Astana September 30 2015
- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
European energy transition презентация
Содержание
- 1. European energy transition
- 2. Table of contents ▶ Status of natural gas
- 3. European Natural Gas Infrastructure © World Energy
- 4. European Natural Gas Demand/Supply © World Energy Council 2014
- 5. EU sets ambitious targets for 2030
- 6. Natural Gas Contract Duration Changes There is
- 7. Table of contents ▶ Status of natural
- 8. Despite the recent turmoil, the outlook for
- 9. orld Energy Council 2014
- 10. 10 Energy transition is happening in a
- 11. EU places high priority on improving energy
- 12. Dynamic innovation and technology are driving changes
- 13. Table of contents ▶ Status of natural
- 15. LNG Capacity 2008, 2014, and expected 2020
Слайд 1© World Energy Council 2014
European Energy Transition: challenges to suppliers
Ged Davis
Executive
Слайд 2Table of contents
▶ Status of natural gas in Europe
© World Energy Council
▶ Forces for change
▶ Challenges for natural gas suppliers
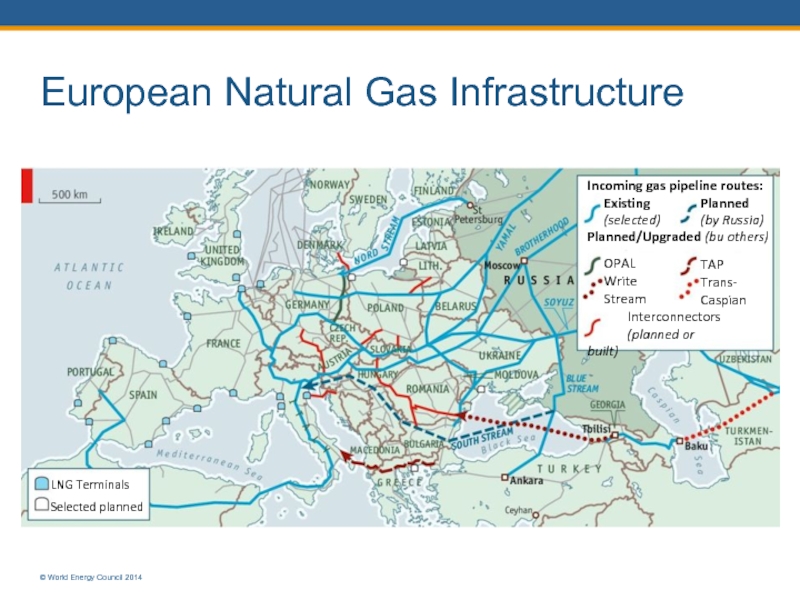
Слайд 3European Natural Gas Infrastructure
© World Energy Council 2014
LNG Terminals
Selected planned
Incoming gas
Existing
(selected)
Planned
(by Russia)
TAP
Trans-
Caspian
Interconnectors
(planned or built)
Planned/Upgraded (bu others)
OPAL
Write
Stream
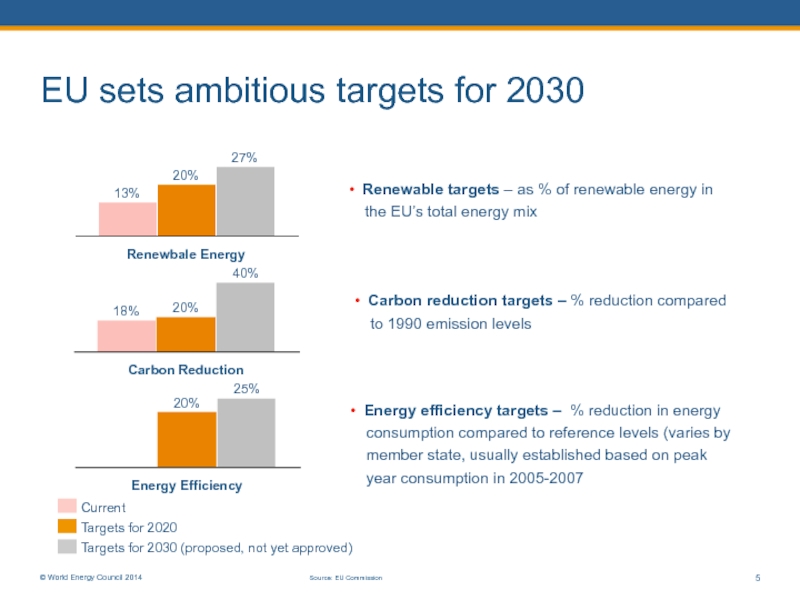
Слайд 5EU sets ambitious targets for 2030
Renewbale Energy
40%
27%
20%
13%
Current
Targets for 2020
Targets for 2030
20%
Carbon Reduction
25%
© World Energy Council 2014
5
Source: EU Commission
18%
20%
Energy Efficiency
• Renewable targets – as % of renewable energy in the EU’s total energy mix
• Carbon reduction targets – % reduction compared to 1990 emission levels
• Energy efficiency targets – % reduction in energy consumption compared to reference levels (varies by member state, usually established based on peak year consumption in 2005-2007
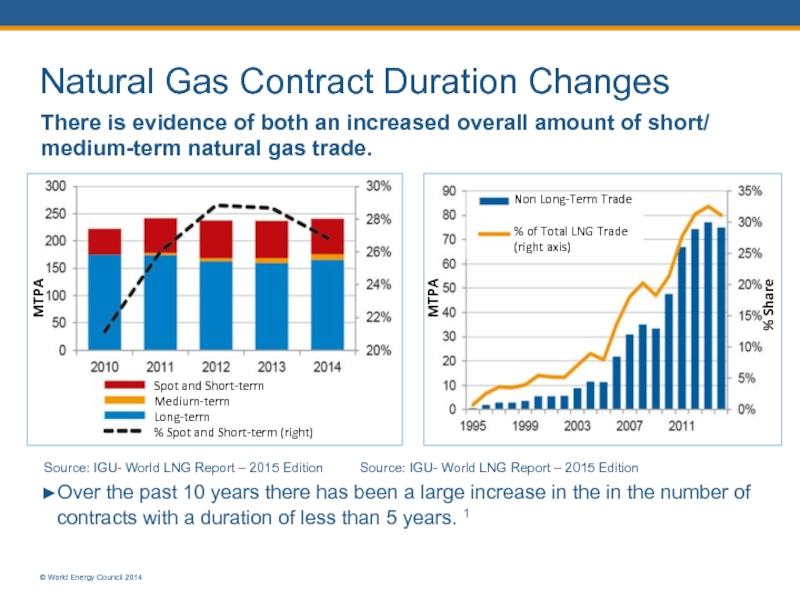
Слайд 6Natural Gas Contract Duration Changes
There is evidence of both an increased
Source: IGU- World LNG Report – 2015 Edition Source: IGU- World LNG Report – 2015 Edition
►Over the past 10 years there has been a large increase in the in the number of contracts with a duration of less than 5 years. 1
© World Energy Council 2014
Spot and Short-term
Medium-term
Long-term
% Spot and Short-term (right)
MTPA
MTPA
% Share
Non Long-Term Trade
% of Total LNG Trade
(right axis)
Слайд 7Table of contents
▶ Status of natural gas in Europe
© World Energy Council
▶ Forces for change
▶ Challenges for natural gas suppliers
Слайд 8Despite the recent turmoil, the outlook for the world economy in
© World Energy Council 2014
▶ The current recovery continues to lack momentum …
▶ Recent indicators point to tepid economic growth in most advanced economies
Confidence indicators and order books are up
Monetary conditions are still loose, investment is picking up
« Austerity » stances are giving way to more neutral policy stances
Some concerns about possible recession before 2020
▶ Yet, several emerging markets are in difficulty
Overemphasis on commodities, lack of reforms, socio-political mismanagement ?
8
Слайд 9orld Energy Council 2014
Will national regulation become more predictable in a
© W
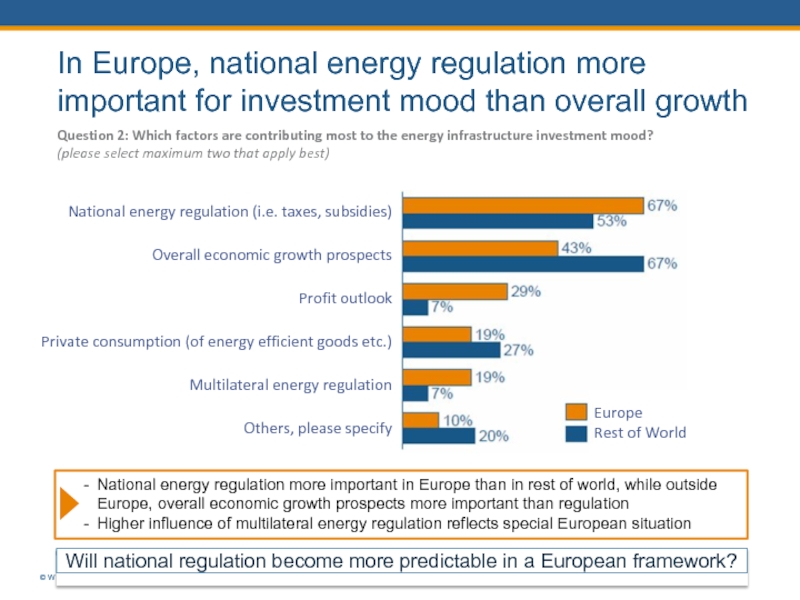
In Europe, national energy regulation more important for investment mood than overall growth
Question 2: Which factors are contributing most to the energy infrastructure investment mood?
(please select maximum two that apply best)
National energy regulation (i.e. taxes, subsidies)
Overall economic growth prospects
Profit outlook
Private consumption (of energy efficient goods etc.)
Multilateral energy regulation
Others, please specify
National energy regulation more important in Europe than in rest of world, while outside
Europe, overall economic growth prospects more important than regulation
Higher influence of multilateral energy regulation reflects special European situation
Europe
Rest of World
Слайд 1010
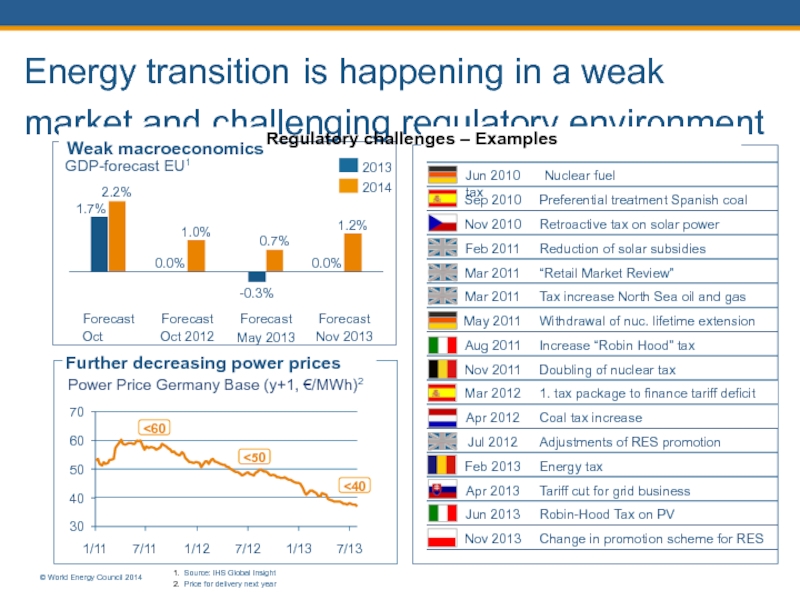
Energy transition is happening in a weak market and challenging regulatory environment
GDP-forecast
2.2%
Forecast Nov 2013
1.2%
0.0%
-0.3%
Forecast May 2013
0.7%
Forecast Oct 2012
1.0%
0.0%
Forecast Oct 2011
1.7%
2013
2014
Weak macroeconomics Regulatory challenges – Examples
30
40
50
60
70
7/11
1/11
7/13
1/13
7/12
1/12
Power Price Germany Base (y+1, €/MWh)2
<60
<50
<40
Further decreasing power prices
Jun 2010 Nuclear fuel tax
Sep 2010
Preferential treatment Spanish coal
Nov 2010
Retroactive tax on solar power
Feb 2011
Reduction of solar subsidies
Mar 2011
“Retail Market Review”
Mar 2011
Tax increase North Sea oil and gas
May 2011
Withdrawal of nuc. lifetime extension
Aug 2011
Increase “Robin Hood” tax
Nov 2011
Doubling of nuclear tax
Mar 2012
1. tax package to finance tariff deficit
Apr 2012
Coal tax increase
Jul 2012
Adjustments of RES promotion
Feb 2013
Energy tax
Apr 2013
Tariff cut for grid business
Jun 2013
Robin-Hood Tax on PV
Nov 2013
Change in promotion scheme for RES
1. Source: IHS Global Insight
2. Price for delivery next year
© World Energy Council 2014
Слайд 11EU places high priority on improving energy security
© World Energy Council
▶ Increasing energy efficiency and reaching the proposed 2030 energy and climate goals.
▶ Increasing energy production in the EU and diversifying supplier countries and routes. This includes further deployment of renewables, sustainable production of fossil fuels, and safe nuclear where the option is chosen. It also entails working effectively with current major energy partners, as well as developing new partners such as countries in the Caspian Basin region.
▶ Completing the internal energy market and building missing infrastructure links to quickly respond to supply disruptions
▶ Strengthening emergency and solidarity mechanisms and protecting critical infrastructure.
▶ Speaking with one voice in external energy policy
11
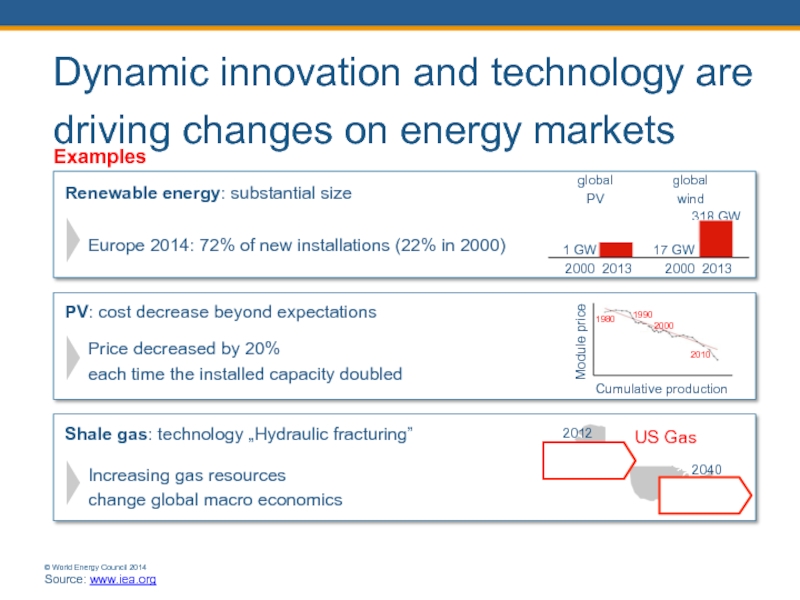
Слайд 12Dynamic innovation and technology are driving changes on energy markets
Examples
US Gas
2040
Net
2012
Net importer with 42 bcm
Price decreased by 20%
each time the installed capacity doubled
139 GW
Europe 2014: 72% of new installations (22% in 2000)
Renewable energy: substantial size
2000 2013
global wind
318 GW
2000 2013
global PV
Module price
1980
1990
2000
2010
Cumulative production
Shale gas: technology „Hydraulic fracturing”
Increasing gas resources change global macro economics
PV: cost decrease beyond expectations
© World Energy Council 2014
Слайд 13Table of contents
▶ Status of natural gas in Europe
▶ Forces for change
© World
▶ Challenges for natural gas suppliers
Слайд 14
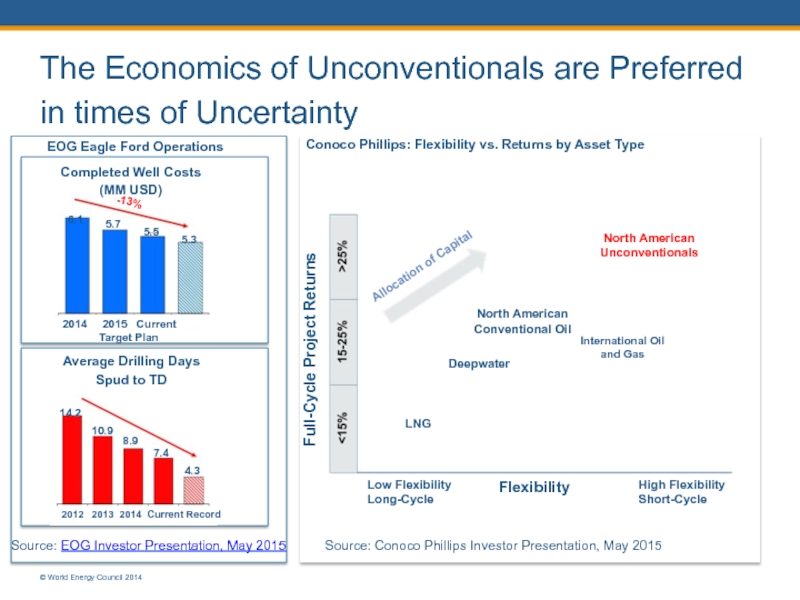
The Economics of Unconventionals are Preferred in times of Uncertainty
Conoco Phillips:
EOG Eagle Ford Operations
Completed Well Costs (MM USD)
6.1
5.7
5.5
5.3
-13%
2014 2015 Current Target Plan
Average Drilling Days Spud to TD
14.2
10.9
8.9
7.4
4.3
2012 2013 2014 Current Record
Source: EOG Investor Presentation, May 2015
© World Energy Council 2014
Source: Conoco Phillips Investor Presentation, May 2015
Слайд 15LNG Capacity 2008, 2014, and
expected 2020 (bcm)
15
© World Energy Council 2014
Legend
*Anticipated
Under Construction Only