with Hadoop/Spark data easily
Optionally, leverage HANA’s multiple data processing engines for developing new insights from business and contextual data.
Spark Extensions
SAP HANA Vora
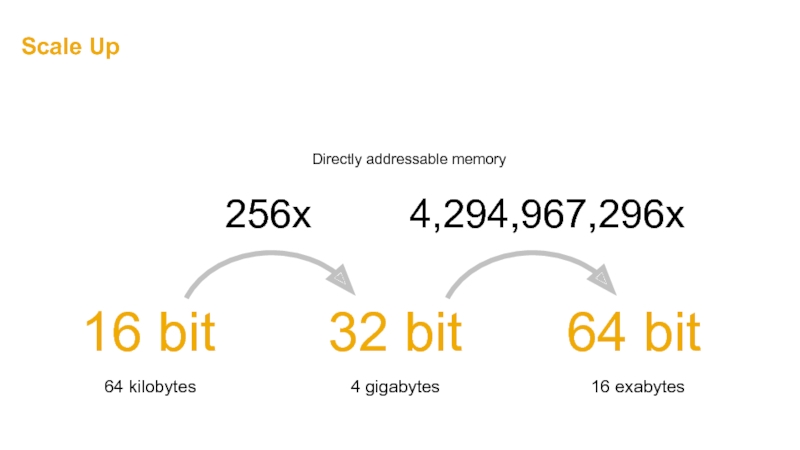
Слайд 45Scale Up
4,294,967,296x
256x
16 bit
32 bit
64 bit
64 kilobytes
4 gigabytes
16 exabytes
Directly addressable memory
Слайд 46What About Scale?
There are now systems with more than half a
Слайд 47Balancing Data Temperature and Costs
Hot
Warm
Cold
Data is accessed frequently
Data is not accessed
Data is only accessed sporadically
Volume
of data
Performance
(and direct cost)
Many different solutions possible
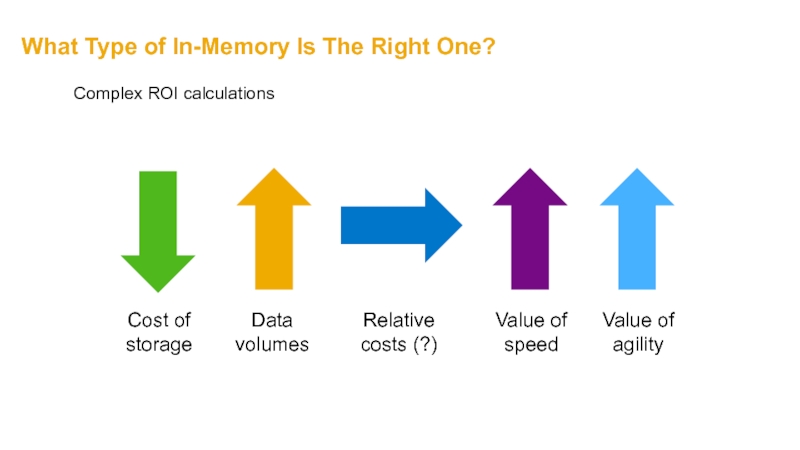
Слайд 48What Type of In-Memory Is The Right One?
Complex ROI calculations
Data volumes
Relative
Cost of storage
Value of speed
Value of agility
Слайд 50Hybrid vs. Pure In-Memory Tradeoffs
data duplication vs single source
replicated vs real-time
unpredictable
Слайд 53Real-Time Operations
Instead of analyzing the shards of glass after the accident,
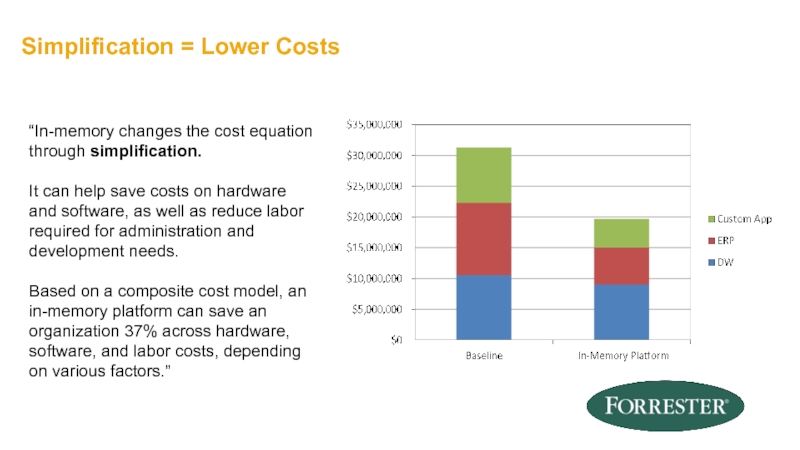
Слайд 55Simplification = Lower Costs
“In-memory changes the cost equation through simplification.
It
Слайд 56Lower Costs
“Don’t let somebody say to you we can’t go in-memory
Donald Feinberg, Gartner
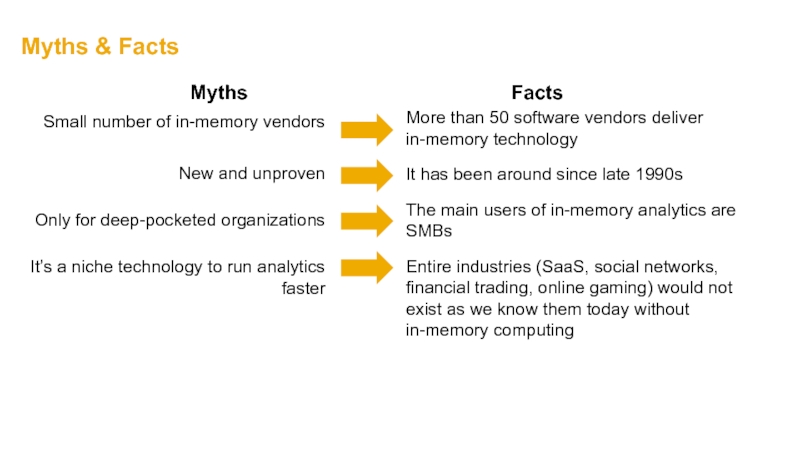
Слайд 60Myths & Facts
It’s a niche technology to run analytics faster
It has
The main users of in-memory analytics are SMBs
Entire industries (SaaS, social networks, financial trading, online gaming) would not exist as we know them today without in-memory computing
More than 50 software vendors deliver in-memory technology
Small number of in-memory vendors
Only for deep-pocketed organizations
New and unproven
Myths
Facts
Слайд 61Business Impact of In-Memory Computing
Reducing applications running cost via data
Improving transactional applications performance
Enabling horizontal, elastic scalability (scale up/down)
Boosting response time in analytical applications
Low latency (<1 microsecond) application messaging
Dramatically shortening batch processes execution time
Enabling real-time, "self-service" business intelligence and unconstrained data exploration
Detecting correlations/patterns across million of events in "a blink of an eye"
Supporting "big data" (big data needs big memory)
Running transactional and analytical applications on the same physical dataset
Run the business
Grow the business
Transform the business
Opportunities:
Business Impact
Слайд 62In-Memory Changes Everything
“In-memory computing will have a long-term, disruptive impact by
— Gartner