- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Enhanced entity-relationship modelling concepts. (Lecture 3) презентация
Содержание
- 2. Enhanced Entity-Relationship Modelling Concepts Lecture 3
- 3. Agenda 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 2.EER concepts specialisation/generalisation 3.Alternative ER/EER notation
- 4. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Cardinality
- 5. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Degree
- 6. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Ternary relationship called ‘Registers’
- 7. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Quaternary relationship called ‘Arranges’
- 8. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Multiplicity
- 9. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Ternary relationship called ‘Registers’
- 10. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Ternary
- 11. 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 Try
- 12. Agenda 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 2.EER concepts specialisation/generalisation 3.Alternative ER/EER notation
- 13. 2.1.The Enhanced Entity-Relationship Model Semantic concepts are
- 14. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation Superclass An entity type that
- 15. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation Superclass/subclass relationship is one-to-one (1:1).
- 16. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation Attribute Inheritance An entity in
- 17. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation Specialization Process of maximizing
- 18. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
- 19. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
- 20. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
- 21. 2.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
- 22. 2.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation Participation constraint
- 23. 2.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation Disjoint constraint
- 24. 2.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation
- 25. 2.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation
- 26. 2.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation
- 27. 2.4. EER
- 28. 2.5. Aggregation Represents a ‘has-a’ or ‘is-part-of’
- 29. 2.6. Composition Specific form of aggregation that
- 30. Agenda 1.Relationships with degree higher then 2 2.EER concepts specialisation/generalisation 3.Alternative ER/EER notation
- 31. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation Meaning ENTITY
- 32. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
- 33. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
- 34. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
- 35. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
- 36. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
- 37. 3.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
- 38. Reading Connolly & Begg, Chapter 13
Слайд 3Agenda
1.Relationships with degree higher then 2
2.EER concepts specialisation/generalisation
3.Alternative ER/EER notation
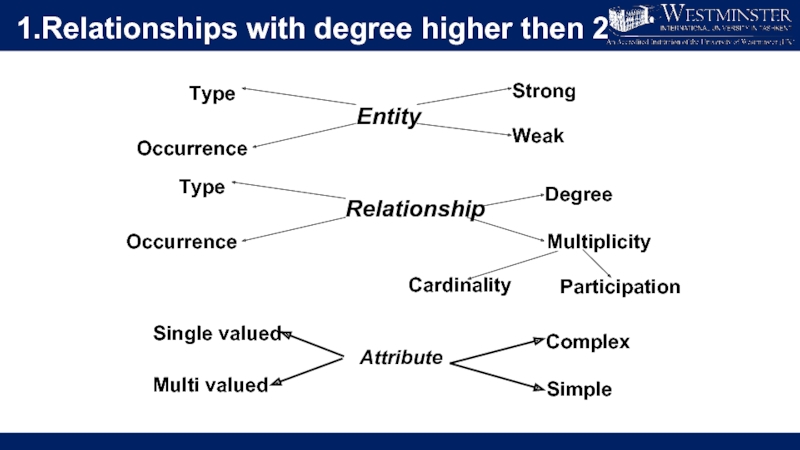
Слайд 41.Relationships with degree higher then 2
Cardinality
Participation
Entity
Type
Occurrence
Strong
Weak
Multiplicity
Relationship
Type
Occurrence
Degree
Attribute
Complex
Simple
Single valued
Multi valued
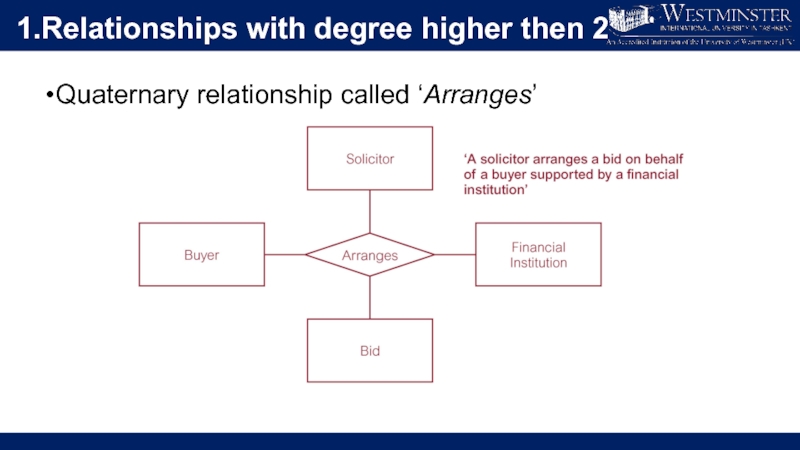
Слайд 51.Relationships with degree higher then 2
Degree of a Relationship
Number of participating
entities in relationship.
Relationship of degree:
two is binary;
three is ternary;
four is quaternary.
Relationship of degree:
two is binary;
three is ternary;
four is quaternary.
Слайд 81.Relationships with degree higher then 2
Multiplicity for Complex Relationships
Number (or
range) of possible occurrences of an entity type in an n-ary relationship when other (n-1) values are fixed.
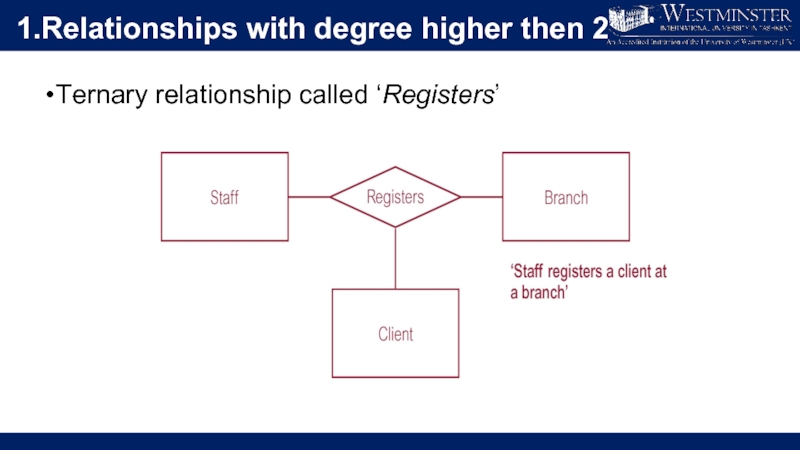
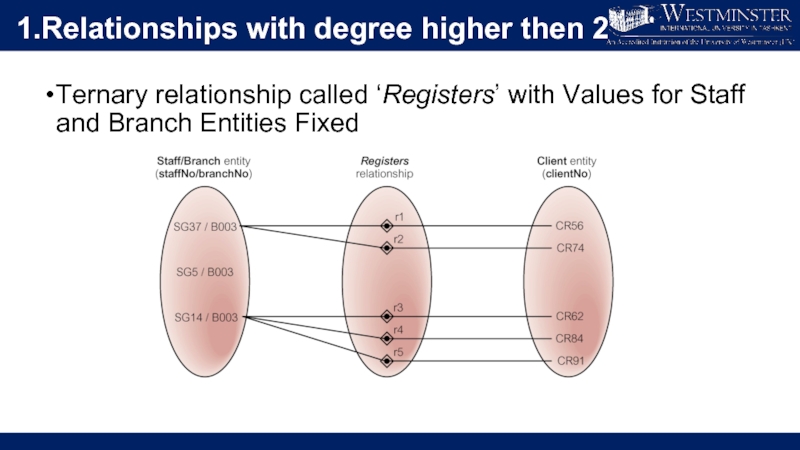
Слайд 101.Relationships with degree higher then 2
Ternary relationship called ‘Registers’ with Values
for Staff and Branch Entities Fixed
Слайд 111.Relationships with degree higher then 2
Try to detect multiplicities for remaining
participating entities in ternary relationship Registers
Note: You can make appropriate assumptions and detect multiplicities accordingly
Note: You can make appropriate assumptions and detect multiplicities accordingly
Слайд 12Agenda
1.Relationships with degree higher then 2
2.EER concepts specialisation/generalisation
3.Alternative ER/EER notation
Слайд 132.1.The Enhanced Entity-Relationship Model
Semantic concepts are incorporated into the original ER
model and called the Enhanced Entity-Relationship (EER) model.
Examples of additional concepts of EER model are:
specialization / generalization;
aggregation;
composition.
Examples of additional concepts of EER model are:
specialization / generalization;
aggregation;
composition.
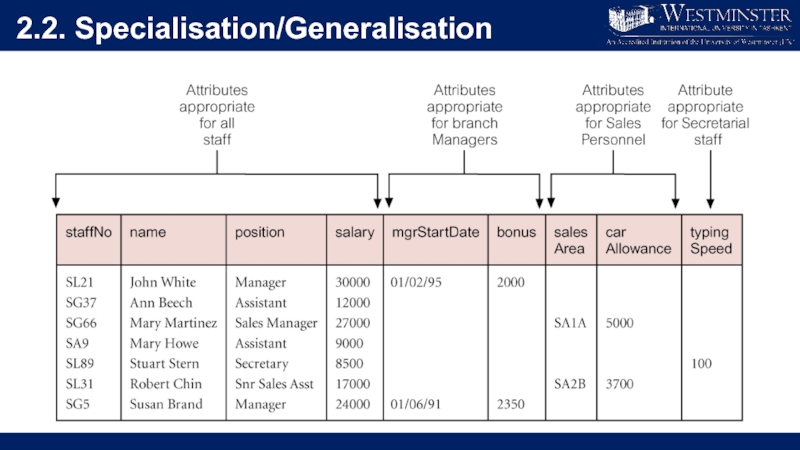
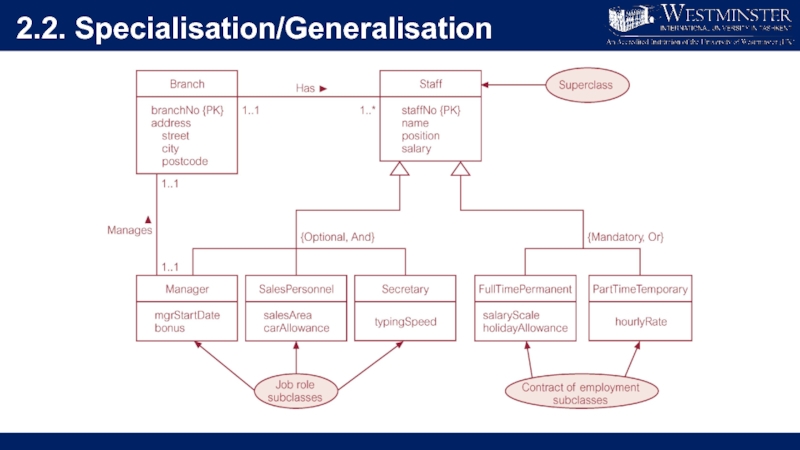
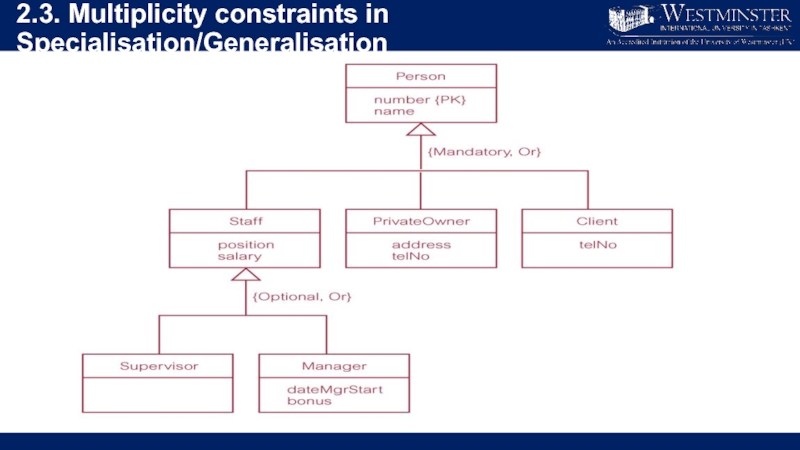
Слайд 142.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
Superclass
An entity type that includes one or more distinct subgroupings
of its occurrences.
Subclass
A distinct subgrouping of occurrences of an entity type.
Subclass
A distinct subgrouping of occurrences of an entity type.
Слайд 152.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
Superclass/subclass relationship is one-to-one (1:1).
Superclass may contain overlapping or
distinct subclasses.
Not all members of a superclass need to be a member of a subclass.
Not all members of a superclass need to be a member of a subclass.
Слайд 162.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
Attribute Inheritance
An entity in a subclass represents same ‘real world’
object as in superclass, and may possess subclass-specific attributes, as well as those associated with the superclass.
Слайд 172.2. Specialisation/Generalisation
Specialization
Process of maximizing differences between members of an entity
by identifying their distinguishing characteristics.
Generalization
Process of minimizing differences between entities by identifying their common characteristics.
Generalization
Process of minimizing differences between entities by identifying their common characteristics.
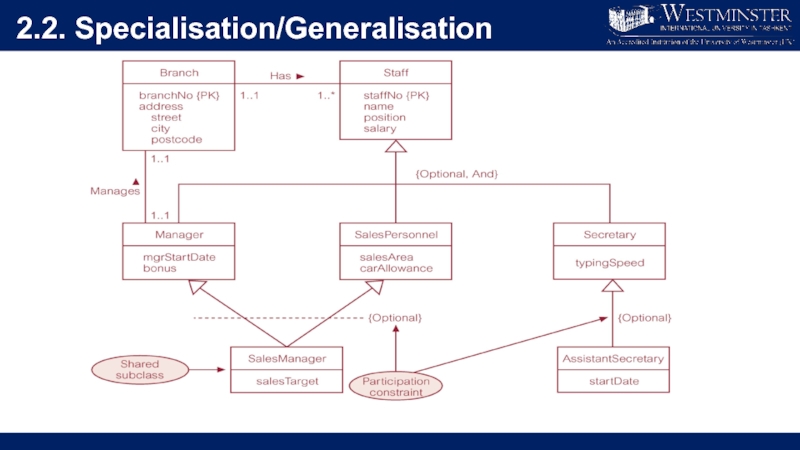
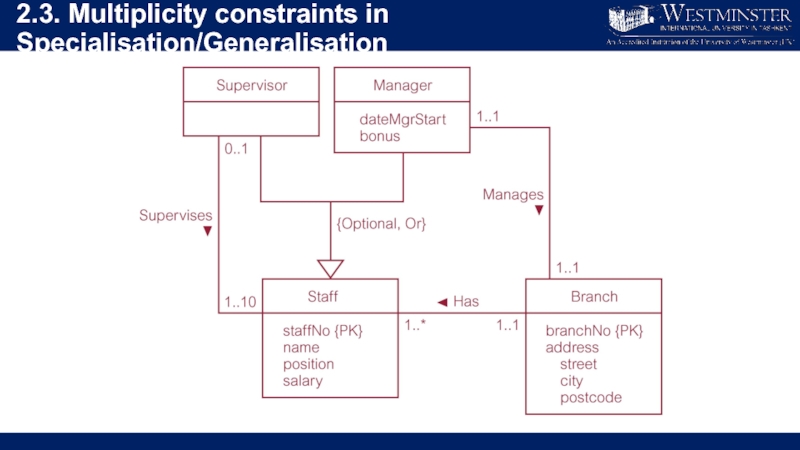
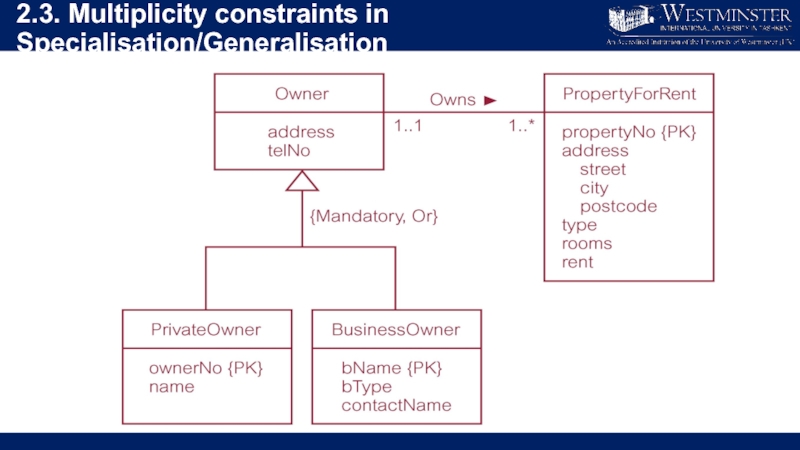
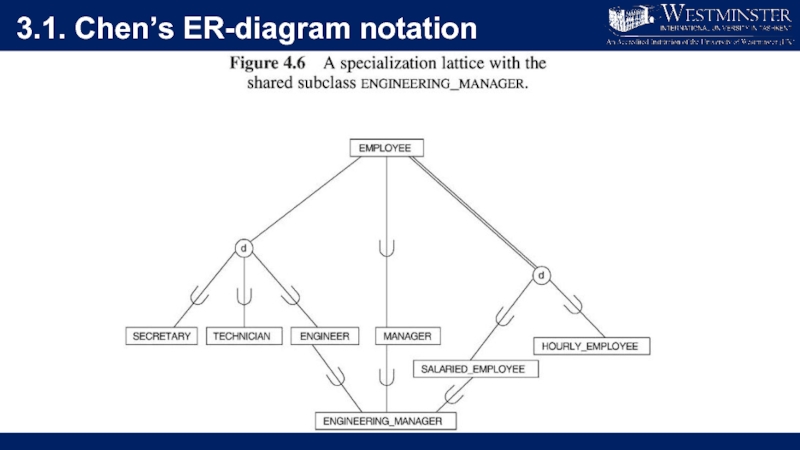
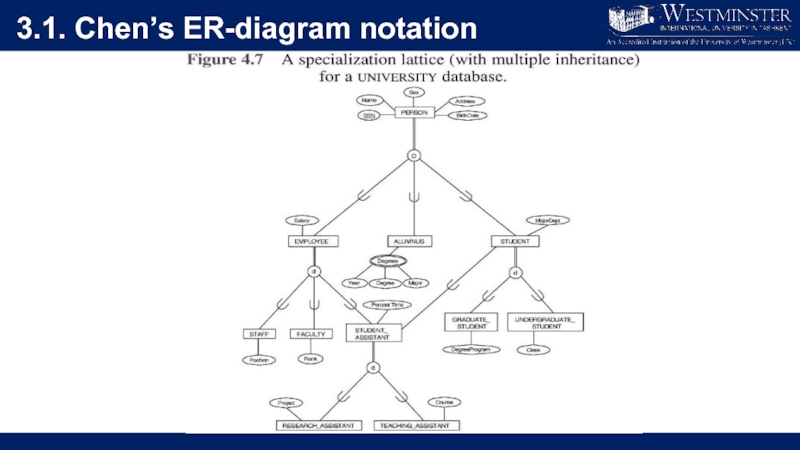
Слайд 222.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation
Participation constraint
Determines whether every member in superclass
must participate as a member of a subclass.
May be mandatory (total) or optional.
May be mandatory (total) or optional.
Слайд 232.3. Multiplicity constraints in Specialisation/Generalisation
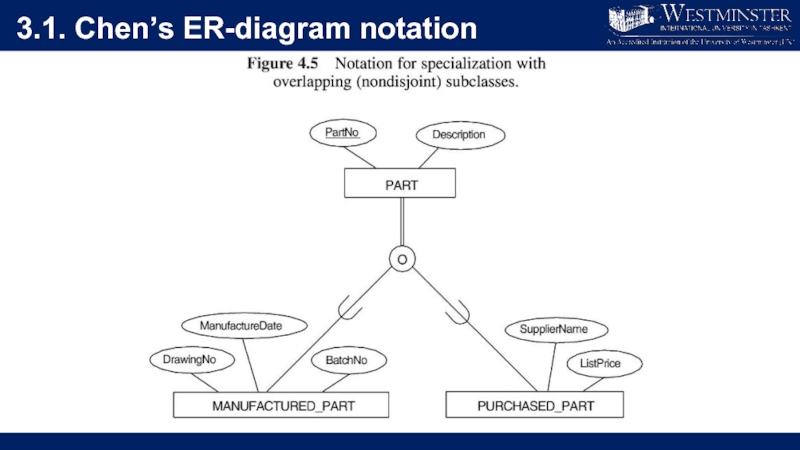
Disjoint constraint
Describes relationship between members of
the subclasses and indicates whether member of a superclass can be a member of one, or more than one, subclass.
May be disjoint (OR) or overlapping (AND)
May be disjoint (OR) or overlapping (AND)
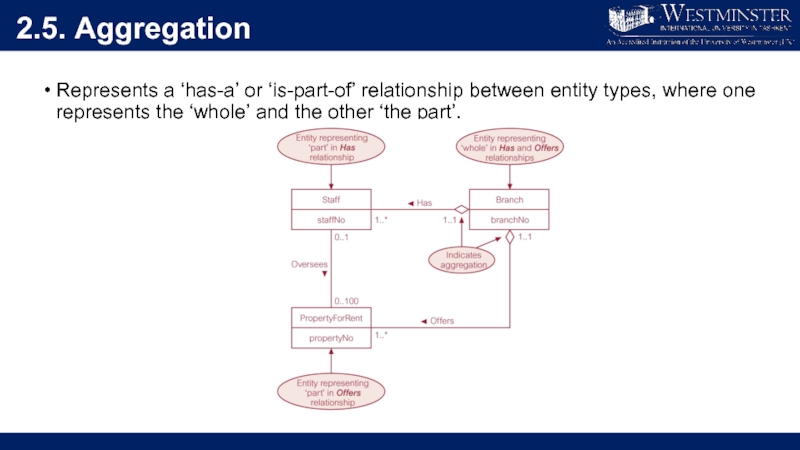
Слайд 282.5. Aggregation
Represents a ‘has-a’ or ‘is-part-of’ relationship between entity types, where
one represents the ‘whole’ and the other ‘the part’.
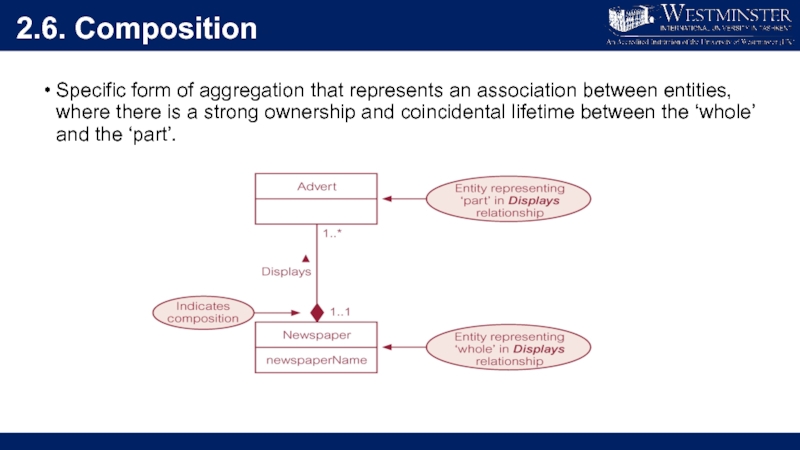
Слайд 292.6. Composition
Specific form of aggregation that represents an association between entities,
where there is a strong ownership and coincidental lifetime between the ‘whole’ and the ‘part’.
Слайд 30Agenda
1.Relationships with degree higher then 2
2.EER concepts specialisation/generalisation
3.Alternative ER/EER notation
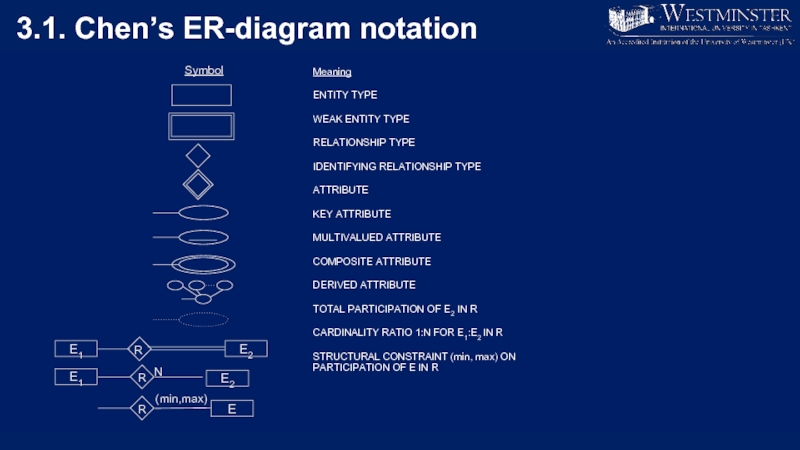
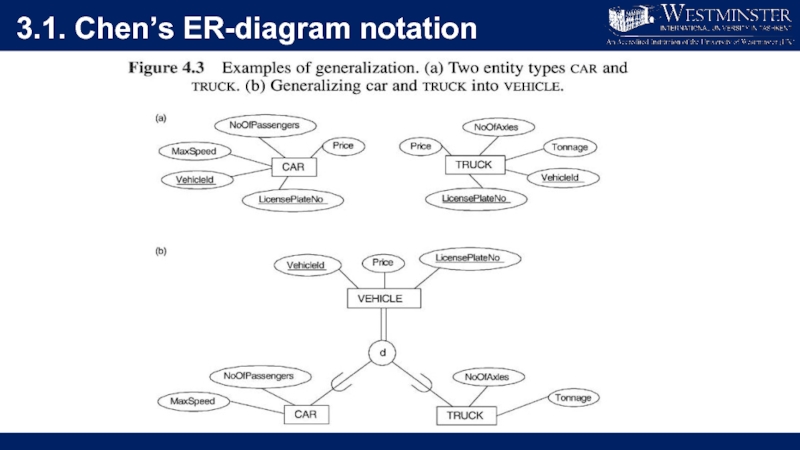
Слайд 313.1. Chen’s ER-diagram notation
Meaning
ENTITY TYPE
WEAK ENTITY TYPE
RELATIONSHIP TYPE
IDENTIFYING RELATIONSHIP TYPE
ATTRIBUTE
KEY ATTRIBUTE
MULTIVALUED
ATTRIBUTE
COMPOSITE ATTRIBUTE
DERIVED ATTRIBUTE
TOTAL PARTICIPATION OF E2 IN R
CARDINALITY RATIO 1:N FOR E1:E2 IN R
STRUCTURAL CONSTRAINT (min, max) ON PARTICIPATION OF E IN R
COMPOSITE ATTRIBUTE
DERIVED ATTRIBUTE
TOTAL PARTICIPATION OF E2 IN R
CARDINALITY RATIO 1:N FOR E1:E2 IN R
STRUCTURAL CONSTRAINT (min, max) ON PARTICIPATION OF E IN R
Symbol
R
E2
E1
R
E2
R
(min,max)
E
N