- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Poland Solution Summary презентация
Содержание
- 2. POLAND SOLUTION SUMMARY POLISH AND ROMANIAN LOCALIZATIONS LEGAL REQUIREMENTS
- 3. Company Set-up Supplier Invoice Currency Rate Based
- 4. Company Set-up Part Transactions List Report Purchase
- 5. COMPANY SET-UP IT APPLIES TO BOTH POLISH AND ROMANIAN LOCALIZATION
- 6. OVERVIEW DEFINE LOCALIZATION Open the Company window.
- 7. SUPPLIER INVOICE CURRENCY RATE BASED ON INVOICE DATE POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 8. According to the Polish requirement, the currency
- 9. To comply with the Polish requirement, the
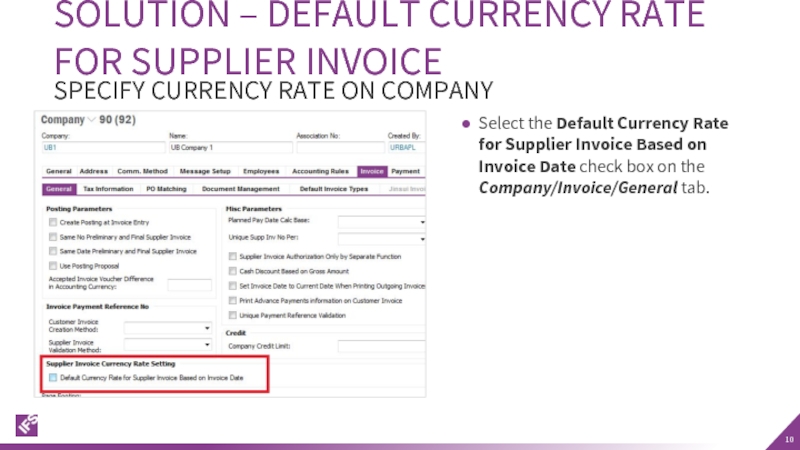
- 10. Select the Default Currency Rate for Supplier
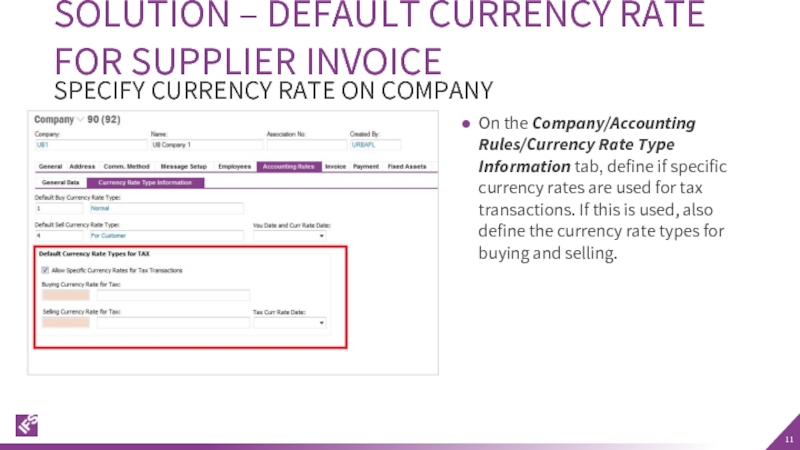
- 11. On the Company/Accounting Rules/Currency Rate Type Information
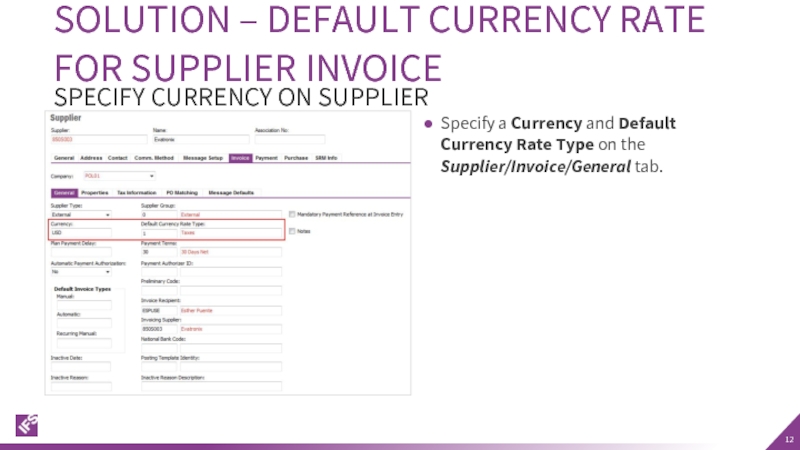
- 12. Specify a Currency and Default Currency Rate
- 13. Invoice date is used to retrieved currency
- 14. ACCESS CONTROL INVENTORY TRANSACTIONS AND RESERVATIONS POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 15. In Poland, it is a legal requirement
- 16. In IFS Applications core version users that
- 17. A new window is added, Inventory/Inventory Access/Inventory
- 18. System controls when a user is reserving
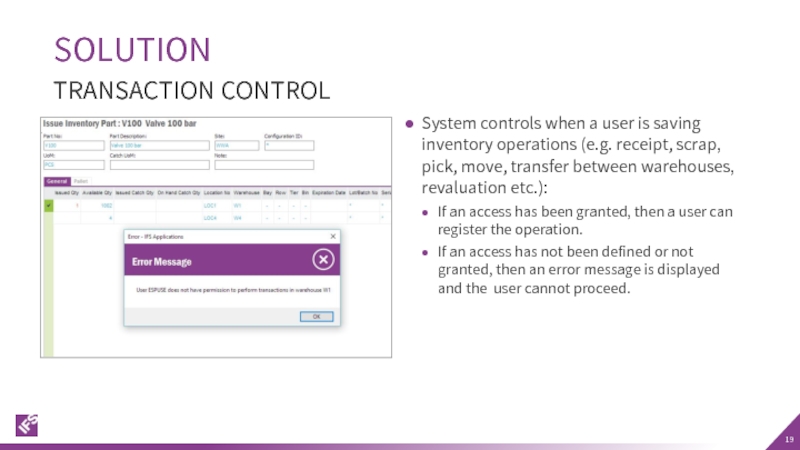
- 19. System controls when a user is saving
- 20. When moving parts directly into the new
- 21. AUTOMATIC RESERVATION When the automatic reservation is
- 22. It is possible to give access rights
- 23. SPECIFIC DATA FOR CUSTOMER INVOICE REPORTS POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 24. The invoice layouts existing in IFS Applications
- 25. The following invoice layouts are changed: Customer
- 26. The standard invoice layouts have been redesigned
- 27. SOLUTION TAX CODES The new column Tax
- 28. The following is added to the invoice
- 29. The following is changed in the standard
- 30. The following is removed from standard report
- 31. SOLUTION CUSTOMER ORDER CORRECTION INVOICE Only lines
- 32. SOLUTION CUSTOMER ORDER COLLECTIVE INVOICE During the
- 33. SOLUTION PRE-PAYMENT BASED DEBET/CREDIT INVOICE Sections Prepayment
- 34. The standard report layout have been changed
- 35. It’s only the following invoice layouts that
- 36. FOLLOW-UP MATERIAL ISSUED AND FINISHED GOODS COSTS POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 37. In Poland and other countries in Eastern
- 38. When issuing components for a shop order,
- 39. For material issue: M40A and M40C posting
- 40. Select the Follow-up material and production costs
- 41. When issuing components from inventory a new
- 42. When receiving the finished goods a new
- 43. OPERATIONS ISSUES SOISS - Issue for shop
- 44. When a component is issued for a
- 45. This covers two activities used to backflush
- 46. In IFS Applications core version it is
- 47. The Follow-up Material and Production Costs check
- 48. CURRENCY RATE CALCULATION FOR OUTGOING PAYMENTS POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 49. This requirement covers the different currency rate
- 50. Inflow – incoming transaction in mixed payment
- 51. SOLUTION OVERVIEW New columns are added in
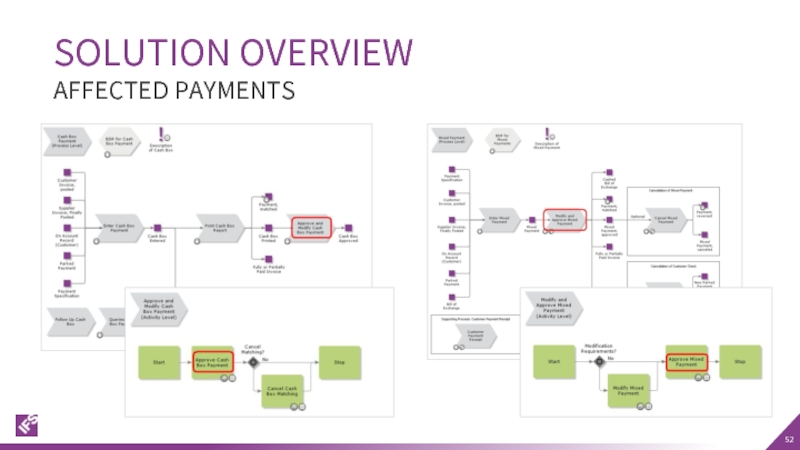
- 52. SOLUTION OVERVIEW AFFECTED PAYMENTS
- 53. When cash account balance is greater than
- 54. Customer inflow from 01-05-16 1000 USD *
- 55. The average currency rate will be calculated
- 56. Customer Inflow from 01-05-16 1000 USD *
- 57. Two options may be used to handle
- 58. In the Cash Accounts window define the
- 59. In the Cash Accounts window the Cash
- 60. In the Cash Accounts window the Cash
- 61. In the Cash Accounts window the Cash
- 62. In the Cash Account Queue window the
- 63. When the Cash Account has negative balance,
- 64. SOLUTION NEGATIVE BALANCE ALGORITHM: FOR AVG AND
- 65. Cash accounts with a currency rate calculation
- 66. DISCOUNTED PRICE ROUNDING POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 67. According to Polish VAT regulations, the invoices
- 68. In order to comply with the Polish
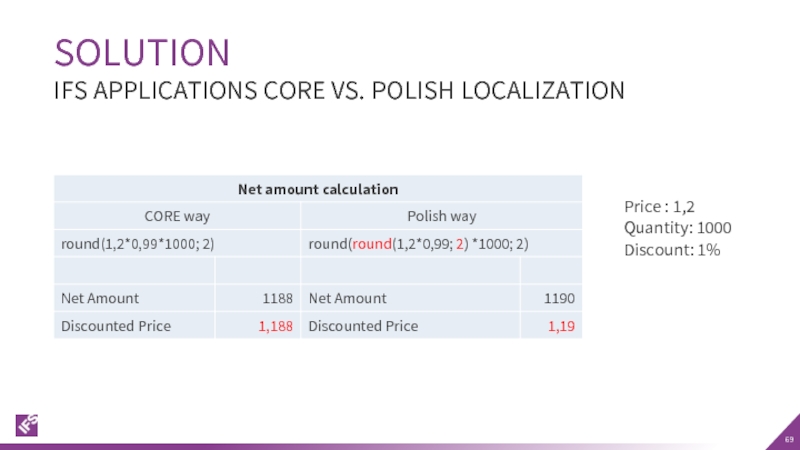
- 69. SOLUTION IFS APPLICATIONS CORE VS. POLISH LOCALIZATION Price : 1,2 Quantity: 1000 Discount: 1%
- 70. 1. Apply Order Line Discount Discounted Price:
- 71. 1. Apply Order Line Discount Discounted Price:
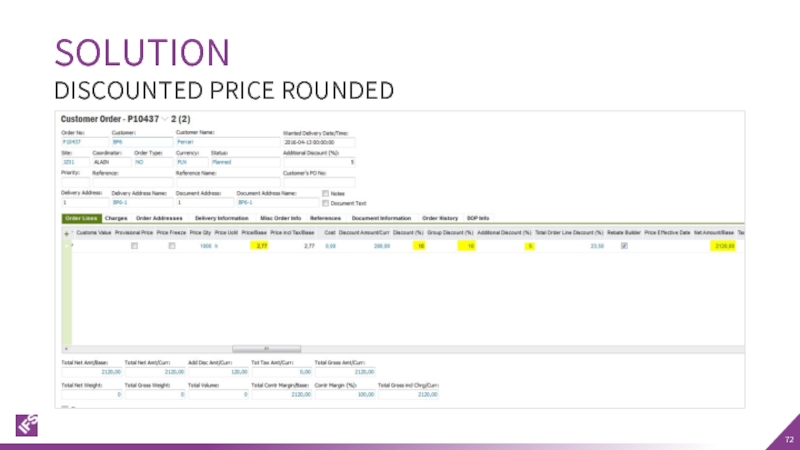
- 72. SOLUTION DISCOUNTED PRICE ROUNDED
- 73. SOLUTION CORE ALGORITHM 1. Apply Order
- 74. Core columns are hidden and the new
- 75. STANDARD AUDIT FILE -TAXES POLISH LOCALIZATION
- 76. Taxpayers are obliged to generate information for
- 77. To meet the Polish new financial reporting
- 78. In the Company Address Details dialog specify
- 79. On the Inventory/Transaction History/Report/Inventory Transaction Report Basic
- 80. In the Accounting Rules/Code String/Code Part Attribute
- 81. In the JPK Parameters window define basic
- 82. In the JPK_FA File Configuration window select
- 83. In the JPK_MAG File Configuration window define
- 84. To prepare a data for the SAF-T
- 85. In the Prapare XML – Files window
- 86. In the Prapare XML – Files window
- 87. There can be only one JPK File
- 88. PART TRANSACTIONS LIST REPORT ROMANIAN LOCALIZATION
- 89. The Romanian company must present specific reports,
- 90. To comply with the legal requirements two
- 91. Order the report under the Order Report
- 92. The report presents all the transactions created
- 93. Order the report under the Order Report
- 94. To run the report automatically, select the
- 95. The report presents all the ARRIVAL transactions
- 96. © 2015 IFS
Слайд 3Company Set-up
Supplier Invoice Currency Rate Based on Invoice Date
Access control to
Specific Data for Customer Invoice Reports
Follow-up Cost on Material Issued and Finished Goods
Cash Account Currency Rate Method
Discounted Price Rounding
CONTENT
LOCALIZATION FOR POLAND
Слайд 4Company Set-up
Part Transactions List Report
Purchase Order Receipts Report
Currency Revaluation
CONTENT
LOCALIZATION FOR ROMANIA
Слайд 6OVERVIEW
DEFINE LOCALIZATION
Open the Company window.
Search for the company.
Select ‚Poland’ in the
For the Romanian part of localization, select ‚Romania’.
Note that Polish company should be created using specific Polish company template.
Слайд 8According to the Polish requirement, the currency rate on supplier invoices
In the IFS Applications core version, the default currency rate for supplier invoice is fetched based on a voucher date.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 9To comply with the Polish requirement, the currency rate for supplier
Invoice date is also used for tax currency rate if the company is set up to use specific currency rates for tax transactions.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
Слайд 10Select the Default Currency Rate for Supplier Invoice Based on Invoice
SOLUTION – DEFAULT CURRENCY RATE FOR SUPPLIER INVOICE
SPECIFY CURRENCY RATE ON COMPANY
Слайд 11On the Company/Accounting Rules/Currency Rate Type Information tab, define if specific
SOLUTION – DEFAULT CURRENCY RATE FOR SUPPLIER INVOICE
SPECIFY CURRENCY RATE ON COMPANY
Слайд 12Specify a Currency and Default Currency Rate Type on the Supplier/Invoice/General
SOLUTION – DEFAULT CURRENCY RATE FOR SUPPLIER INVOICE
SPECIFY CURRENCY ON SUPPLIER
Слайд 13Invoice date is used to retrieved currency rate in the Manual
If company is set up to use specific currency rates for tax transactions, this currency rate is also based on invoice date.
SOLUTION
ENTER SUPPLIER INVOICE
Слайд 15In Poland, it is a legal requirement that a warehouse manager
Due to this requirement, only authorized personnel may change quantity and/or value of material in warehouses and make reservations.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 16In IFS Applications core version users that are connected to sites
Inventory transactions: Controls are added when a user is saving inventory operations (e.g. receipt, scrap, pick, move, transfer between warehouses, revaluation etc.):
If an access has been granted the user can register the operation
If an access has not been defined or not granted an error message is displayed and the user cannot proceed
Reservations: Controls are added when a user is reserving inventory parts (e.g. customer order, work order, shop order, material requisition:
If access has been granted the user can reserve the quantity
If access has not been defined or not granted an error message is displayed and the user cannot proceed
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
Слайд 17A new window is added, Inventory/Inventory Access/Inventory Access Basic Data, which
The window consists of two tabs:
User/Inventory - Use this tab to work with one user at a time.
Inventory/User - Use this tab to work with one warehouse at a time.
SOLUTION
INVENTORY ACCESS BASIC DATA
Слайд 18System controls when a user is reserving inventory parts (e.g. customer
If an access has been granted, then a user can reserve the quantity.
If an access has not been defined or not granted then an error message is displayed and a user cannot proceed.
SOLUTION
RESERVATION CONTROL
Слайд 19System controls when a user is saving inventory operations (e.g. receipt,
If an access has been granted, then a user can register the operation.
If an access has not been defined or not granted, then an error message is displayed and the user cannot proceed.
SOLUTION
TRANSACTION CONTROL
Слайд 20When moving parts directly into the new inventory the user needs
When moving into transit the user can put the material into transit, but then he cannot move them from transit into the target location without an access to the target warehouse. An error message is displayed.
SOLUTION
TRANSACTION CONTROL EXAMPLES
Слайд 21AUTOMATIC RESERVATION
When the automatic reservation is used, the system decides, using
EXCEPTIONS IN ACCESS RIGHTS
For changing inventory part locations between two sites, the user must be authorized to warehouses in both sites. During transport to another site, two transactions are generated; INVM-OUT (direction -) and INVM-TRIN (direction 0). The second transaction, INVM-TRIN, refers to a target location. If the user that moves parts to transport does not have an access, transactions cannot be completed.
MISCELLANEOUS
Слайд 22It is possible to give access rights to a warehouse to
If the user does not have warehouse access defined or the access is set to ‚No’, both implying the same thing, the user cannot perform operations.
NOTE
Слайд 24The invoice layouts existing in IFS Applications core version meet all
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 25The following invoice layouts are changed:
Customer Order Invoice/Customer Correction Invoice
Customer Collective
Prepayment Based Invoice
Instant Invoice
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
Слайд 26The standard invoice layouts have been redesigned according to the requirements
Report layouts have been redesigned according to a layout template which has been agreed with IFS Poland.
Company payment and document addresses are added to the report header.
Tax amount and gross amount are added to the report lines.
Company Tax ID is printed differently depending on whether the goods are delivered to a domestic or a foreign customer.
When the Tax Character field in the Accounting Rules/Tax/Tax Codes window is set to Tax Free or No Tax, then report texts “TF” or “NT” is printed instead of the tax rate. If tax rate is different than 0% the parameter must be set to Normal.
Customer delivery address is printed in the header of the collection invoice report when the address is the same on all the invoiced orders. Otherwise it will be printed for each invoice line separately.
Customer Order Corrective Invoice report contains only the invoice lines which have been modified by the user.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
Слайд 27SOLUTION
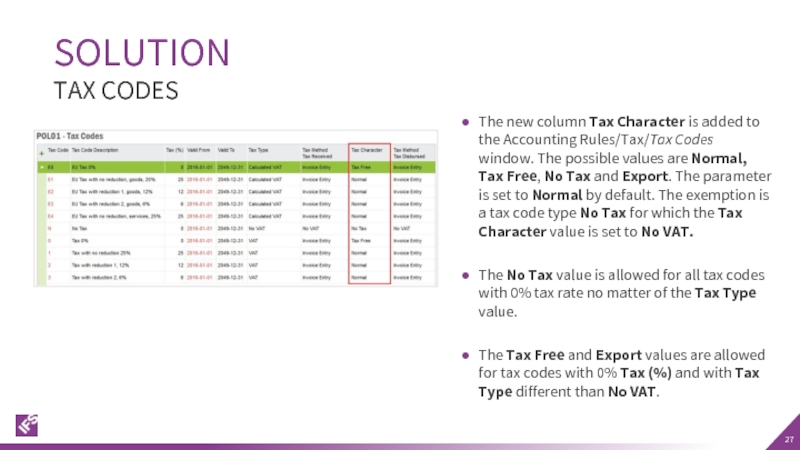
TAX CODES
The new column Tax Character is added to the Accounting
The No Tax value is allowed for all tax codes with 0% tax rate no matter of the Tax Type value.
The Tax Free and Export values are allowed for tax codes with 0% Tax (%) and with Tax Type different than No VAT.
Слайд 28The following is added to the invoice layout:
Company addresses - A
Company Tax Identity No (NIP) - Company Tax Identity Number is printed next to the company document address. The value is retrieved from the Tax ID Number field on the Company/Invoice/Tax Information tab.
Fee Amount and Gross Amount - New columns: the Fee Amount and Gross Amount are added to the report line.
Signatures - Two new fields for the seler and buyer signatures have been added at the end of the report.
SOLUTION
CUSTOMER ORDER DEBIT INVOICE
Слайд 29The following is changed in the standard report layouts:
Tax Rate (Tax
Tax Character Normal or Export values: a tax rate defined in a tax code basic data is printed
Tax Character Tax Free value: a translatable report text ‘TF’ is printed
Tax Character No Tax value: a translatable report text ‘NT’ is printed
Totals and Tax Totals sections - The sections which present the information total invoice amount and total amount per tax code have been redesigned. The column labels have been removed from the tax totals sections and are printed in the proper report line columns.
SOLUTION
CUSTOMER ORDER DEBIT INVOICE
Слайд 30The following is removed from standard report layouts:
Sales Quantity and Sales
Total Amount and Total Discount columns is not printed in the Tax Totals section
SOLUTION
CUSTOMER ORDER DEBIT INVOICE
Слайд 31SOLUTION
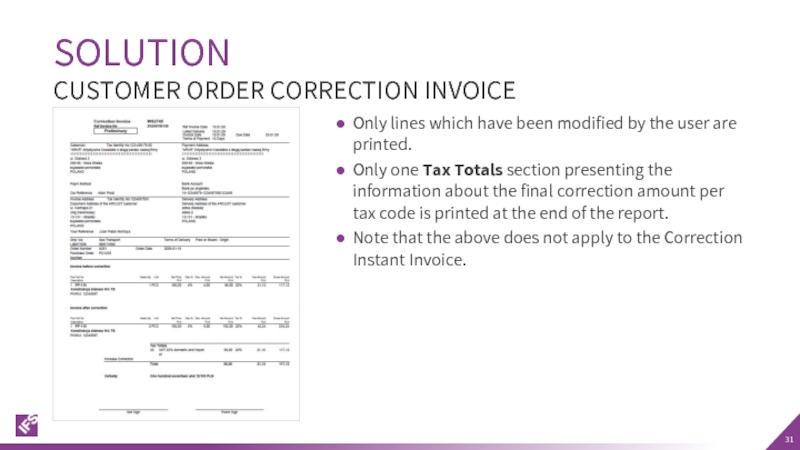
CUSTOMER ORDER CORRECTION INVOICE
Only lines which have been modified by the
Only one Tax Totals section presenting the information about the final correction amount per tax code is printed at the end of the report.
Note that the above does not apply to the Correction Instant Invoice.
Слайд 32SOLUTION
CUSTOMER ORDER COLLECTIVE INVOICE
During the print, the system checks if the
If yes, the address is printed in the header part of the report in the same way like on debit invoices, instead of for each invoice line;
If not, it will be handled as in IFS Applications core version: no information is printed in the header, the corresponding delivery addresses is printed for each invoice line.
Note: if the delivery addresses are specific for customer order lines (which are not marked as Default) this will be handled as an exception and will always be printed under invoice line regardless of the above validation.
Слайд 33SOLUTION
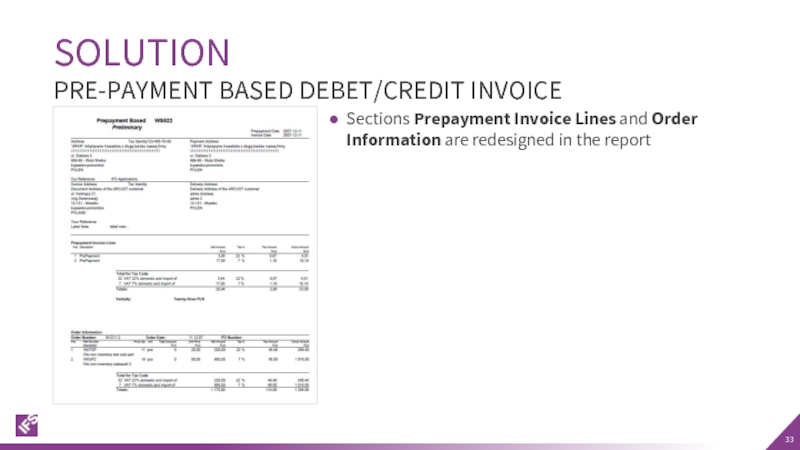
PRE-PAYMENT BASED DEBET/CREDIT INVOICE
Sections Prepayment Invoice Lines and Order Information are
Слайд 34The standard report layout have been changed by adding new fields
Note: The changes described for Print Customer Order Correction Invoice will not be applied for Correction Instant Invoice. Therefore the report will contain all the registered invoice lines, including the ones which have not been changed
SOLUTION
INSTANT INVOICE
Слайд 35It’s only the following invoice layouts that are changed:
Customer Order Invoice/Customer
Customer Collective Invoice
Prepayment Based Invoice
Instant Invoice
DELIMITATIONS
Слайд 37In Poland and other countries in Eastern Europe it is a
The accumulative value of components issued for production and finished goods received into inventory should be posted on the separate accounts as cost of material consumption and settlement of production costs.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 38When issuing components for a shop order, additional postings are created
When receiving manufactured material into inventory from a shop order, additional postings are created to follow-up the finished goods.
This allows to post the value of materials issued from inventory on the new Cost of material consumption account (account group 400) and value of finished goods received into inventory on the new Settlement of production costs account (account group 580).
In addition, the new postings are created during inventory revaluation on each found issue or receipt transaction.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
Слайд 39For material issue:
M40A and M40C posting types must have been defined
For receiving finished goods:
M40B and M40D posting types must have been defined for the company
PREREQUISITES
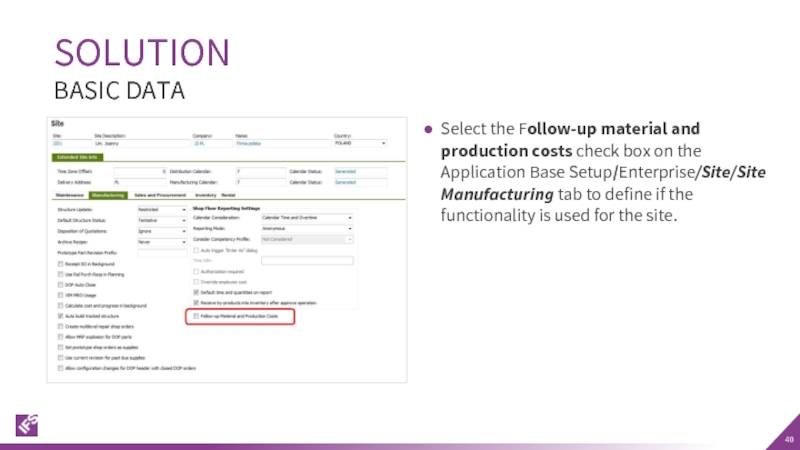
Слайд 40Select the Follow-up material and production costs check box on the
SOLUTION
BASIC DATA
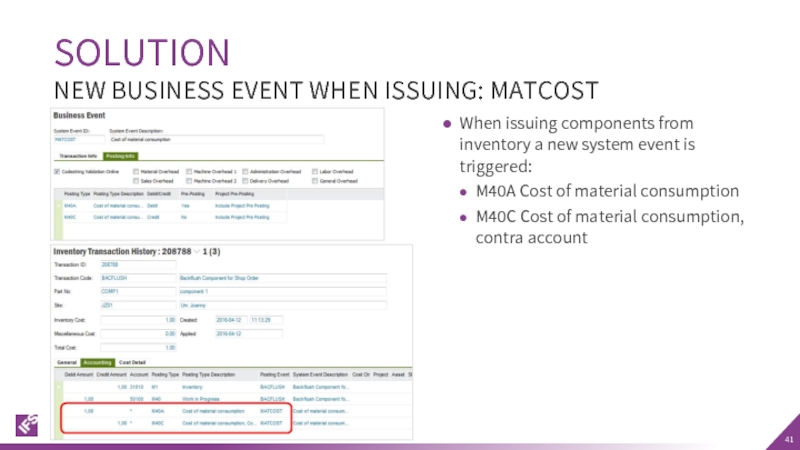
Слайд 41When issuing components from inventory a new system event is triggered:
M40A
M40C Cost of material consumption, contra account
SOLUTION
NEW BUSINESS EVENT WHEN ISSUING: MATCOST
Слайд 42When receiving the finished goods a new business event is triggered:
M40B
M40D Settlement of production costs, Contra Account
SOLUTION
NEW BUSINESS EVENT WHEN RECEIVING: PRODCOST
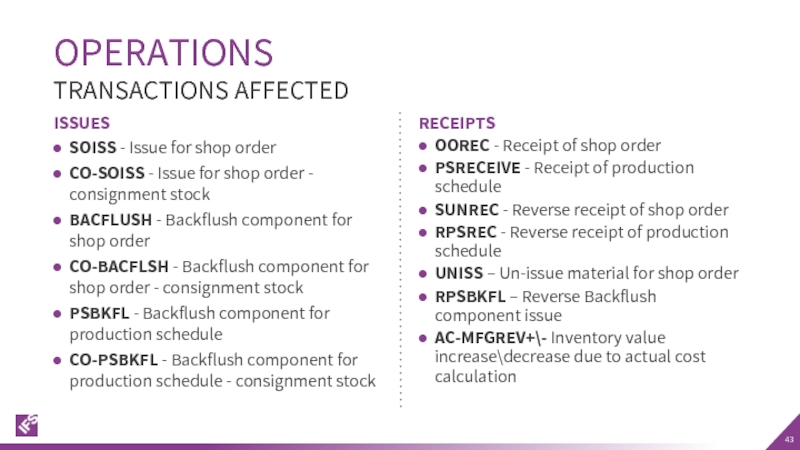
Слайд 43OPERATIONS
ISSUES
SOISS - Issue for shop order
CO-SOISS - Issue for shop order
BACFLUSH - Backflush component for shop order
CO-BACFLSH - Backflush component for shop order - consignment stock
PSBKFL - Backflush component for production schedule
CO-PSBKFL - Backflush component for production schedule - consignment stock
RECEIPTS
OOREC - Receipt of shop order
PSRECEIVE - Receipt of production schedule
SUNREC - Reverse receipt of shop order
RPSREC - Reverse receipt of production schedule
UNISS – Un-issue material for shop order
RPSBKFL – Reverse Backflush component issue
AC-MFGREV+\- Inventory value increase\decrease due to actual cost calculation
TRANSACTIONS AFFECTED
Слайд 44When a component is issued for a shop order its costs
M40A – Cost of materials consumption posting type debit
M40C – Cost of material consumption, Contra Account credit
When a finished good is received from a shop order its total cost is booked on
M40D – Settlement of production costs, Contra Account debit
M40B – Settlement of production costs posting type credit
Control type values (account, code c, etc.) for the new posting types are always fetched according to the attributes (like accounting group, product code) of the inventory part defined in the inventory transaction record. It means that control type values for M40A depends on component part data, not parent part data like it works when M40 postings are created.
SOLUTION
ACTIVITY REPORT SHOP ORDER
Слайд 45This covers two activities used to backflush components:
Issue components automatically
Receive
The backflush transactions are created when components are issued automatically via the Material Actions/Issue… right mouse buton menu option in the Shop Order window, or if the Backflush check box is selected when receiving manufactured part in the Manufacturing/Shop Order/Receive Shop Order window.
If the Follow-up material and production costs check box is selected for a site of a shop order then a component inventory value is also booked on M40A (Db) and M40C (Cr).
SOLUTION
ACTIVITY BACKFLUSH COMPONENTS
Слайд 46In IFS Applications core version it is possible to update inventory
The inventory transactions are updated either by adding new postings (Transaction Based) or by updating the existing ones (Period Weighted Average)
The functionality is set for an inventory part by selecting one of the two options:
Transaction Based, which is allowed for inventory valuation method Weighted Average and any cost level or for inventory valuation method Standard Cost and cost level Cost Per Serial
Periodic Weighted Average, which is allowed for inventory valuation method Standard Cost
Based on requirements from Poland the new M40x postings are created on each issue or receipt transaction.
INVENTORY REVALUATION
Слайд 47The Follow-up Material and Production Costs check box, placed on the
DELIMITATIONS
Слайд 49This requirement covers the different currency rate methods for bank and
The rate for the outgoing transaction is calculated based on the incoming transactions.
The different methods for calculating currency rates are weighted average (AVG) and FIFO.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 50Inflow – incoming transaction in mixed payment or cash box, balance
Outflow – outgoing transaction in mixed payment or cash box, balance is decreased on cash account.
SOLUTION
TERMS
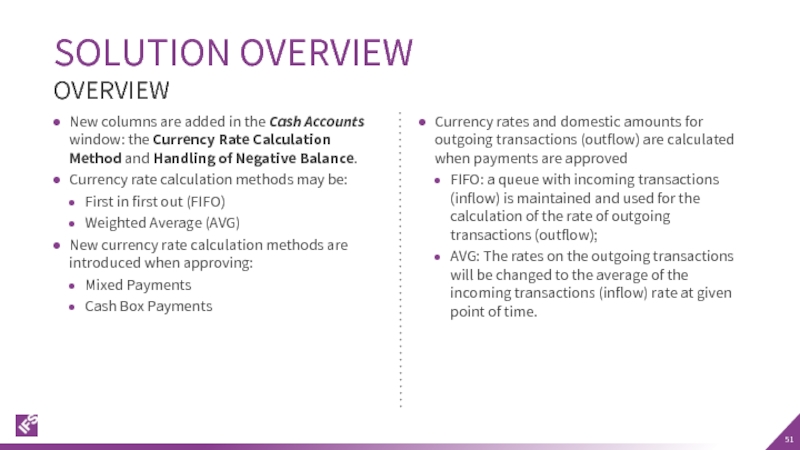
Слайд 51SOLUTION OVERVIEW
New columns are added in the Cash Accounts window: the
Currency rate calculation methods may be:
First in first out (FIFO)
Weighted Average (AVG)
New currency rate calculation methods are introduced when approving:
Mixed Payments
Cash Box Payments
OVERVIEW
Currency rates and domestic amounts for outgoing transactions (outflow) are calculated when payments are approved
FIFO: a queue with incoming transactions (inflow) is maintained and used for the calculation of the rate of outgoing transactions (outflow);
AVG: The rates on the outgoing transactions will be changed to the average of the incoming transactions (inflow) rate at given point of time.
Слайд 53When cash account balance is greater than zero each incoming transaction
For outgoing transactions (e.g. supplier payments) the rows in the the FIFO queue are consumed to calculate the currency rate.
SOLUTION OVERVIEW
FIRST IN FIRST OUT (FIFO)
Currency rate for outgoing transaction = FIFO rows of the queue
Слайд 54Customer inflow from 01-05-16 1000 USD * 3,5 = 3500 PLN
Customer
Supplier outflow from 03-05-16 1200 USD * ?
Value in PLN is calculated 1000 * 3,5 = 3500 and 200 * 4,0 = 800; 3500 + 800 = 4300
Currency rate for supplier outflow - 4300 : 1200 = 3,583333…..
When supplier invoice is paid currency differences are calculated as the difference between currency rate from invoice and calculated according to FIFO method.
SOLUTION OVERVIEW
FIFO EXAMPLE
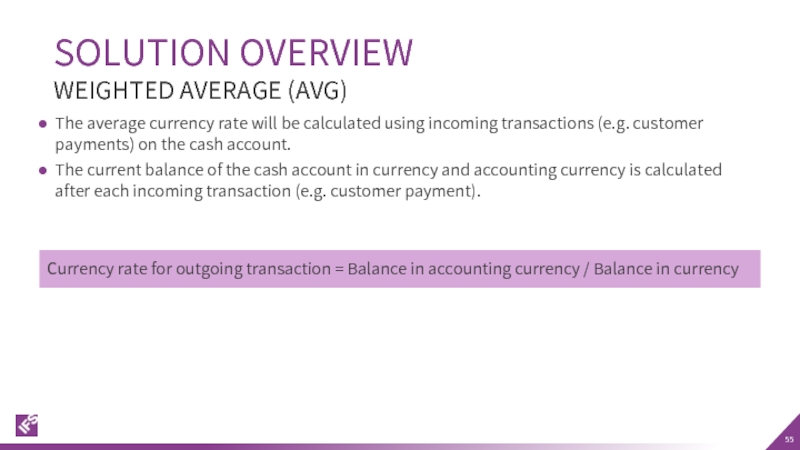
Слайд 55The average currency rate will be calculated using incoming transactions (e.g.
The current balance of the cash account in currency and accounting currency is calculated after each incoming transaction (e.g. customer payment).
SOLUTION OVERVIEW
WEIGHTED AVERAGE (AVG)
Currency rate for outgoing transaction = Balance in accounting currency / Balance in currency
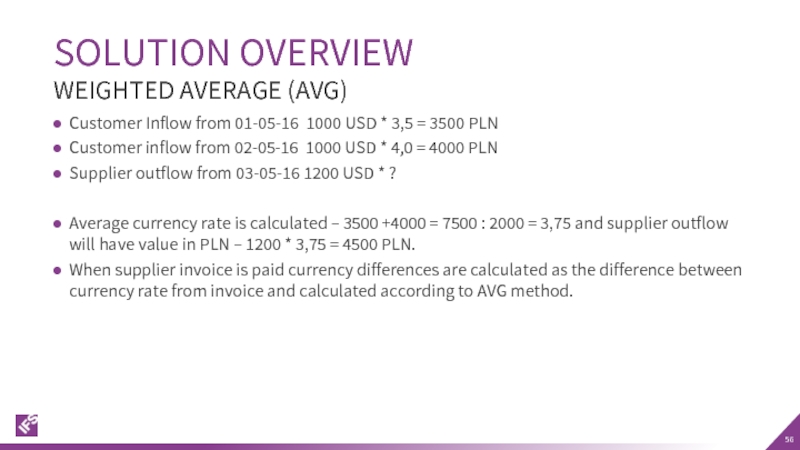
Слайд 56Customer Inflow from 01-05-16 1000 USD * 3,5 = 3500 PLN
Customer
Supplier outflow from 03-05-16 1200 USD * ?
Average currency rate is calculated – 3500 +4000 = 7500 : 2000 = 3,75 and supplier outflow will have value in PLN – 1200 * 3,75 = 4500 PLN.
When supplier invoice is paid currency differences are calculated as the difference between currency rate from invoice and calculated according to AVG method.
SOLUTION OVERVIEW
WEIGHTED AVERAGE (AVG)
Слайд 57Two options may be used to handle negative balances, Calculate Currency
Outflow Rate Used for AGV Example
There is a negative balance with 750 USD *3,9 = 2925 PLN value on a cash acount;
In first step a value of 500 USD is paid off with currency rate 3,8 on the Mixed Payment/General tab. But on the Mixed Payment/Transactions tab, a currency rate from an outflow which caused negative balance is copied and the new 3,9 rate is used in a voucher. As the result, currency differences are not calculated.
In case that more than one outflow with different currency rates caused a negative balance, then after this balance is changed to positive, currency rates will be used proportionally.
A negative balance created by two outflows example:
250 USD * 3,9 = 975 PLN
300 USD * 4,5 = 1350 PLN
Later a value of 550 USD and 2325 PLN (975+1350) was paid off because when balance in USD is zero also value in PLN must be zero. A currency rate is calculated 2325 : 550 = 4,22727….. and voucher lines are created without currency differences.
SOLUTION OVERVIEW
WEIGHTED AVERAGE (AVG) NEGATIVE BALANCES
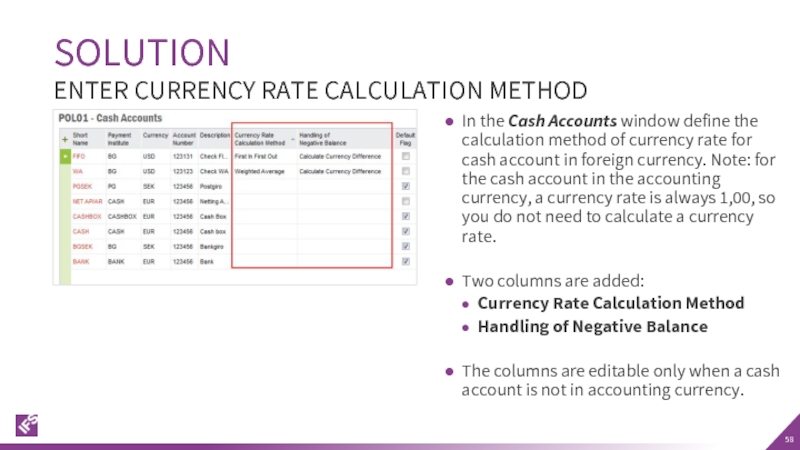
Слайд 58In the Cash Accounts window define the calculation method of currency
Two columns are added:
Currency Rate Calculation Method
Handling of Negative Balance
The columns are editable only when a cash account is not in accounting currency.
SOLUTION
ENTER CURRENCY RATE CALCULATION METHOD
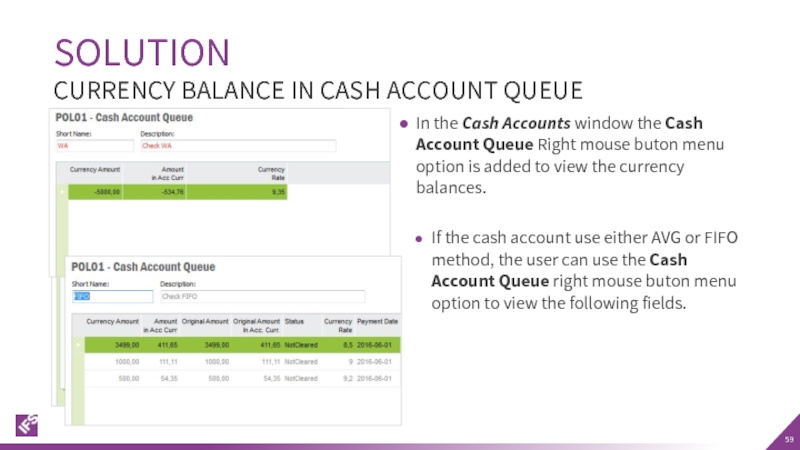
Слайд 59In the Cash Accounts window the Cash Account Queue Right mouse
If the cash account use either AVG or FIFO method, the user can use the Cash Account Queue right mouse buton menu option to view the following fields.
SOLUTION
CURRENCY BALANCE IN CASH ACCOUNT QUEUE
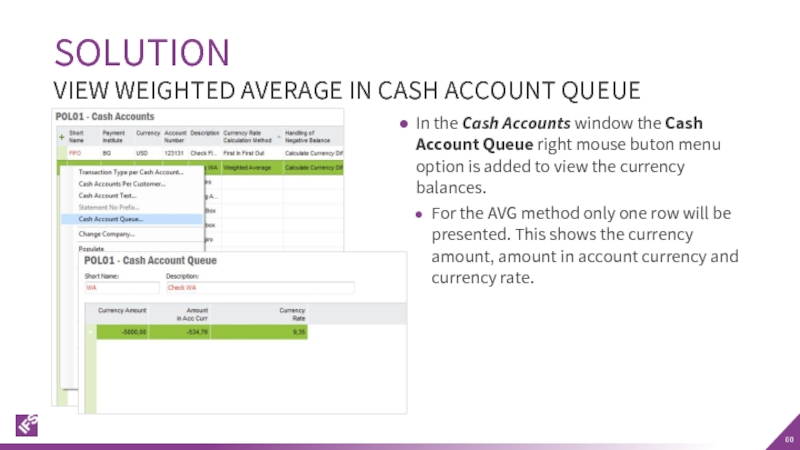
Слайд 60In the Cash Accounts window the Cash Account Queue right mouse
For the AVG method only one row will be presented. This shows the currency amount, amount in account currency and currency rate.
SOLUTION
VIEW WEIGHTED AVERAGE IN CASH ACCOUNT QUEUE
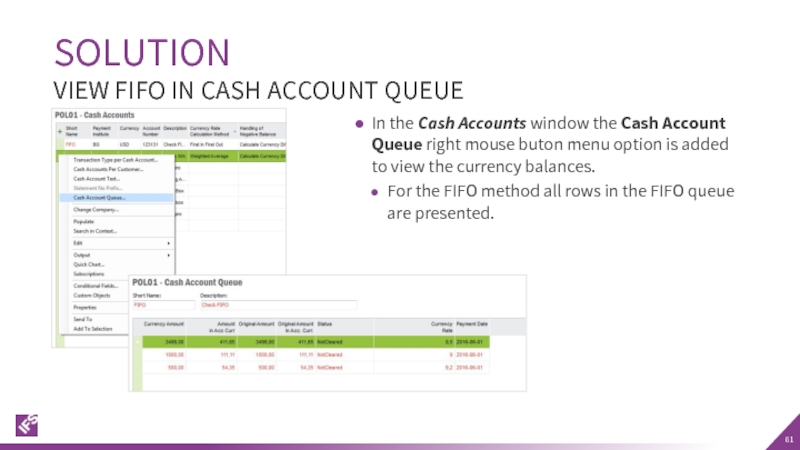
Слайд 61In the Cash Accounts window the Cash Account Queue right mouse
For the FIFO method all rows in the FIFO queue are presented.
SOLUTION
VIEW FIFO IN CASH ACCOUNT QUEUE
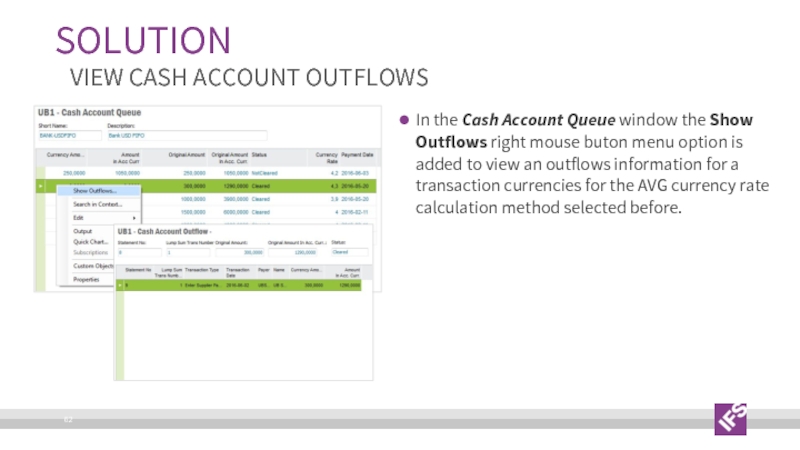
Слайд 62In the Cash Account Queue window the Show Outflows right mouse
SOLUTION
VIEW CASH ACCOUNT OUTFLOWS
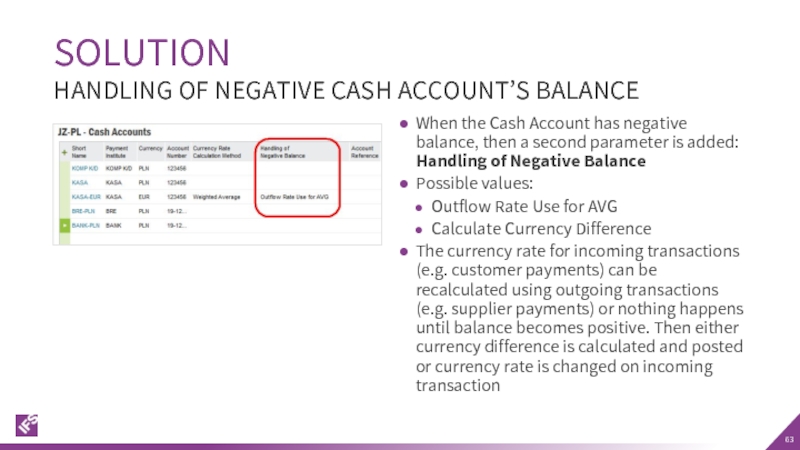
Слайд 63When the Cash Account has negative balance, then a second parameter
Possible values:
Outflow Rate Use for AVG
Calculate Currency Difference
The currency rate for incoming transactions (e.g. customer payments) can be recalculated using outgoing transactions (e.g. supplier payments) or nothing happens until balance becomes positive. Then either currency difference is calculated and posted or currency rate is changed on incoming transaction
SOLUTION
HANDLING OF NEGATIVE CASH ACCOUNT’S BALANCE
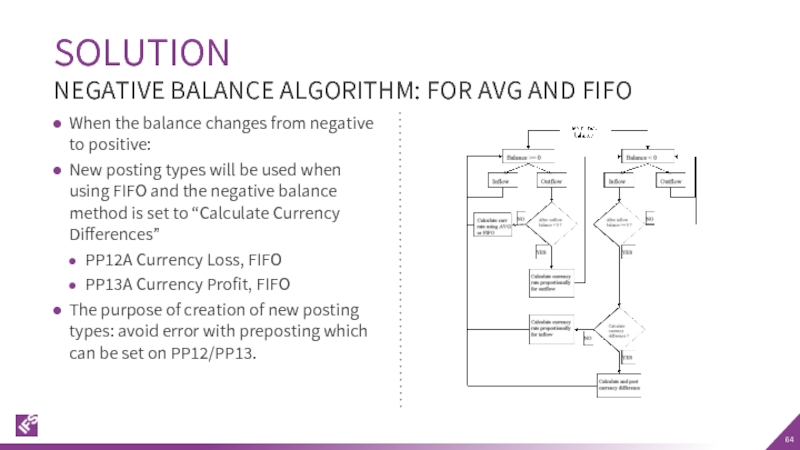
Слайд 64SOLUTION
NEGATIVE BALANCE ALGORITHM: FOR AVG AND FIFO
When the balance changes from
New posting types will be used when using FIFO and the negative balance method is set to “Calculate Currency Differences”
PP12A Currency Loss, FIFO
PP13A Currency Profit, FIFO
The purpose of creation of new posting types: avoid error with preposting which can be set on PP12/PP13.
Слайд 65Cash accounts with a currency rate calculation method defined cannot be
In case when FIFO method is used, only the last mixed payment can be cancelled.
DELIMITATIONS
Слайд 67According to Polish VAT regulations, the invoices have to include price
The discounted price must be rounded to two decimals and net amount must be calculated as discounted price multiplied by quantity.
In IFS Applications core version, the net amount is calculated as price * quantity, then discounts are applied and the discounted price is rounded.
The difference in calculation formula in core and the Polish localization result in slightly different values.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 68In order to comply with the Polish VAT regulations and business
The percentage (%) will be recalculated so that the standard algorithm for net amount calculation becomes usable for Polish customers.
The calculation on the net amount is not changed.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
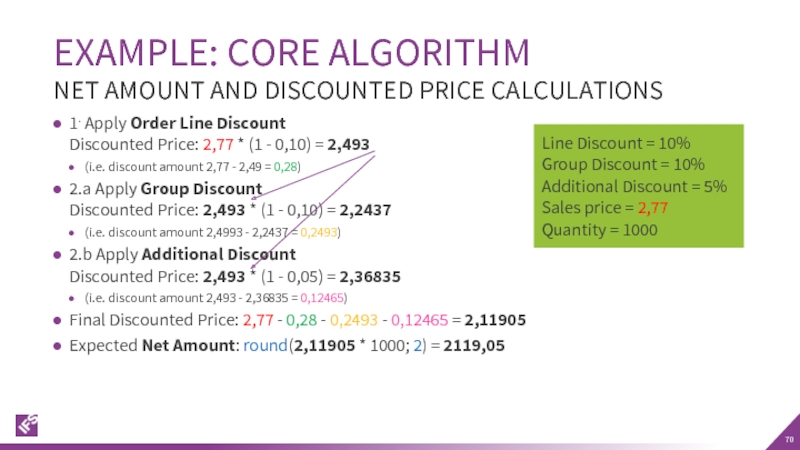
Слайд 701. Apply Order Line Discount Discounted Price: 2,77 * (1 - 0,10)
(i.e. discount amount 2,77 - 2,49 = 0,28)
2.a Apply Group Discount Discounted Price: 2,493 * (1 - 0,10) = 2,2437
(i.e. discount amount 2,4993 - 2,2437 = 0,2493)
2.b Apply Additional Discount Discounted Price: 2,493 * (1 - 0,05) = 2,36835
(i.e. discount amount 2,493 - 2,36835 = 0,12465)
Final Discounted Price: 2,77 - 0,28 - 0,2493 - 0,12465 = 2,11905
Expected Net Amount: round(2,11905 * 1000; 2) = 2119,05
EXAMPLE: CORE ALGORITHM
NET AMOUNT AND DISCOUNTED PRICE CALCULATIONS
Line Discount = 10%
Group Discount = 10%
Additional Discount = 5%
Sales price = 2,77
Quantity = 1000
Слайд 711. Apply Order Line Discount Discounted Price: round(2,77 * (1 - 0,10);
(i.e. discount amount 2,77 - 2,49 = 0,28)
2.a Apply Group Discount Discounted Price: round(2,49 * (1 - 0,10); 2) = 2,24
(i.e. discount amount 2,49 - 2,24 = 0,25)
2.b Apply Additional Discount Discounted Price: round(2,49 * (1 - 0,05); 2) = 2,37
(i.e. discount amount 2,49 - 2,37 = 0,12)
Final Discounted Price: 2,77 - 0,28 - 0,25 - 0,12 = 2,12
Expected Net Amount: round(2,12 * 1000; 2) = 2120
EXAMPLE: POLISH ALGORITHM
NET AMOUNT AND DISCOUNTED PRICE CALCULATIONS
Line Discount = 10%
Group Discount = 10%
Additional Discount = 5%
Sales price = 2,77
Quantity = 1000
Слайд 73SOLUTION
CORE ALGORITHM
1. Apply Order Line Discount
Discounted Price: 2,77 * (1 -
2.a Apply Group Discount Discounted Price: 2,493 * (1 - 0,10) = 2,2437
2.b Apply Additional Discount Discounted Price: 2,493 * (1 - 0,05) = 2,36835
Final Discounted Price: 2,77 - 0,28 - 0,2493 - 0,12465 = 2,11905
Expected Net Amount: round(2,11905 * 1000; 2) = 2119,05
POLISH ALGORITHM
1. Apply Order Line Discount
Discounted Price: round(2,77 * (1 - 0,10); 2) = 2,49
2.a Apply Group Discount
Discounted Price: round(2,49 * (1 - 0,10); 2) = 2,24
2.b Apply Additional Discount
Discounted Price: round(2,49 * (1 - 0,05); 2) = 2,37
Final Discounted Price: 2,77 - 0,28 - 0,25 - 0,12 = 2,12
Expected Net Amount: round(2,12 * 1000; 2) = 2120
COMPARISON
Слайд 74Core columns are hidden and the new columns for discounts are
DELIMITATIONS
Слайд 76Taxpayers are obliged to generate information for authorities in a form
The new reports are to be presented in XML form:
JPK_FA – customer invoices report;
JPK_VAT – sales and purchase records;
JPK_WB – account books;
JPK_MAG – inventory record
There is a legal obligation to provide specific data blocks in Polish, so data presented in an output xml file must be in Polish.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 77To meet the Polish new financial reporting requirements, the SAF-T (JPK)
General Ledger is improved to provide reports generation:
To define a basic data the new windows are introduced: JPK Parameters, JPK_FA File Configuration and JPK_MAG File Configuration.
To prepare report data new windows are added: Invoice Data (JPK_FA), Tax Data(JPK_VAT), Mixed Payment Data(JPK_WB), Account Books Data (JPK_KR) and Inventory Data (JPK_MAG).
To generate XML file an operation is added to be used after a basic data is defined and prepared.
Generated and exported xml file is sent to the authorities.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
Слайд 78In the Company Address Details dialog specify House No like
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW - PREREQUISITIONS
Слайд 79On the Inventory/Transaction History/Report/Inventory Transaction Report Basic Data/Report Types tab define
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW - PREREQUISITIONS
Слайд 80In the Accounting Rules/Code String/Code Part Attribute Connection window define a
Connect the attribute and attribute value to accounts used for SAF-TAX reporting in the Attribute Value window.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW - PREREQUISITIONS
Слайд 81In the JPK Parameters window define basic data required to prepare
Select the required Tax Office, Company Address, Report related to VAT 7 and values for the specific XML columns.
SOLUTION
SAF-TAX BASIC DATA CONFIGURATION FOR TAX REPORTING
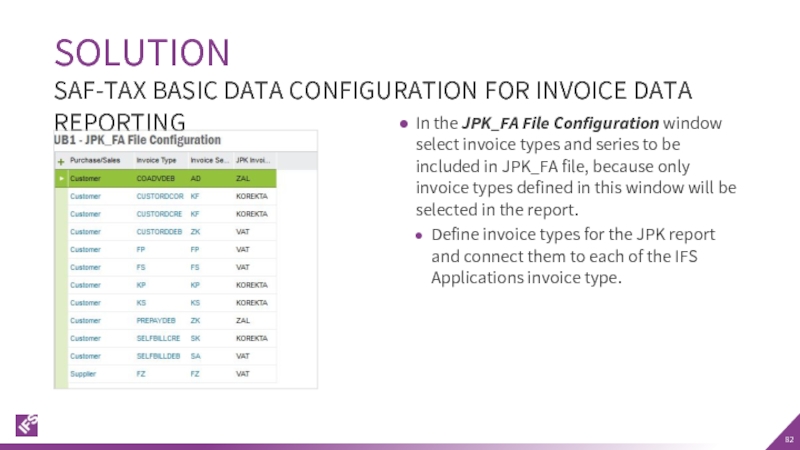
Слайд 82In the JPK_FA File Configuration window select invoice types and series
Define invoice types for the JPK report and connect them to each of the IFS Applications invoice type.
SOLUTION
SAF-TAX BASIC DATA CONFIGURATION FOR INVOICE DATA REPORTING
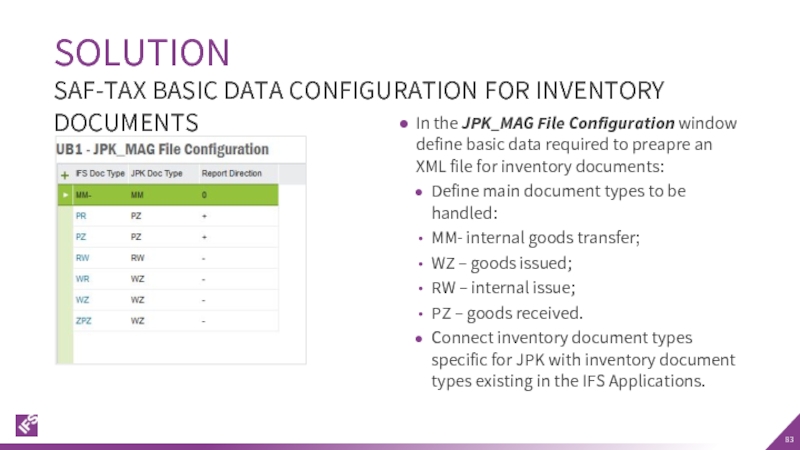
Слайд 83In the JPK_MAG File Configuration window define basic data required to
Define main document types to be handled:
MM- internal goods transfer;
WZ – goods issued;
RW – internal issue;
PZ – goods received.
Connect inventory document types specific for JPK with inventory document types existing in the IFS Applications.
SOLUTION
SAF-TAX BASIC DATA CONFIGURATION FOR INVENTORY DOCUMENTS
Слайд 84To prepare a data for the SAF-T (JPK) reports enter one
MAG for inventory documents reporting;
VAT for tax reporting;
KR for account books reporting
FA for invoice data reporting
WB for mixed payment reporting.
SOLUTION
SAF-TAX RECORD CREATION
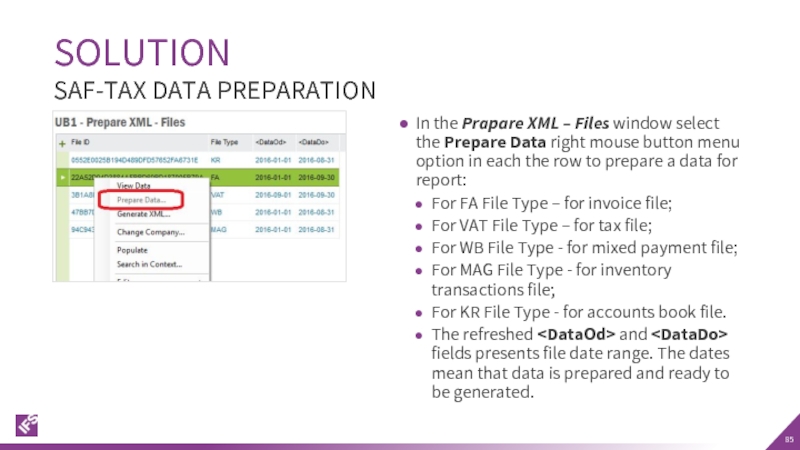
Слайд 85In the Prapare XML – Files window select the Prepare Data
For FA File Type – for invoice file;
For VAT File Type – for tax file;
For WB File Type - for mixed payment file;
For MAG File Type - for inventory transactions file;
For KR File Type - for accounts book file.
The refreshed
SOLUTION
SAF-TAX DATA PREPARATION
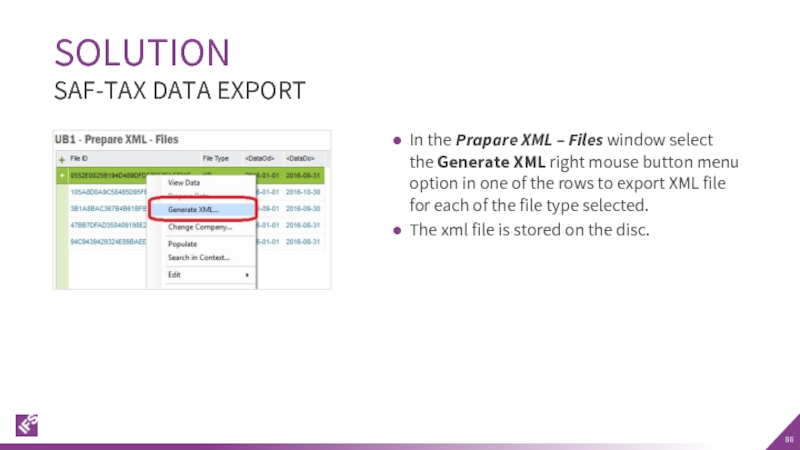
Слайд 86In the Prapare XML – Files window select the Generate XML
The xml file is stored on the disc.
SOLUTION
SAF-TAX DATA EXPORT
Слайд 87There can be only one JPK File Type at a time
Only customer invoices are handled, even though in the JPK_FA File Configuration window also supplier invoices can be selected.
DELIMITATIONS
Слайд 89The Romanian company must present specific reports, like:
A list of inventory
An arrival report after purchased goods are received into inventory.
BACKGROUND
LEGAL REQUIREMENTS OVERVIEW
Слайд 90To comply with the legal requirements two reports are introduced:
Inventory Part
Purchase Order Receipts Report.
The Inventory Part Transaction List is a monthly report that presents the transactions for the inventory part for a given month and also opening and closing balances expressed both in quantitative and monetary terms as well as information about inventory documents.
The transactions are presented for a given site, location group, generated for a given statistic year and statistic period.
The Purchase Order Receipts Report report presents information on received goods, like company and supplier addresses, part numbers, received quantities and part prices.
SOLUTION
OVERVIEW
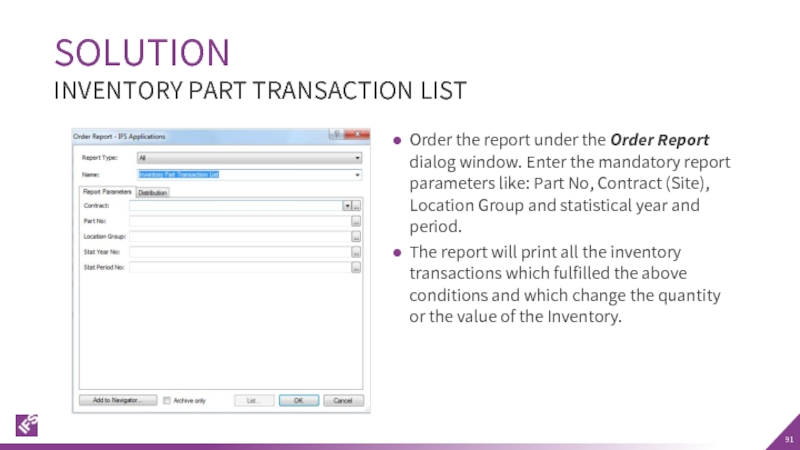
Слайд 91Order the report under the Order Report dialog window. Enter the
The report will print all the inventory transactions which fulfilled the above conditions and which change the quantity or the value of the Inventory.
SOLUTION
INVENTORY PART TRANSACTION LIST
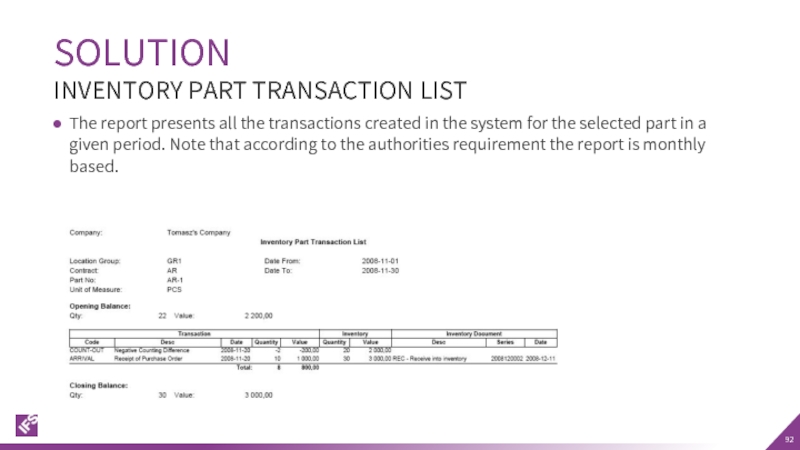
Слайд 92The report presents all the transactions created in the system for
SOLUTION
INVENTORY PART TRANSACTION LIST
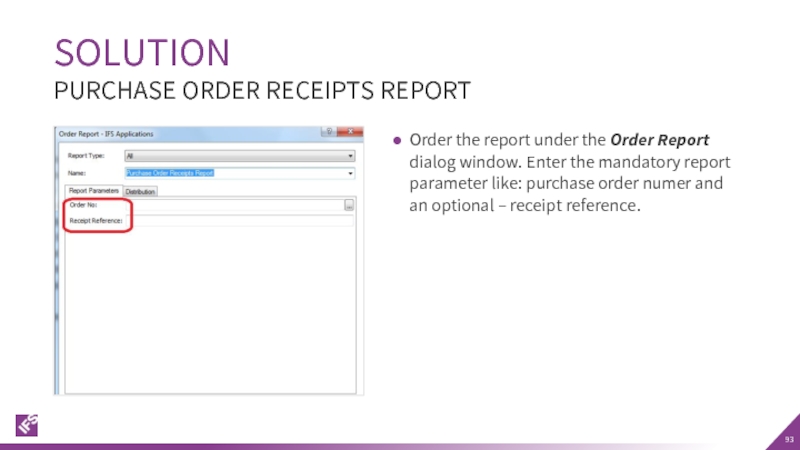
Слайд 93Order the report under the Order Report dialog window. Enter the
SOLUTION
PURCHASE ORDER RECEIPTS REPORT
Слайд 94To run the report automatically, select the Print Arrival Report check
SOLUTION
PURCHASE ORDER RECEIPTS REPORT
Слайд 95The report presents all the ARRIVAL transactions type that has been
The inventory transactions are grouped by part number and location number.
SOLUTION
PURCHASE ORDER RECEIPTS REPORT