- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
State Establishment “N.N. Alexandrov National Cancer Centre of Belarus” презентация
Содержание
- 1. State Establishment “N.N. Alexandrov National Cancer Centre of Belarus”
- 2. THE COUNCIL OF MINISTERS OF THE BYELORUSSIAN
- 3. 1960 y. N.N. Alexandrov – the founder and
- 4. Administration building
- 5. Modernized building for oncological mammalogical department
- 6. Laboratory building
- 7. Recreational pavilions in pedestrian zones on the Centre territory
- 8. With the Decree of President of the
- 9. SE N.N.Alexandrov NCCB SE COH NCCB 5
- 10. Centre Structure At the base of
- 11. Research Trends organizing anticancer struggle, studying cancer
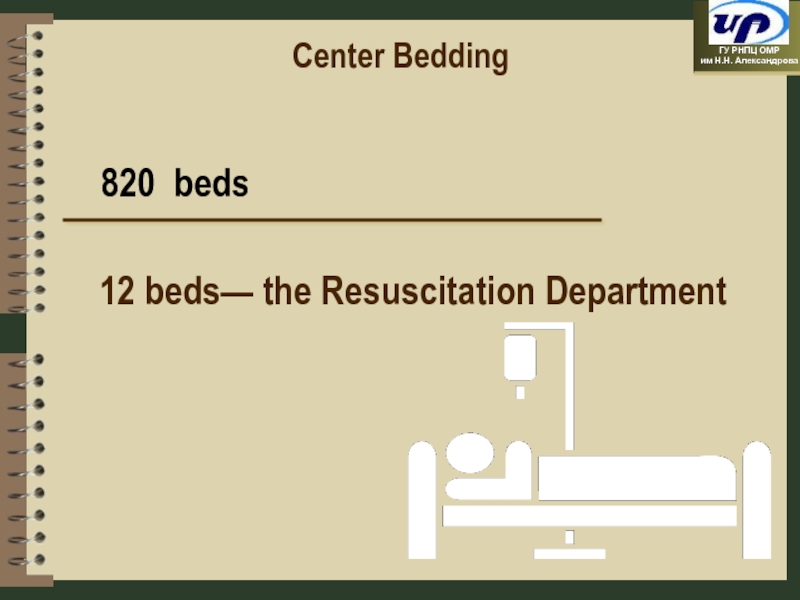
- 12. Center Bedding 820 beds 12 beds— the Resuscitation Department
- 13. Hospitalized Patients 19343 Annually more than
- 14. Diagnostic Base of the Centre
- 15. Practically, the whole specter of biochemical, clinical,
- 16. Laboratory of Molecular Oncogenomics Specter of
- 17. Translocation t(11,14) under lymphoma from mantle zone
- 18. Laboratory of Molecular Cytogenetics
- 19. Morphological Methods of Investigation
- 20. Distribution of protein ER in tumour cell
- 21. Distribution of protein c-erbB-2 in tumour cell
- 22. Telepathology system for giving on-line consultations on
- 23. Radiodiagnosis The department is equipped with
- 24. Computer roentgen tomographs
- 25. Magnetic resonance tomograph
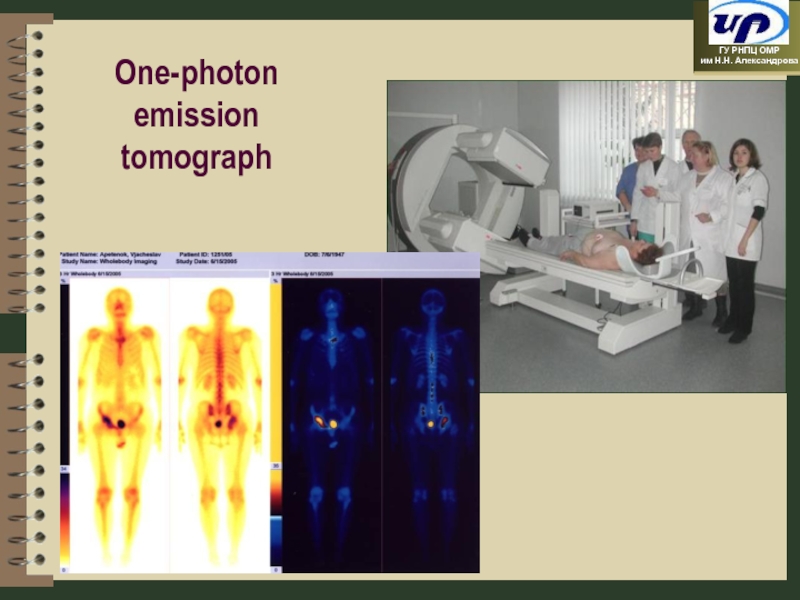
- 26. One-photon emission tomograph
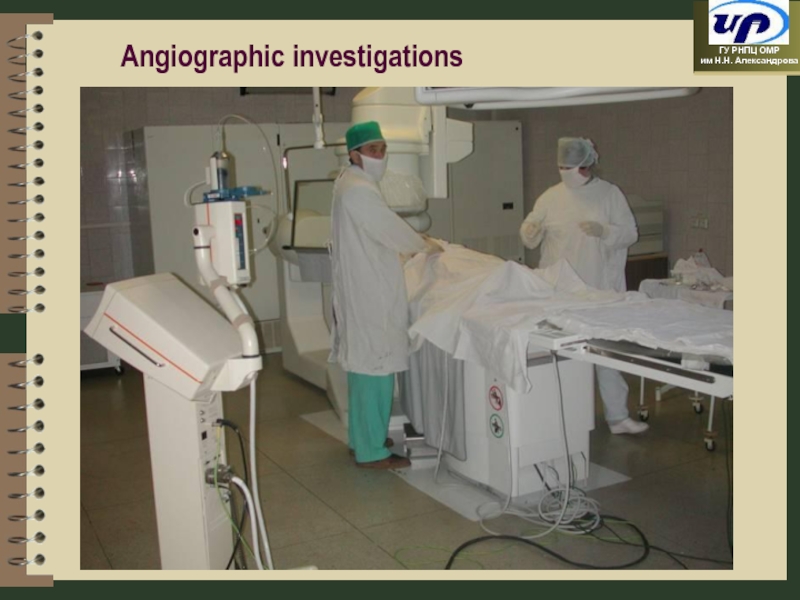
- 27. Angiographic investigations
- 28. Ultrasound investigations USI scanners in the expert class
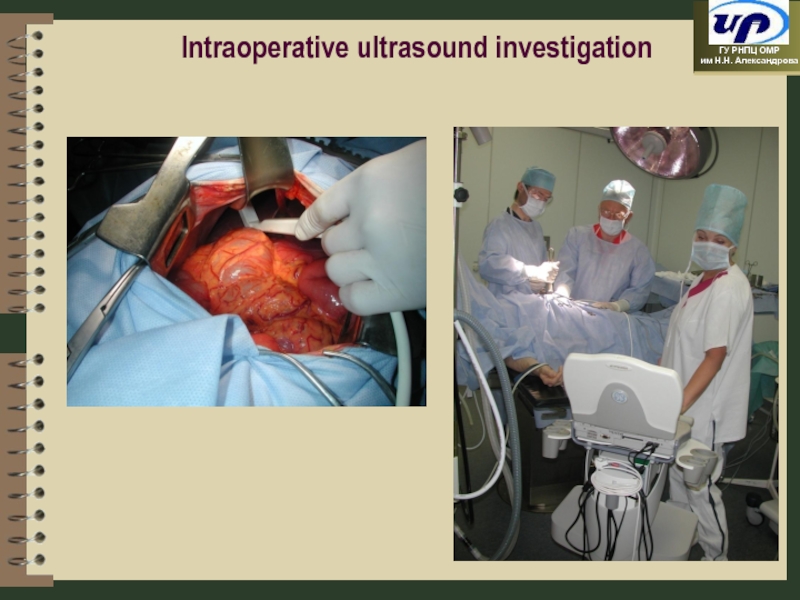
- 29. Intraoperative ultrasound investigation
- 30. Diagnosing Bladder Cancer on the Basis of
- 31. Efficacy of Clinical Use of 5-ALA (Alamin)
- 32. Highly Technological Methods of Treatment
- 33. Surgical Activities Totally, there were made 2007
- 34. Highly Technological Medical Interventions Combined operations with
- 35. Pancreatectomy under total pancreas cancer, with pylorus
- 36. Multicomponent management of patients with primary liver
- 37. method of combined and radiation treatment of
- 38. reconstruction of mandible using titanium implants; use
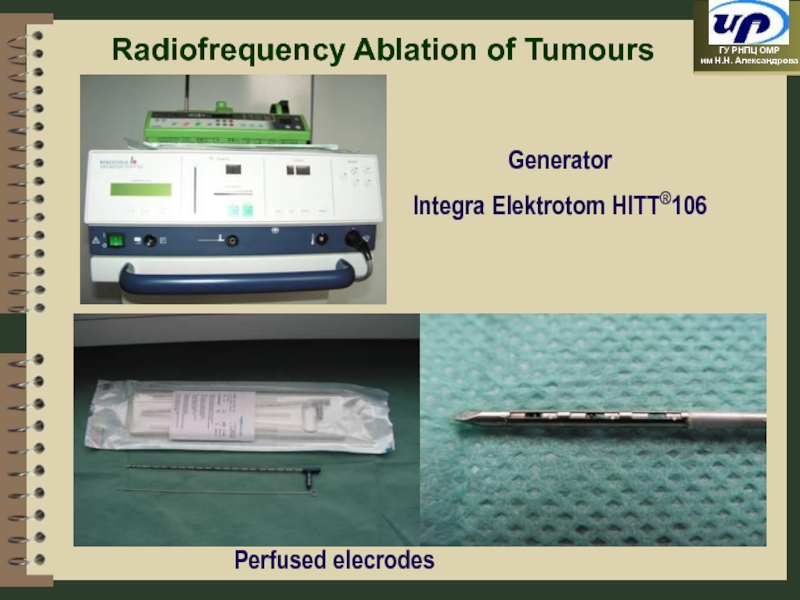
- 39. Radiofrequency Ablation of Tumours Perfused elecrodes Generator Integra Elektrotom HITT®106
- 40. Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Tumour Liver
- 41. Radiofrequency Ablation of Pulmonary Neoplasm Computer tomograms
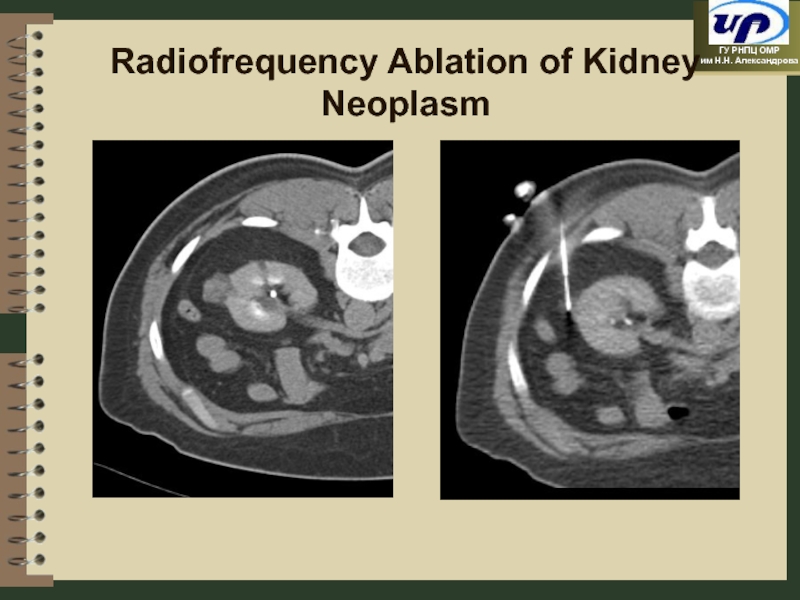
- 42. Radiofrequency Ablation of Kidney Neoplasm
- 43. Endoscopic Operations Laparascopic: splenectomy,adrenalectomy, nephrectomy, radical prostatectomy,
- 44. OPERATIONS UNDER HEAD AND NECK TUMOURS
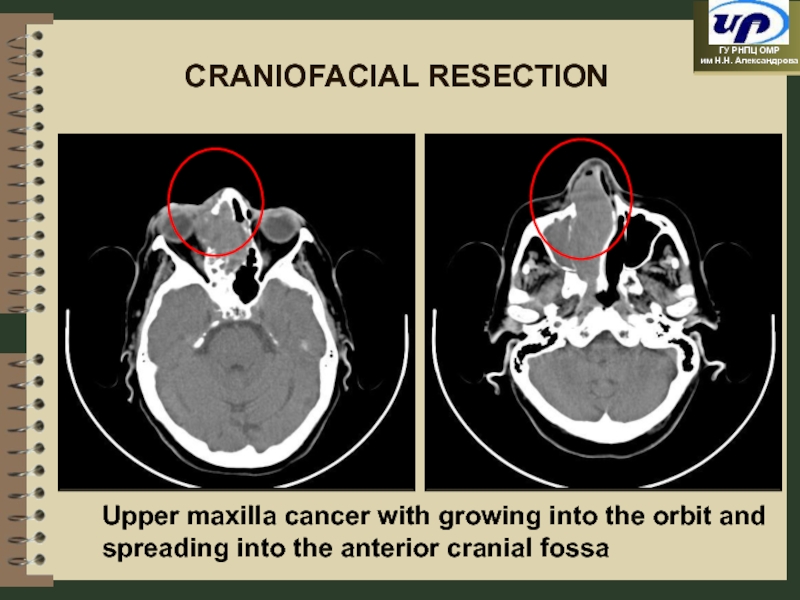
- 45. Upper maxilla cancer with growing into
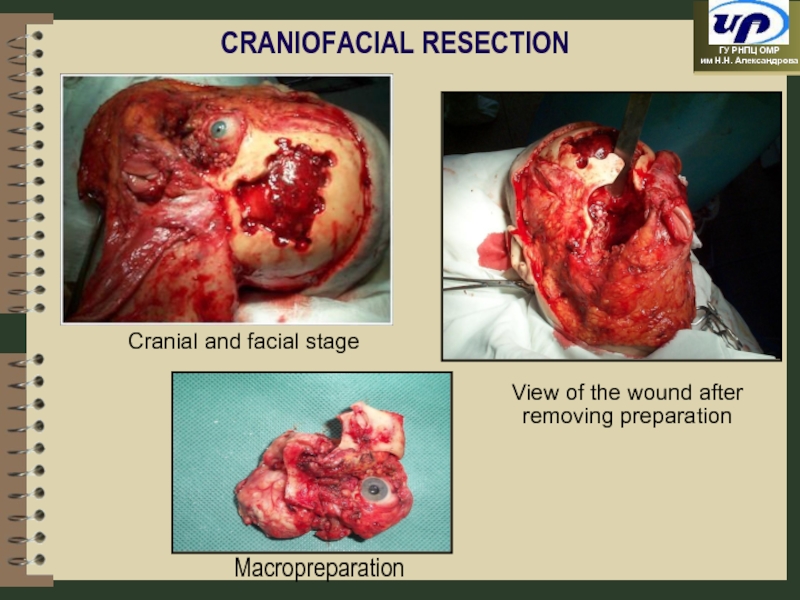
- 46. CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION Cranial and facial stage
- 47. TECHNOLOGY OF TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL SHUNTING WITH VOCAL PROSTHESIS INSERTING SET FOR INSERTING VOCAL PROSTHESES
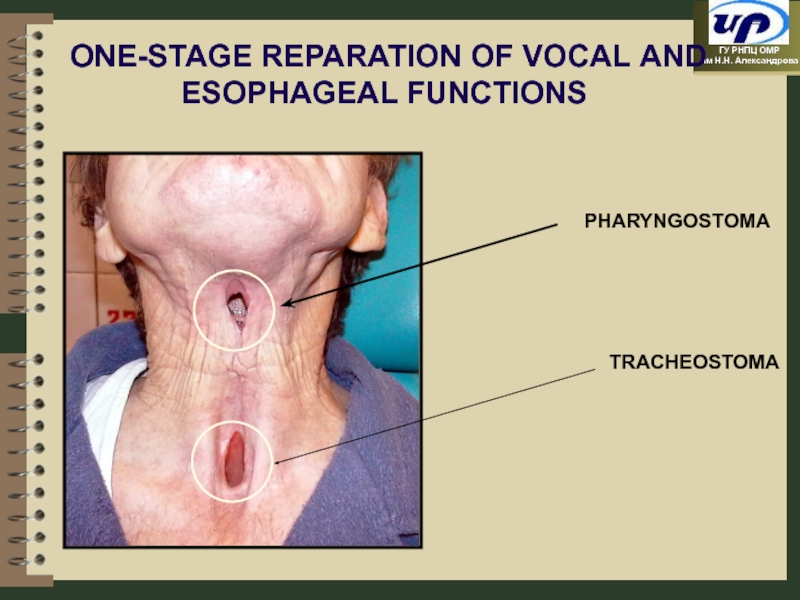
- 48. ONE-STAGE REPARATION OF VOCAL AND ESOPHAGEAL FUNCTIONS PHARYNGOSTOMA TRACHEOSTOMA
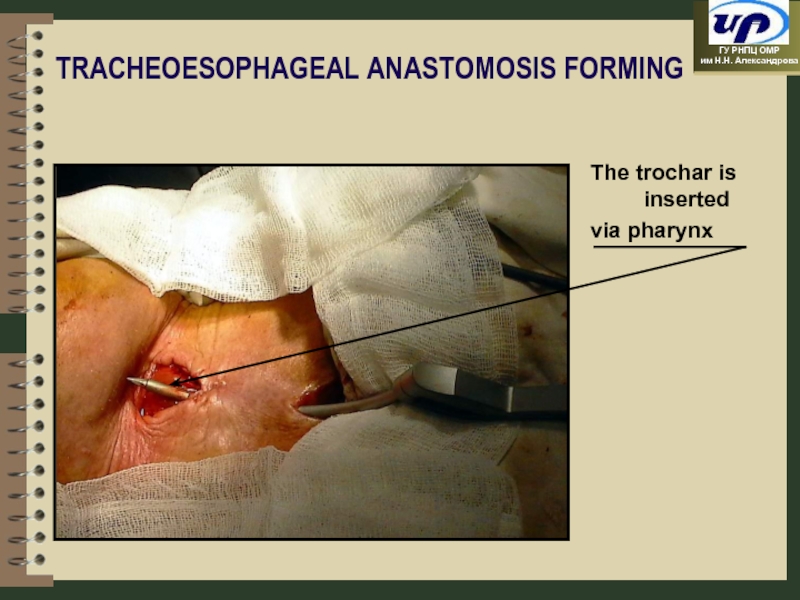
- 49. TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL ANASTOMOSIS FORMING The trochar is inserted via pharynx
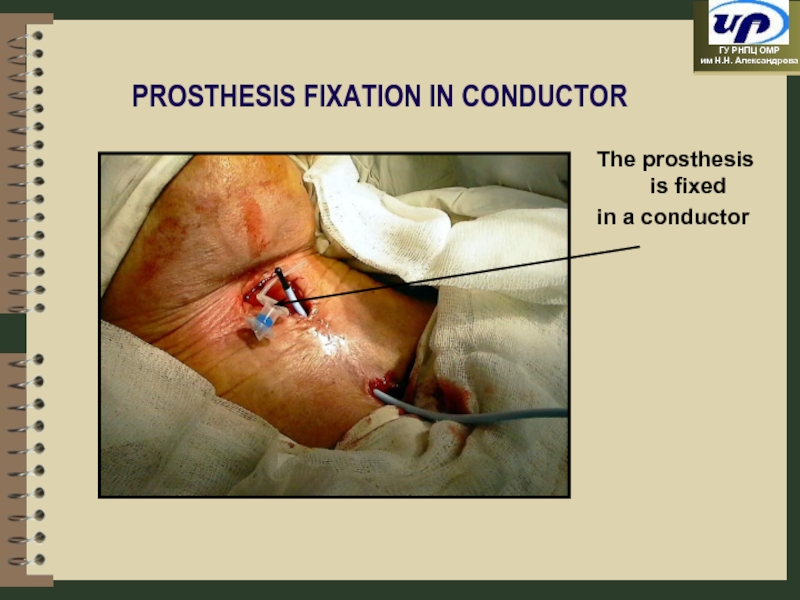
- 50. PROSTHESIS FIXATION IN CONDUCTOR The prosthesis is fixed in a conductor
- 51. PHARYNX ANTERIOR WALL FORMING WITH LOCAL TISSUES Vocal prosthesis
- 52. THE SKIN DEFECT IS REMOVED WITH SKIN AND MUSCULAR PECTORAL GRAFT
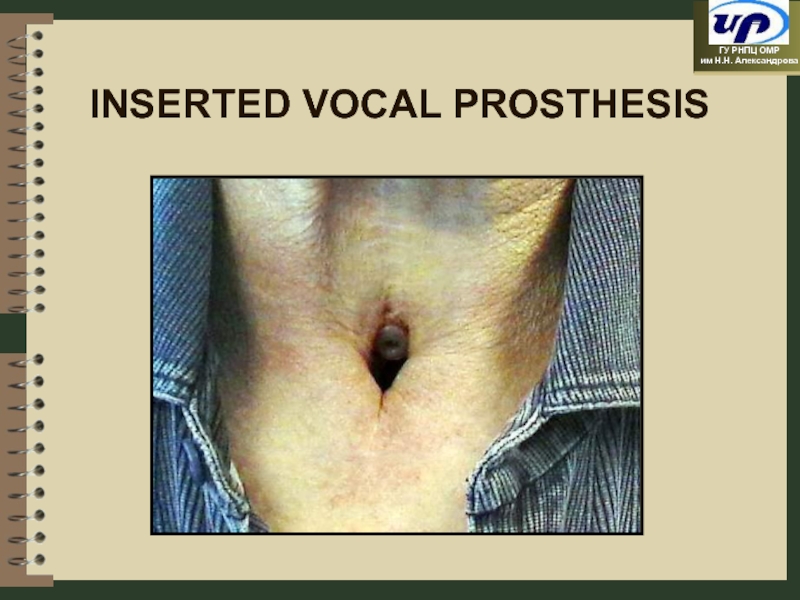
- 53. INSERTED VOCAL PROSTHESIS
- 54. Plastic Operations in Patients with Breast Cancer
- 55. Patient Z, 34 y.o. Diagnosis: left breast
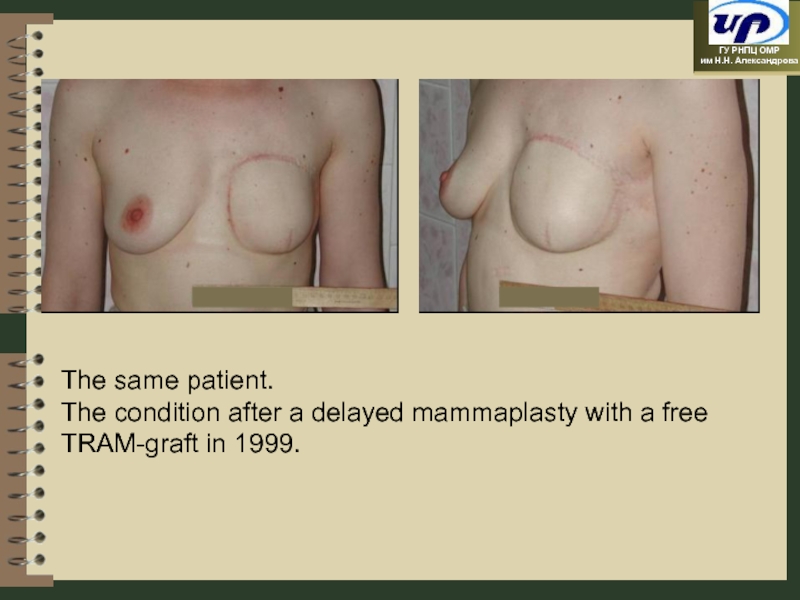
- 56. The same patient. The condition after a
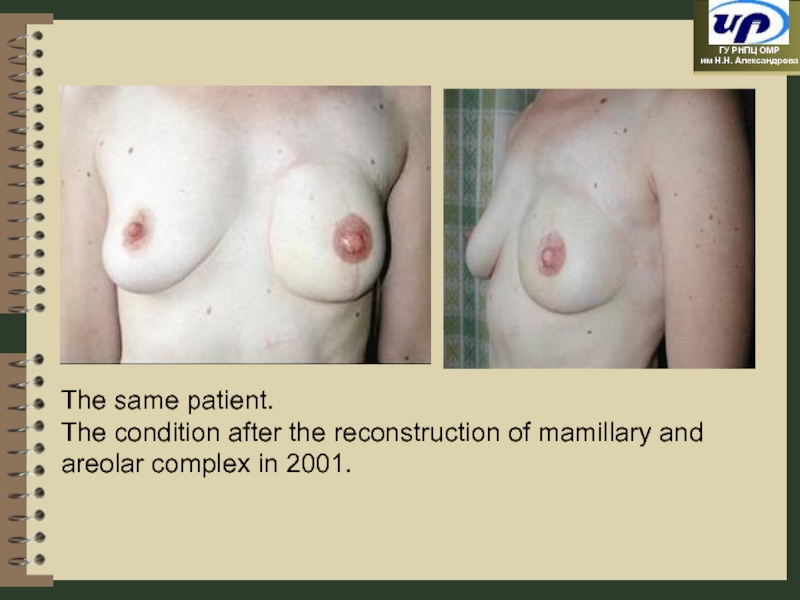
- 57. The same patient. The condition after the reconstruction of mamillary and areolar complex in 2001.
- 58. Right breast cancer Т2N1М0. The condition
- 59. Postmastectomy Syndrome
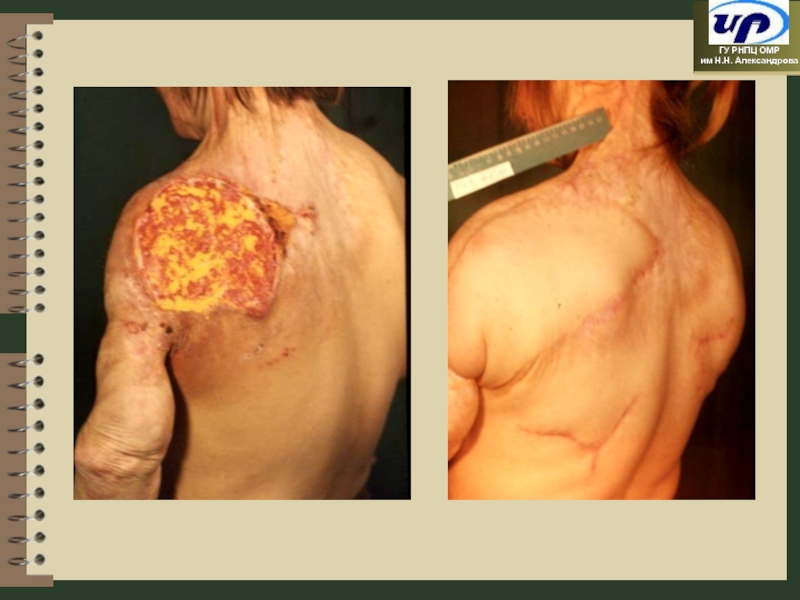
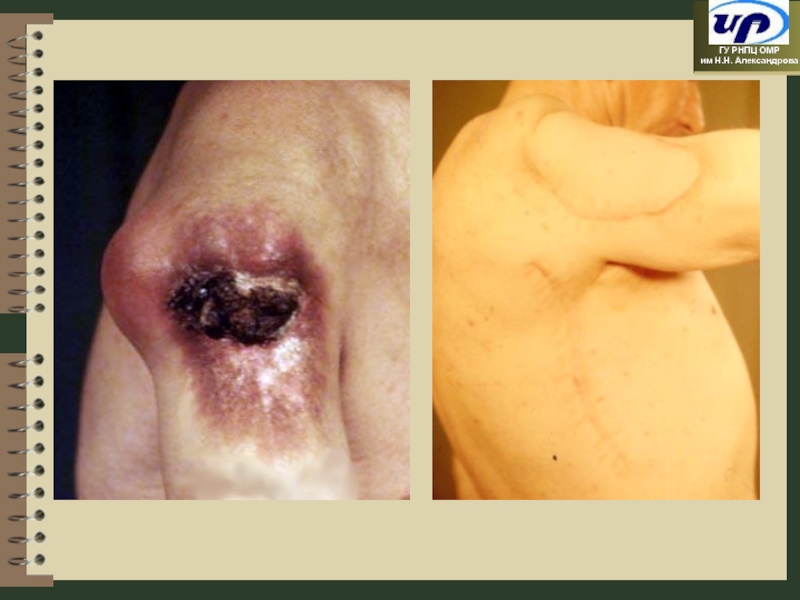
- 60. Plasty of Soft Tissues
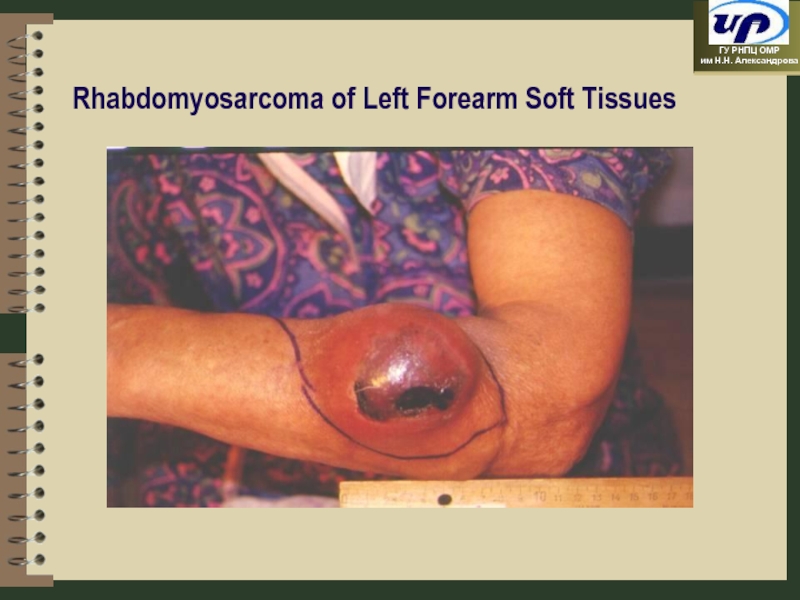
- 63. Rhabdomyosarcoma of Left Forearm Soft Tissues
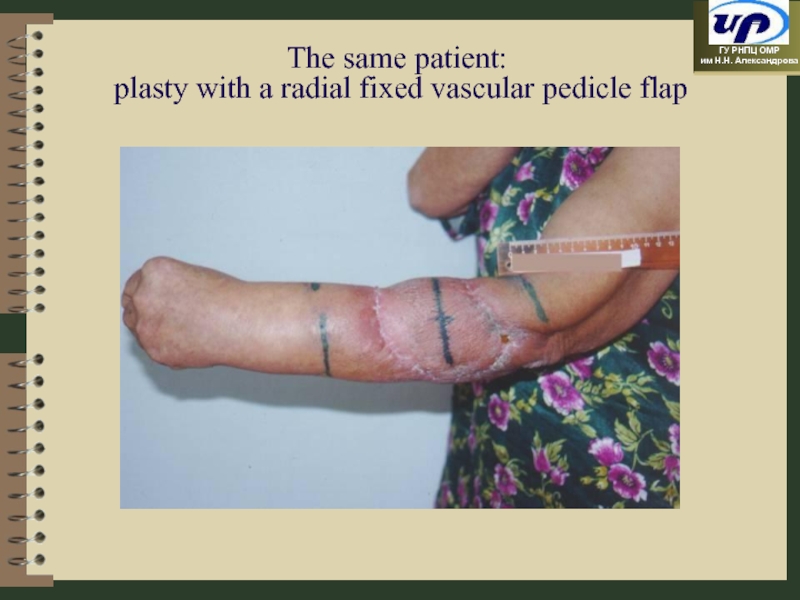
- 64. The same patient: plasty with a radial fixed vascular pedicle flap
- 65. Operations Preserving Organs under Bone Tumours
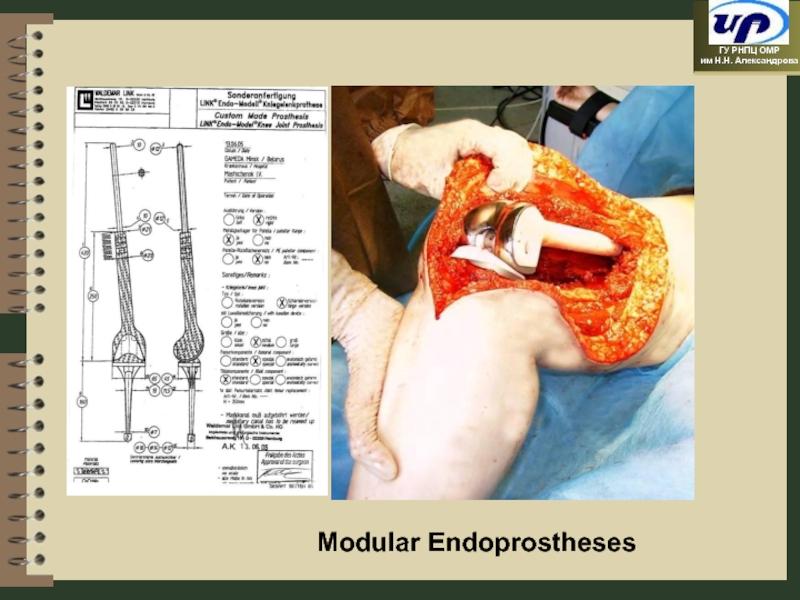
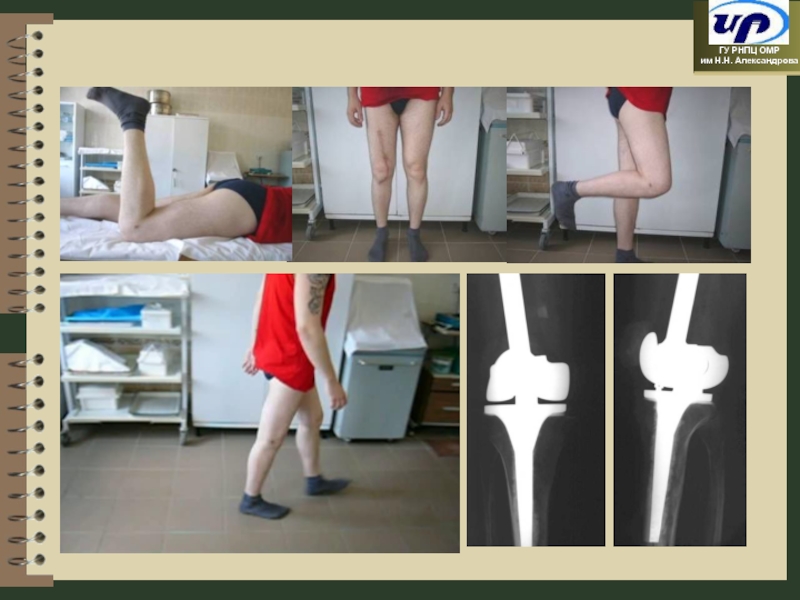
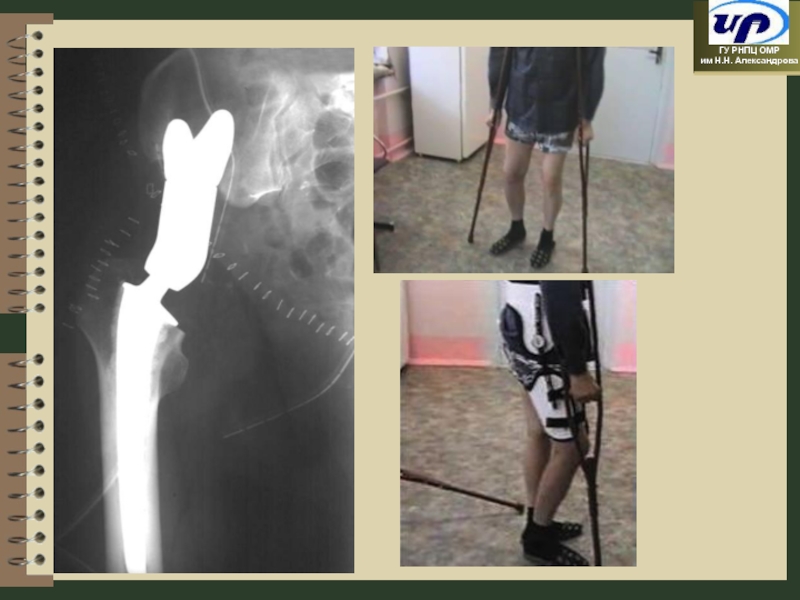
- 66. Modular Endoprostheses
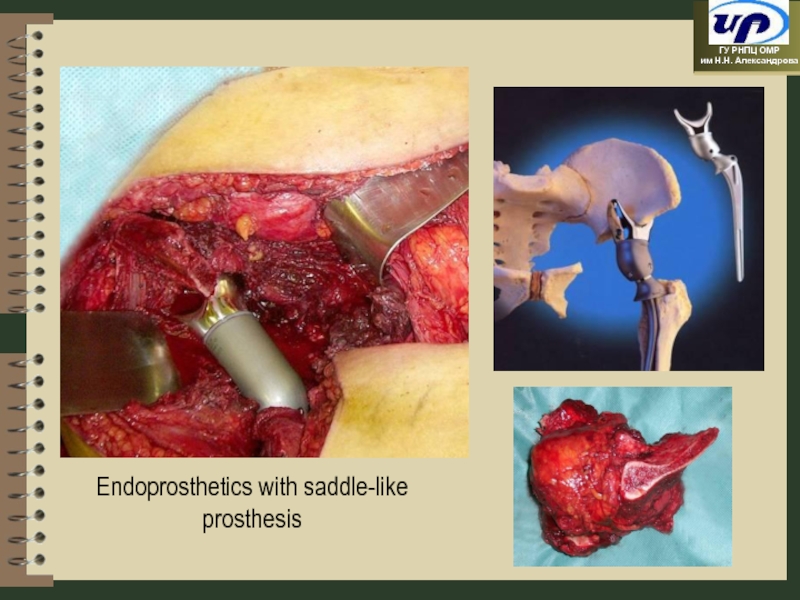
- 69. Endoprosthetics with saddle-like prosthesis
- 71. Lung Cancer and Mediastrium Tumours
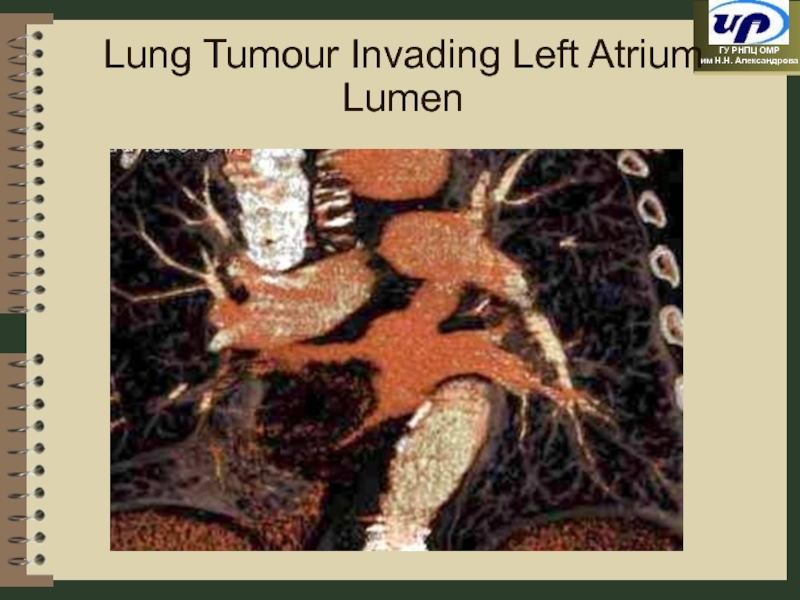
- 72. Lung Tumour Invading Left Atrium Lumen
- 73. Tumour in Left Atrium Lumen
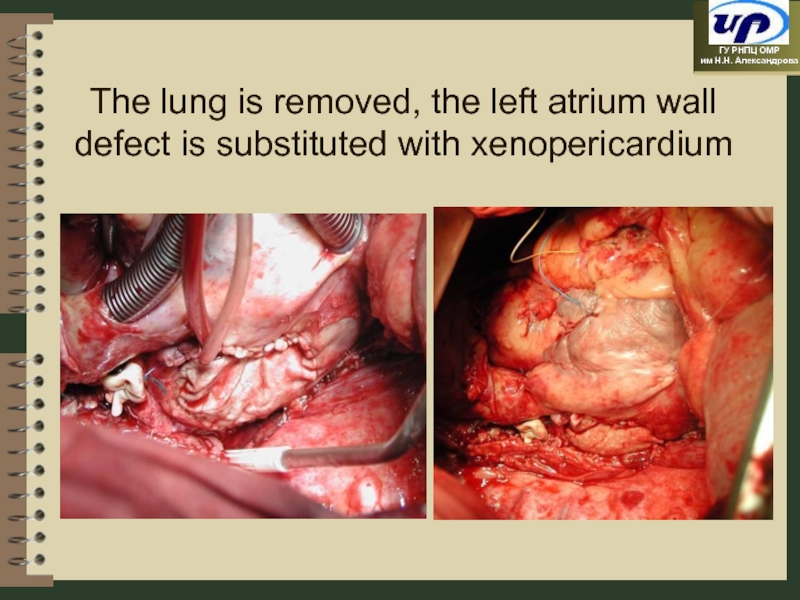
- 74. The lung is removed, the left atrium wall defect is substituted with xenopericardium
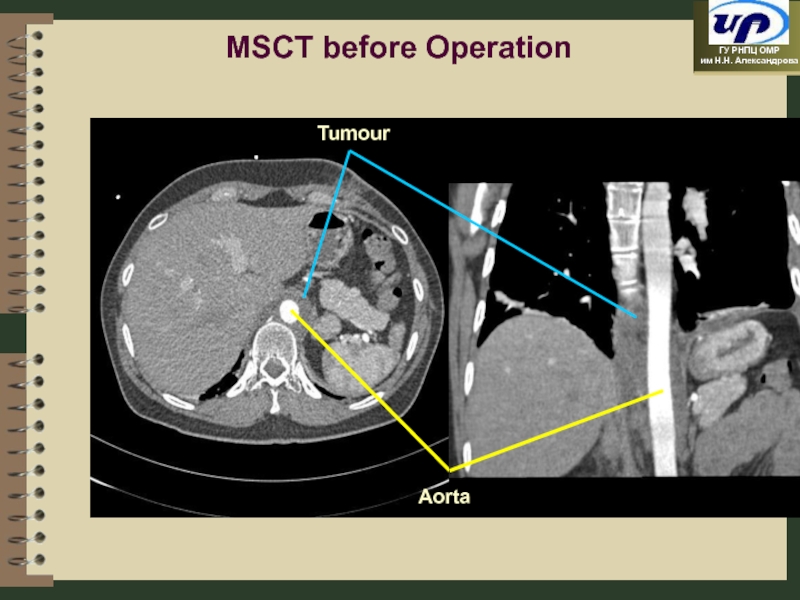
- 75. MSCT before Operation
- 76. Detecting Site of Thoracic and Abdominal Aorta
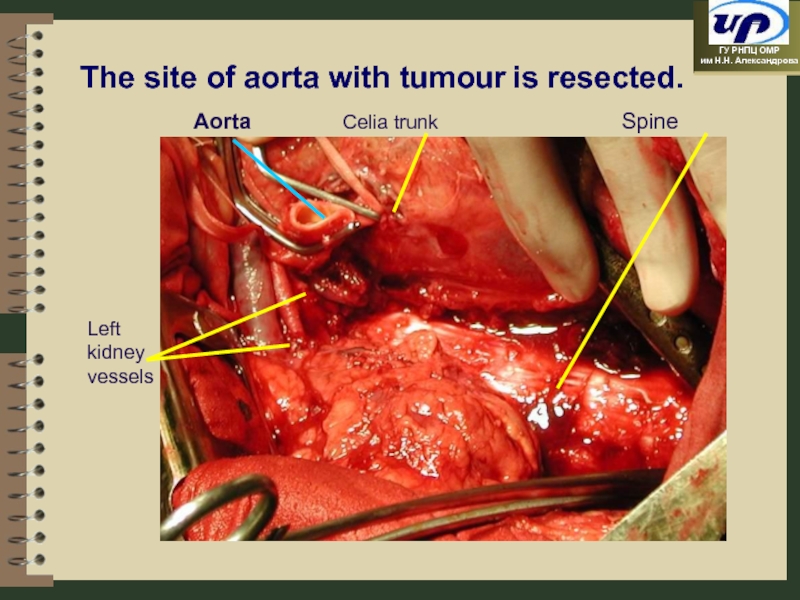
- 77. Spine Left kidney vessels Aorta The
- 78. Esophagus Left kidney vessels Aorta prosthesis The prosthesis is made to aorta. Celia trunk SMА
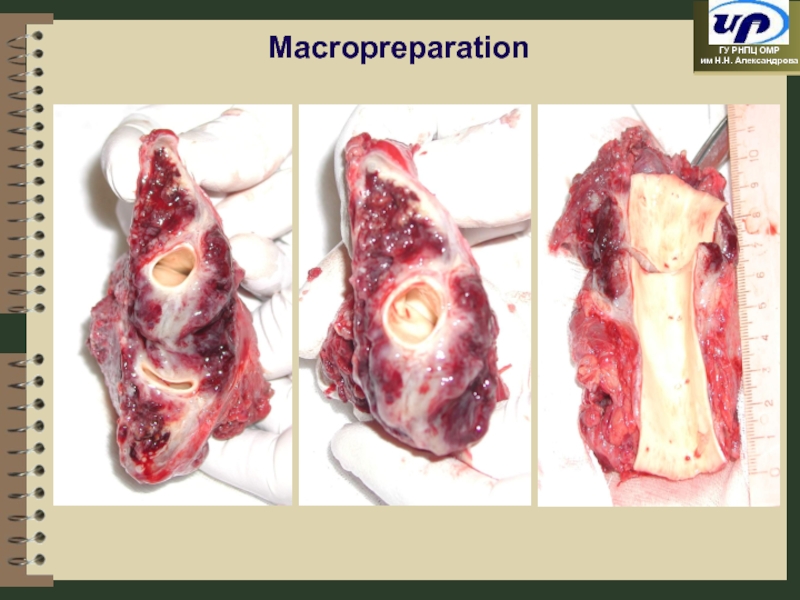
- 79. Macropreparation
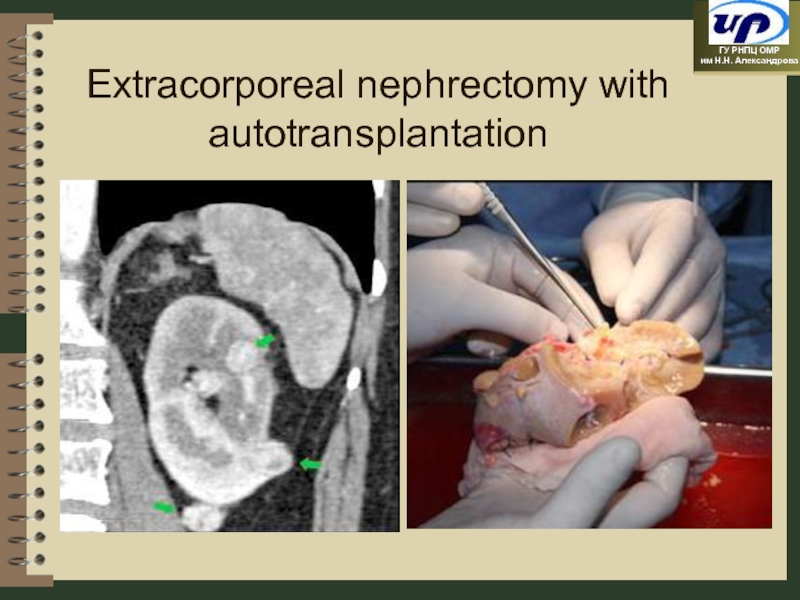
- 80. Extracorporeal nephrectomy with autotransplantation
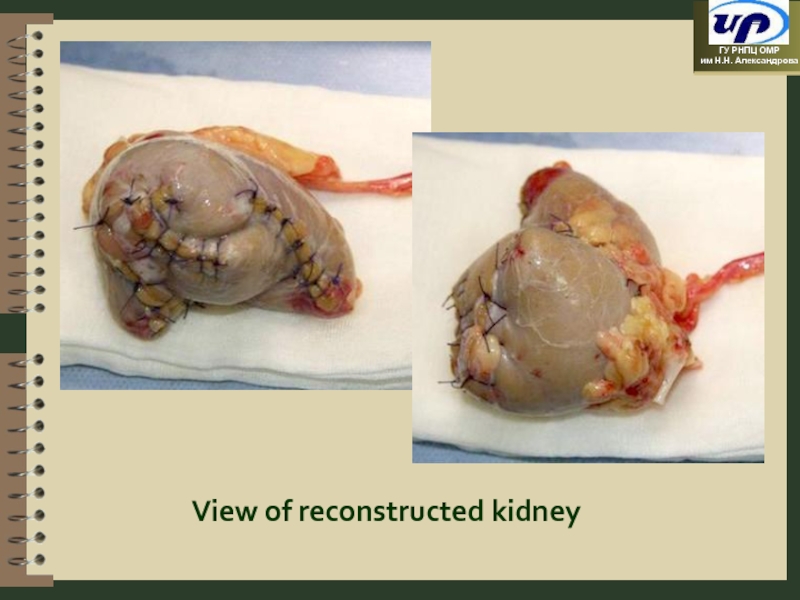
- 81. View of reconstructed kidney
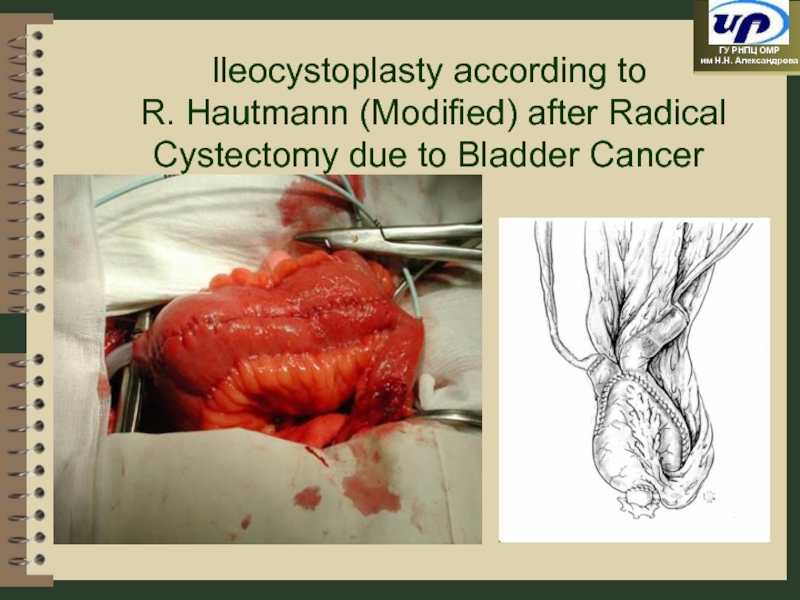
- 82. Ileocystoplasty according to R. Hautmann (Modified) after Radical Cystectomy due to Bladder Cancer
- 83. Operating Block
- 84. Resuscitation Department
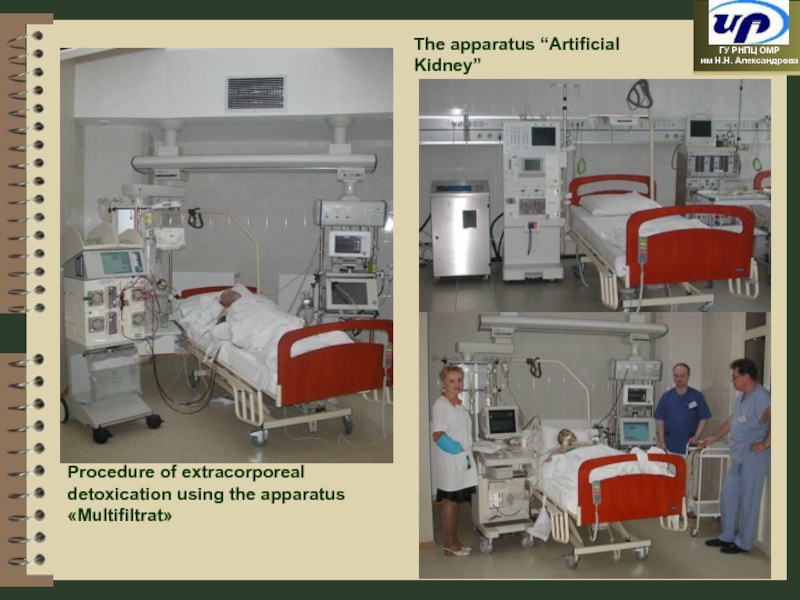
- 85. The apparatus “Artificial Kidney” Procedure of extracorporeal detoxication using the apparatus «Multifiltrat»
- 86. Radiotherapy
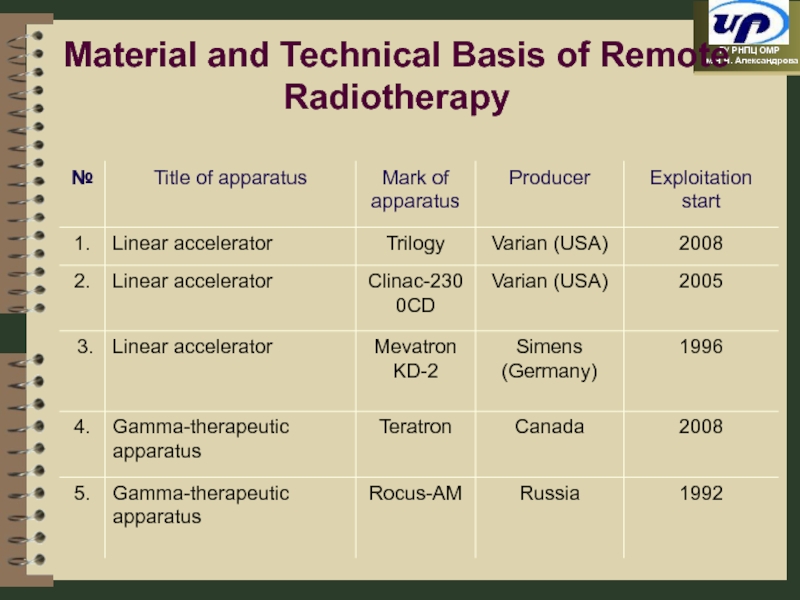
- 87. Material and Technical Basis of Remote Radiotherapy
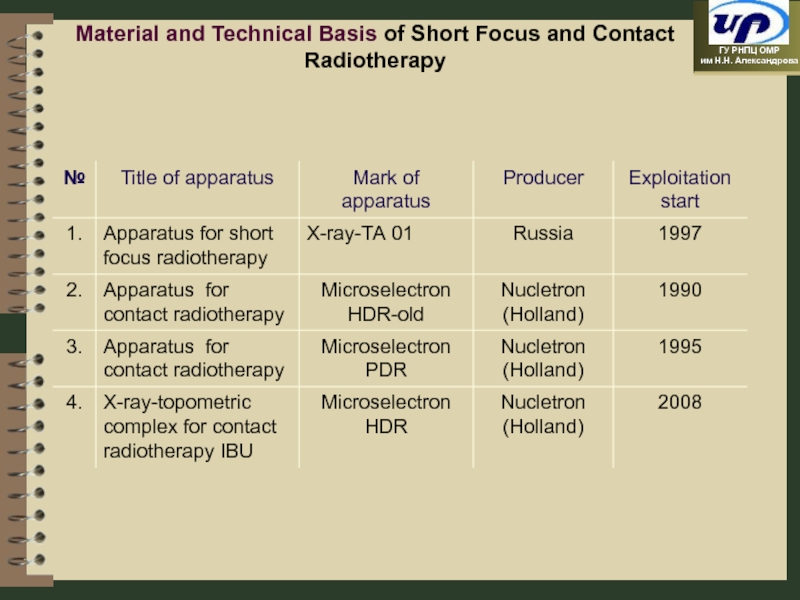
- 88. Material and Technical Basis of Short Focus and Contact Radiotherapy
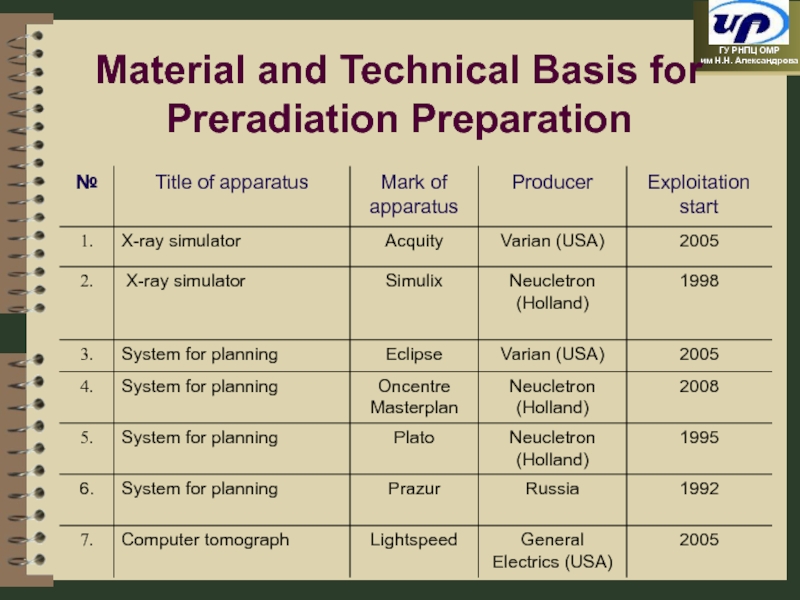
- 89. Material and Technical Basis for Preradiation Preparation
- 90. Material and Technical Basis (Auxiliary Devices and Dosimetry)
- 91. Linear accelerator with 2 photon energies
- 93. High Technologies in Radiotherapy Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy
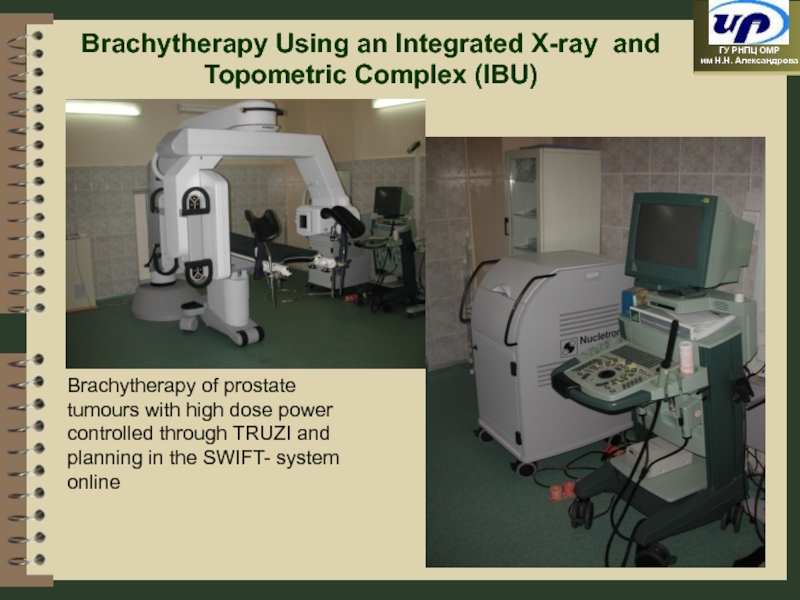
- 94. Brachytherapy Using an Integrated X-ray and
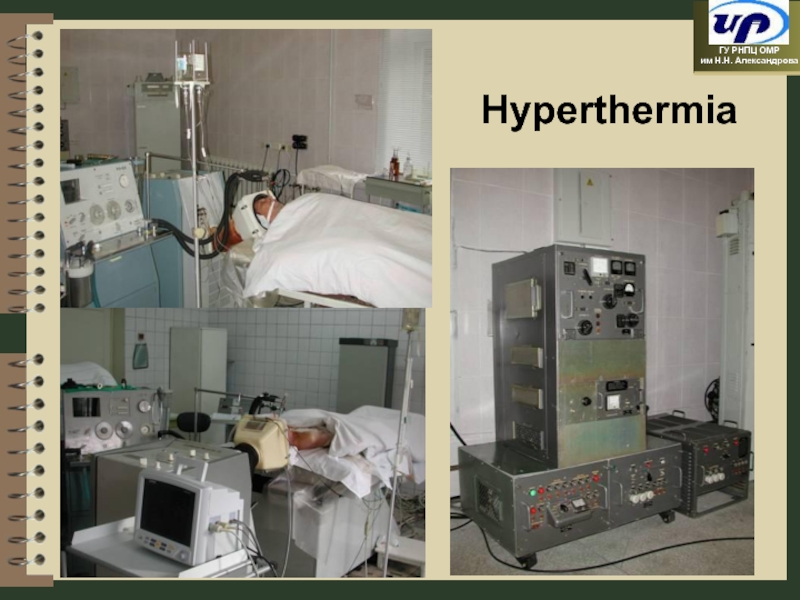
- 95. Hyperthermia
- 96. Equipment for Photodynamic Therapy and Diagnosis «Metalaz-M» «Kamin-Video» «Lesa-6» «LD-680»
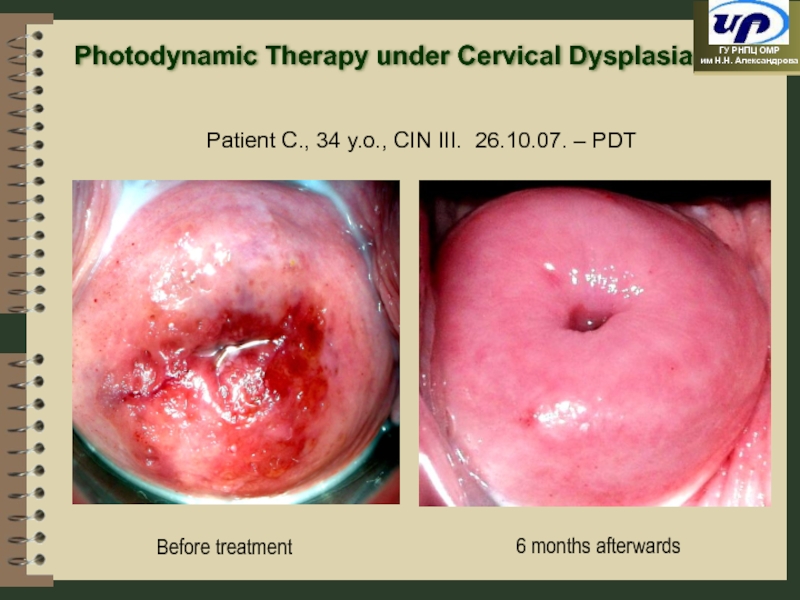
- 97. 6 months afterwards Patient C., 34 y.o.,
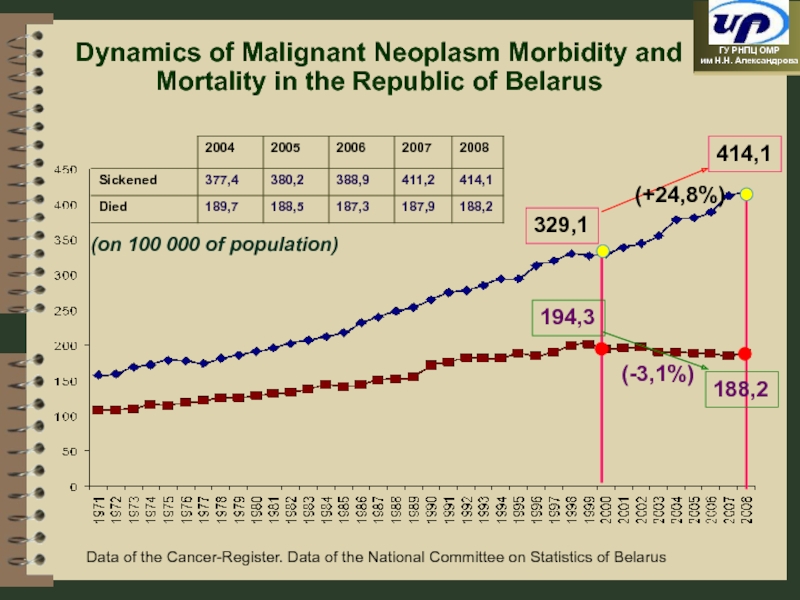
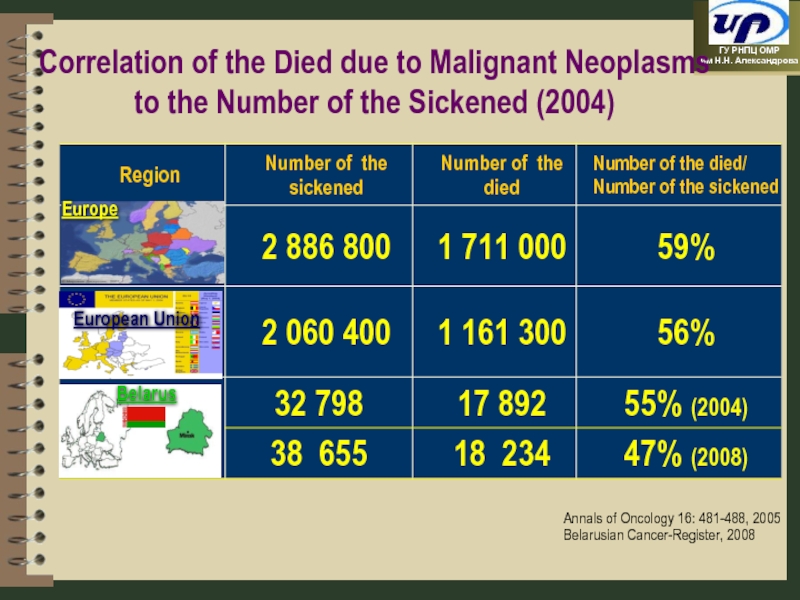
- 98. Dynamics of Malignant Neoplasm Morbidity and Mortality
- 99. Europe Belarus European Union Annals of
Слайд 2THE COUNCIL OF MINISTERS OF THE BYELORUSSIAN SSR
Resolution On Intensifying Cancer
from May
The Council of Ministers of the Byelorussian SSR states that the level of researches on malignant neoplasm diseases is absolutely insufficient in medical and research institutes and establishments of the Byelorussian SSR. There is no material and technical basis for experimental studying the most important problem in the republic. Some oncological dispensaries (Mogilev, Gomel and others) are located in premises, inadequate in area, Vitebsk and Grodno dispensaries have no in-patient departments; there are no hostels-hotels for oncological patients undergoing out-patient treatment. With the aim to create necessary conditions for organizing and conducting broad experimental and clinical researches on cancer problem at an up-to-date level, training highly qualified specialists-oncologists as well as improving prophylactic and medical help to patients with malignant diseases, the BSSR Council of Ministers
D e c i d e s:
1. To take into consideration that in the seven-year plan, the BSSR Public Health Ministry forsees constructing a 200-bedded research institute of oncology and medical radiology in a zone out of Minsk; 5 oncological dispensaries with radiological and in-patient departments.
Слайд 31960 y.
N.N. Alexandrov – the founder and first director near a model
.
Слайд 8With the Decree of President of the Republic of Belarus Alexandr
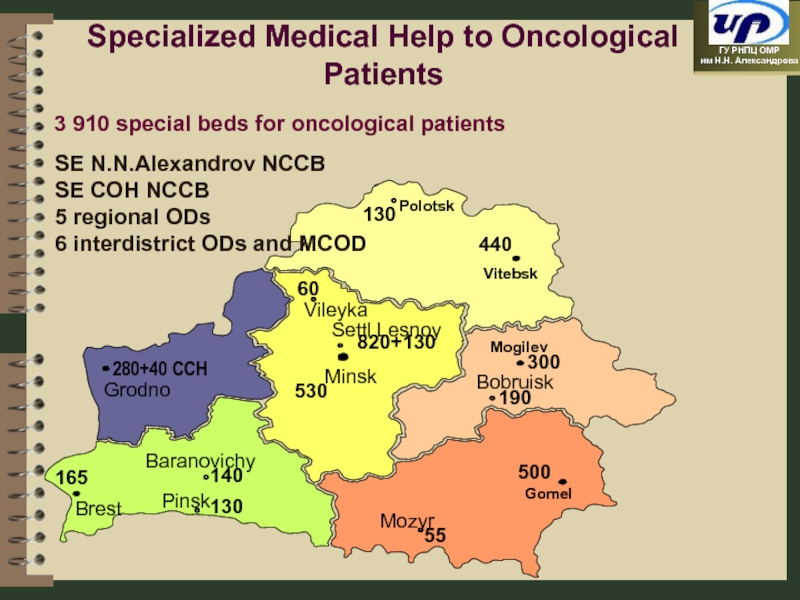
Слайд 9SE N.N.Alexandrov NCCB
SE COH NCCB
5 regional ODs
6 interdistrict ODs and MCOD
Specialized
3 910 special beds for oncological patients
Слайд 10Centre Structure
At the base of the Centre, the BelMAPO Oncology Department
14.00.14 – oncology
14.00.19 – radiodiagnosis, radiotherapy
Слайд 11Research Trends
organizing anticancer struggle, studying cancer epidemiology and prophylaxis
developing new technologies
developing new technologies for managing patients with malignant neoplasms
developing new technologies for rehabilitation and bettering quality of oncological patients’ life
carrying out clinical trials of new drugs
improving medical and technical basis of the oncological service of the republic
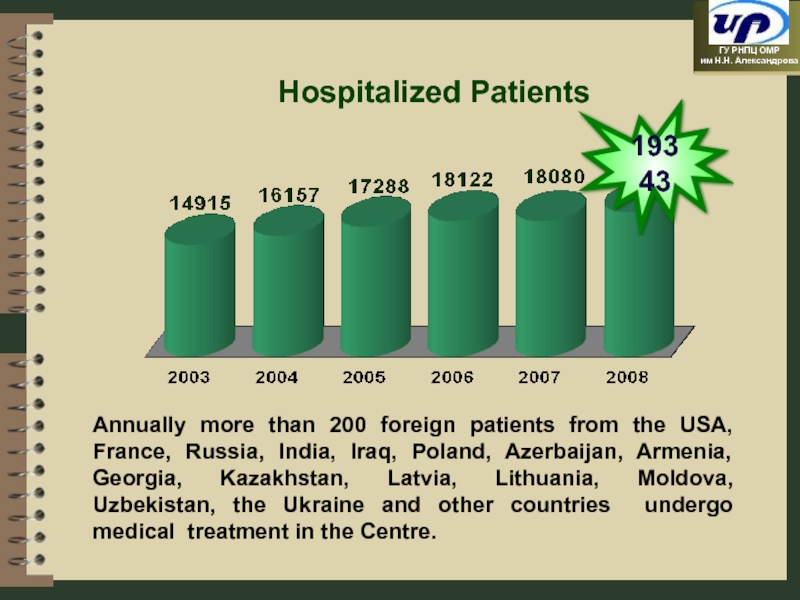
Слайд 13Hospitalized Patients
19343
Annually more than 200 foreign patients from the USA,
Слайд 15Practically, the whole specter of biochemical, clinical, immunohistological, radioisotopic, molecular and
Laboratory Diagnosis
Слайд 16
Laboratory of Molecular Oncogenomics
Specter of Performed Investigations
Detecting mutations in genes
Detecting mutations in genes hereditarily associated with breast and ovarian cancer (BRCA1 and BRCA2) development
Identifying mutations in genes hereditarily associated with colon cancer (APC, K-ras, MLH1, MSH2, BCL2) development
Assessing a residual minimal disease under malignant neoplasms of breast, lung and prostate
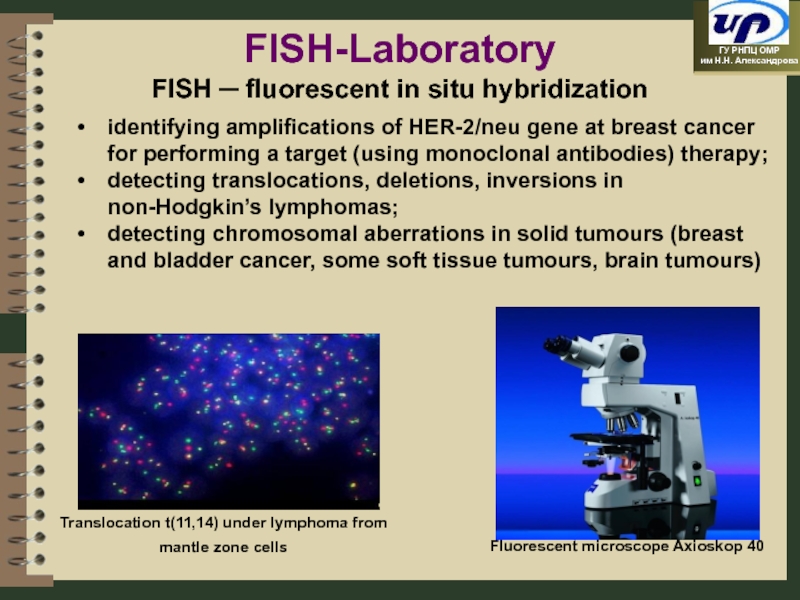
Слайд 17Translocation t(11,14) under lymphoma from mantle zone cells
Fluorescent microscope Axioskop
FISH-Laboratory
FISH ─ fluorescent in situ hybridization
identifying amplifications of HER-2/neu gene at breast cancer for performing a target (using monoclonal antibodies) therapy;
detecting translocations, deletions, inversions in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas;
detecting chromosomal aberrations in solid tumours (breast and bladder cancer, some soft tissue tumours, brain tumours)
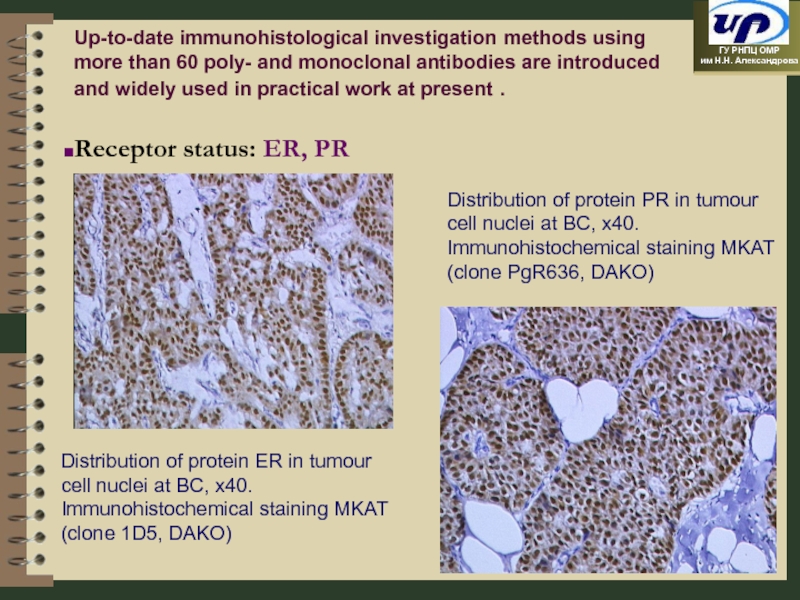
Слайд 20Distribution of protein ER in tumour cell nuclei at BC, x40.
Immunohistochemical
Distribution of protein PR in tumour cell nuclei at BC, x40.
Immunohistochemical staining MKAT (clone PgR636, DAKO)
Receptor status: ER, PR
Up-to-date immunohistological investigation methods using more than 60 poly- and monoclonal antibodies are introduced and widely used in practical work at present .
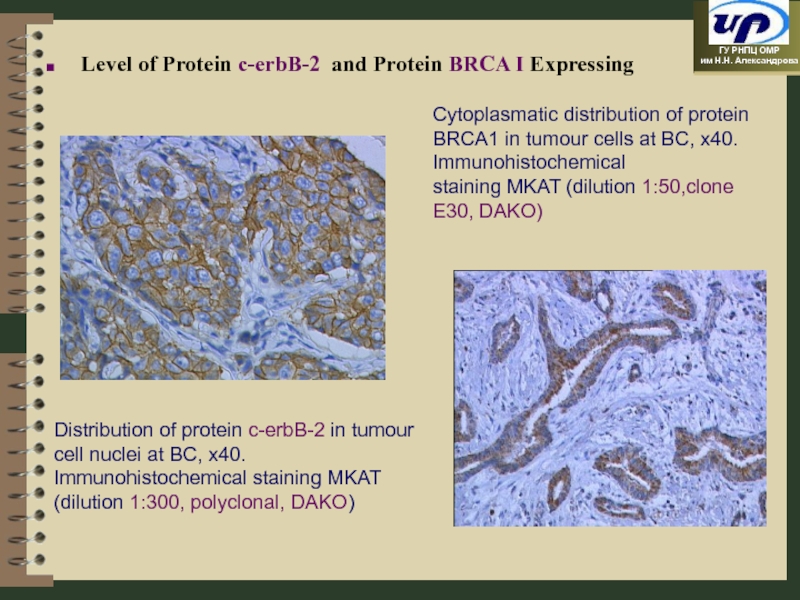
Слайд 21Distribution of protein c-erbB-2 in tumour cell nuclei at BC, x40.
Immunohistochemical
Level of Protein c-erbB-2 and Protein BRCA I Expressing
Cytoplasmatic distribution of protein BRCA1 in tumour cells at BC, x40.
Immunohistochemical
staining MKAT (dilution 1:50,clone E30, DAKO)
Слайд 22Telepathology system for giving on-line consultations on morphological preparations
Modern equipment
Слайд 23 Radiodiagnosis
The department is equipped with modern, mainly, digital diagnostic instruments securing
At the base of the department one realizes a big work on training specialists in radiodiagnosis for medical institutions of the oncological profile of the Republic of Belarus (at working places and conducting thematic seminars). The permanent school for advanced training of radiodiagnosticians of Minsk region has been functioning here for 5 years.
Слайд 30Diagnosing Bladder Cancer on the Basis of Photodynamic Effect
Bladder cancer manifestation
А – white lit;
B – blue lit (λ = 400 nm),
one can see additionally detected bladder tumours
А
B
Слайд 31Efficacy of Clinical Use of 5-ALA (Alamin) of the Belarusian Production
Additional
Obligate precancer is detected in 13% of patients
Слайд 33Surgical Activities
Totally, there were made
2007 — 9 323 operations
2008 — 10
There were operated 2007 — 9 027 patients
2008 — 9 721 patients
Слайд 34Highly Technological Medical Interventions
Combined operations with resection and prosthetics of arch
Bronchoplastic operations with resection and plasty of pulmonary artery and vena cava superior at lung cancer
Intrapleural and intra-abdominal thermochemotherapy in patients with pleural mesothelioma and metastatic involvement of abdomen
Pancreoduodenal resections at pancreas head cancer, with pylorus being saved
Слайд 35Pancreatectomy under total pancreas cancer, with pylorus constrictor being saved
Gastropancreatoduodenal resections
Biliary stenting at pancreas head cancer complicated with mechanical jaundice
Management of liver and lung metastatic lesions using radiofrequency ablation
Extended operative interventions into liver with removing 6 segments
Radical cystectomy with forming artificial bladder from intestine
Слайд 36Multicomponent management of patients with primary liver cancer and colorectal cancer
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy
Extracorporeal nephrectomy
Operations under brain and skull base tumours
Reconstructive and plastic operations using a microsurgical technique
Photodynamic diagnosis and therapy using original Belarusian drugs (5-aminolevulinic acid, fotolon)
Слайд 37method of combined and radiation treatment of patients with supratentorial gliomas
pneumoectomy with resection and prosthetics of descending aorta;
distal resection of pancreas with resection and angioplasty of celiac trunk;
exenteration of pelvis at locally spread cervical cancer;
monoblock hystervaginavulvectomy with lymphaden-ectomy;
fluorescent diagnosis and photodynamic therapy for precancer cervical diseases;
subtotal laryngectomy;
High Technologies Introduced in 2008
Слайд 38reconstruction of mandible using titanium implants;
use of the navigation system for
shunting operations under brain tumours;
extraperitoneal videoassisted radical prostatectomy;
extracorporeal nephrectomy with autotransplantation;
videoassisted nephroablation;
subtotal coloproctectomy with forming intestine reservoir and ileoanal anastomosis;
intersphincter proctectomy;
stenting esophagus and trachea.
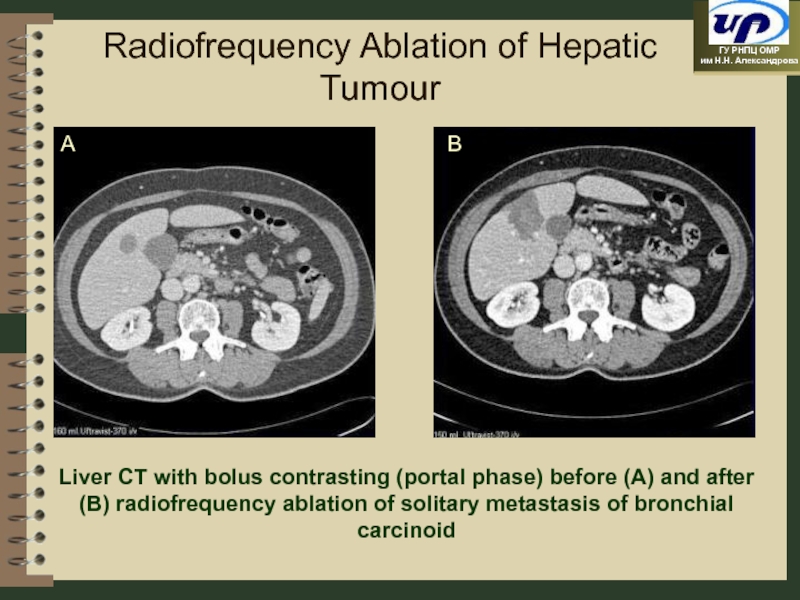
Слайд 40
Radiofrequency Ablation of Hepatic Tumour
Liver CT with bolus contrasting (portal phase)
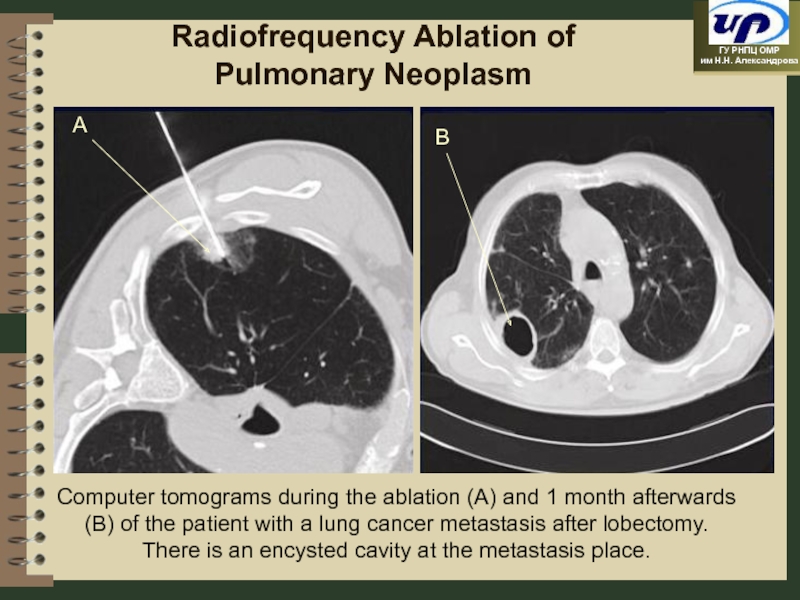
Слайд 41Radiofrequency Ablation of Pulmonary Neoplasm
Computer tomograms during the ablation (A) and
Слайд 43Endoscopic Operations
Laparascopic: splenectomy,adrenalectomy, nephrectomy, radical prostatectomy, obstructive resection of sigmoid colon
Thoracoscopic: lobectomy, thymectomy, removing posterior mediastinum, parasternal lymphadenectomy at breast cancer.
Videoassisted mediastinoscopy
100% of morphological verification of pathological changes of mediastinum lymphnodes.
10% of changed diagnoses after mediastinoscopy
Complications – 0,32%.
Слайд 45
Upper maxilla cancer with growing into the orbit and spreading into
CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION
Слайд 46CRANIOFACIAL RESECTION
Cranial and facial stage
View of the wound after removing
Macropreparation
Слайд 47TECHNOLOGY OF TRACHEOESOPHAGEAL SHUNTING WITH VOCAL PROSTHESIS INSERTING
SET FOR INSERTING VOCAL
Слайд 55Patient Z, 34 y.o.
Diagnosis: left breast cancer T2N0M0G2.
The condition after
DELAYED MAMMAPLASTY
Слайд 57The same patient.
The condition after the reconstruction of mamillary and areolar
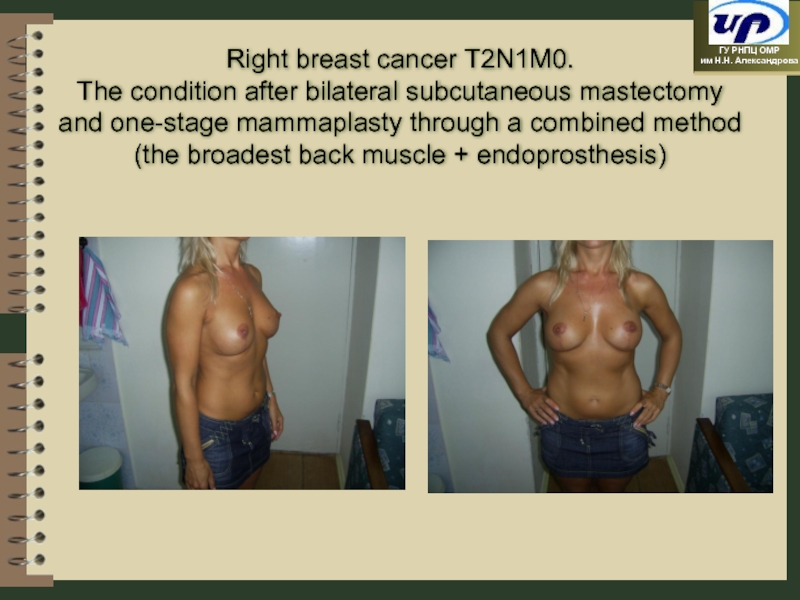
Слайд 58Right breast cancer Т2N1М0.
The condition after bilateral subcutaneous mastectomy and
(the broadest back muscle + endoprosthesis)
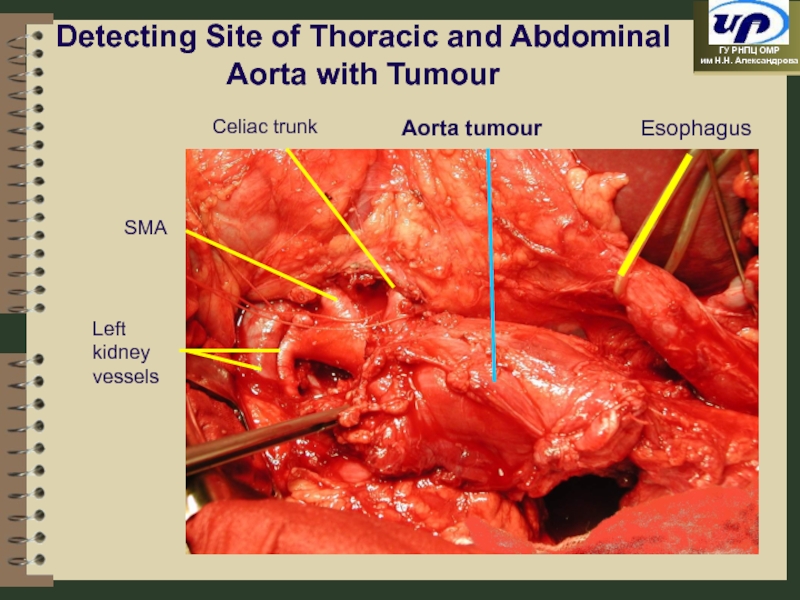
Слайд 76Detecting Site of Thoracic and Abdominal Aorta with Tumour
Esophagus
Celiac trunk
SMA
Left kidney
Aorta tumour
Слайд 82Ileocystoplasty according to R. Hautmann (Modified) after Radical Cystectomy due
Слайд 85The apparatus “Artificial Kidney”
Procedure of extracorporeal detoxication using the apparatus «Multifiltrat»
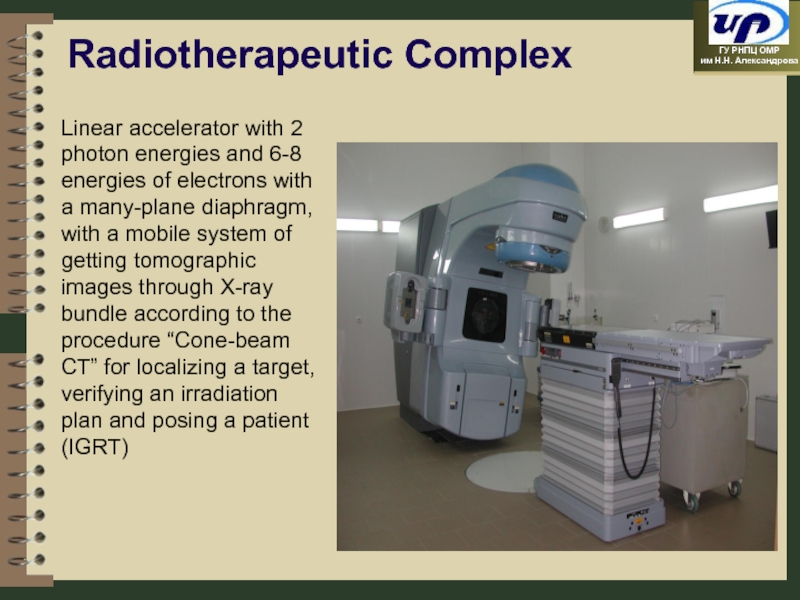
Слайд 91
Linear accelerator with 2 photon energies and 6-8 energies of electrons
Radiotherapeutic Complex
Слайд 93High Technologies in Radiotherapy
Three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy
Radiotherapy with modulating dose intensity
Stereotaxic radiotherapy
Four-dimensional conformal radiotherapy
Слайд 94
Brachytherapy Using an Integrated X-ray and Topometric Complex (IBU)
Brachytherapy of prostate
Слайд 976 months afterwards
Patient C., 34 y.o., CIN III. 26.10.07. – PDT
Before
Photodynamic Therapy under Cervical Dysplasia
Слайд 98Dynamics of Malignant Neoplasm Morbidity and Mortality in the Republic of
194,3
(-3,1%)
329,1
414,1
188,2
(on 100 000 of population)
(+24,8%)
Data of the Cancer-Register. Data of the National Committee on Statistics of Belarus