- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Exploring How Routing Works презентация
Содержание
- 1. Exploring How Routing Works
- 2. Outline Overview Routers Routers and the IP
- 3. Routers Linksys Cisco 2610 Router
- 4. router# show ip route
- 5. Routers and the IP Packet Delivery Process
- 6. Path Determination
- 7. Routing Tables
- 8. Routing Table Entries Directly connected: Router attaches
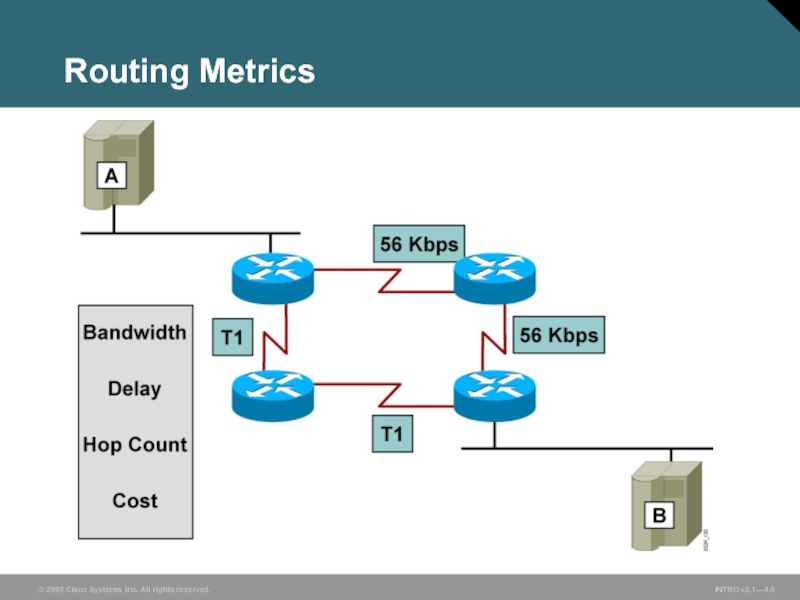
- 9. Routing Metrics
- 10. Distance Vector Routing Protocols Passes periodic copies
- 11. Link-State Routing Protocols After initial flood, passes small event-triggered link-state updates to all other routers
- 12. Summary Routers have certain components that are
- 13. Summary (Cont.) Routers determine the optimal path
- 14. Summary (Cont.) Distance vector routing protocols build
Слайд 2Outline
Overview
Routers
Routers and the IP Packet Delivery Process
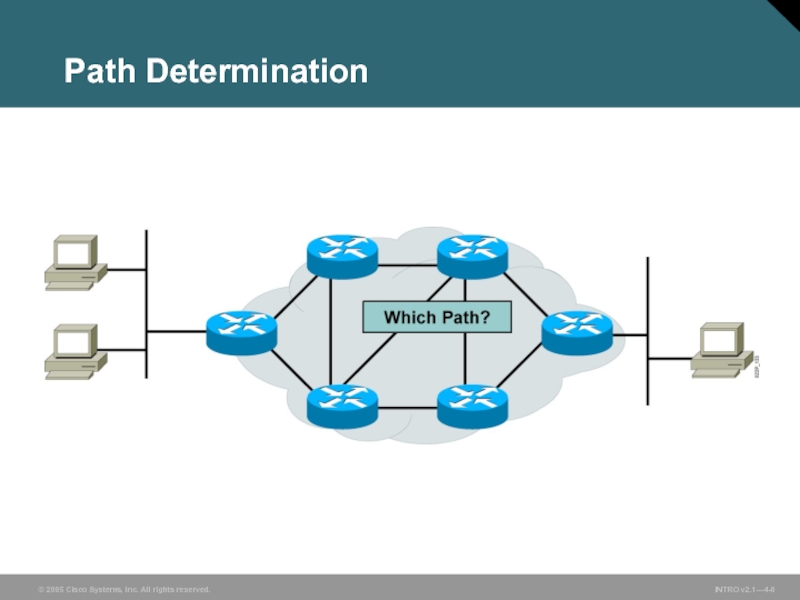
Path Determination
Routing Tables
Static, Dynamic, Directly
Dynamic Routing Protocols
Summary
Lab Exercise 4-1: Creating a Default Gateway
Слайд 4 router# show ip route
D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/25789217] via
R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/4] via 10.1.1.2
O 192.168.3.0/24 [110/229840] via 10.1.1.3
1
2
Lets other routers know about changes
Determines where to forward packets
Router Functions
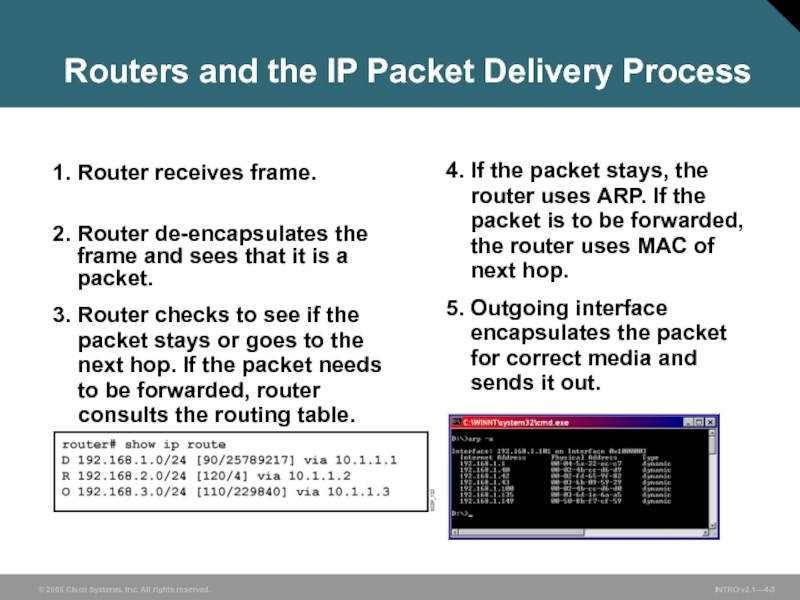
Слайд 5Routers and the IP Packet Delivery Process
1. Router receives frame.
2. Router
3. Router checks to see if the
packet stays or goes to the next hop. If the packet needs to be forwarded, router consults the routing table.
4. If the packet stays, the
router uses ARP. If the
packet is to be forwarded,
the router uses MAC of
next hop.
5. Outgoing interface
encapsulates the packet
for correct media and
sends it out.
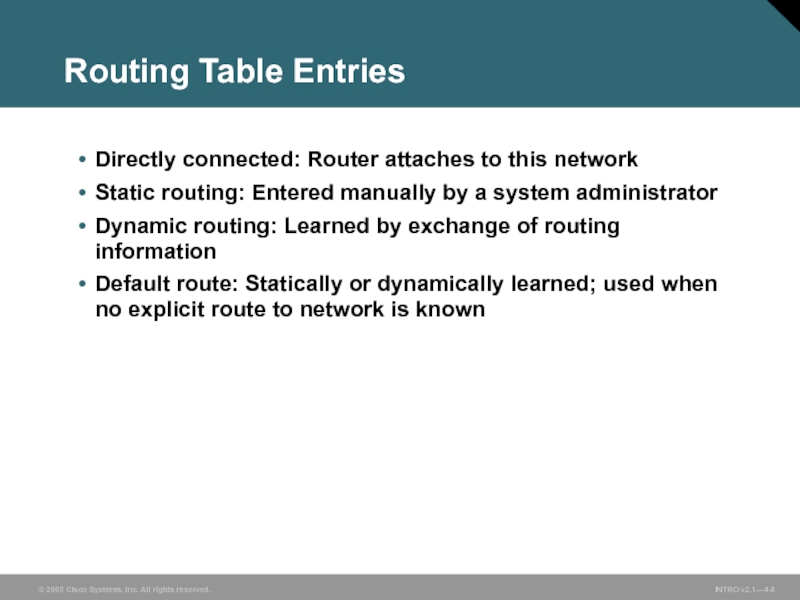
Слайд 8Routing Table Entries
Directly connected: Router attaches to this network
Static routing: Entered
Dynamic routing: Learned by exchange of routing information
Default route: Statically or dynamically learned; used when no explicit route to network is known
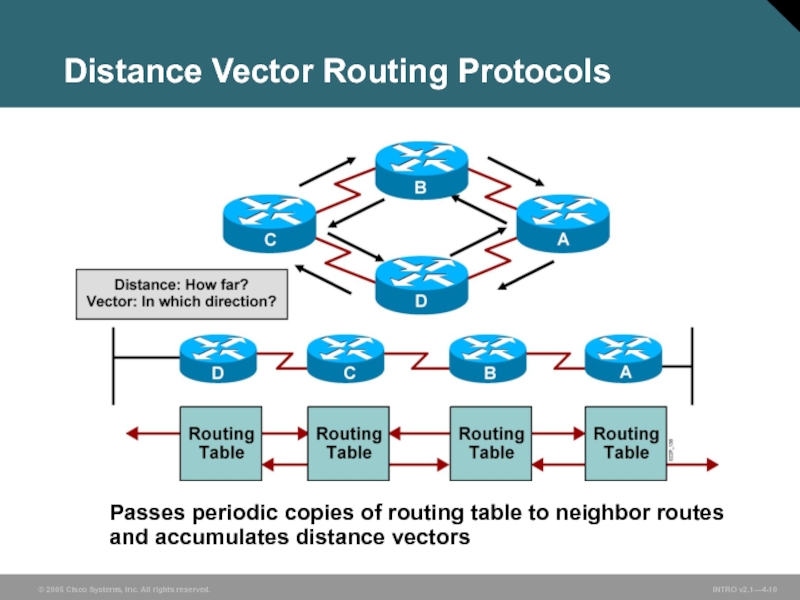
Слайд 10Distance Vector Routing Protocols
Passes periodic copies of routing table to neighbor
Слайд 11Link-State Routing Protocols
After initial flood, passes small event-triggered link-state updates to
Слайд 12Summary
Routers have certain components that are also found in computers and
Routers have these two primary functions in the IP packet delivery process: maintaining routing tables and determining the best path to used to forward packets.
Слайд 13Summary (Cont.)
Routers determine the optimal path for forwarding IP packets between
Routing tables provide an ordered list of best paths to known networks, and include information such as destination, next-hop associations, and routing metrics.
Routing algorithms process the received updates and populate the routing table with the best route.
Commonly used routing metrics include bandwidth, delay, hop count, and cost.
Слайд 14Summary (Cont.)
Distance vector routing protocols build and update routing tables automatically
Link-state routing protocols build and update routing tables automatically, running the SPF algorithms against the link-state database to determine the best paths, and flood routing information about their own links to all the routers in the network.
Cisco developed EIGRP, which combines the best features of the distance vector and link-state routing protocol.

![router# show ip route D 192.168.1.0/24 [90/25789217] via 10.1.1.1 R 192.168.2.0/24 [120/4]](/img/tmb/3/248776/8936b2a6920b2409577b6894daf32b69-800x.jpg)