Командоформирующая игра“Race for the truth”
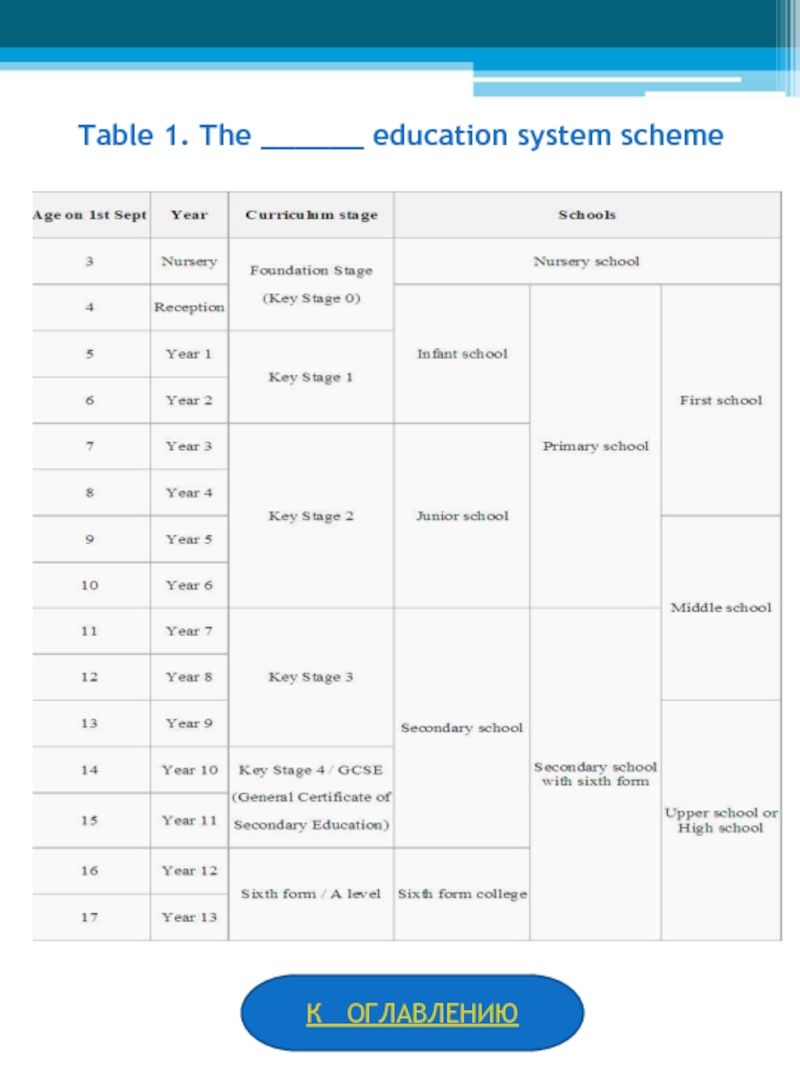
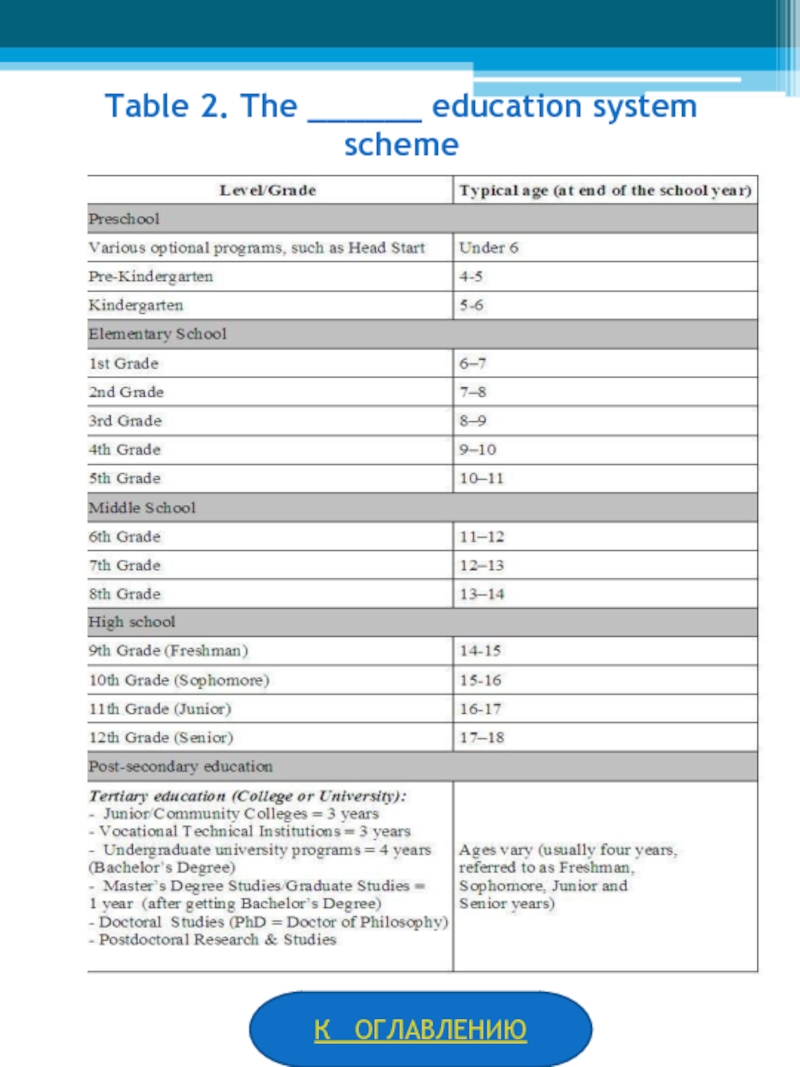
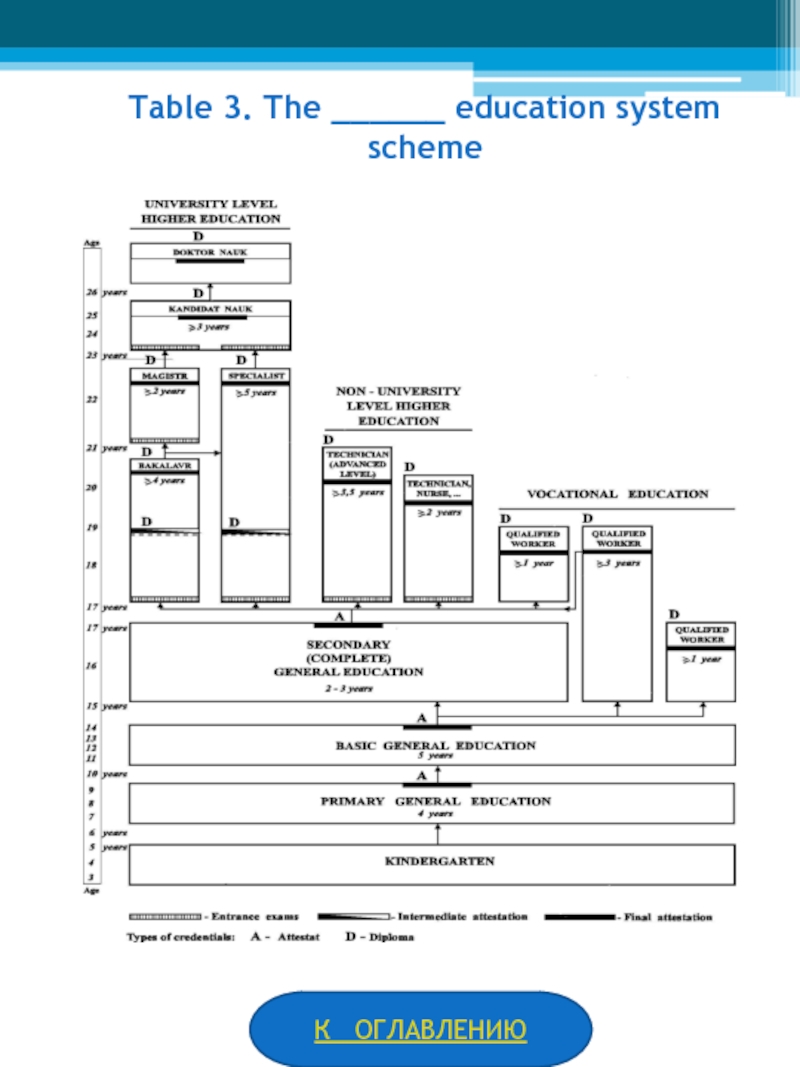
Упражнения на закрепление «What do you remember about Russian, American and English education?”
Грамматический блок: The Future Simple Tense
Новая лексика по тексту A “My alma mater: Siberian State Aerospace University”
Текст A:“My alma mater: Siberian State Aerospace University”
Упражнения на отработку новой лексики по тексту A: игра “Who wants to be a Millionaire student”,“Password”,“Undercover”
Упражнения на отработку текста A и грамматической темы
Проект “University sightseeing excursion”
Часть 1
ОГЛАВЛЕНИЕ





![Task 2. Remember the words directly connected with the topic “Education”. EDUCATION [‚edʒʋ’keɪʃən] – образование](/img/tmb/4/312704/067a6daa0dcff25f4050ba183cd99b50-800x.jpg)
![HIGHER EDUCATION[’haɪə ‚edʒʋ’keɪʃən] –высшее образованиеVOCATIONAL TECHNICAL EDUCATION[vəʋ’keɪʃənəl ’teknɪkəl‚edʒʋ’keɪʃən] – профессиональное техническое образование UNDERGRADUATE COURSE[‚ʌndər’grædʒu:ɪt kɔ:rs]](/img/tmb/4/312704/1d88f5fbcc954b7ebd1a477475750fb6-800x.jpg)
![MASTER’S DEGREE[’mæstəs dɪ’gri:] –степень магистраACADEMIC YEAR [‚ækə’demɪk jɪə] –учебный год BREAK TIME[breɪk taɪm] – перемена,](/img/tmb/4/312704/4f4bcaa4e0762f3e3736dab74d22fbb5-800x.jpg)
![FACULTY[’fækəltɪ] – факультетMARK [mɑ:k] – отметка GRADUATIONокончание учебного заведения DROP OUT выбывать, бросать (учебу, работу)К ОГЛАВЛЕНИЮ](/img/tmb/4/312704/d915132793b351009e375db105c42f8b-800x.jpg)











![MACHINE-BUILDING FACTORY [mə’ʃi:n‚bɪldɪŋ ’fæktərɪ] –машиностроительный завод This is a plant consisting of one or more](/img/tmb/4/312704/b97613335be25da573ae3ee88c4abad4-800x.jpg)
![BRANCH[bræntʃ] –ветка, отделениеThis is a division of some larger or more complex organization. К ОГЛАВЛЕНИЮ](/img/tmb/4/312704/81b0c69f0ef8e1d714694c9cc7d5fd87-800x.jpg)






