- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Process, Power and Marine Division. Piping Task презентация
Содержание
- 1. Process, Power and Marine Division. Piping Task
- 2. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 3. © 20049. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 4. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 5. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 6. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 7. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 8. PIPING HIERARCHY: PIPE FEATURES A pipe feature
- 9. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 10. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 11. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
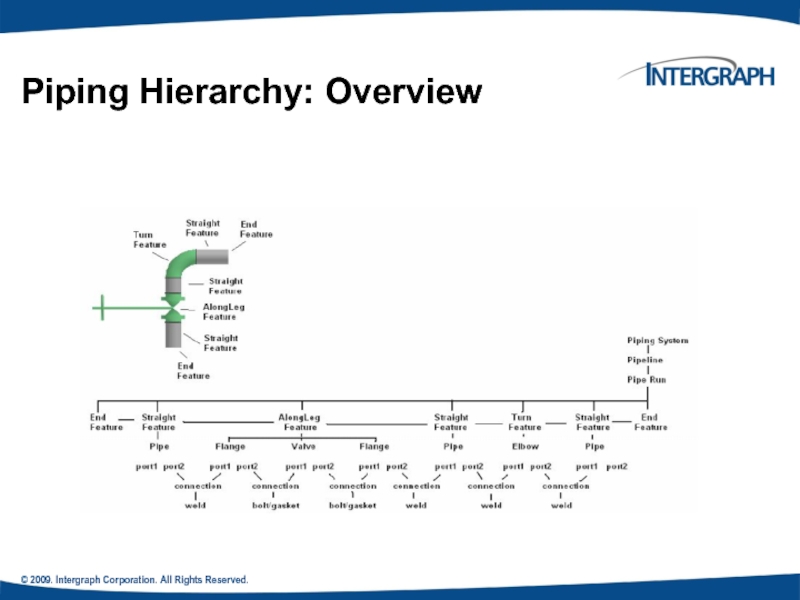
- 12. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Piping Hierarchy: Overview
- 13. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 14. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 15. © © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights
- 16. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 17. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 18. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 19. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 20. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 21. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 22. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
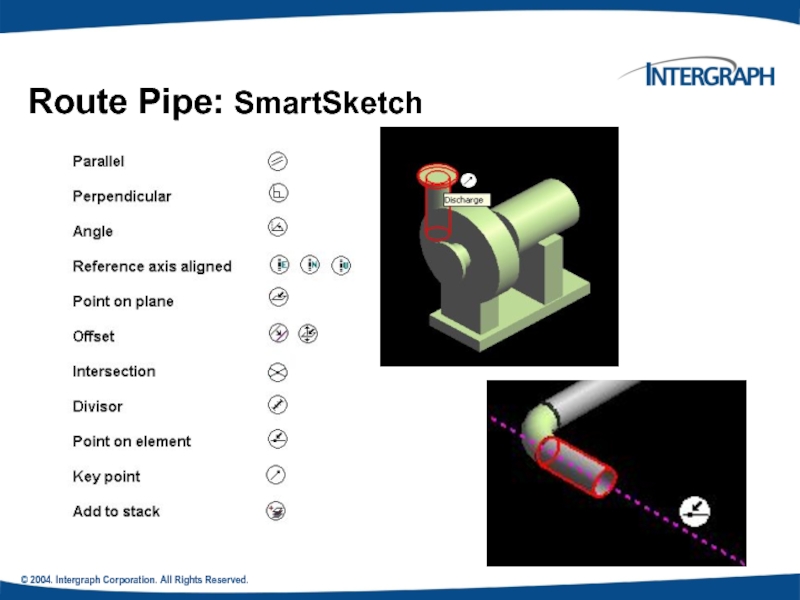
- 23. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Route Pipe: SmartSketch
- 24. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 25. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 26. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 27. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 28. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 29. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 30. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved. Example: Delete Straight Features
- 31. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 32. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 33. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 34. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 35. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 36. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 37. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 38. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 39. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 40. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 41. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 42. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 43. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 44. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 45. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 46. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 47. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 48. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 49. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 50. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 51. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 52. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 53. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 54. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 55. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 56. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 57. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 58. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 59. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 60. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 61. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 62. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 63. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 64. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 65. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 66. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 67. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 68. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 69. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 70. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 71. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 72. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 73. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 74. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 75. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 76. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 77. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 78. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 79. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 80. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 81. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 82. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 83. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 84. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 85. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 86. © 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
- 87. © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Слайд 2© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Agenda
Piping Hierarchy
Route Pipes
Inserting Components
Routing a
Routing Pipes from the P&ID
Placing Instruments
Placing Piping Specialty Items
Placing Taps
Inserting Splits
Слайд 3© 20049. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Agenda Conti’
Manipulating Views
Creating Spools
Sequencing Objects
Creating
Слайд 4© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
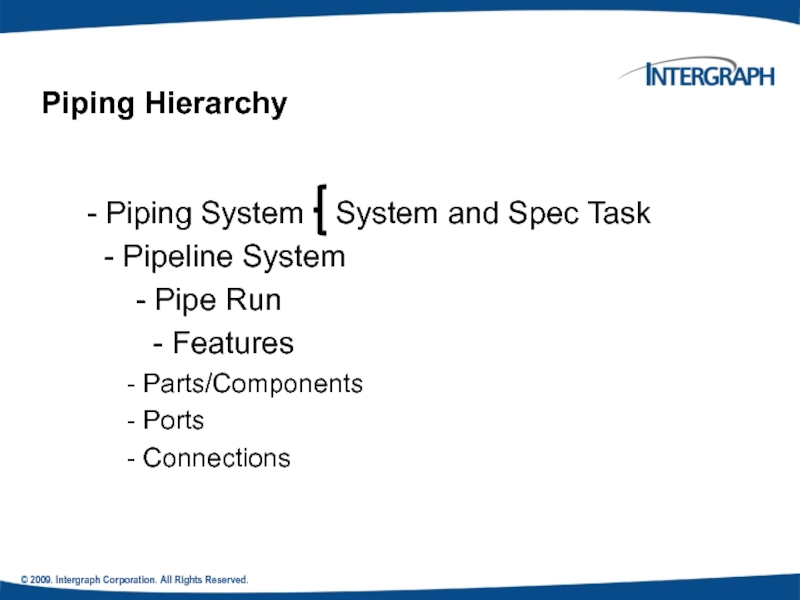
- Piping System System and
- Pipeline System
- Pipe Run
- Features
- Parts/Components
- Ports
- Connections
Piping Hierarchy
Слайд 5© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Hierarchy: Pipe System
A piping
Слайд 6© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
A pipeline system is a
Piping Hierarchy: Pipeline
Слайд 7© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
.
A pipe run is a
Piping Hierarchy: Pipe Run
Pipe Run 1
Pipe Run 2
6” NPD
4” NPD
Слайд 8PIPING HIERARCHY: PIPE FEATURES
A pipe feature is a logical collection of
© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Turn Feature
Straight Feature
End Feature
Run Change Feature
Along Leg Feature
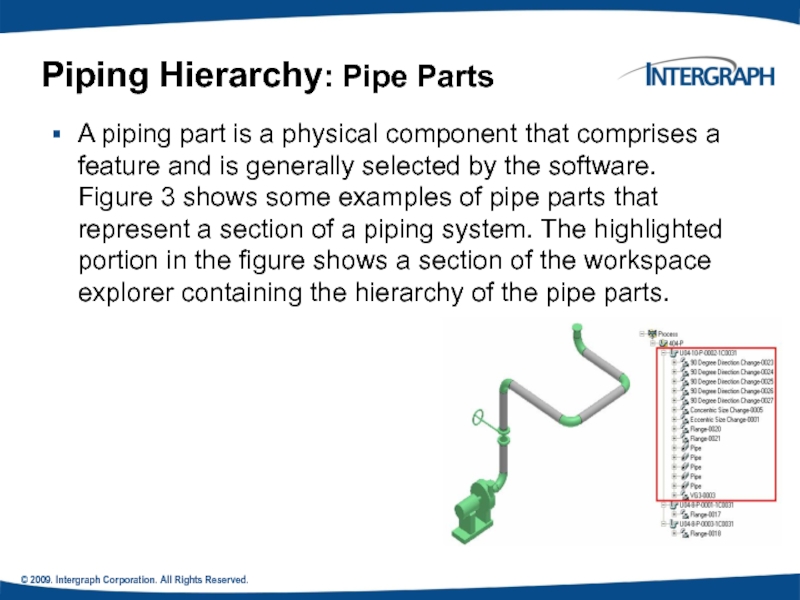
Слайд 9© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
A piping part is a
Piping Hierarchy: Pipe Parts
Слайд 10© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
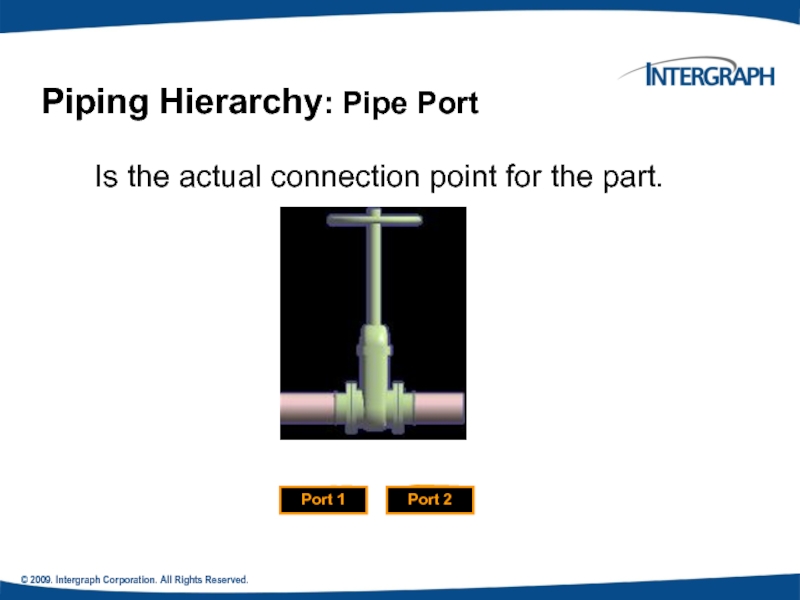
Is the actual connection point
Piping Hierarchy: Pipe Port
Port 2
Port 1
Слайд 11© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
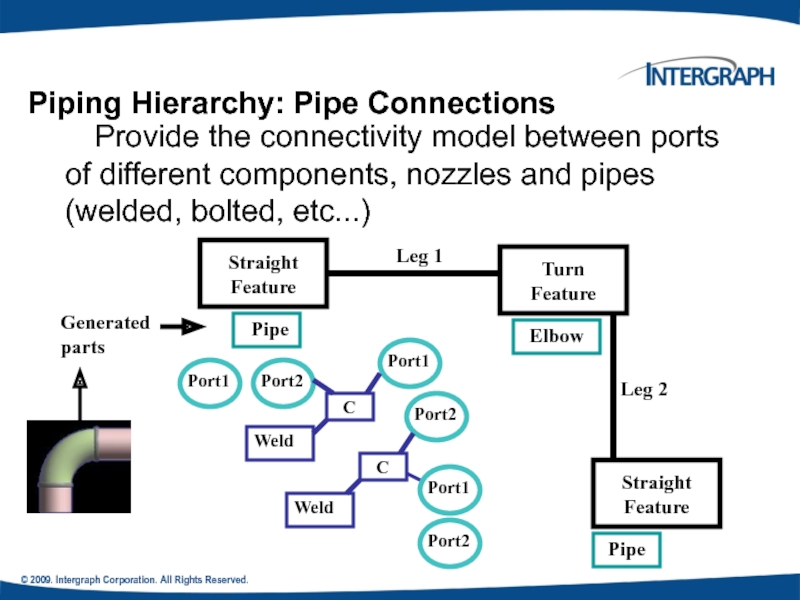
Provide the connectivity model between
Piping Hierarchy: Pipe Connections
Turn Feature
Straight Feature
Straight Feature
Pipe
Elbow
Pipe
Port2
Port1
Port1
Port2
Port1
Port2
C
Leg 1
Generated parts
Weld
Weld
C
Leg 2
Слайд 13© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
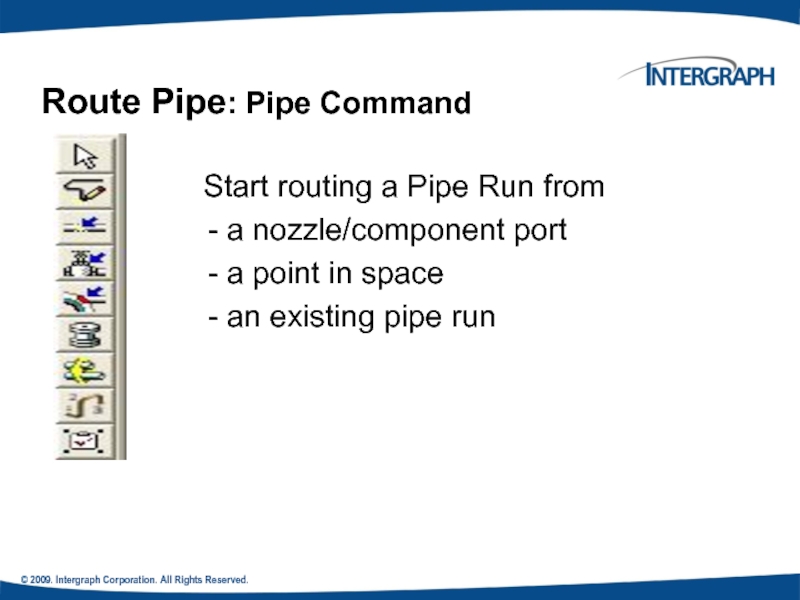
Start routing a Pipe Run
- a nozzle/component port
- a point in space
- an existing pipe run
Route Pipe: Pipe Command
Слайд 14© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Route Pipe: Cardinal Points
Route a
Routing by invert elevation is supported for use in modeling underground piping.
Слайд 15© © 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
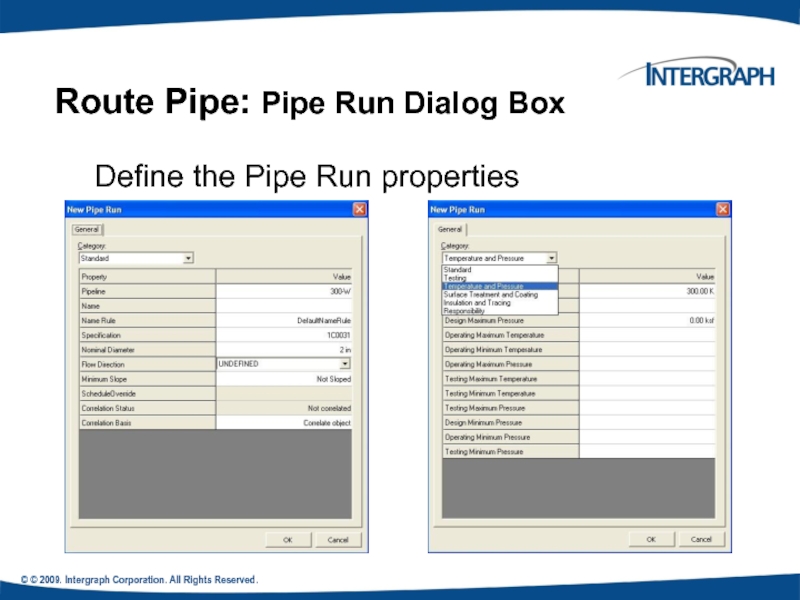
Define the Pipe Run
Route Pipe: Pipe Run Dialog Box
Слайд 16© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
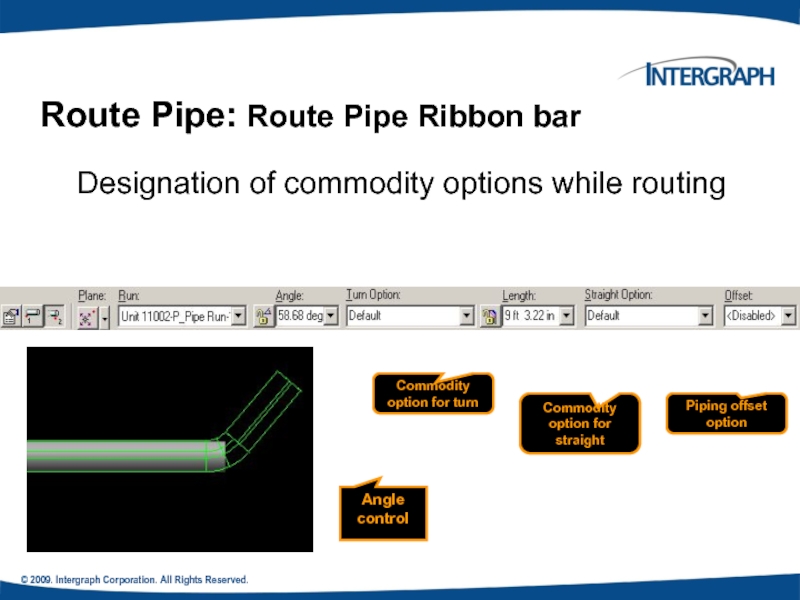
Route Pipe: Route Pipe Ribbon
Designation of commodity options while routing
Commodity option for turn
Commodity option for straight
Angle control
Piping offset option
Слайд 17© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
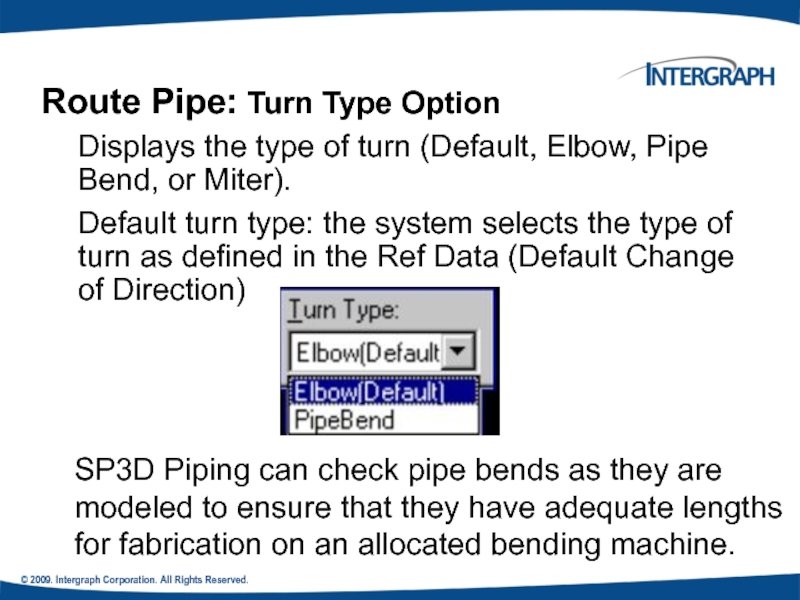
Route Pipe: Turn Type Option
Displays
Default turn type: the system selects the type of turn as defined in the Ref Data (Default Change of Direction)
SP3D Piping can check pipe bends as they are modeled to ensure that they have adequate lengths for fabrication on an allocated bending machine.
Слайд 18© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
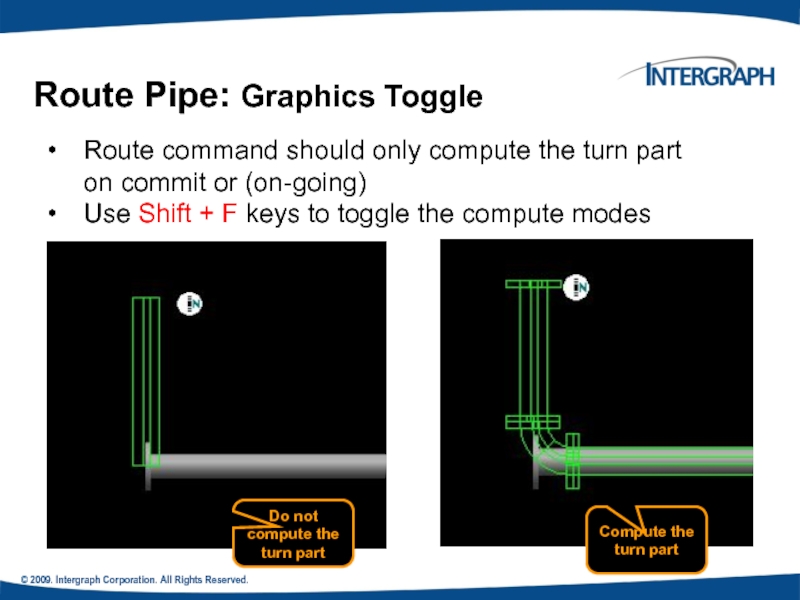
Route Pipe: Graphics Toggle
Route command
Use Shift + F keys to toggle the compute modes
Do not compute the turn part
Compute the turn part
Слайд 19© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
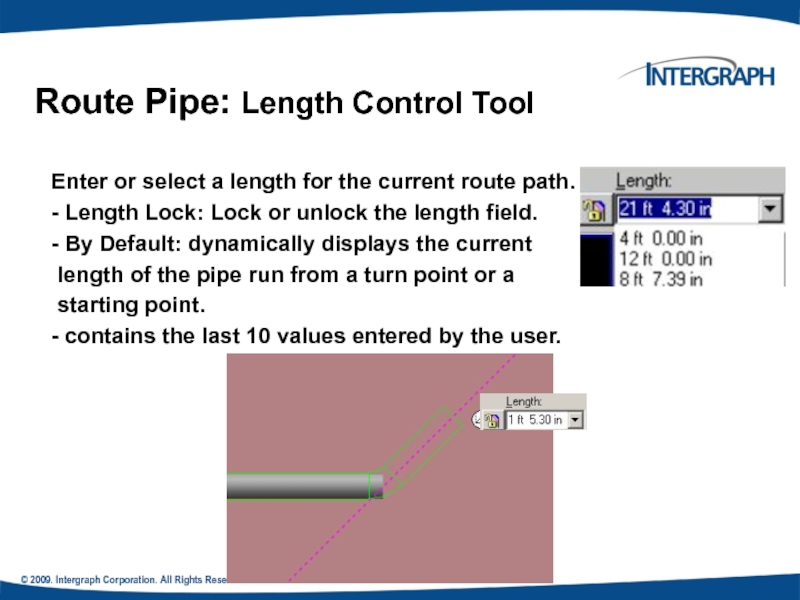
Route Pipe: Length Control Tool
Enter
- Length Lock: Lock or unlock the length field.
- By Default: dynamically displays the current
length of the pipe run from a turn point or a
starting point.
- contains the last 10 values entered by the user.
Слайд 20© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
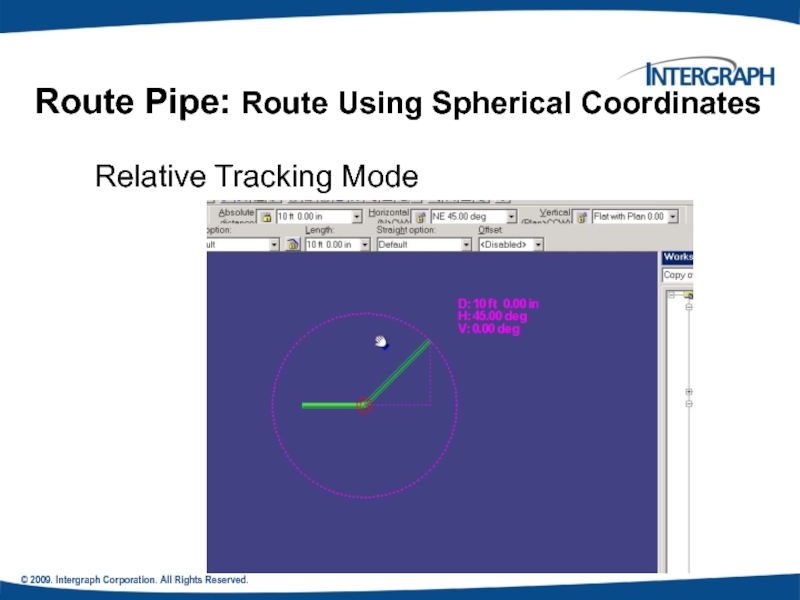
Relative Tracking Mode
Route Pipe: Route
Слайд 21© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
All Rights Reserved.
Offset Control Tool
If
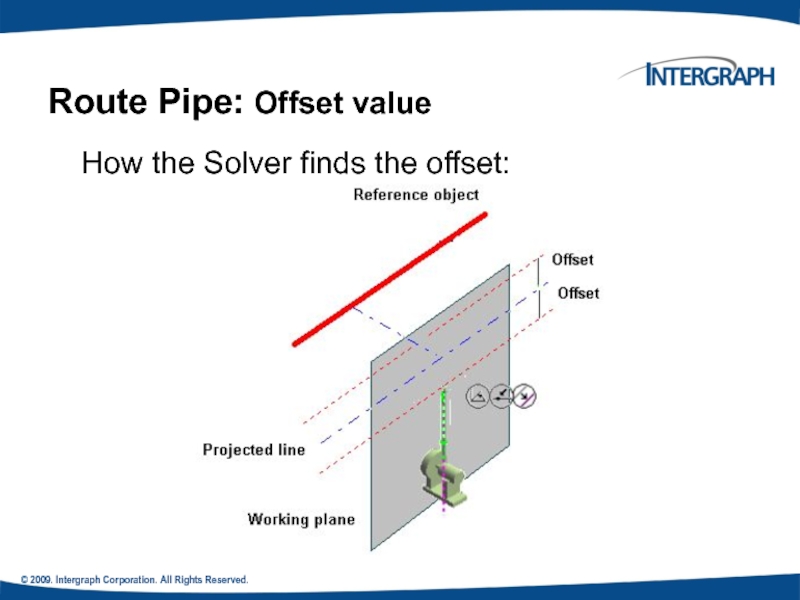
An offset SmartSketch point is found on either side of the referenced plane or linear element.
Route Pipe: Offset Value
North
Слайд 22© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Route Pipe: Offset value
How the
Слайд 24© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
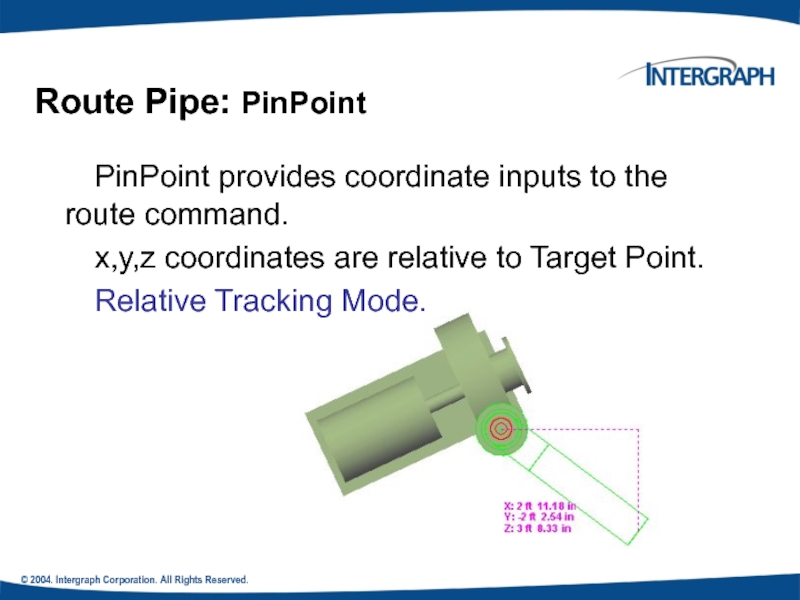
PinPoint provides coordinate inputs to
x,y,z coordinates are relative to Target Point.
Relative Tracking Mode.
Route Pipe: PinPoint
Слайд 25© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
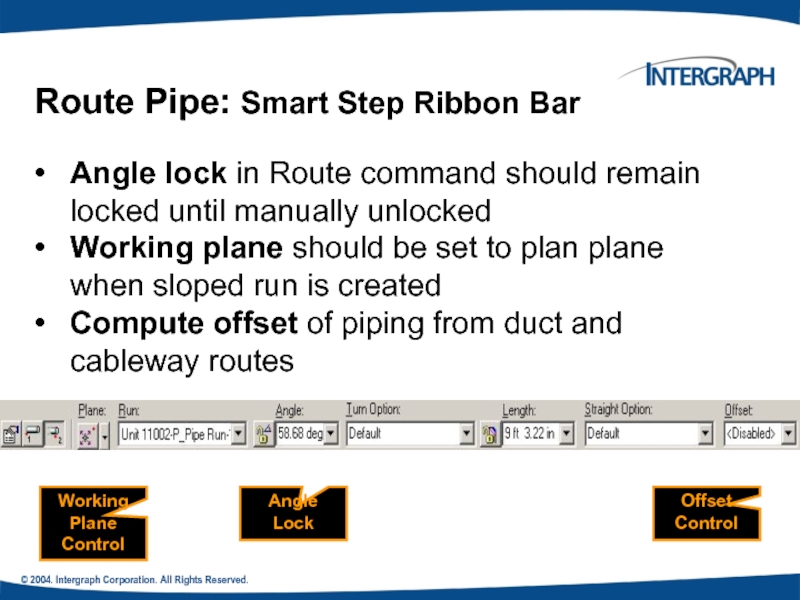
Angle lock in Route command
Working plane should be set to plan plane when sloped run is created
Compute offset of piping from duct and cableway routes
Route Pipe: Smart Step Ribbon Bar
Working Plane Control
Angle Lock
Offset Control
Слайд 26© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
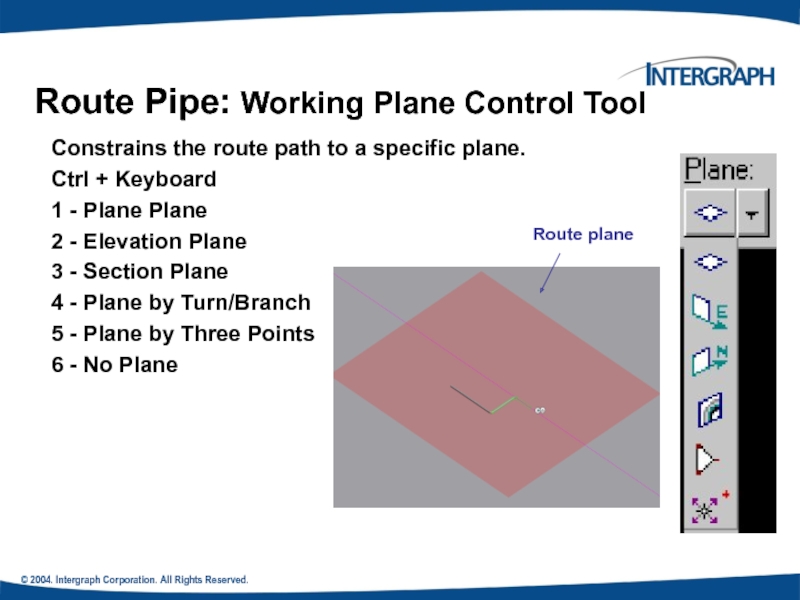
Route Pipe: Working Plane Control
Constrains the route path to a specific plane.
Ctrl + Keyboard
1 - Plane Plane
2 - Elevation Plane
3 - Section Plane
4 - Plane by Turn/Branch
5 - Plane by Three Points
6 - No Plane
Route plane
Слайд 27© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
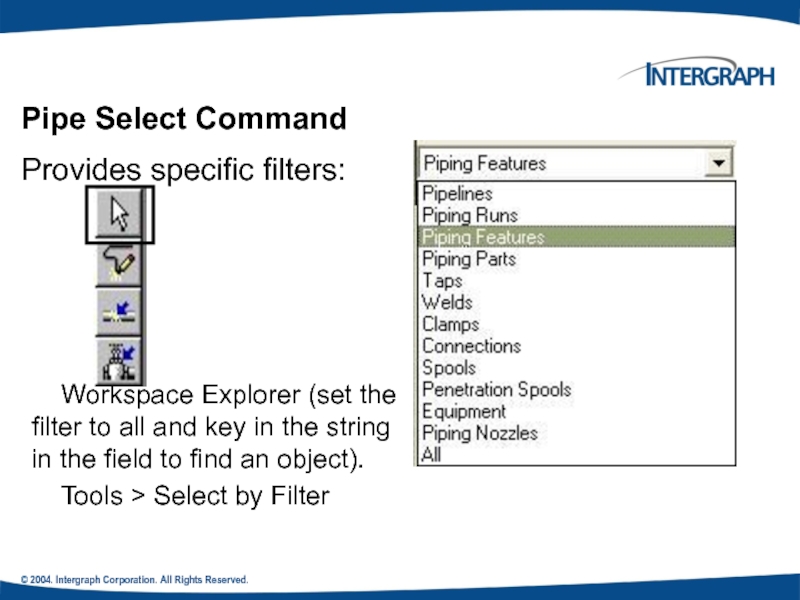
Pipe Select Command
Provides specific filters:
Workspace
Tools > Select by Filter
Слайд 28© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Deleting a pipeline deletes all
Delete a Pipeline
Слайд 29© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Deleting the run deletes all
The software attempts to maintain the design integrity of the model by adjusting all previously connected features.
Delete a Pipe Run
Слайд 31© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
When you select an end
Run To or From End Features or Nozzle
Слайд 32© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
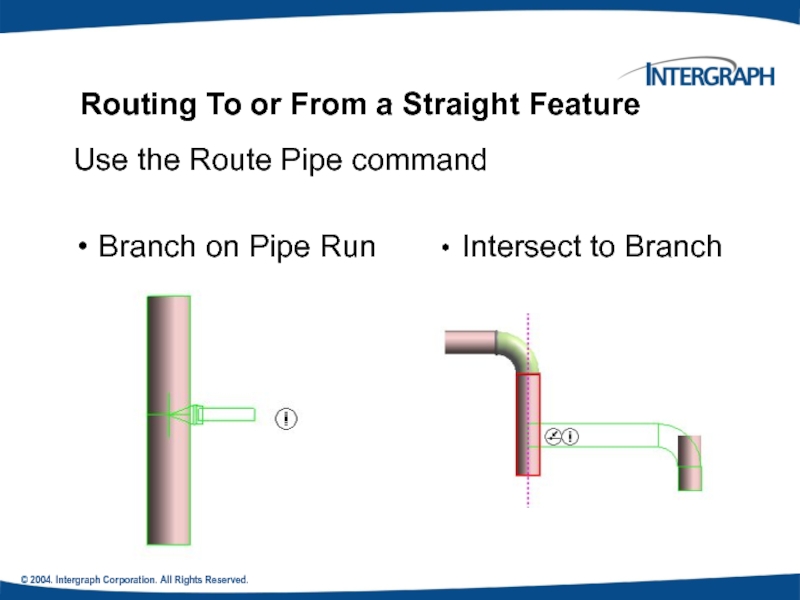
Routing To or From a
Use the Route Pipe command
Branch on Pipe Run
Intersect to Branch
Слайд 33© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
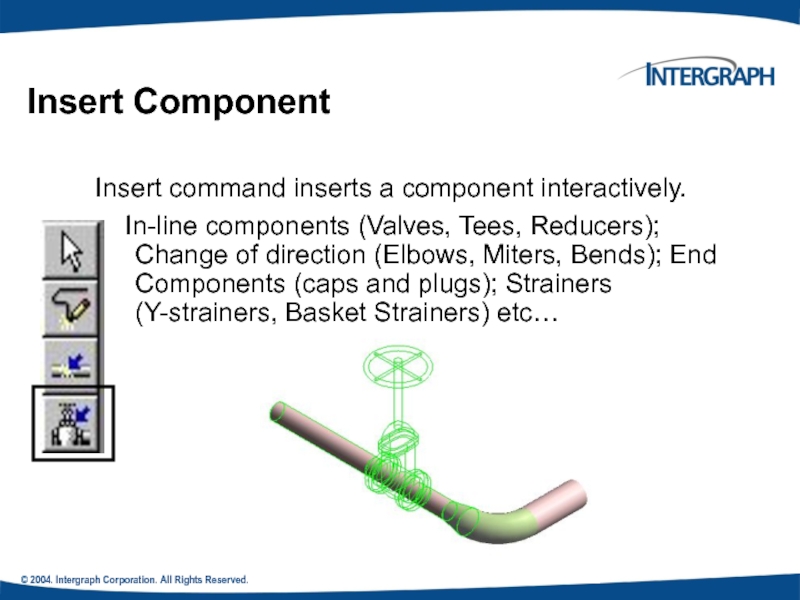
Insert Component
Insert command inserts a
In-line components (Valves, Tees, Reducers); Change of direction (Elbows, Miters, Bends); End Components (caps and plugs); Strainers (Y-strainers, Basket Strainers) etc…
Слайд 34© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
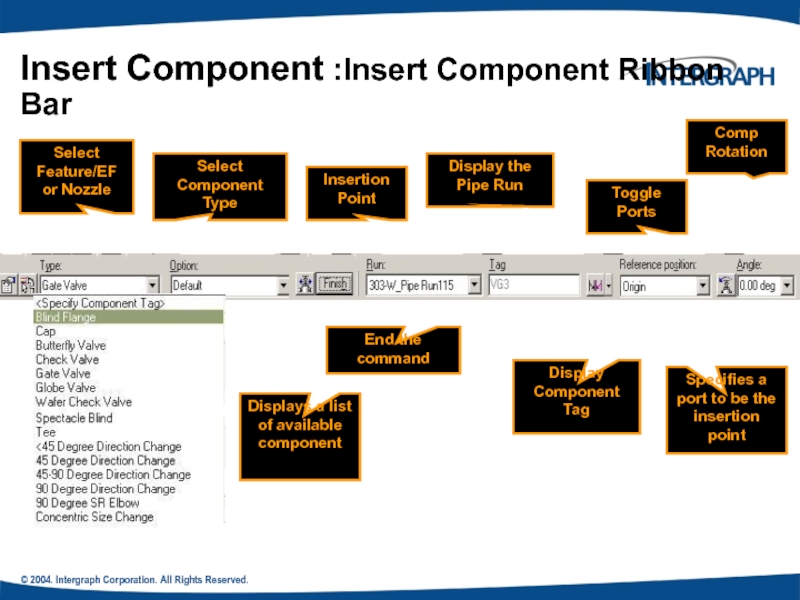
Insert Component :Insert Component Ribbon
Select Feature/EF or Nozzle
Select Component Type
Displays a list of available component
Insertion Point
End the command
Display the Pipe Run
Display Component Tag
Toggle Ports
Specifies a port to be the insertion point
Comp Rotation
Слайд 35© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
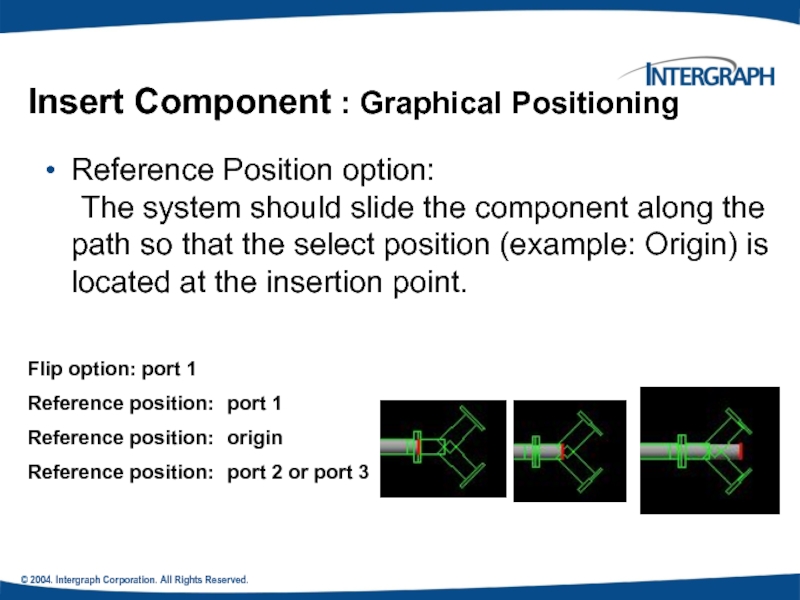
Insert Component : Graphical Positioning
Reference Position option:
The system should slide the component along the path so that the select position (example: Origin) is located at the insertion point.
Flip option: port 1
Reference position: port 1
Reference position: origin
Reference position: port 2 or port 3
Слайд 36© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
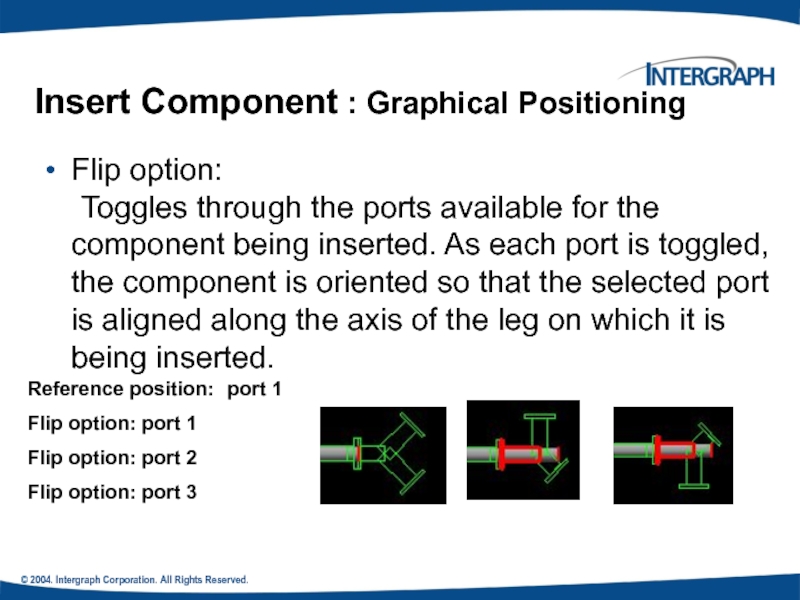
Insert Component : Graphical Positioning
Flip
Toggles through the ports available for the component being inserted. As each port is toggled, the component is oriented so that the selected port is aligned along the axis of the leg on which it is being inserted.
Reference position: port 1
Flip option: port 1
Flip option: port 2
Flip option: port 3
Слайд 37© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
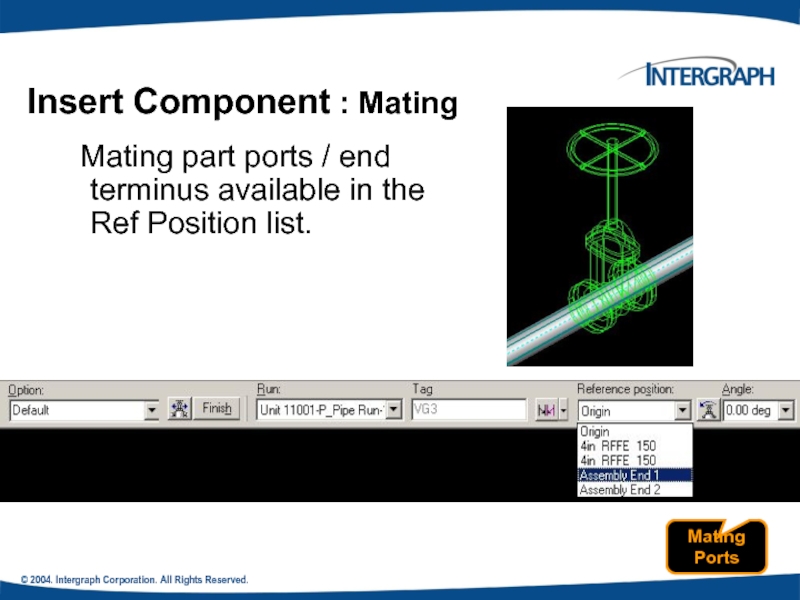
Insert Component : Mating
Mating part
Mating Ports
Слайд 38© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
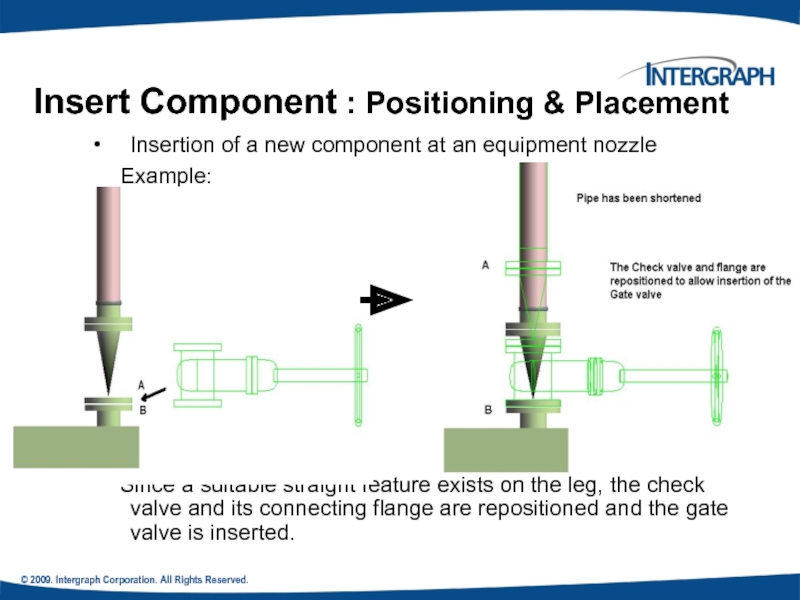
Insert Component : Positioning &
Insertion of a new component at an equipment nozzle
Example:
Since a suitable straight feature exists on the leg, the check valve and its connecting flange are repositioned and the gate valve is inserted.
Слайд 39© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Routing Sloped Pipe
Underground piping collects
Слайд 41© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
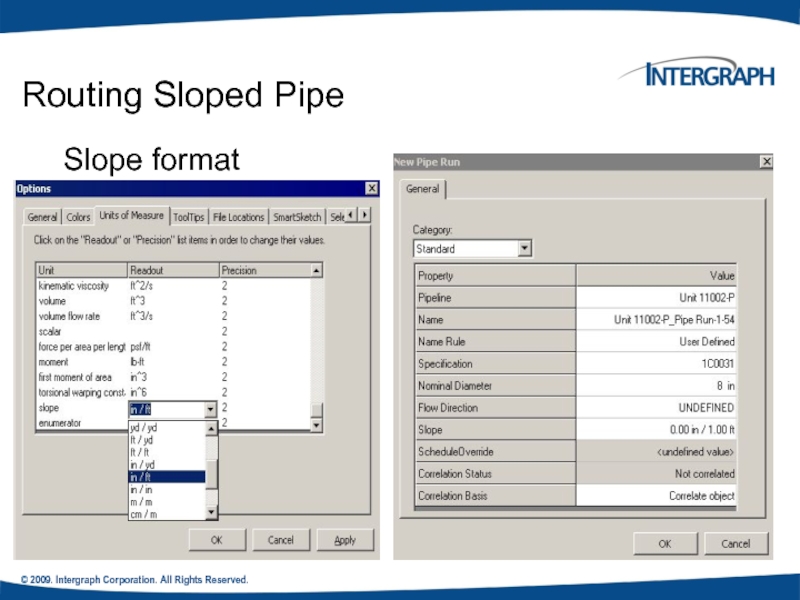
Routing Sloped Pipe
Specify Slope on
Слайд 42© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Routing Sloped Pipe: Slope Direction
Specify Slope Direction
Turn Slope Lock On/Off
Слайд 43© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Reserved.
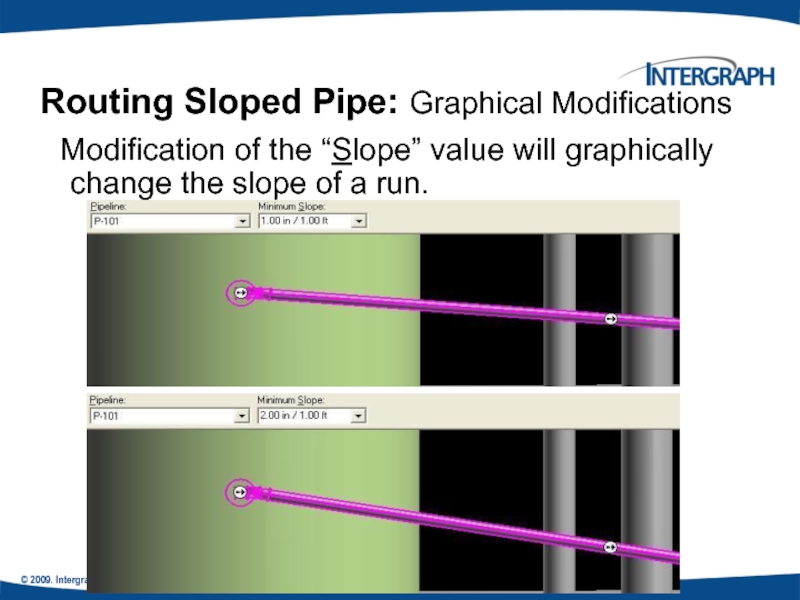
Modification of the “Slope” value
Routing Sloped Pipe: Graphical Modifications
Слайд 44© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
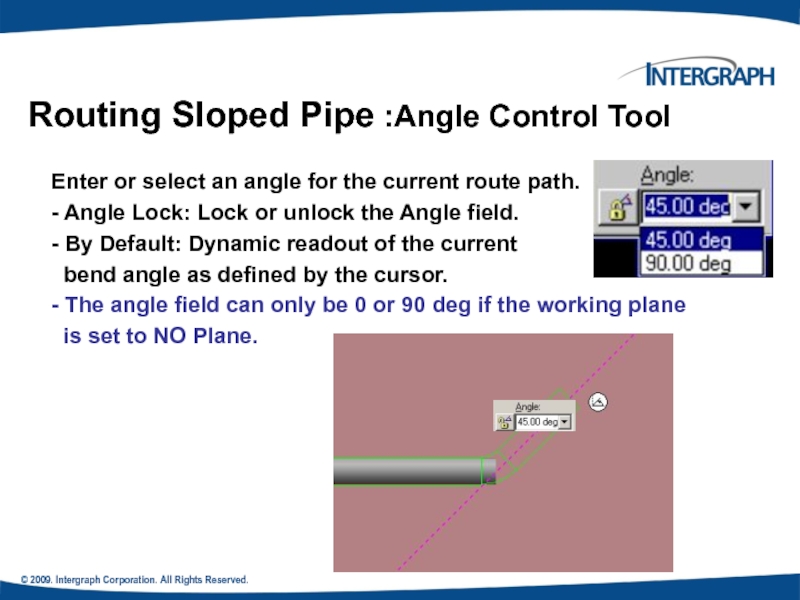
Routing Sloped Pipe :Angle Control
Enter or select an angle for the current route path.
- Angle Lock: Lock or unlock the Angle field.
- By Default: Dynamic readout of the current
bend angle as defined by the cursor.
- The angle field can only be 0 or 90 deg if the working plane
is set to NO Plane.
Слайд 45© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Practice Labs
Route Pipes
Inserting Components
Routing Sloped Pipe
Слайд 46© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Integrated Environment
While designing or
In an integrated environment, you publish and retrieve data from and to SP3D by using a central repository. During a publish operation, data such as drawings, reports, and 3D models transfers to a central repository. During a retrieve operation, the system retrieves P&IDs, Plant Break Down Structure, Project List, Work Breakdown Structure, Electrical Cable Schedules, and Instrumentation Dimensional Data Sheets from the central repository
Слайд 47© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Retrieving Data from a P&ID
You can retrieve piping, instrumentation, and equipment data from P&ID in the integrated environment. You can use P&ID to access items, such as equipment, piping information, and SmartPlant Instrumentation dimension data, to help create the appropriate 3D design objects. For example, after you retrieve data from P&ID, you can use the P&ID File Viewer window in SP3D for guidance in routing pipes, inserting components and instruments, and placing equipment in the 3D model.
Слайд 48© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
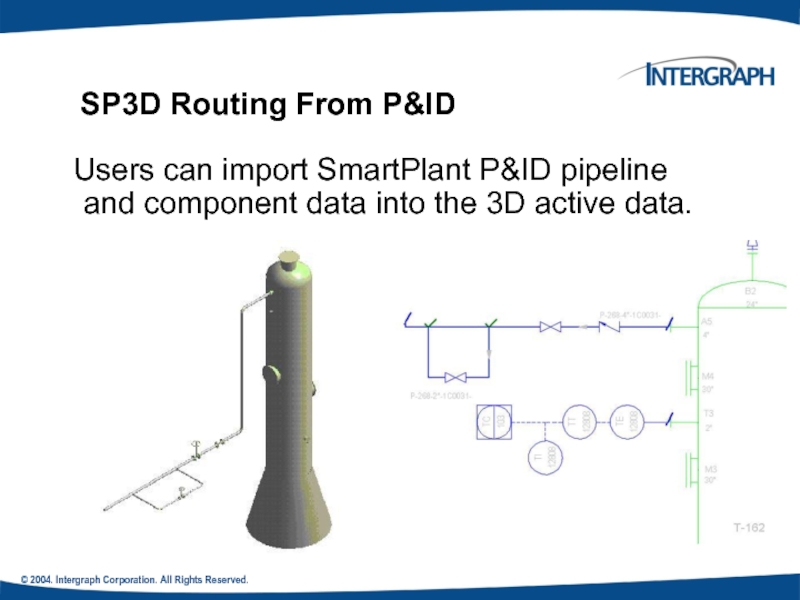
SP3D Routing From P&ID
Users can
Слайд 49© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
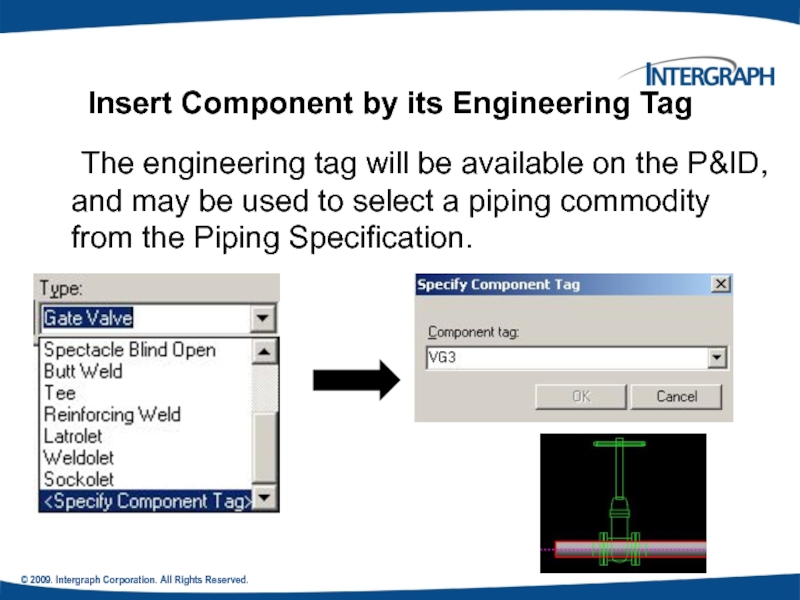
The engineering tag will be
Insert Component by its Engineering Tag
Слайд 50© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
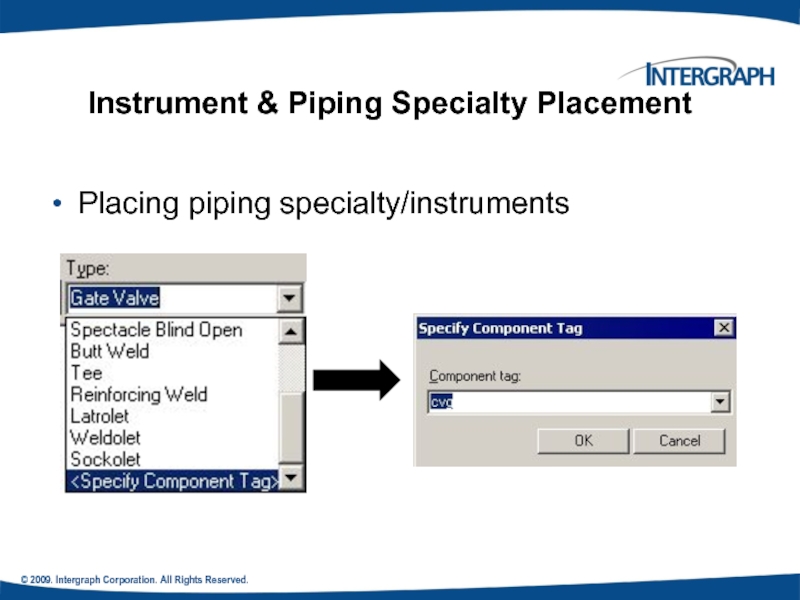
Instrument & Piping Specialty Placement
We
1. Stock item: Stock items represent those piping items that are purchased from a manufacturer’s catalog, where no real engineering is required other than selecting the correct size, material, etc.
2. Custom-engineered item: custom engineered items are built items according to the process.
Слайд 51© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Instrument & Piping Specialty Placement
Placing
Слайд 52© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
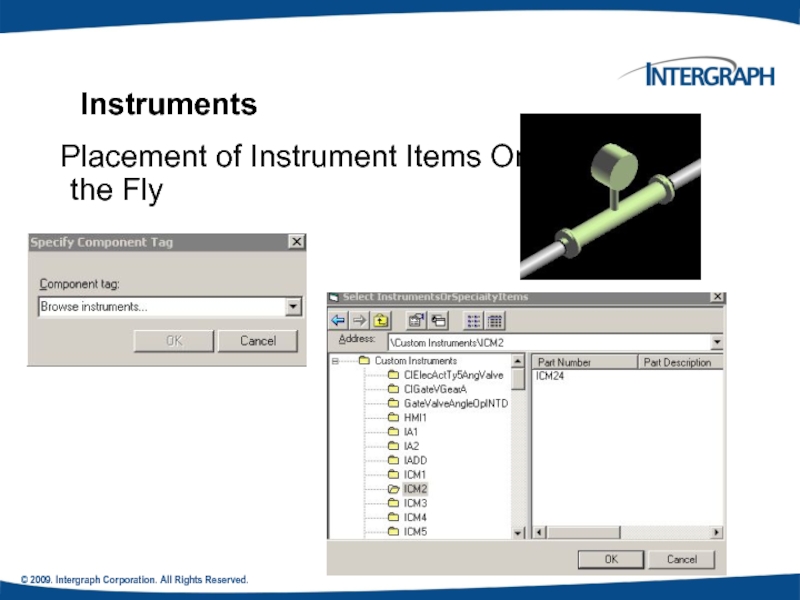
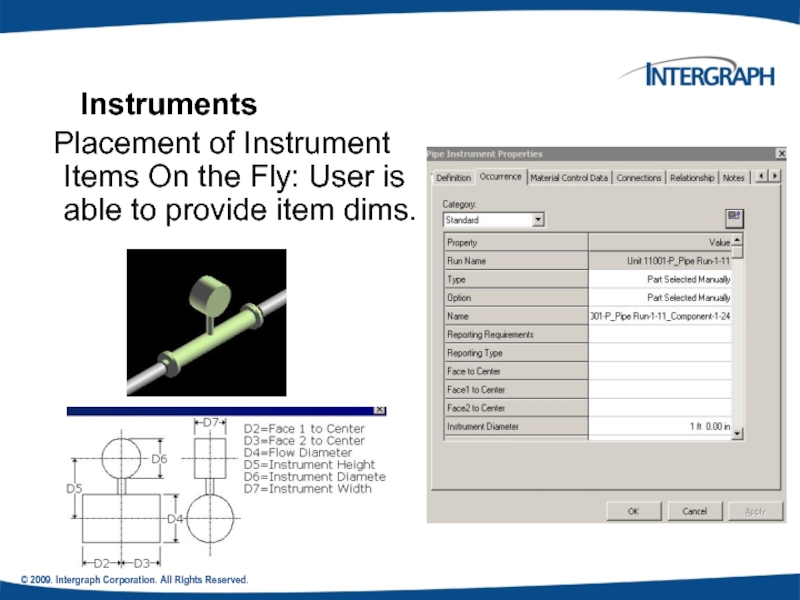
Instruments
Placement of Instrument Items On
Слайд 53© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Placement of Instrument Items On
Instruments
Слайд 54© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
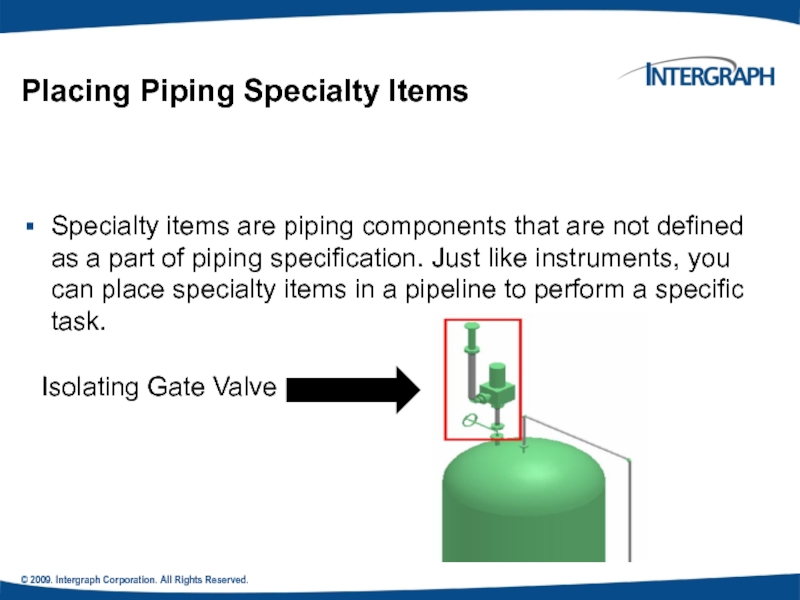
Placing Piping Specialty Items
Specialty items
Isolating Gate Valve
Слайд 55© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Specialty Items Types
Stock specialty
Custom specialty items: These items are typically driven by parameters. Therefore, you can change their size and shape after placing them in the model.
Слайд 56© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
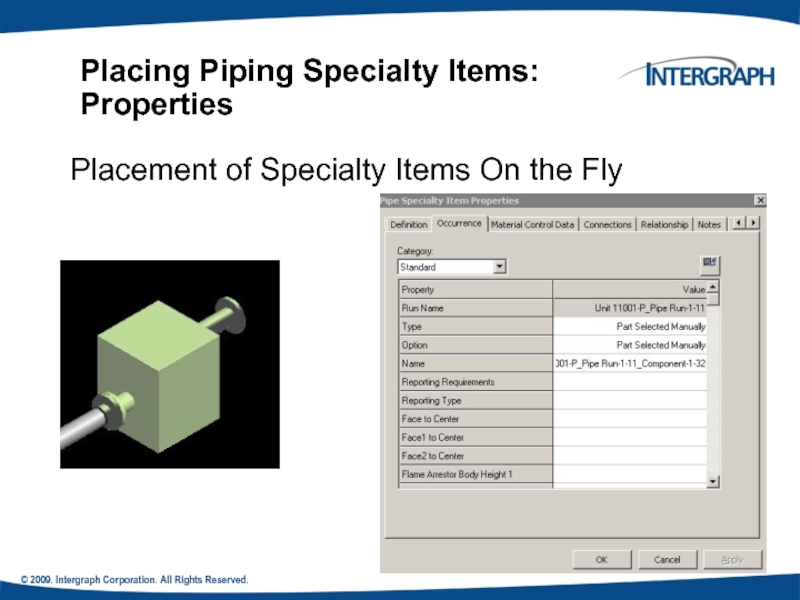
Placing Piping Specialty Items: Properties
Placement
Слайд 57© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Insert Tap
Use this command when
Слайд 58© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
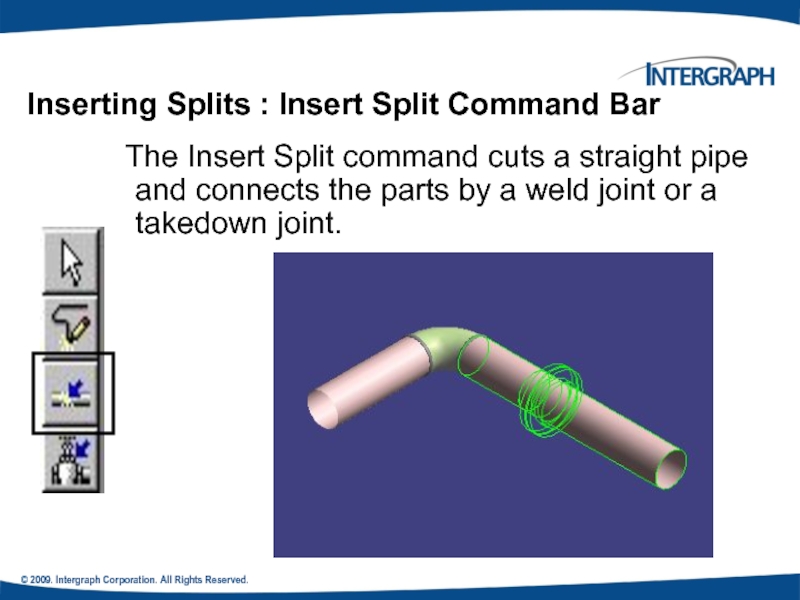
Inserting Splits : Insert Split
The Insert Split command cuts a straight pipe and connects the parts by a weld joint or a takedown joint.
Слайд 59© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
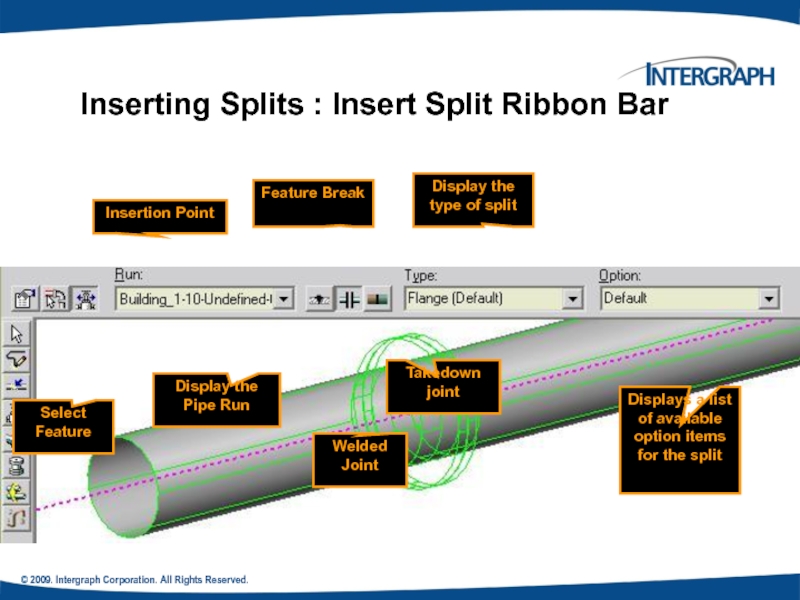
Inserting Splits : Insert Split
Welded Joint
Select Feature
Display the type of split
Insertion Point
Display the Pipe Run
Takedown joint
Displays a list of available option items for the split
Feature Break
Слайд 60© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
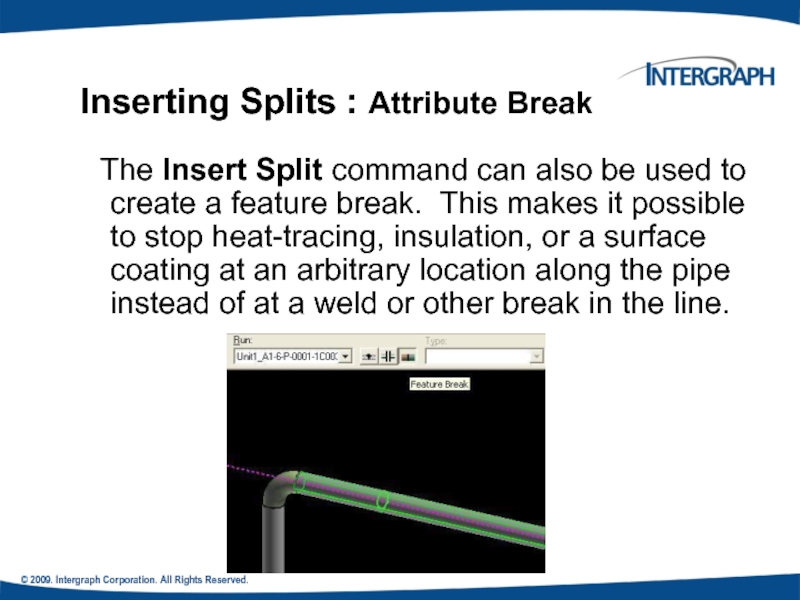
Inserting Splits : Attribute Break
The Insert Split command can also be used to create a feature break. This makes it possible to stop heat-tracing, insulation, or a surface coating at an arbitrary location along the pipe instead of at a weld or other break in the line.
Слайд 61© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
.
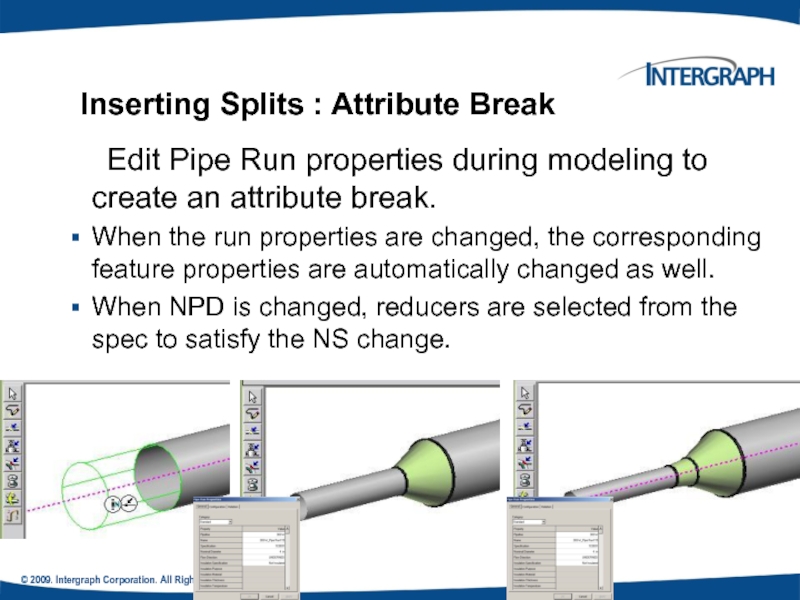
Edit Pipe Run properties during
When the run properties are changed, the corresponding feature properties are automatically changed as well.
When NPD is changed, reducers are selected from the spec to satisfy the NS change.
Inserting Splits : Attribute Break
Слайд 62© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Routing Pipes from P&ID
Placing
Placing Piping Specialty Items
Placing Taps
Placing Splits
Piping Practice Labs
Слайд 63© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Manipulation : Edit Straight
Moving a SF moves the entire leg to which the feature is connected.
The move direction is always perpendicular to the axis of the SF.
A branch feature (BF) connected to the moved leg maintains its original angle.
Movement stops when parts on the associated leg overlap, or when they overlap with adjacent parts on connected legs.
Слайд 64© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
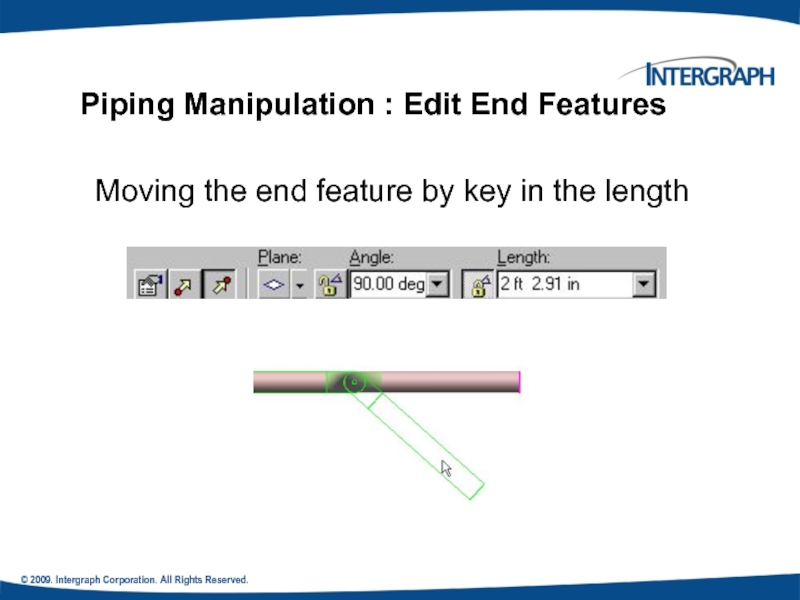
Piping Manipulation : Edit End
Moving the end feature by key in the length
Слайд 65© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
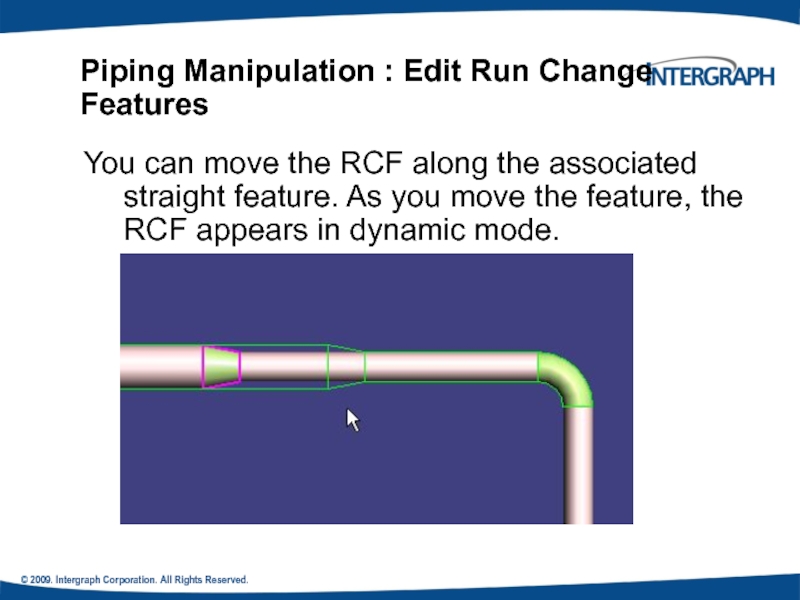
Piping Manipulation : Edit Run
You can move the RCF along the associated straight feature. As you move the feature, the RCF appears in dynamic mode.
Слайд 66© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Manipulation : Editing Features
Shift
Move selected legs
- Point along tool
Слайд 67© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
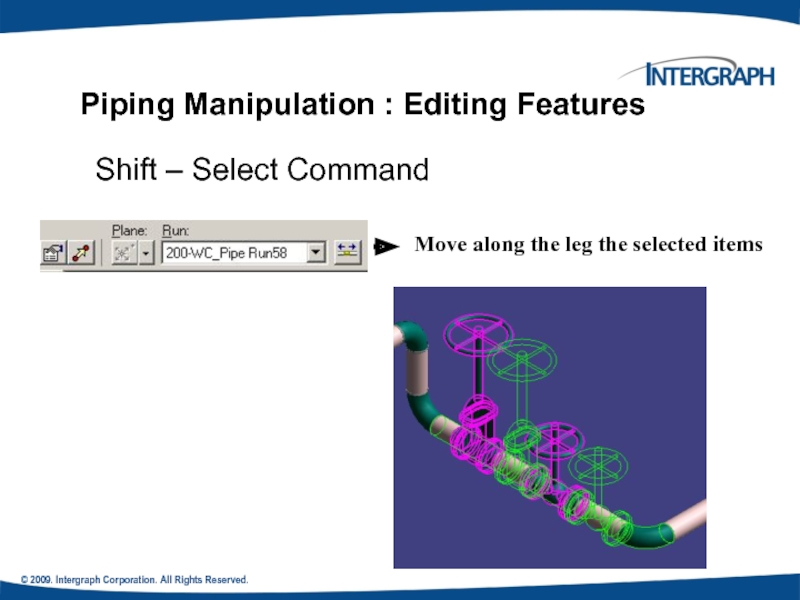
Piping Manipulation : Editing Features
Shift
Move along the leg the selected items
Слайд 68© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Manipulation : Editing Features
Shift
Turn off the moving along the leg
Слайд 69© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
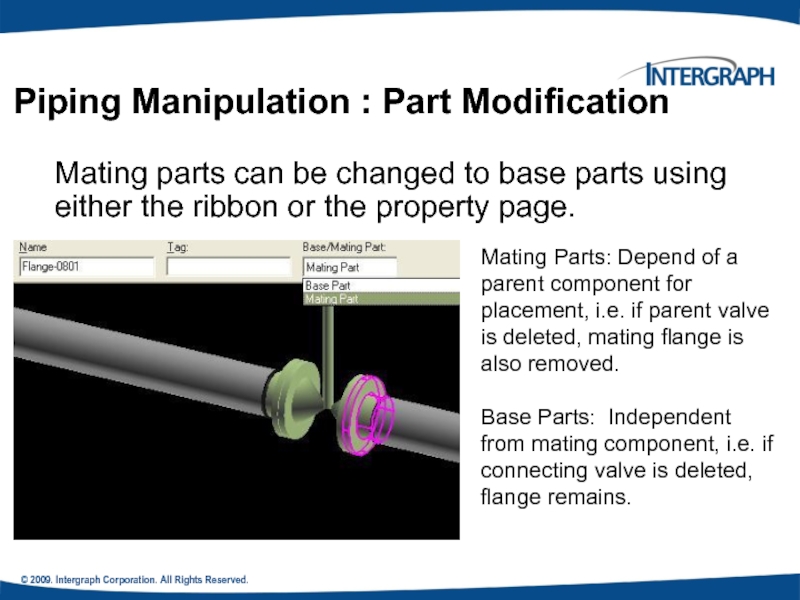
Mating parts can be changed
Piping Manipulation : Part Modification
Mating Parts: Depend of a parent component for placement, i.e. if parent valve is deleted, mating flange is also removed.
Base Parts: Independent from mating component, i.e. if connecting valve is deleted, flange remains.
Слайд 70© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Operator may replace item with
Presentation of only one short code for a particular item.
If a component has been generated automatically by the solver, the user sees two entries in the Type list for that object: one with a "Default" suffix signifying that this part is rule generated and one without the suffix.
Piping Manipulation : Item Replacement
Слайд 71© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
.
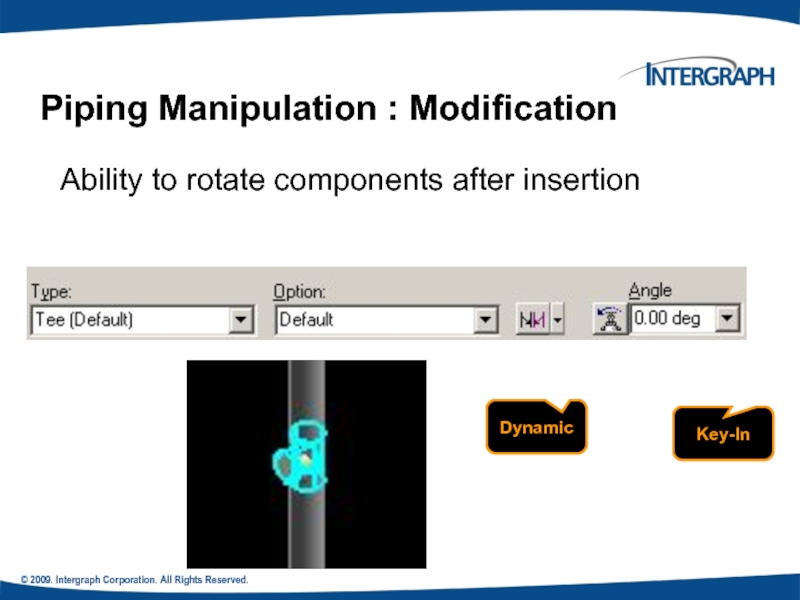
New Enhancement in V4
Ability
Key-In
Piping Manipulation : Modification
Dynamic
Слайд 72© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
New Enhancement in V4
Copy/Paste
Mirror Copy command is available
Creation of a connection (geometry permitting) when multiple objects are moved and placed on another object
Piping Manipulation : Modification
Слайд 73© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Right clicking on pipe run
Piping Properties : Properties
Слайд 74© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
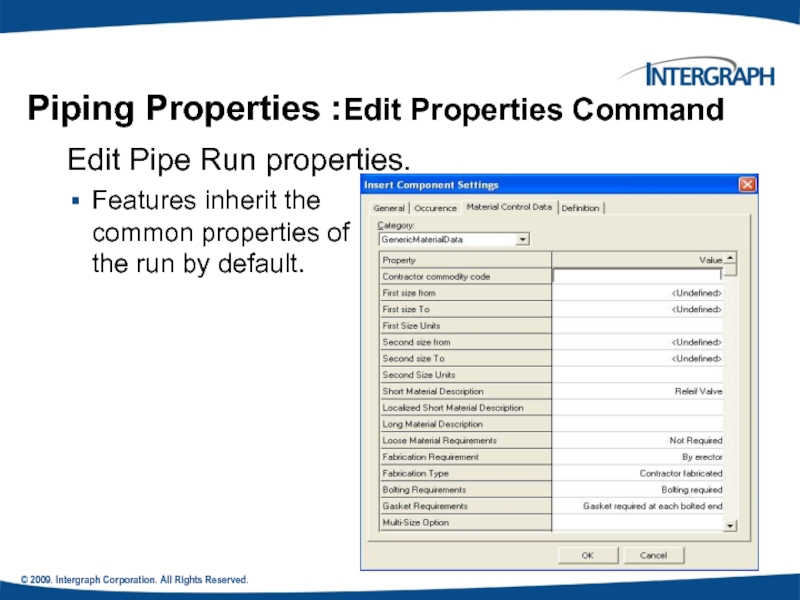
.
Piping Properties :Edit Properties Command
Edit
Features inherit the common properties of the run by default.
Слайд 75© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
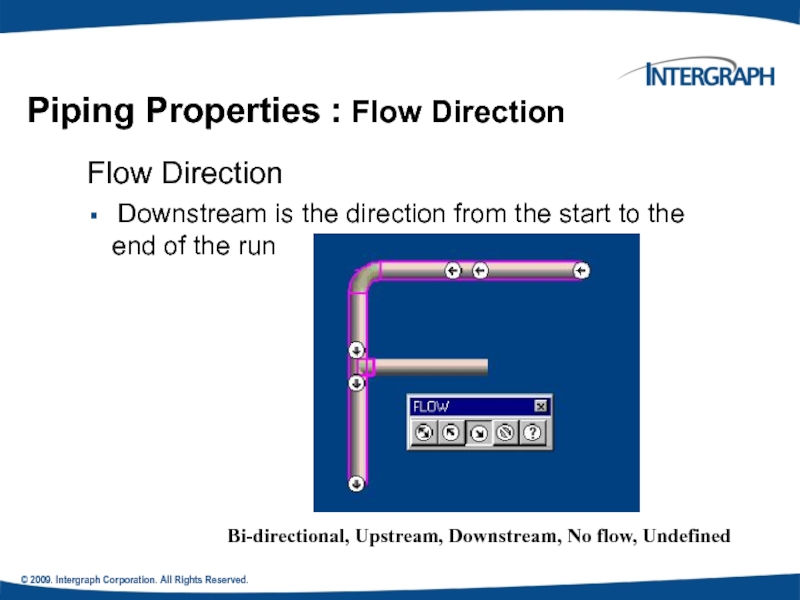
Piping Properties : Flow Direction
Flow
Downstream is the direction from the start to the end of the run
Bi-directional, Upstream, Downstream, No flow, Undefined
Слайд 76© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
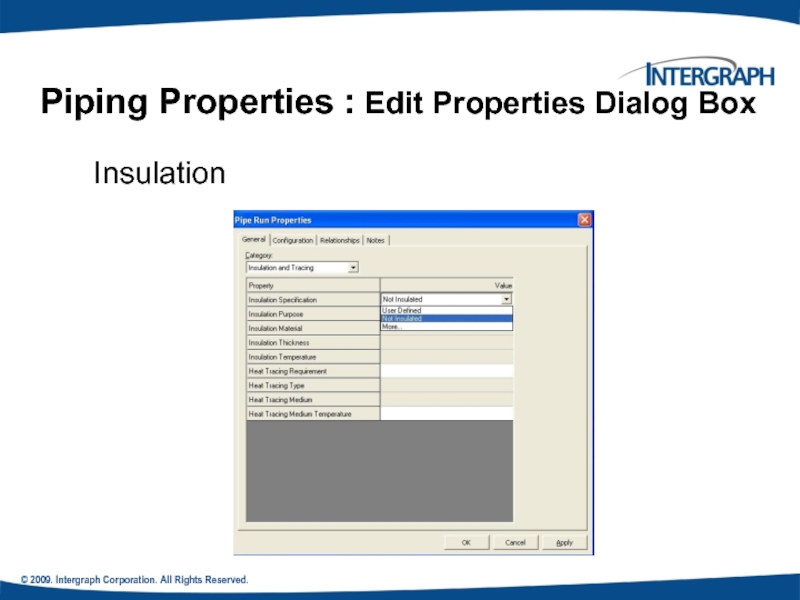
Piping Properties : Edit Properties
Insulation
Слайд 77© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Piping Properties : Edit Properties
Edit Pipe Run properties
Relation Tab displays all the relationships defined for the selected pipe run.
Слайд 78© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Pipe cut lengths to reflect
Piping Properties : Edit Properties Dialog Box
Слайд 79© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Ability to insert notes on
Piping Properties : Inserting notes
Слайд 80© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
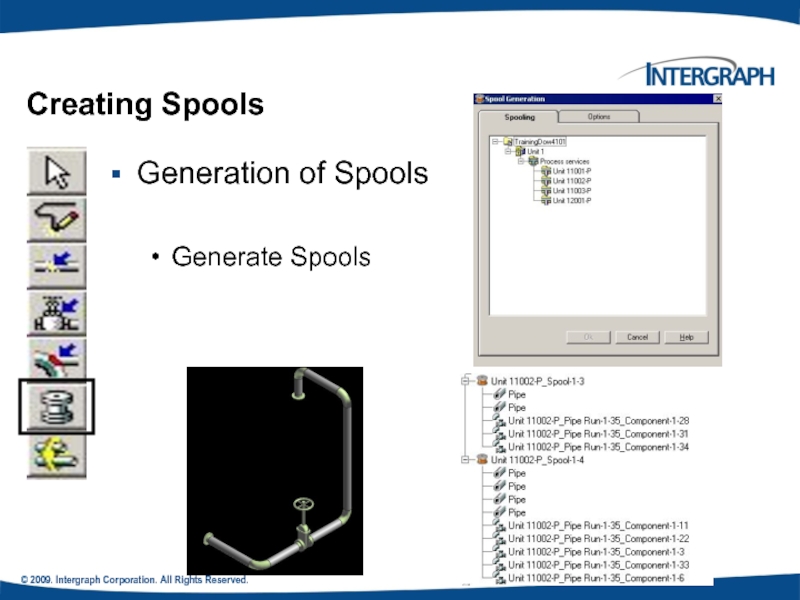
Creating Spools
Generation of Spools
Generate Spools
Слайд 81© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
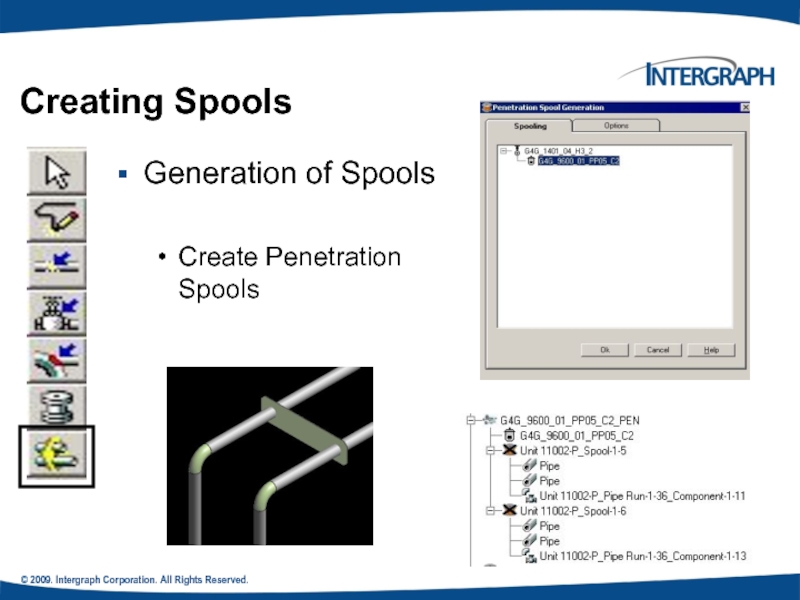
Generation of Spools
Create Penetration
Creating Spools
Слайд 82© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Naming of Spools
Spooling options
Creating Spools
Слайд 83© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Breaks at unions by system
Breaks
Creating Spools
Слайд 84© 2009. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
.
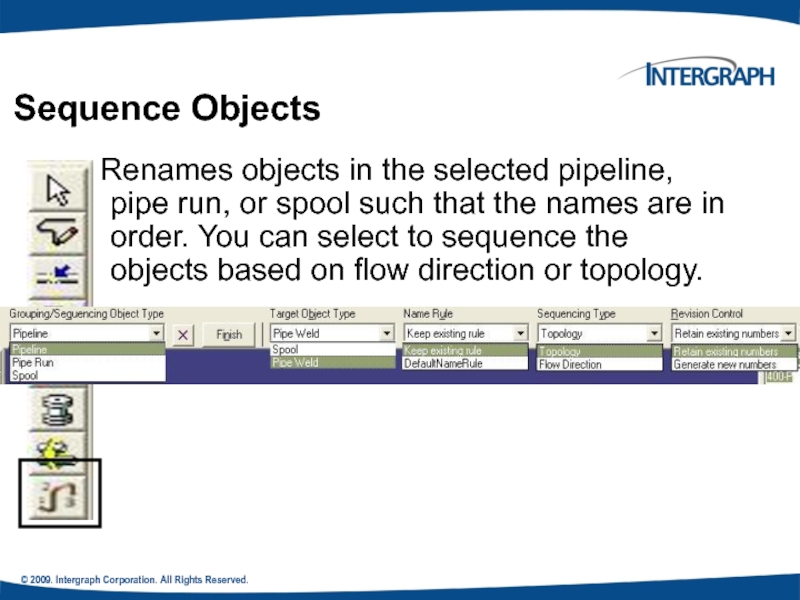
Sequence Objects
Renames objects in the
Слайд 85© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
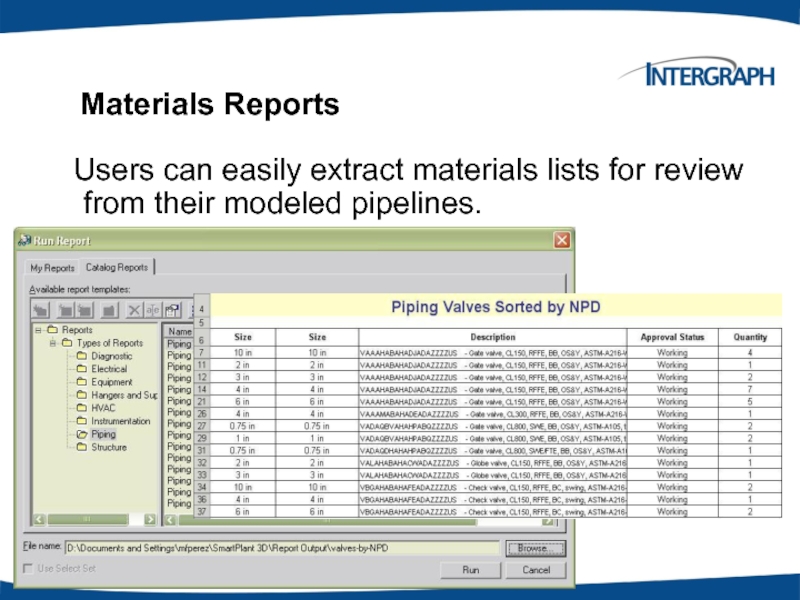
Materials Reports
Users can easily extract
Слайд 86© 2004. Intergraph Corporation. All Rights Reserved.
Manipulating Piping Objects
Creating Spools
Sequencing Objects
Creating
Piping Practice Labs