- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lesson 3 презентация
Содержание
- 1. Lesson 3
- 2. Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, you
- 3. Objectives (Cont.) Describe the benefits of intrusion
- 4. Intrusion Detection Terminology
- 5. Intrusion Detection Ability to detect attacks against networks, including network devices and hosts.
- 6. False Alarms False positive—A situation in which
- 7. True Alarms True positive—A situation in which
- 8. Vulnerabilities and Exploits A vulnerability is a
- 9. Intrusion Detection Technologies
- 10. Profile-Based Intrusion Detection Also known as anomaly
- 11. Signature-Based Intrusion Detection Also known as misuse
- 12. Protocol Analysis Intrusion detection analysis is performed
- 13. Responsive Reactive IDSs can respond to an
- 14. Network-Based Intrusion Detection Systems
- 15. NIDS Features Sensors are connected to network
- 16. Management server Corporate network DNS server
- 17. Host-Based Intrusion Prevention System
- 18. HIPS Features Agent software installed on each
- 19. Firewall Corporate network DNS
- 20. Intrusion Protection Benefits
- 21. Intrusion Protection Benefits Intrusion protection provides: Enhanced
- 22. Active Defense System A complete intrusion protection
- 23. Cisco IDS Solution Active Defense System Network
- 24. Defense in Depth—A Layer Solution Application-level encryption
- 25. Network Sensor Platforms
- 26. Network Sensor Features Active responses TCP resets
- 27. Cisco IDS Family
- 28. Network Sensor—Cisco 4200 Series Appliance Appliance solution
- 29. Switch Sensor—Cisco Catalyst 6500 IDSM-2 Switch-integrated intrusion
- 30. Router Sensor—IDS Network Module for Access Routers
- 31. Router Sensor—Cisco IOS IDS Router IDS technology
- 32. Firewall Sensor—PIX Firewall IDS Firewall integrated intrusion
- 33. Host-Based Intrusion Protection System
- 34. Cisco Security Agent Features Active protection
- 35. Cisco Security Agent Architecture Windows and Solaris
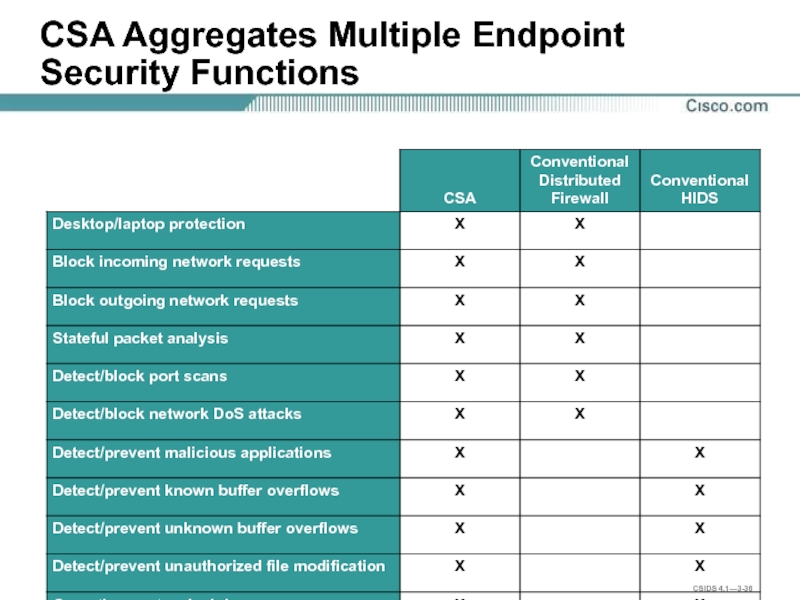
- 36. CSA Aggregates Multiple Endpoint Security Functions
- 37. Sensor Appliances
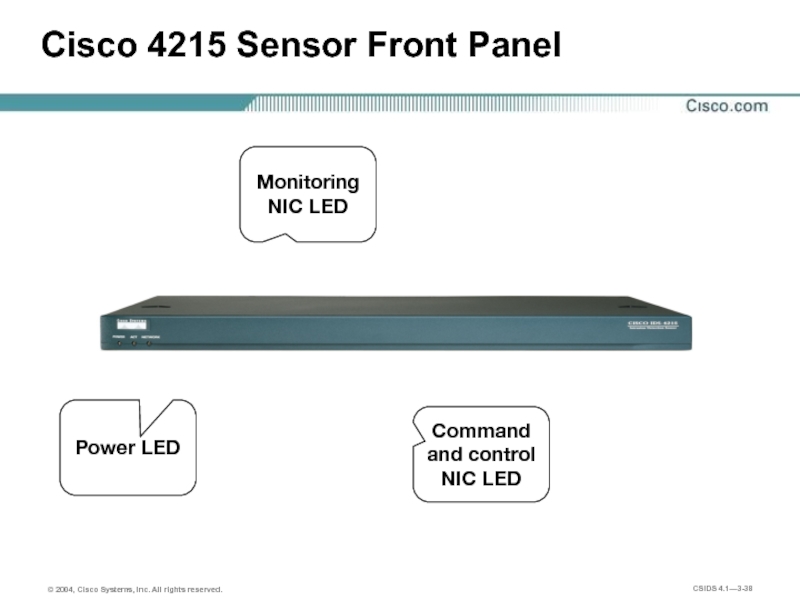
- 38. Cisco 4215 Sensor Front Panel Monitoring NIC LED Power LED Command and control NIC LED
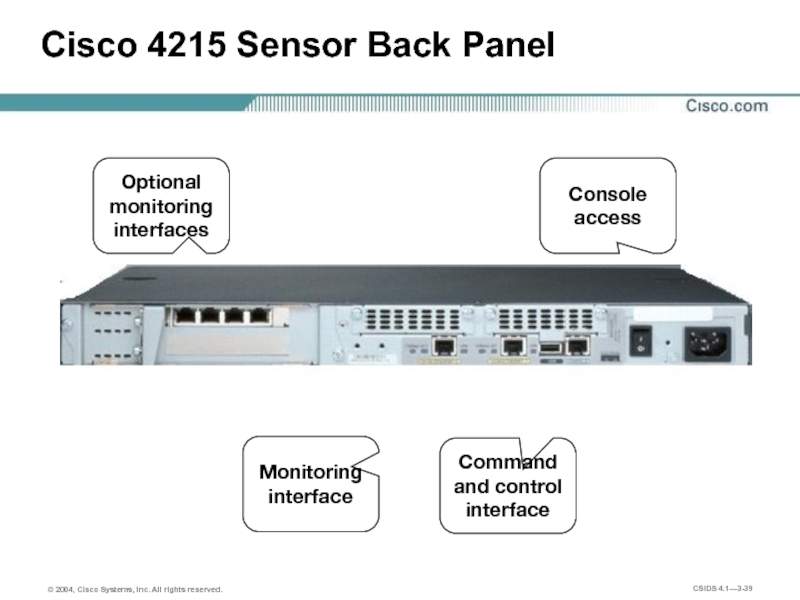
- 39. Cisco 4215 Sensor Back Panel Monitoring interface
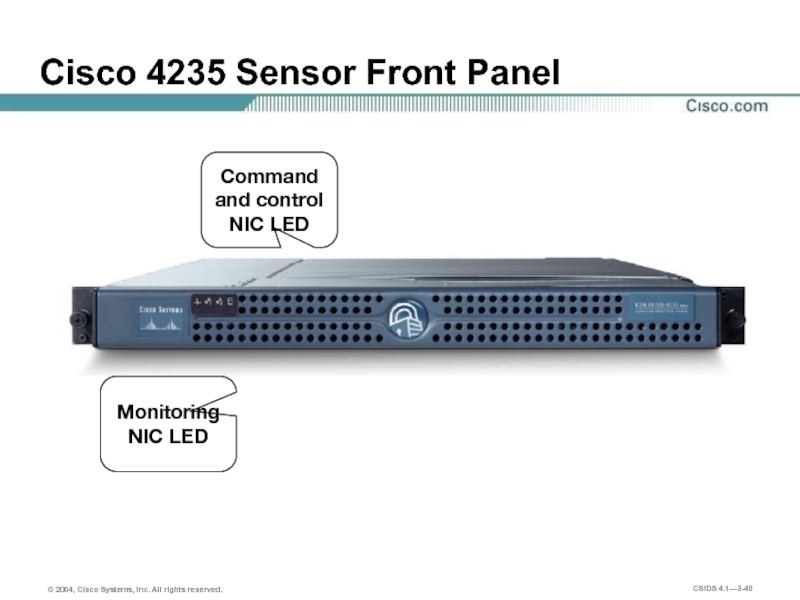
- 40. Cisco 4235 Sensor Front Panel Monitoring NIC LED Command and control NIC LED
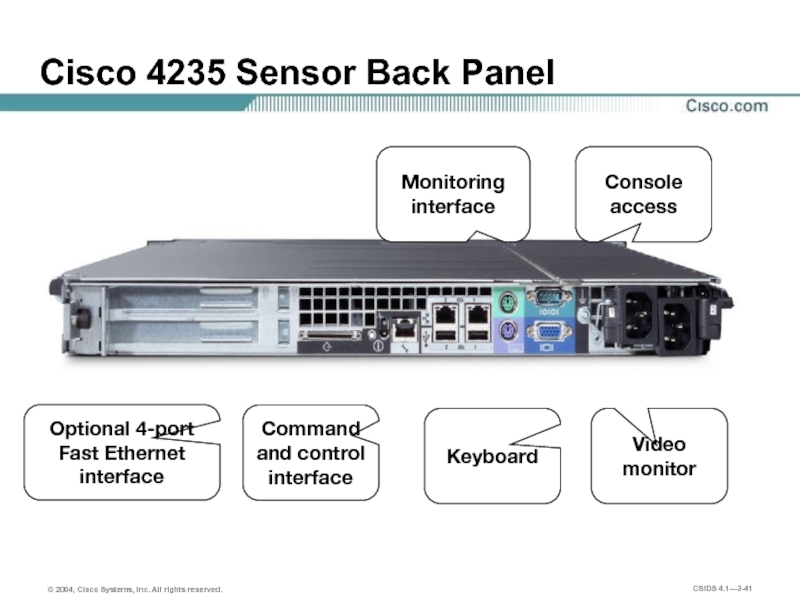
- 41. Cisco 4235 Sensor Back Panel Video monitor
- 42. Cisco 4250 Sensor Front Panel Monitoring NIC LED Command and control NIC LED
- 43. Cisco 4250 Sensor Back Panel Video monitor
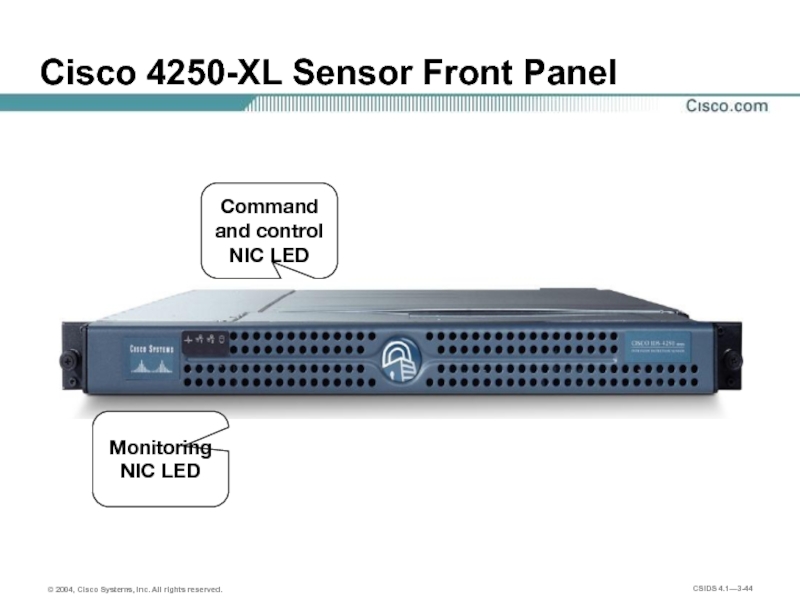
- 44. Cisco 4250-XL Sensor Front Panel Monitoring NIC LED Command and control NIC LED
- 45. Cisco 4250-XL Sensor Back Panel Reset interface
- 46. Cisco IDS XL Card
- 47. Deploying Cisco IDS
- 48. Sensor Selection Factors Network media—Ethernet, Fast Ethernet,
- 49. Sensor Deployment Considerations Number of Sensors Sensor placement Management and monitoring options External Sensor communications
- 50. Deployment of Sensors
- 51. Sensor Placement Sensor on
- 52. Summary
- 53. Summary Intrusion detection is the ability to
- 54. Summary (Cont.) A HIPS provides individual host
- 55. Summary (Cont.) A defense-in-depth security solution is
Слайд 2Objectives
Upon completion of this lesson, you will be able to perform
Define intrusion detection.
Explain the difference between true and false and positive and negative alarms.
Describe the relationship between vulnerabilities and exploits.
Explain the similarities and differences among the various intrusion detection technologies.
Explain the differences between HIPS and NIDS.
Слайд 3Objectives (Cont.)
Describe the benefits of intrusion protection.
Describe the network sensors that
Describe the Cisco Security Agent.
Describe the considerations necessary for selection, placement, and deployment of network intrusion protection.
Слайд 5Intrusion Detection
Ability to detect attacks against networks, including network devices and
Слайд 6False Alarms
False positive—A situation in which normal traffic or a benign
False negative—A situation in which a signature is not fired when offending traffic is detected. An actual attack is not detected.
Слайд 7True Alarms
True positive—A situation in which a signature is fired properly
True negative—A situation in which a signature is not fired when nonoffending traffic is detected. Normal traffic or a benign action does not cause an alarm.
Слайд 8Vulnerabilities and Exploits
A vulnerability is a weakness that compromises either the
Poor passwords
Improper input handling
Insecure communication
An exploit is the mechanism used to leverage a vulnerability.
Password guessing tools
Shell scripts
Executable code
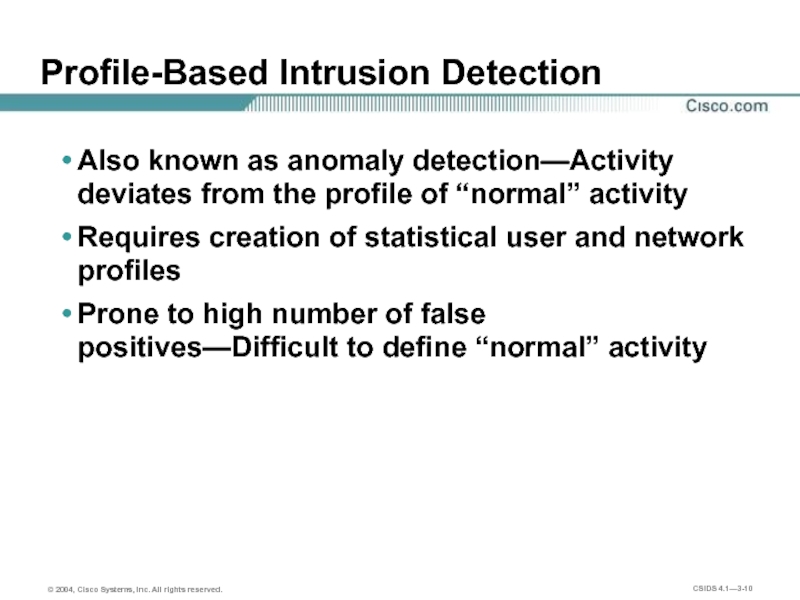
Слайд 10Profile-Based Intrusion Detection
Also known as anomaly detection—Activity deviates from the profile
Requires creation of statistical user and network profiles
Prone to high number of false positives—Difficult to define “normal” activity
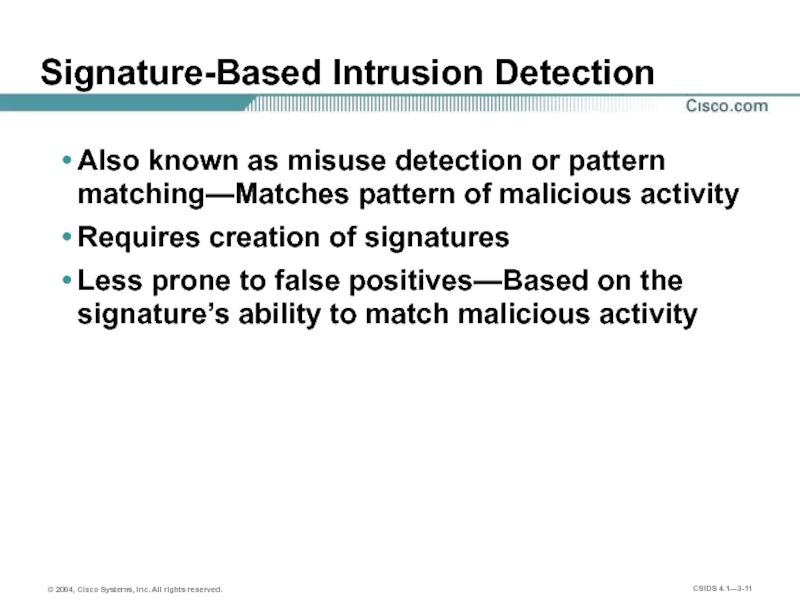
Слайд 11Signature-Based Intrusion Detection
Also known as misuse detection or pattern matching—Matches pattern
Requires creation of signatures
Less prone to false positives—Based on the signature’s ability to match malicious activity
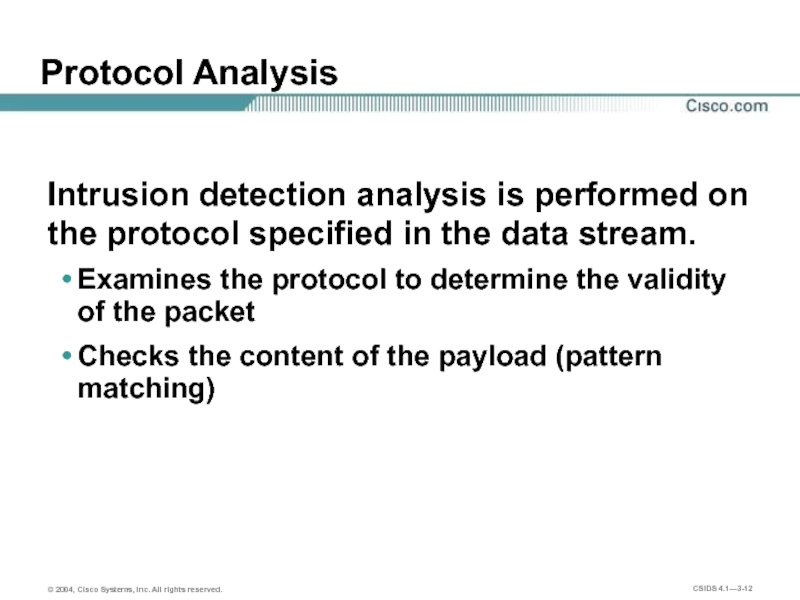
Слайд 12Protocol Analysis
Intrusion detection analysis is performed on the protocol specified in
Examines the protocol to determine the validity of the packet
Checks the content of the payload (pattern matching)
Слайд 13Responsive
Reactive IDSs can respond to an attack in any of the
Terminate session (TCP resets)
Block offending traffic (ACL)
Create session log files (IP logging)
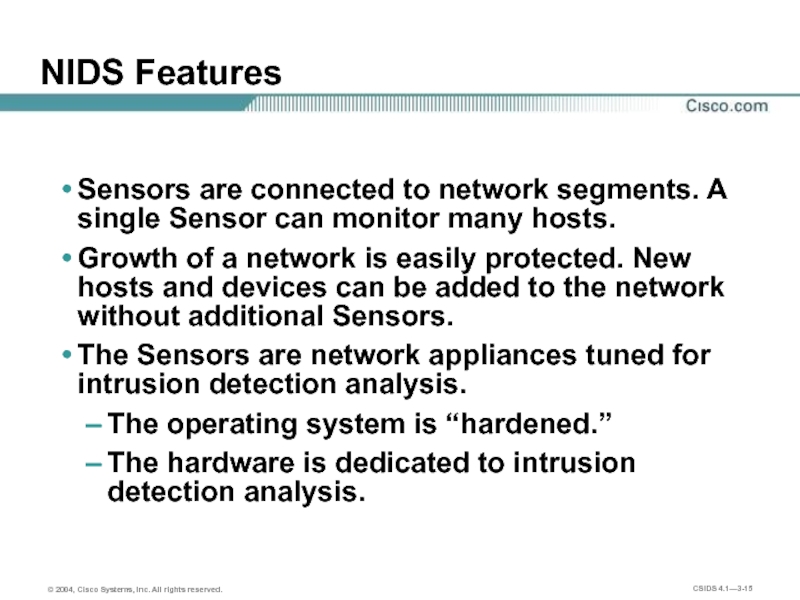
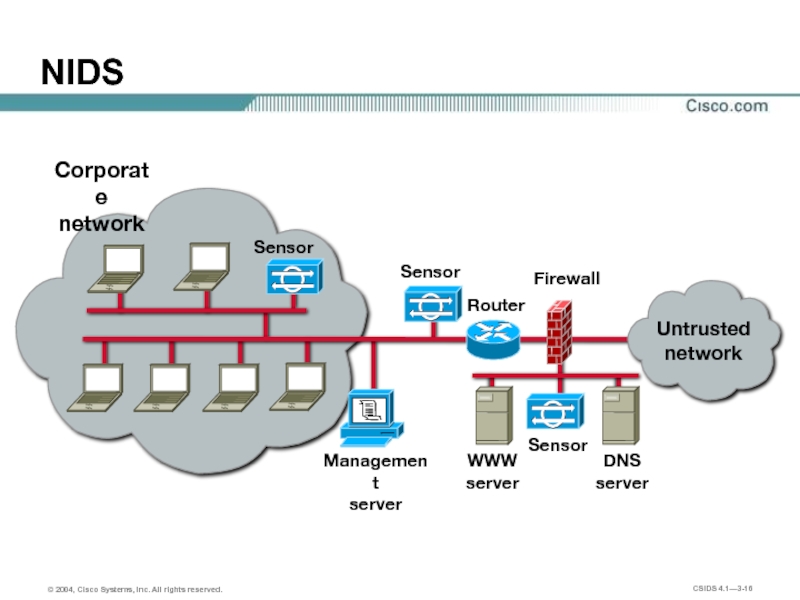
Слайд 15NIDS Features
Sensors are connected to network segments. A single Sensor can
Growth of a network is easily protected. New hosts and devices can be added to the network without additional Sensors.
The Sensors are network appliances tuned for intrusion detection analysis.
The operating system is “hardened.”
The hardware is dedicated to intrusion detection analysis.
Слайд 16
Management
server
Corporate
network
DNS
server
WWW
server
Sensor
Sensor
Firewall
NIDS
Sensor
Untrusted
network
Router
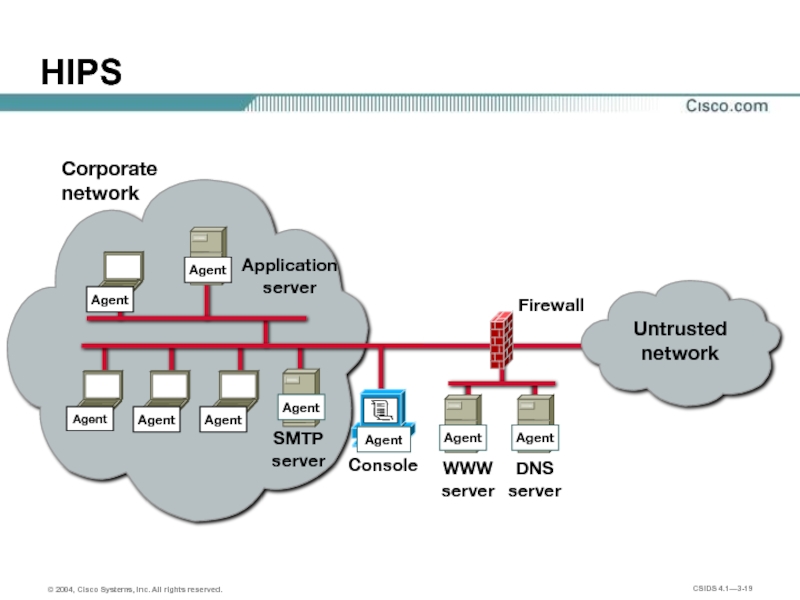
Слайд 18HIPS Features
Agent software installed on each host
Provides individual host detection and
Does not require special hardware
Слайд 19
Firewall
Corporate
network
DNS
server
WWW
server
Agent
Agent
HIPS
Console
Agent
SMTP
server
Application
server
Agent
Untrusted
network
Agent
Agent
Agent
Agent
Agent
Слайд 21Intrusion Protection Benefits
Intrusion protection provides:
Enhanced security over “classic” technologies
Advanced technology to
Increased resiliency of e-business systems and applications
Effective mitigation of malicious activity and insider threats
Broad visibility into the corporate data stream
Greater protection against known and unknown threats
Слайд 22Active Defense System
A complete intrusion protection solution focuses on the following:
Detection—Identify
Prevention—Stop the detected attack from executing.
Reaction—Immunize the system against future attacks from a malicious source.
Слайд 23Cisco IDS Solution Active Defense System
Network Sensors—Overlaid network protection
Switch Sensors—Integrated switch
Router Sensors—Integrated router protection
Firewall Sensors—Integrated firewall protection feature
Host Agents—Server and desktop protection
Comprehensive management—Robust system management and monitoring
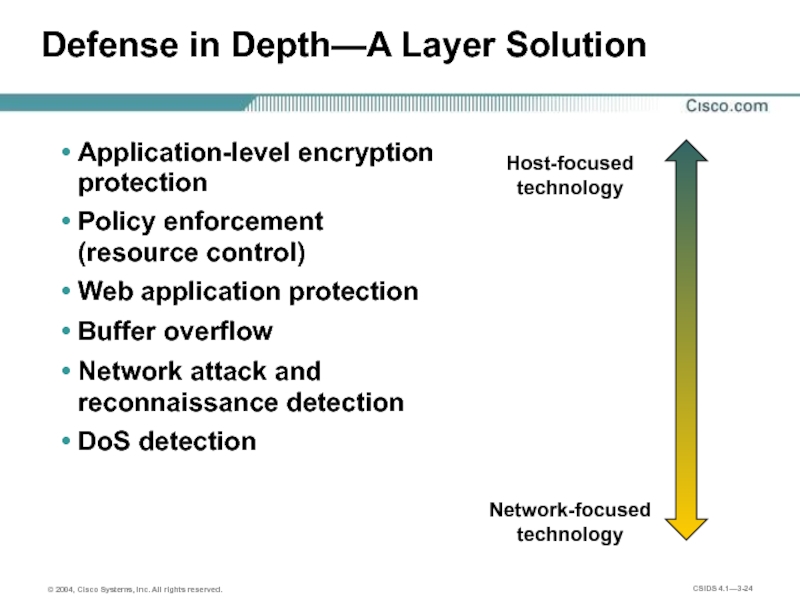
Слайд 24Defense in Depth—A Layer Solution
Application-level encryption protection
Policy enforcement (resource control)
Web application
Buffer overflow
Network attack and reconnaissance detection
DoS detection
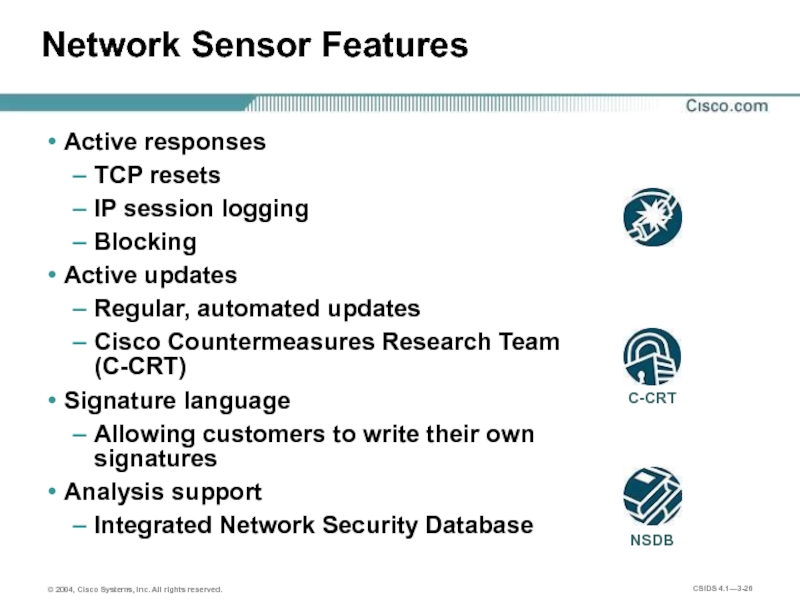
Слайд 26Network Sensor Features
Active responses
TCP resets
IP session logging
Blocking
Active updates
Regular, automated
Cisco Countermeasures Research Team (C-CRT)
Signature language
Allowing customers to write their own signatures
Analysis support
Integrated Network Security Database
C-CRT
NSDB
Слайд 27
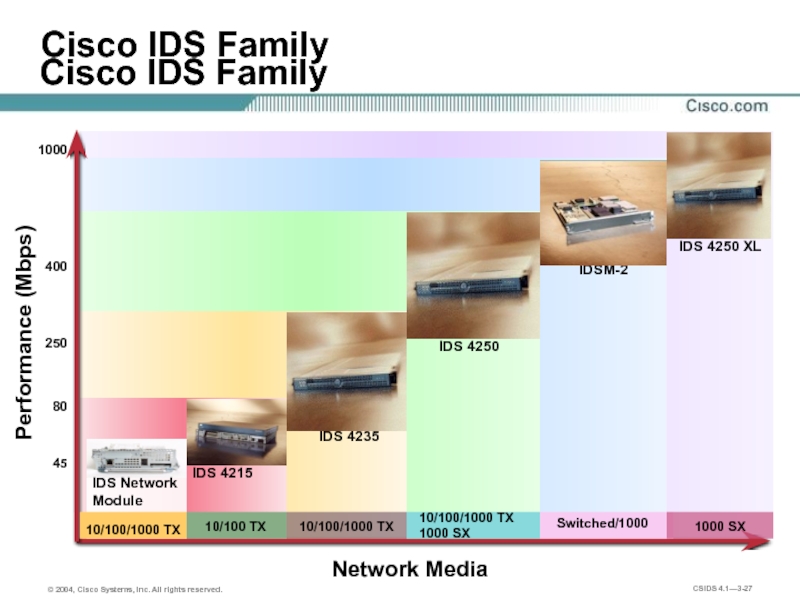
Cisco IDS Family
Performance (Mbps)
Network Media
Cisco IDS Family
IDSM-2
IDS 4235
IDS 4250
IDS 4215
IDS 4250
45
1000
400
80
250
IDS Network
Module
10/100/1000 TX
1000 SX
10/100 TX
1000 SX
Switched/1000
10/100/1000 TX
10/100/1000 TX
Слайд 28Network Sensor—Cisco 4200 Series Appliance
Appliance solution focused on protecting network devices,
Sophisticated attack detection
Network attacks
Application attacks
DoS attacks
Fragmented attacks
Whisker anti-IDS protection
Active responses
Blocking
TCP resets
IP logging
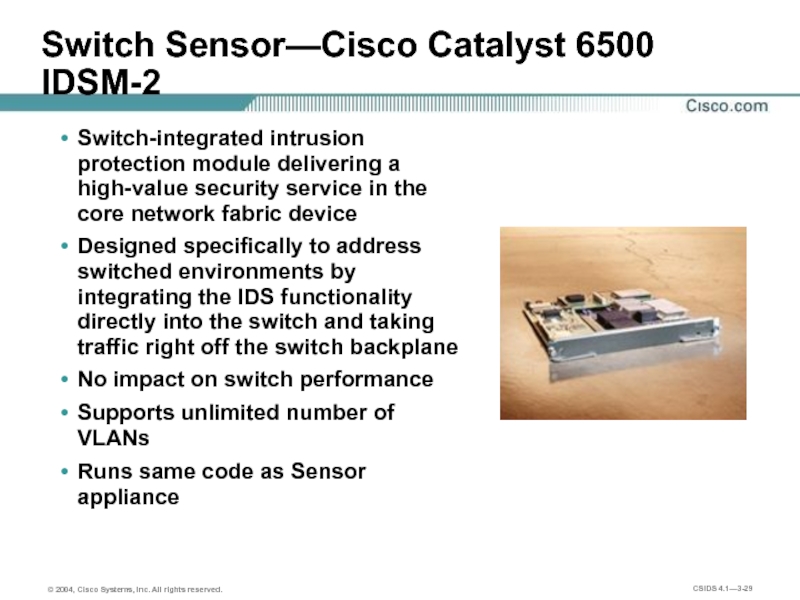
Слайд 29Switch Sensor—Cisco Catalyst 6500 IDSM-2
Switch-integrated intrusion protection module delivering a
high-value
Designed specifically to address switched environments by integrating the IDS functionality directly into the switch and taking traffic right off the switch backplane
No impact on switch performance
Supports unlimited number of VLANs
Runs same code as Sensor appliance
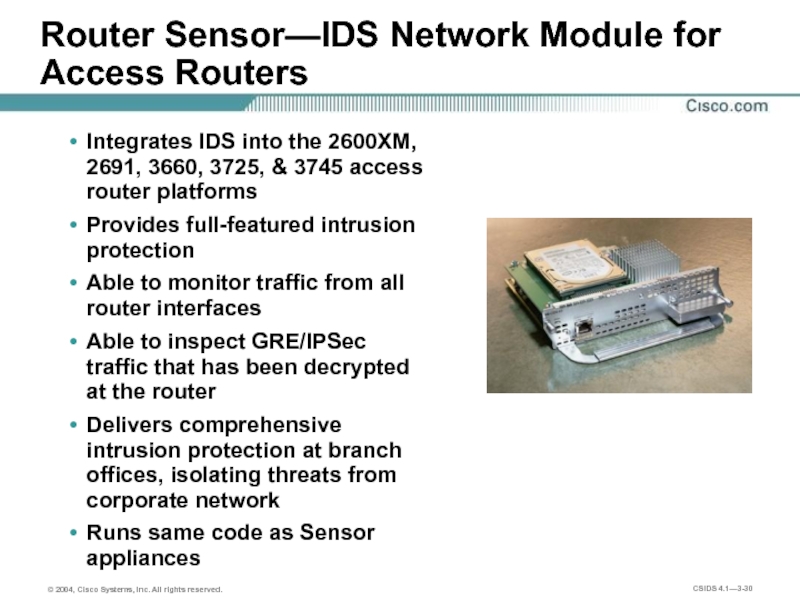
Слайд 30Router Sensor—IDS Network Module for Access Routers
Integrates IDS into the 2600XM,
Provides full-featured intrusion protection
Able to monitor traffic from all router interfaces
Able to inspect GRE/IPSec traffic that has been decrypted at the router
Delivers comprehensive intrusion protection at branch offices, isolating threats from corporate network
Runs same code as Sensor appliances
Слайд 31Router Sensor—Cisco IOS IDS
Router IDS technology targeted at lower-risk environments
Software—Cisco IOS
Platforms—830, 1700, 2600, 3600, 7100, 7200, 7500, and RSM Series routers
Signatures—100
Syslog or PostOffice alarming
Responses—Drop, block, and reset
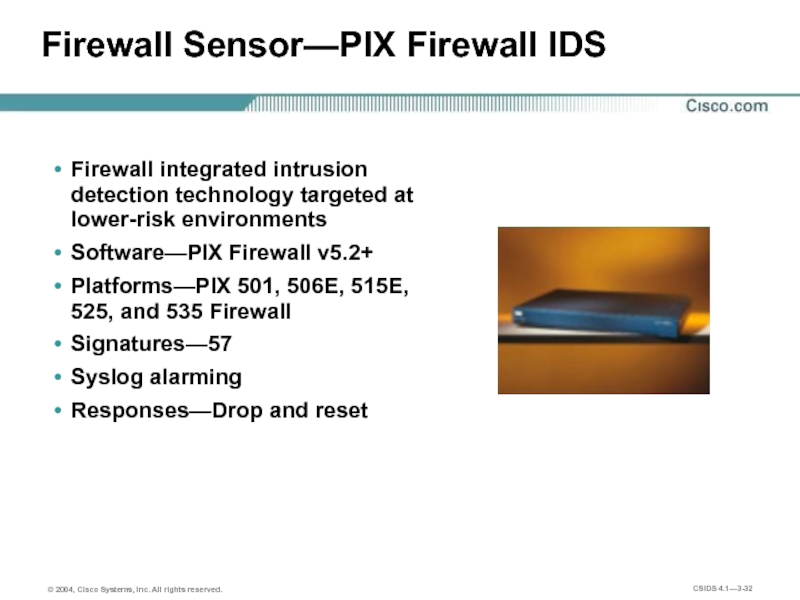
Слайд 32Firewall Sensor—PIX Firewall IDS
Firewall integrated intrusion detection technology targeted at lower-risk
Software—PIX Firewall v5.2+
Platforms—PIX 501, 506E, 515E, 525, and 535 Firewall
Signatures—57
Syslog alarming
Responses—Drop and reset
Слайд 34Cisco Security Agent Features
Active protection
Protects application and operating system against
Prevents access to server resources before unauthorized activity occurs
Uses behavior-based technology
Consists of two products
Agents
Management Center
Automatic Agent deployment
Up to 5,000 agents
Transparent to end users
Active update capabilities—Security policy and software updates propagated to Agents without operator intervention
5–10% Agent CPU overhead
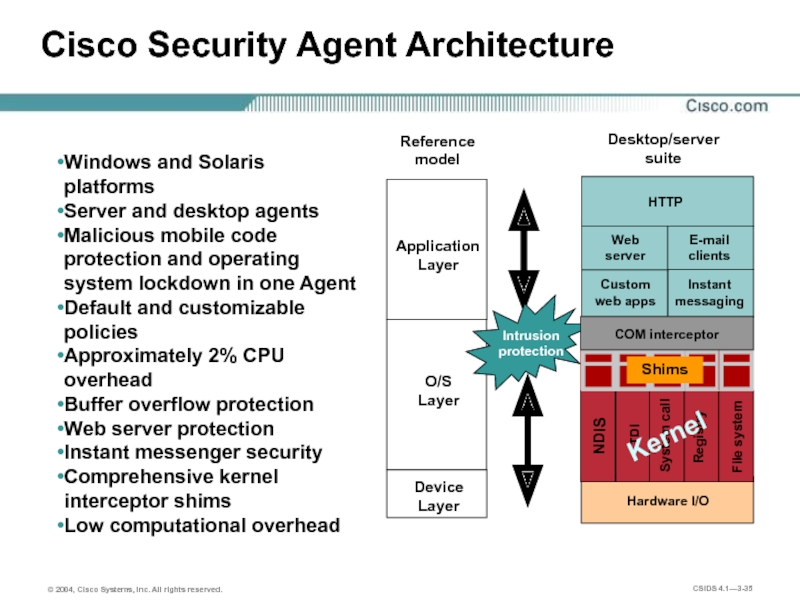
Слайд 35Cisco Security Agent Architecture
Windows and Solaris platforms
Server and desktop agents
Malicious mobile
Default and customizable policies
Approximately 2% CPU overhead
Buffer overflow protection
Web server protection
Instant messenger security
Comprehensive kernel interceptor shims
Low computational overhead
Слайд 39Cisco 4215 Sensor Back Panel
Monitoring interface
Command and control
interface
Console access
Optional monitoring
interfaces
Слайд 41Cisco 4235 Sensor Back Panel
Video
monitor
Keyboard
Monitoring interface
Command and control interface
Console access
Optional 4-port
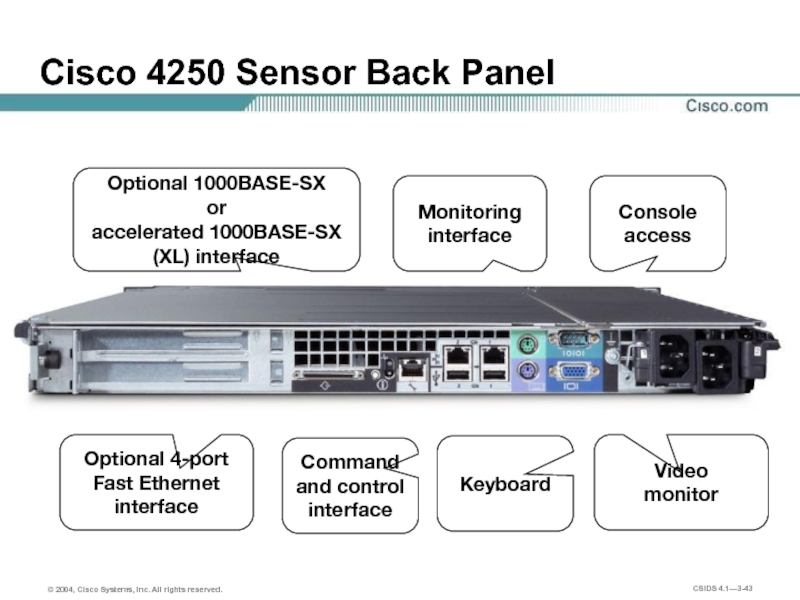
Слайд 43Cisco 4250 Sensor Back Panel
Video
monitor
Keyboard
Monitoring interface
Command and control interface
Console access
Optional 1000BASE-SX
or
accelerated
Optional 4-port Fast Ethernet interface
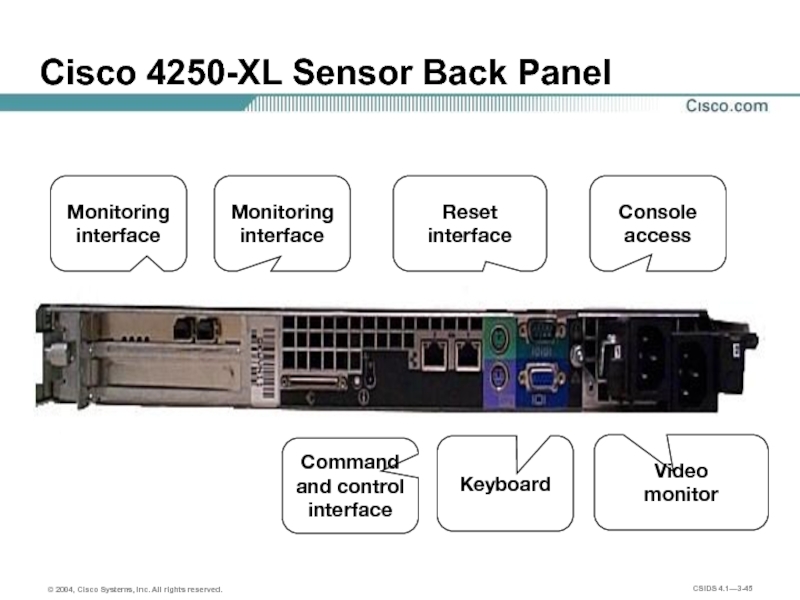
Слайд 45Cisco 4250-XL Sensor Back Panel
Reset interface
Command and control interface
Keyboard
Video
monitor
Console access
Monitoring interface
Monitoring
Слайд 48Sensor Selection Factors
Network media—Ethernet, Fast Ethernet, and Gigabit Ethernet
Intrusion detection analysis
Network environment—T1/E1, switched, multiple T3/E3, OC-12, and Gigabit
Слайд 49Sensor Deployment Considerations
Number of Sensors
Sensor placement
Management and monitoring options
External Sensor communications
Слайд 50
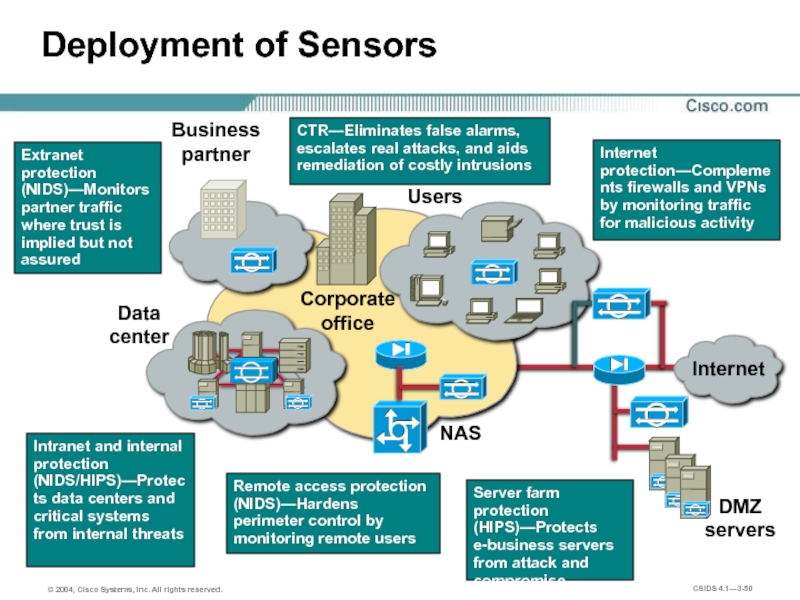
Deployment of Sensors
DMZ
servers
Internet
NAS
Data
center
Users
Corporate office
Business
partner
Remote access protection (NIDS)—Hardens perimeter
Intranet and internal protection (NIDS/HIPS)—Protects data centers and critical systems from internal threats
Server farm protection (HIPS)—Protects e-business servers from attack and compromise
Internet protection—Complements firewalls and VPNs by monitoring traffic for malicious activity
Extranet protection (NIDS)—Monitors partner traffic where trust is implied but not assured
CTR—Eliminates false alarms, escalates real attacks, and aids remediation of costly intrusions
Слайд 51
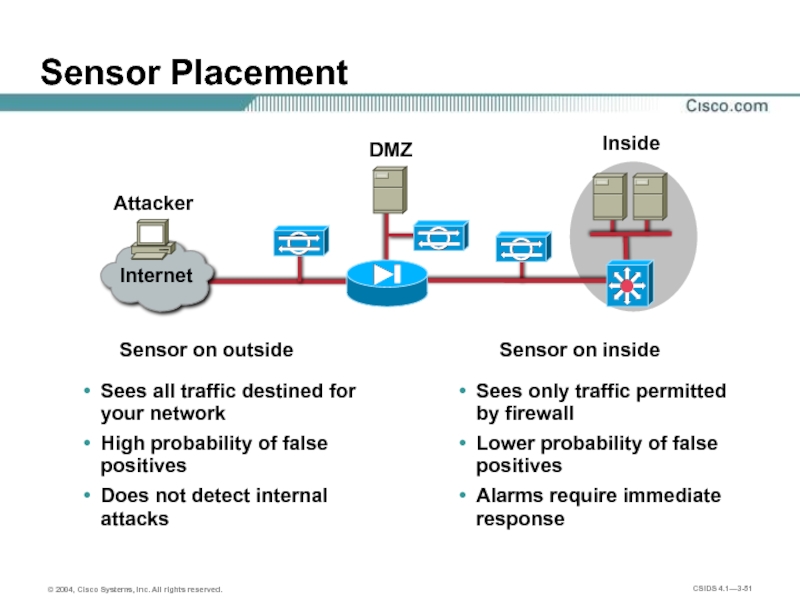
Sensor Placement
Sensor on outside
Sensor on inside
Attacker
Inside
DMZ
Sees all traffic destined for your
High probability of false positives
Does not detect internal attacks
Sees only traffic permitted by firewall
Lower probability of false positives
Alarms require immediate response
Internet
Слайд 53Summary
Intrusion detection is the ability to detect attacks against networks, including
Exploits leverage vulnerabilities associated with a system.
False positive alarms can be triggered by normal network activity.
True positive alarms are signatures that are triggered as expected.
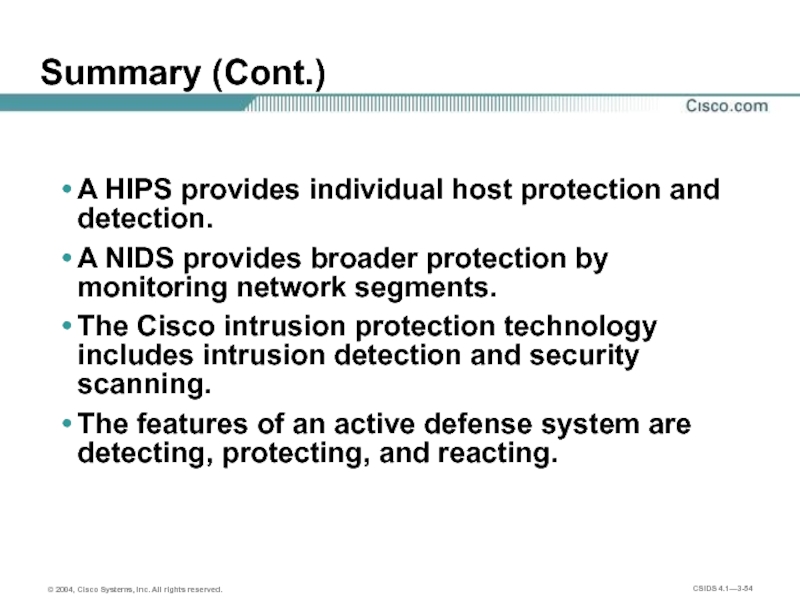
Слайд 54Summary (Cont.)
A HIPS provides individual host protection and detection.
A NIDS provides
The Cisco intrusion protection technology includes intrusion detection and security scanning.
The features of an active defense system are detecting, protecting, and reacting.
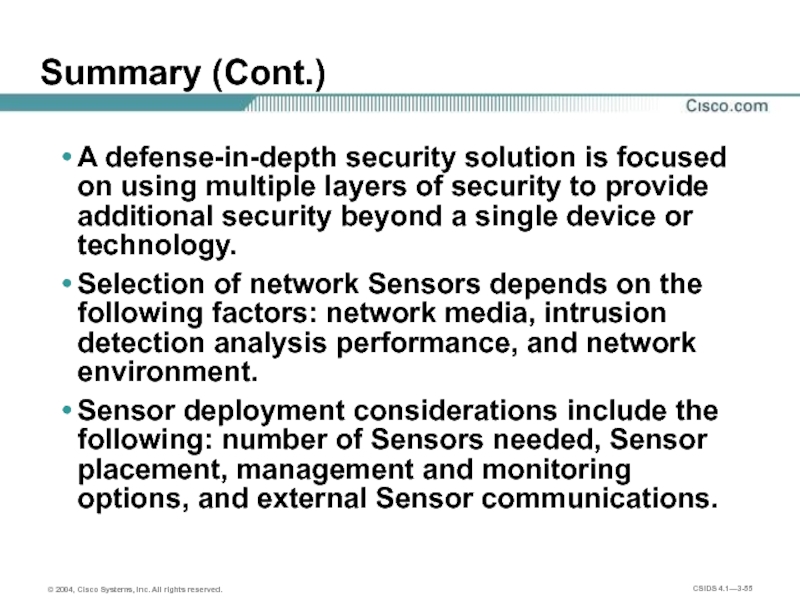
Слайд 55Summary (Cont.)
A defense-in-depth security solution is focused on using multiple layers
Selection of network Sensors depends on the following factors: network media, intrusion detection analysis performance, and network environment.
Sensor deployment considerations include the following: number of Sensors needed, Sensor placement, management and monitoring options, and external Sensor communications.