- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Privacy in The Digital Age – Legal Scenario (With specific reference to India) презентация
Содержание
- 1. Privacy in The Digital Age – Legal Scenario (With specific reference to India)
- 2. Agenda Privacy Data Privacy Different categories/types of
- 3. Privacy To separate/seclude from the rest Types – Personal privacy Informational Organizational
- 4. We’ll expect reasonable privacy in life…..but then…!
- 5. information/data privacy Attitude of an organization or
- 6. Personally Identifiable Information US Privacy Laws
- 7. PERSONAL DATA AND SENSITIVE PERSONAL DATA
- 8. SENSITIVE PERSONAL DATA/INFORMATION The Information Technology
- 9. India on privacy Constitution of India Art.
- 10. Key Issues Liability of Company (Sec. 85)
- 11. Preamble of the IT Act Purpose behind
- 12. Section 43 – Unauthorised access Unauthorised Access
- 13. If any person without permission of the
- 14. Cases decided u/Sec. 43 Thomas Raju vs.
- 15. Sec. 43a – compensation for failure to
- 16. Who is liable? Sec. 85 Company
- 17. Issues What is Sensitive Personal data
- 18. solution The Information Technology (Reasonable security practices
- 19. SPDI Password Health condition Sexual
- 20. Reasonable Security Practices Rule 8 - IT
- 21. Auditing Necessary to get the codes or
- 22. Compliance Policies
- 23. Collection of Information About obtaining consent of
- 24. Collection of Information Provider should know –
- 25. Privacy policy Policy about handling of SPDI
- 26. Disclosure of Information Disclosure – Prior
- 27. Transfer of information Transfer to be made
- 28. Sec 72(A) (Criminal offence) Punishment for Disclosure
- 29. Other provisions u/it act Section 66E
- 30. Some of the Global laws
- 31. Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act (GLBA, USA) Focuses on finance
- 32. The Federal Information Security Management Act of
- 33. Data Protection Directive (EU) European Union directive
- 34. Other laws in the US Children's Internet
- 35. Mom’s gyan
- 36. Protect your own privacy Understand – the
- 37. If you are a company Am I
- 40. GET IN TOUCH PHONE +919623444448 EMAIL CONTACT@SAGARRAHURKAR.COM
Слайд 2Agenda
Privacy
Data Privacy
Different categories/types of Private data
Indian Legal scenario on Privacy
Some of
Mom’s gyan
Слайд 4We’ll expect reasonable privacy in life…..but then…!
….and so many other ways
Слайд 5information/data privacy
Attitude of an organization or individual to determine what data
Private data is known as –
Personally Identifiable Information (PII)
Personal data
Sensitive Personal Data/Information
Слайд 6Personally Identifiable Information
US Privacy Laws
Information that can be used on
Слайд 7PERSONAL DATA AND SENSITIVE PERSONAL DATA
Data Protection Act – UK
Personal
Sensitive personal data - Personal data consisting of information as to –
the racial or ethnic origin of the data subject,
his political opinions,
his religious/spiritual beliefs
His professional associations,
his physical or mental health or condition,
his sexual life,
the commission or alleged commission by him of any offence, or
any proceedings for any offence committed or alleged to have been committed by him, the disposal of such proceedings or the sentence of any court in such proceedings.
Слайд 8SENSITIVE PERSONAL DATA/INFORMATION
The Information Technology Act, 2000 (Amd. 2008) –
SPDI
Password
Health
condition
Sexual orientation
Health records
Bio-metrics
Financial info
Rule 3 - IT (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal data or information) Rules, 2011
Слайд 9India on privacy
Constitution of India
Art. 19 - Freedom of Speech and
Art. 21 – Right to Life and Personal Liberty
IT Act, 2000 (Amd. 2008)
Data privacy
Personal privacy
Powers of Government
Liability of Intermediary
Слайд 10Key Issues
Liability of Company (Sec. 85)
Data protection – Concern for outsourcing
Privacy – Individual’s concern
Increasing Government control/interference
Слайд 11Preamble of the IT Act
Purpose behind enacting IT Act –
To provide
To facilitate e-governance
To provide remedy to cyber crimes
To provide legal recognition to digital evidence
Preamble doesn’t specify that the Act aims @ establishing IT Security framework in India
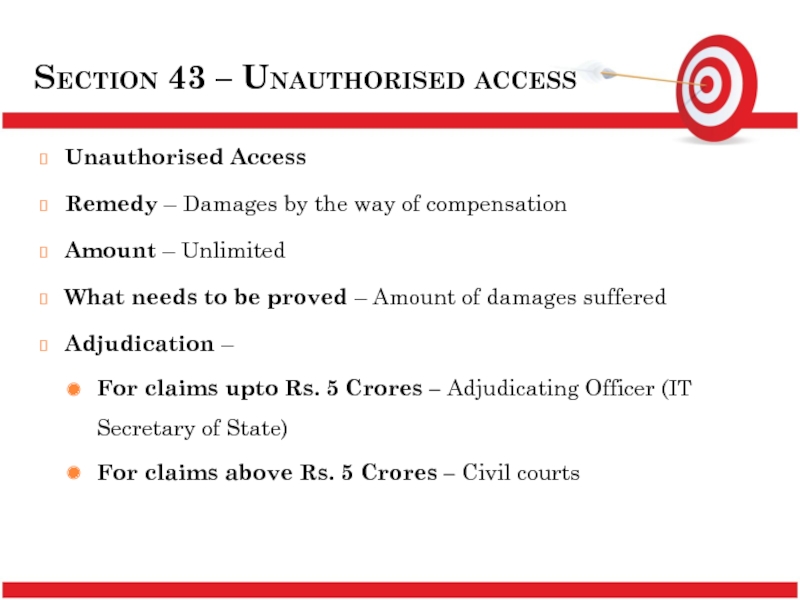
Слайд 12Section 43 – Unauthorised access
Unauthorised Access
Remedy – Damages by the way
Amount – Unlimited
What needs to be proved – Amount of damages suffered
Adjudication –
For claims upto Rs. 5 Crores – Adjudicating Officer (IT Secretary of State)
For claims above Rs. 5 Crores – Civil courts
Слайд 13If any person without permission of the owner or incharge of
Accesses or secures access to a computer
Downloads, copies or extracts data
Introduces computer contaminant or virus
Damages computer
Disrupts computer or network
Causes denial of access
Provides assistance to facilitate illegal access
Charges the services availed of by a person on the account of another person
Destroys, deletes, alters , diminishes value or utility or affects injuriously
Steals, conceals, destroys or alters computer source code
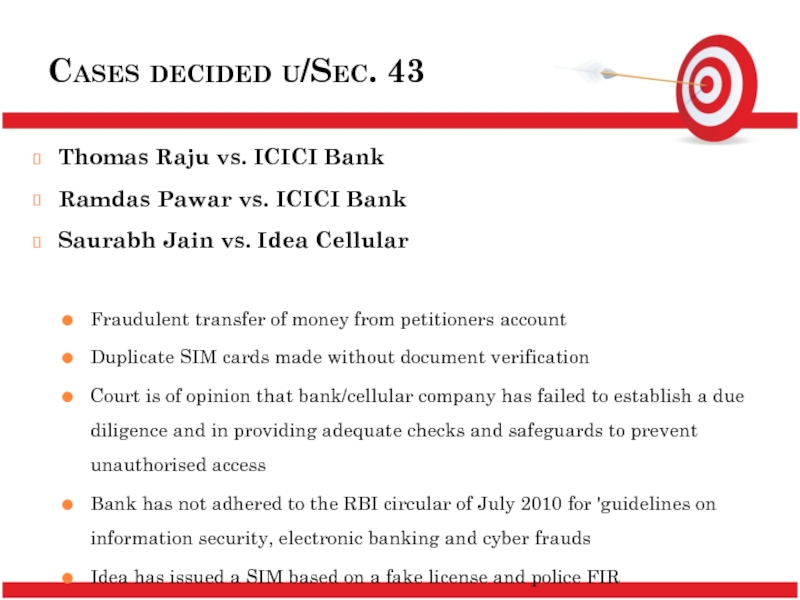
Слайд 14Cases decided u/Sec. 43
Thomas Raju vs. ICICI Bank
Ramdas Pawar vs. ICICI
Saurabh Jain vs. Idea Cellular
Fraudulent transfer of money from petitioners account
Duplicate SIM cards made without document verification
Court is of opinion that bank/cellular company has failed to establish a due diligence and in providing adequate checks and safeguards to prevent unauthorised access
Bank has not adhered to the RBI circular of July 2010 for 'guidelines on information security, electronic banking and cyber frauds
Idea has issued a SIM based on a fake license and police FIR
Слайд 15Sec. 43a – compensation for failure to
protect data
If a body corporate,
Liability – Damages by the way of Compensation – Unlimited damages
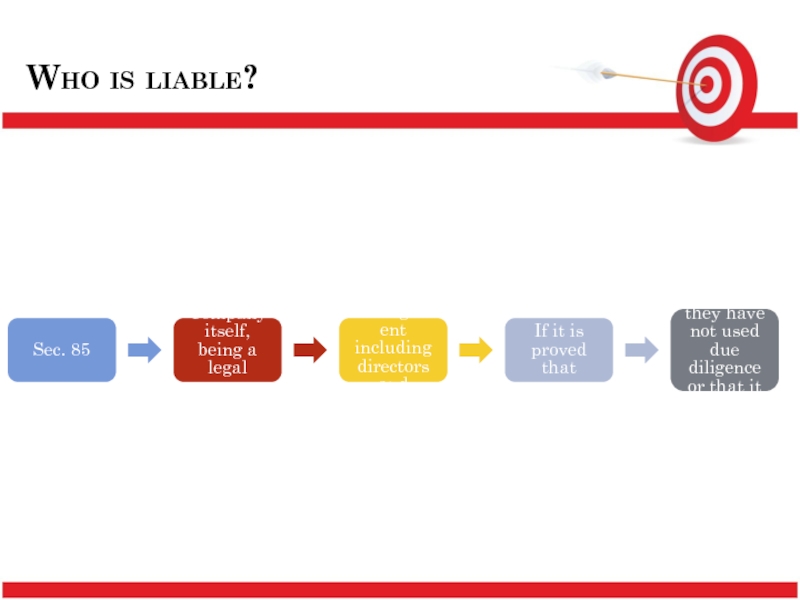
Слайд 16Who is liable?
Sec. 85
Company itself, being a legal person
Top management including
Managers
If it is proved that
they had knowledge of the contravention or they have not used due diligence or that it was caused due to their negligence
Слайд 17Issues
What is Sensitive Personal data or Information?
What are Reasonable Security Practices
Слайд 18solution
The Information Technology (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal
Enforceable from 11th April, 11
To be read with Sec. 43A
Слайд 19SPDI
Password
Health
condition
Sexual orientation
Health records
Bio-metrics
Financial info
SENSITIVE PERSONAL DATA OR INFORMATION
Rule 3 - IT
Слайд 20Reasonable Security Practices
Rule 8 - IT (Reasonable security practices and procedures
Слайд 21Auditing
Necessary to get the codes or procedure certified or audited on
Needs to be done by the Government Certified Auditor who will be known as “Govt. Certified IT Auditor”
Not appointed yet
Слайд 23Collection of Information
About obtaining consent of the information provider
Consent in writing
Need to specify –
Fact that SPDI is being collected
What type of SPDI is collected?
How long SPDI will be held?
Rule 5 - IT (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal data or information) Rules, 2011
Слайд 24Collection of Information
Provider should know –
Purpose of collection
Intended recipients
Details of the
Body Corporate not to retain information longer than required
Option should be given to withdraw the information provided
SPDI shall be used only for the purpose for which it has been collected
Shall appoint “Grievance Officer” to address any discrepancies and grievances about information in a timely manner – Max. time – One month
Слайд 25Privacy policy
Policy about handling of SPDI
Shall be published on website or
Shall provide for –
Type of SPDI collected
Purpose of collection and usage
Clear and easily accessible statements of IT Sec. practices and policies
Statement that the reasonable security practices and procedures as provided under rule 8 have been complied
Rule 4 - IT (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal data or information) Rules, 2011
Слайд 26Disclosure of Information
Disclosure –
Prior permission of provider necessary before disclosure
Disclosure clause needs to be specified in the original contract OR
Must be necessary by law
Third party receiving SPDI shall not disclose it further
Rule 6 - IT (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal data or information) Rules, 2011
Слайд 27Transfer of information
Transfer to be made only if it is necessary
Disclosure clause should be a part of Privacy and Disclosure Policy
Transferee to ensure same level of data protection is adhered while and after transfer
Details of transferee should be given to provider
Rule 7 - IT (Reasonable security practices and procedures and sensitive personal data or information) Rules, 2011
Слайд 28Sec 72(A) (Criminal offence)
Punishment for Disclosure of information in breach of
Knowingly or intentionally disclosing “Personal Information" in breach of lawful contract
IMP – Follow contract
Punishment - Imprisonment upto 3 years or fine up to 5 lakh or with both (Cognizable but Bailable)
Слайд 29Other provisions u/it act
Section 66E – Punishment for Violation of
Popularly known as Voyeurism
Covers acts like hiding cameras in changing rooms, hotel rooms, etc.
Punishment –imprisonment upto 3 years or fine upto Rs. 2 lakh or both
Section 67C – Preservation and retention of information by intermediaries
Section 69 – Power to issue directions for interception or monitoring or decryption of any information through any computer resources.
Section 69A – Power to issue directions for blocking public access to any information through any computer resource
Section 69B – Power to authorize to monitor and collect traffic data or information through any computer resource for cyber security
Section 79 – Intermediary not liable in certain circumstances
Слайд 31Gramm–Leach–Bliley Act (GLBA, USA)
Focuses on finance
Safeguards Rule - Disclosure of Nonpublic
It requires financial institutions to develop a written information security plan that describes how the company is prepared for, and plans to continue to protect clients’ nonpublic personal information.
This plan must include –
Denoting at least one employee to manage the safeguards,
Constructing a thorough risk analysis on each department handling the nonpublic information,
Develop, monitor and test a program to secure the information, and
Change the safeguards as needed with the changes in how information is collected, stored and used
Слайд 32The Federal Information Security Management Act of 2002 (FISMA, USA)
Focus on
Emphasized on “risk-based policy for cost-effective security”
Responsibility attached to federal agencies, NIST and the Office of Management and Budget (OMB) to strengthen information system security
Not mandatory
No penalty for non-compliance
Слайд 33Data Protection Directive (EU)
European Union directive regulating the processing of personal
Protection of individual’s personal data and its free movement
Coming soon - European Data Protection Regulation
Not mandatory
No penalty for non-compliance
Слайд 34Other laws in the US
Children's Internet Protection Act of 2001 (CIPA)
Children's Online Privacy Protection Act of 1998 (COPPA)
Driver's Privacy Protection Act of 1994
Telephone Consumer Protection Act of 1991 (TCPA)
Video Privacy Protection Act of 1988
Electronic Communications Privacy Act of 1986 (ECPA)
Privacy Protection Act of 1980 (PPA)
Right to Financial Privacy Act of 1978 (RFPA)
Family Education Rights and Privacy Act of 1974
Privacy Act of 1974
Слайд 36Protect your own privacy
Understand – the type of personal information you
Always ask –
WHY they want it ?
HOW will they use it ?
WHO will it will be shared with ?
Will YOU get access to it ?
Know your rights
Question if you are in doubt
Слайд 37If you are a company
Am I complying with Law?
Do you manage
Am I collecting only the what is REALLY needed and not more ?
Have I differentiated between Sensitive Personal Information and other information?
Do I protect information even during Transit/Process ?
How are you making sure all employees know their responsibilities and rights ?
How will you extend the data privacy protection to your third-parties, vendors ?
What will you do if there is a privacy breach ?
Do you in-house competences to conduct basic investigations ?