- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Defining and Configuring Neighbor Discovery презентация
Содержание
- 1. Defining and Configuring Neighbor Discovery
- 2. ICMPv6 ICMPv6 is similar to ICMPv4: Provides
- 3. MTU = 1300 Path MTU Discovery MTU
- 4. Maximum Transmission Unit IPv4 MTU >=
- 5. IPv6 over Data Link Layers IPv6 is
- 6. IPv6 over Ethernet IPv6 has a specific
- 7. 000000X0 02 00 90 27 00 90
- 8. Neighbor Discovery Neighbor discovery: Queries for duplicate
- 9. Solicited-Node Multicast Address Solicited-node address: Multicast address
- 10. FF02 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 33
- 11. Duplicate Address Detection ICMP type = 135
- 12. ICMP type = 136
- 13. Neighbor Discovery: Neighbor Solicitation (Cont.) Neighbor Advertisement
- 14. Neighbor Discovery: Autoconfiguration Autoconfiguration Stateless Uses neighbor discovery router advertisements Stateful Uses DHCPv6 service
- 15. Routers send periodic router advertisements to the
- 16. Neighbor Discovery Parameters Router advertisements: Default router
- 17. Neighbor Discovery Parameters (Cont.) Router advertisements: Default
- 18. Neighbor Discovery: Router Solicitations At boot time,
- 19. Stateless Autoconfiguration Router solicitations are sent by
- 20. Router advertisement packet definitions: ICMP type =
- 21. Value of Autoconfiguration IPv6 address autoconfiguration enables
- 22. ipv6 nd prefix | default
- 23. LAN2: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64 LAN1: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 Router Advertisement Ethernet1
- 24. LAN1: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 LAN2: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64 Ethernet0 Ethernet1 Ethernet0
- 25. LAN1: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 LAN2: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64 Ethernet0 Ethernet1 Ethernet0
- 26. Network Prefix: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 interface Ethernet0 ipv6
- 27. interface Ethernet0 ipv6 nd prefix
- 28. Summary ICMP messages are used for many
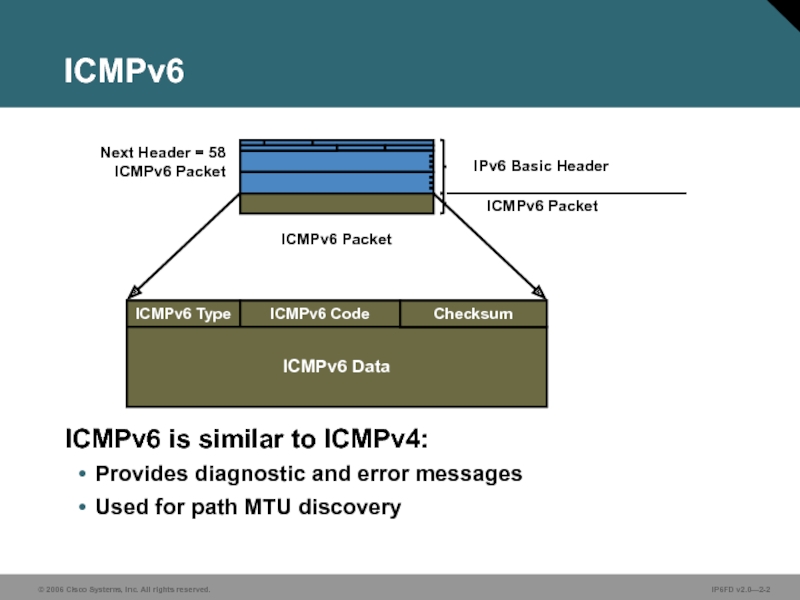
Слайд 2ICMPv6
ICMPv6 is similar to ICMPv4:
Provides diagnostic and error messages
Used for path
ICMPv6 Type
ICMPv6 Code
ICMPv6 Data
Checksum
IPv6 Basic Header
ICMPv6 Packet
Next Header = 58 ICMPv6 Packet
ICMPv6 Packet
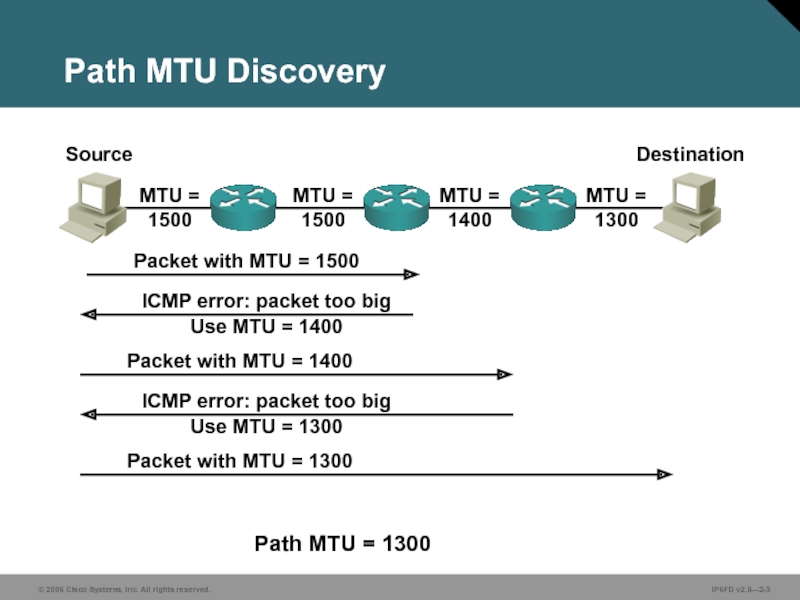
Слайд 3MTU = 1300
Path MTU Discovery
MTU = 1500
MTU = 1500
MTU = 1400
Packet
ICMP error: packet too big Use MTU = 1400
Packet with MTU = 1400
ICMP error: packet too big Use MTU = 1300
Packet with MTU = 1300
Path MTU = 1300
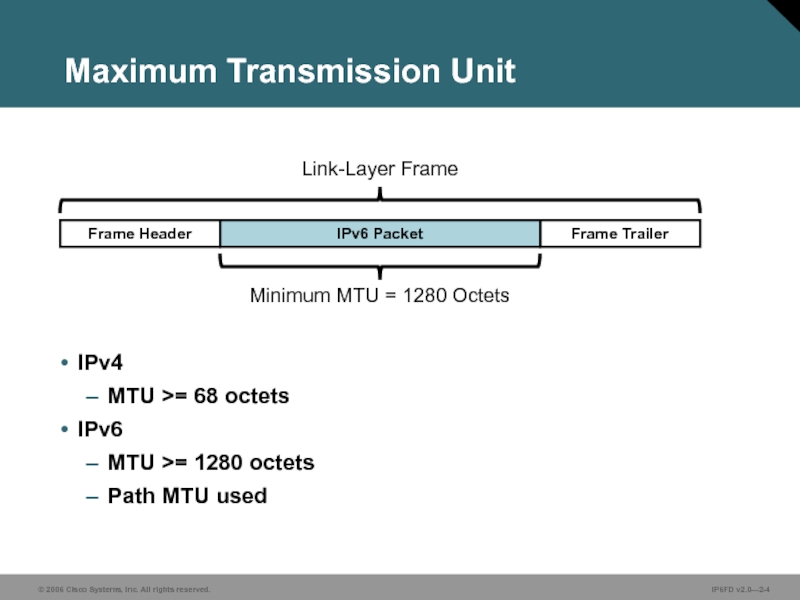
Слайд 4Maximum Transmission Unit
IPv4
MTU >= 68 octets
IPv6
MTU >= 1280 octets
Path
Frame Header
Frame Trailer
IPv6 Packet
Minimum MTU = 1280 Octets
Link-Layer Frame
Слайд 5IPv6 over Data Link Layers
IPv6 is defined for most data link
Ethernet
PPP
FDDI
Token Ring
HDLC
Nonbroadcast multiaccess
ATM
Frame Relay
IEEE 1394
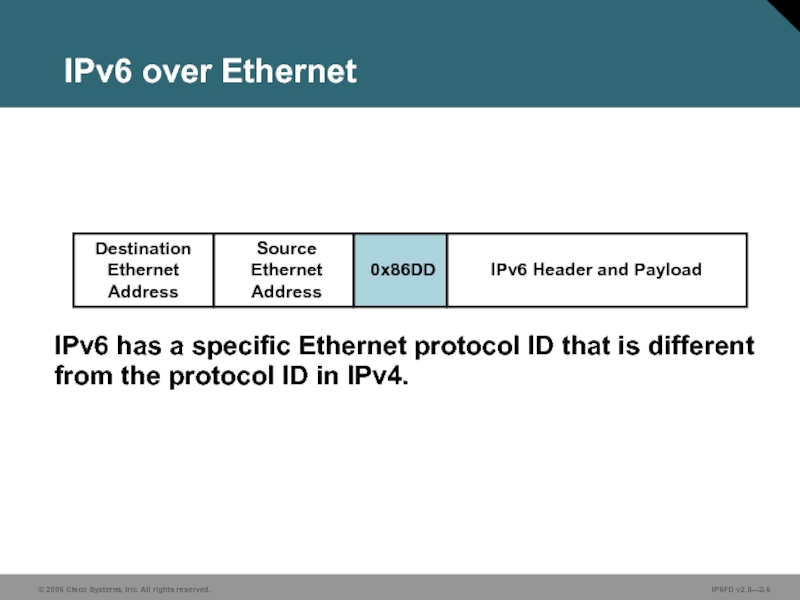
Слайд 6IPv6 over Ethernet
IPv6 has a specific Ethernet protocol ID that is
Destination Ethernet Address
IPv6 Header and Payload
0x86DD
Source Ethernet Address
Слайд 7000000X0
02
00
90
27
00
90
27
90
27
17
FC
0F
17
FC
0F
FF
FE
Modified EUI-64 Format
A modified EUI-64 address is formed by inserting "FFFE"
where X =
1 = universally unique
0 = locally unique
X = 1
Ethernet MAC Address (48 Bits)
64-Bit Version
U/L Bit
Modified EUI-64 Address
00
90
27
17
FC
0F
17
FC
0F
FF
FE
FF
FE
Слайд 8Neighbor Discovery
Neighbor discovery:
Queries for duplicate address detection
Determines the link layer address
Finds neighbor routers on link
Achieved by using ICMPv6 with IPv6 multicast
Слайд 9Solicited-Node Multicast Address
Solicited-node address:
Multicast address with a link-local scope
Formed by a
Prefix
0
Lower 24
Interface ID
FF02
FF
24 Bits
IPv6 Address
Solicited-Node Multicast Address
0001
Слайд 10FF02
0000
0000
0000
0000
0001
33
33
FF17
FC0F
17
FC
0F
FF
Multicast Mapping over Ethernet
IPv6 Solicited-Node Multicast Address
Corresponding Ethernet Address
Multicast
2001
0DB8
1001
000F
02C0
10FF
FC0F
IPv6 Address
FE
17
Слайд 11Duplicate Address Detection
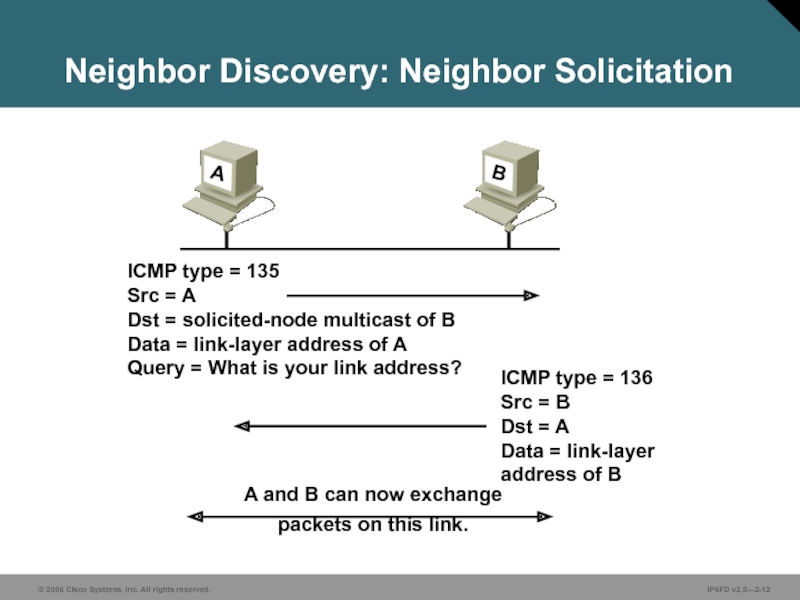
ICMP type = 135
DAD uses neighbor solicitation to verify the existence of an address to be configured.
Слайд 12ICMP type = 136
ICMP type = 135 Src = A Dst = solicited-node multicast of B Data = link-layer address of A Query = What is your link address?
A and B can now exchange packets on this link.
Neighbor Discovery: Neighbor Solicitation
Слайд 13Neighbor Discovery: Neighbor Solicitation (Cont.)
Neighbor Advertisement Message
R: router flag, indicates sender
S: solicited flag, indicates message sent in response to a neighbor solicitation
O: override flag, indicates advertisement should override existing neighbor cache entry
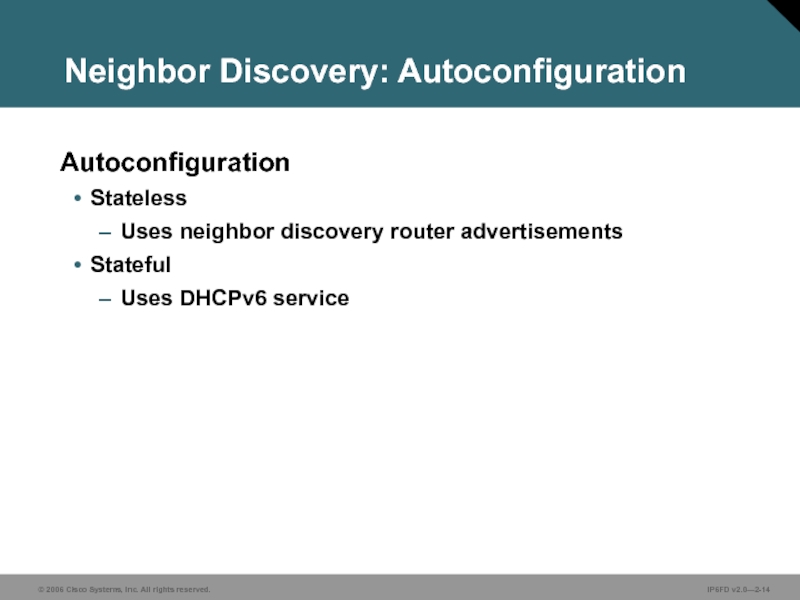
Слайд 14Neighbor Discovery: Autoconfiguration
Autoconfiguration
Stateless
Uses neighbor discovery router advertisements
Stateful
Uses DHCPv6 service
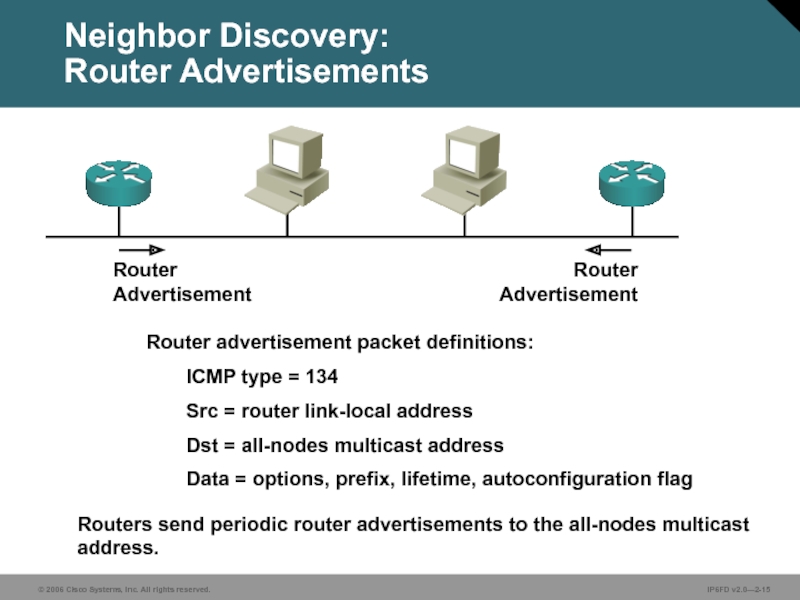
Слайд 15Routers send periodic router advertisements to the all-nodes multicast address.
Router
ICMP type = 134
Src = router link-local address
Dst = all-nodes multicast address
Data = options, prefix, lifetime, autoconfiguration flag
Router
Advertisement
Neighbor Discovery:
Router Advertisements
Router
Advertisement
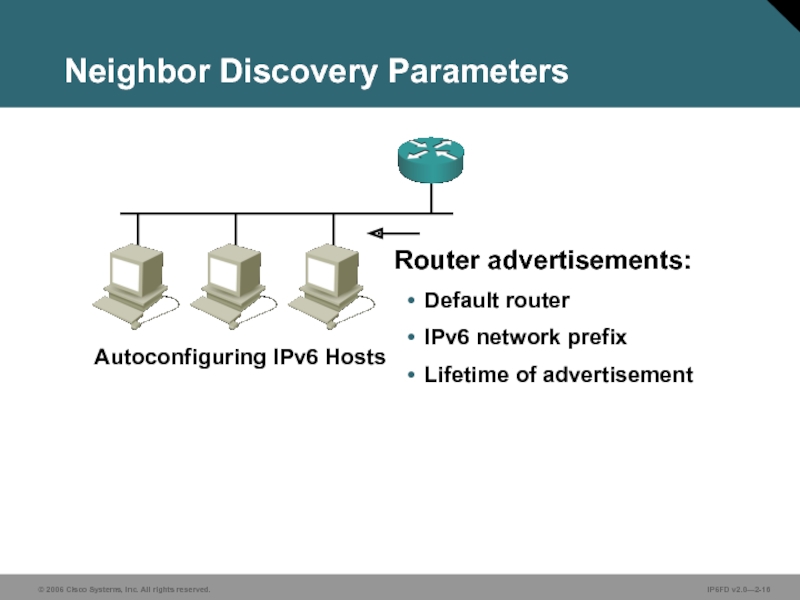
Слайд 16Neighbor Discovery Parameters
Router advertisements:
Default router
IPv6 network prefix
Lifetime of advertisement
Autoconfiguring IPv6 Hosts
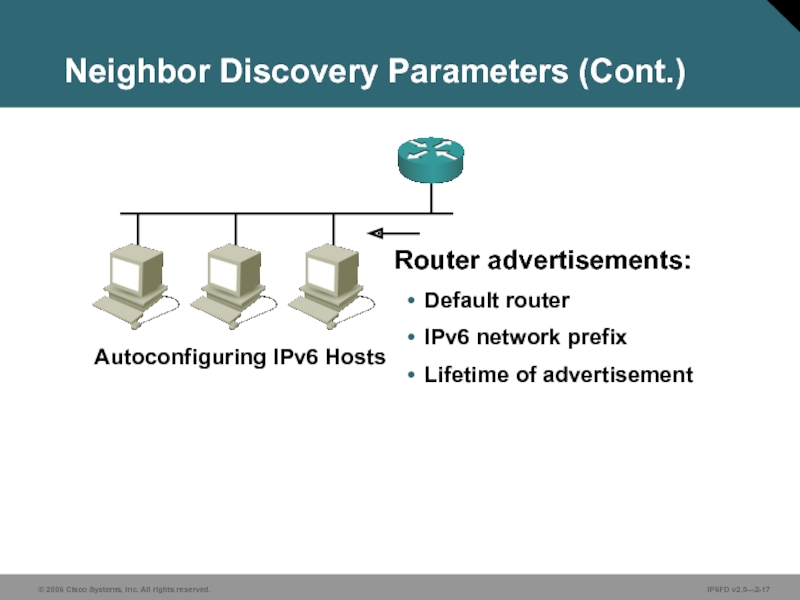
Слайд 17Neighbor Discovery Parameters (Cont.)
Router advertisements:
Default router
IPv6 network prefix
Lifetime of advertisement
Autoconfiguring IPv6
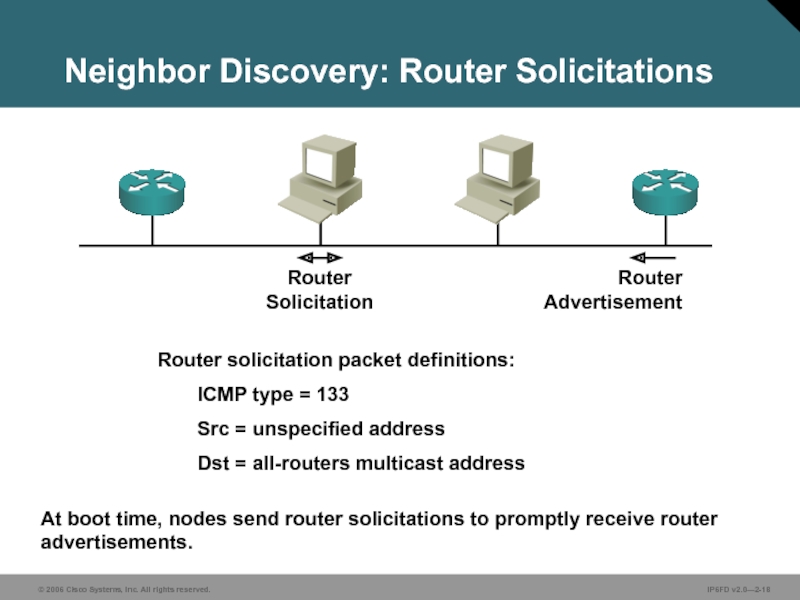
Слайд 18Neighbor Discovery: Router Solicitations
At boot time, nodes send router solicitations to
Router solicitation packet definitions:
ICMP type = 133
Src = unspecified address
Dst = all-routers multicast address
Router
Advertisement
Router
Solicitation
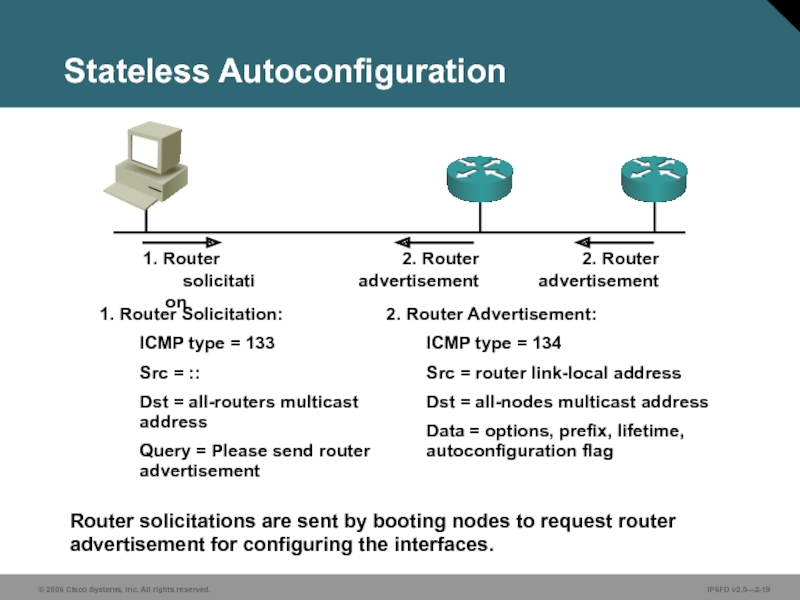
Слайд 19Stateless Autoconfiguration
Router solicitations are sent by booting nodes to request router
1. Router Solicitation:
ICMP type = 133
Src = ::
Dst = all-routers multicast
address
Query = Please send router advertisement
2. Router
advertisement
1. Router
solicitation
2. Router Advertisement:
ICMP type = 134
Src = router link-local address
Dst = all-nodes multicast address
Data = options, prefix, lifetime, autoconfiguration flag
2. Router
advertisement
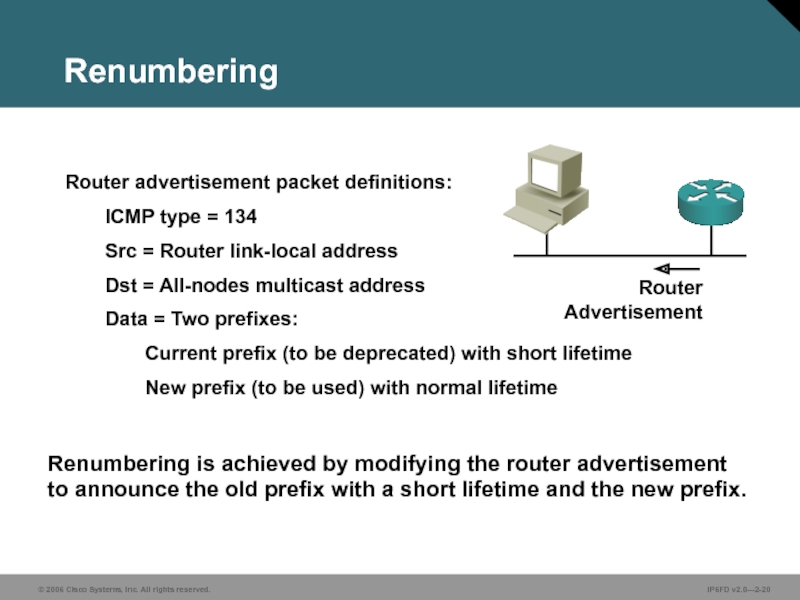
Слайд 20Router advertisement packet definitions:
ICMP type = 134
Src = Router link-local address
Dst
Data = Two prefixes:
Current prefix (to be deprecated) with short lifetime
New prefix (to be used) with normal lifetime
Renumbering
Renumbering is achieved by modifying the router advertisement to announce the old prefix with a short lifetime and the new prefix.
Router
Advertisement
Слайд 21Value of Autoconfiguration
IPv6 address autoconfiguration enables “plug-and-play.”
Nodes may be deployed without
Mobile devices (phones, PDAs, autos)
Home electronics (TVs, DVRs, appliances)
Field telemetry (oil pipeline gauges)
Autoconfiguration enables massive deployment (millions) of IPv6 nodes.
Слайд 22ipv6 nd prefix | default
[at
[off-link] [no-autoconfig] ]
router(config-if)#
Used to modify prefix advertisement parameters on an interface from their default values.
Cisco IOS Neighbor Discovery Command Syntax
Слайд 23LAN2: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64
LAN1: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64
Router Advertisement
Ethernet1
Ethernet0
Ethernet0
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:c18:1::2/64
ipv6 nd prefix
interface Ethernet1
ipv6 address 2001:db8:c18:2::1/64
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:2::/64 2000 1800
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 address 2001:db8:c18:1::1/64
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 2000 1800
Router2
Router1
Cisco IOS Command for Overriding
the Neighbor Discovery Defaults
Router Advertisement
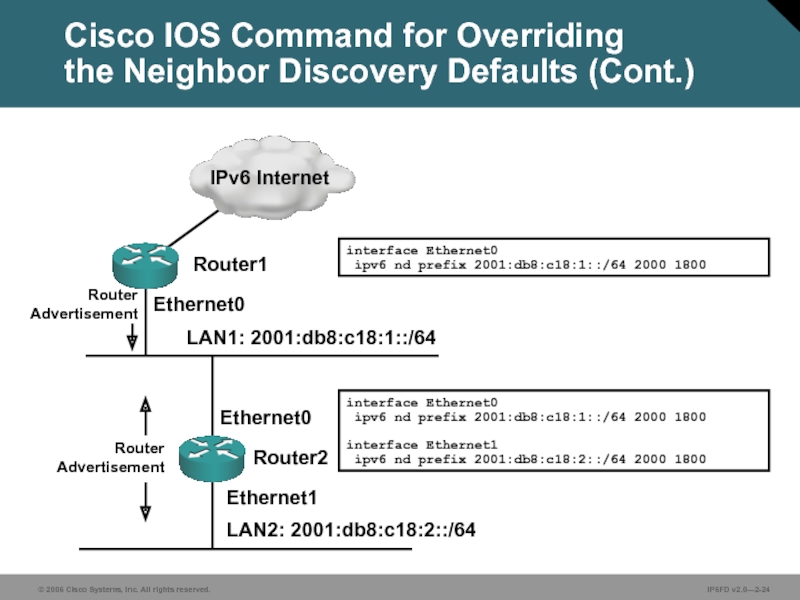
Слайд 24LAN1: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64
LAN2: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64
Ethernet0
Ethernet1
Ethernet0
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 2000 1800
interface Ethernet1
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 2000 1800
Router2
Router1
Cisco IOS Command for Overriding
the Neighbor Discovery Defaults (Cont.)
Router Advertisement
Router Advertisement
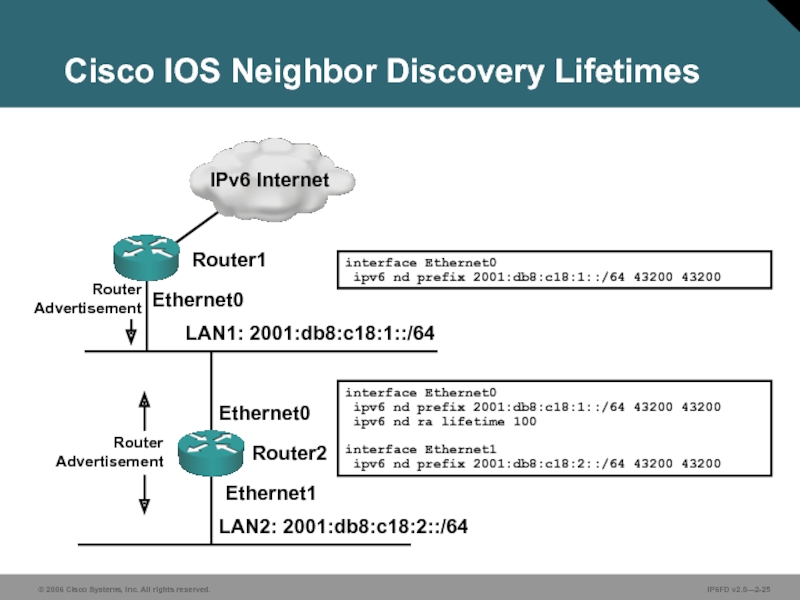
Слайд 25LAN1: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64
LAN2: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64
Ethernet0
Ethernet1
Ethernet0
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 43200 43200
ipv6
interface Ethernet1
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:2::/64 43200 43200
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 43200 43200
Router2
Router1
Cisco IOS Neighbor Discovery Lifetimes
Router Advertisement
Router Advertisement
Слайд 26Network Prefix: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 43200 43200
Host Configuration:
Autoconfiguring
preferred address 2001:db8:c18:1:260:8ff:fede:8fbe
Router Configuration before Renumbering:
Router Advertisements
Cisco IOS Network Prefix Renumbering Scenario
Слайд 27
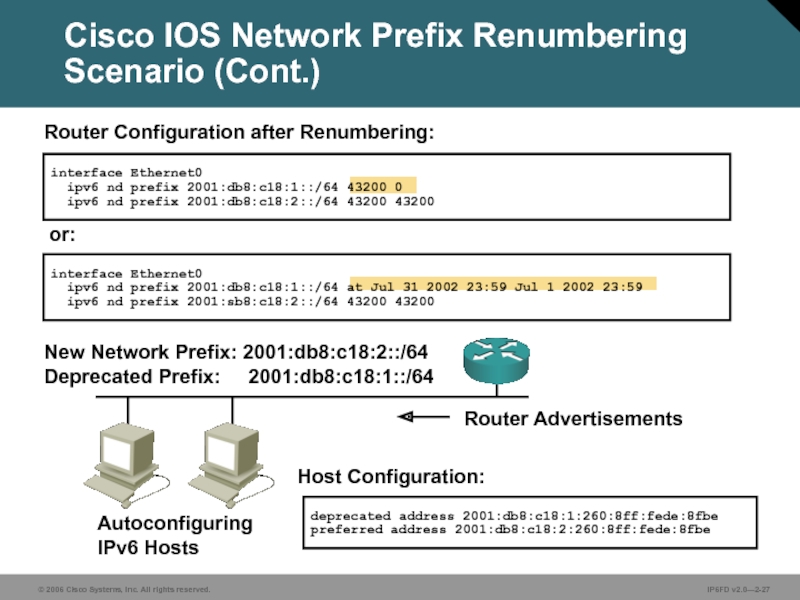
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 43200 0
ipv6 nd
New Network Prefix: 2001:db8:c18:2::/64
Deprecated Prefix: 2001:db8:c18:1::/64
Host Configuration:
Autoconfiguring
IPv6 Hosts
deprecated address 2001:db8:c18:1:260:8ff:fede:8fbe
preferred address 2001:db8:c18:2:260:8ff:fede:8fbe
Router Configuration after Renumbering:
Router Advertisements
interface Ethernet0
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:db8:c18:1::/64 at Jul 31 2002 23:59 Jul 1 2002 23:59
ipv6 nd prefix 2001:sb8:c18:2::/64 43200 43200
Cisco IOS Network Prefix Renumbering Scenario (Cont.)
or:
Слайд 28Summary
ICMP messages are used for many IPv6 functions, including path MTU
Path MTU is performed by nodes in an effort to determine the largest packet size they can send to a given destination. It is based on a process of sending large packets and listening for ICMPv6 error messages.
Neighbor discovery is a critical process that allows neighbors to determine the link-layer address associated with a given IPv6 address. It also allows hosts to receive prefix information to configure a global-scope address and find the default router.
Before a node can use an address, it must test it for uniqueness on the link. DAD is a process by which a node with a "tentative" address that it would like to use determines if that address is already in use.
Autoconfiguration provides a type of network “plug-and-play,” easily supporting millions of transient nodes and enabling a network environment with support for mobile phones, field sensors, and home appliances.
Cisco routers are IPv6-ready and are configured for IPv6 functions on a global and per-interface basis, depending on the function being enabled.







![ipv6 nd prefix | default [ [ ] |](/img/tmb/3/297830/c417e1febded15c5ab11c0a9fef0394b-800x.jpg)