- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Что такое Grid? презентация
Содержание
- 1. Что такое Grid?
- 2. План выступления Ранние определения GRID Понятие
- 3. „We will probably see
- 4. Идеалистическое представление о GRID
- 5. Скоординированное разделение ресурсов - Виртуальная Организация
- 6. The LHC Computing Model Tier2 Centre
- 7. The LHC Computing Model Tier2 SINP
- 8. Gilder’s Law (32X in 4 yrs) Storage
- 9. Перспективы развития ресурсов для GRID С 1986
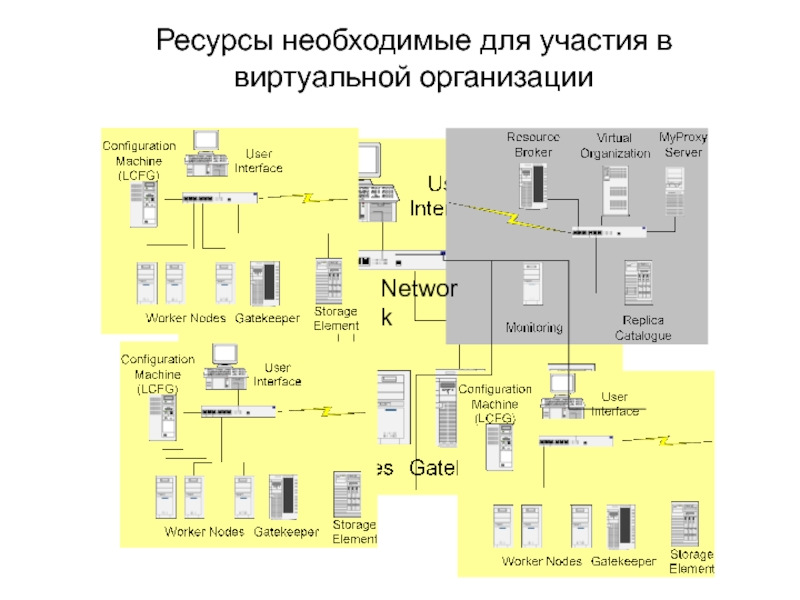
- 10. Network Ресурсы необходимые для участия в виртуальной организации
- 11. Упрощенное взаимодействие сервисов/ Серверов )
- 12. The LHC Computing Model Tier2 SINP
- 13. EGEE: Partners Leverage national resources in a
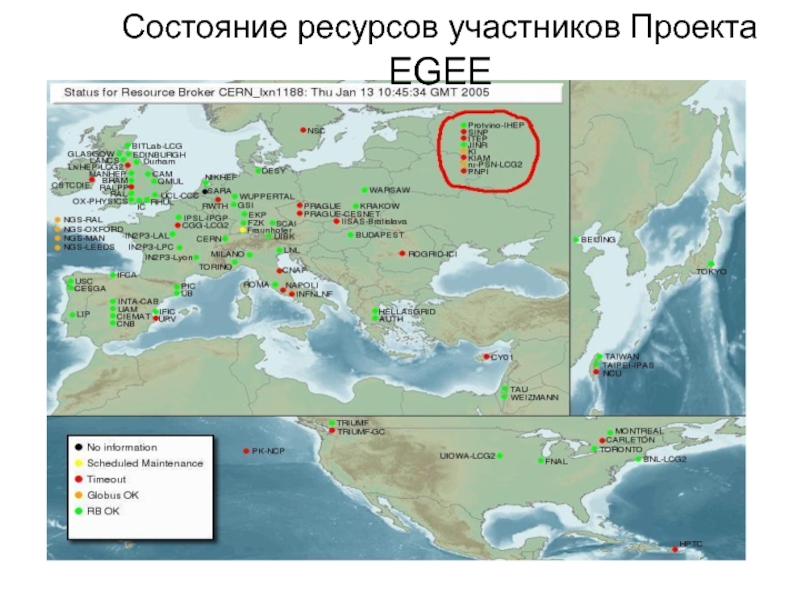
- 14. Состояние ресурсов участников Проекта EGEE
- 15. EGEE Activities JRA1: Middleware Engineering and Integration
- 16. EGEE activities’ relative sizes “Networking” (NA1-5): 30%
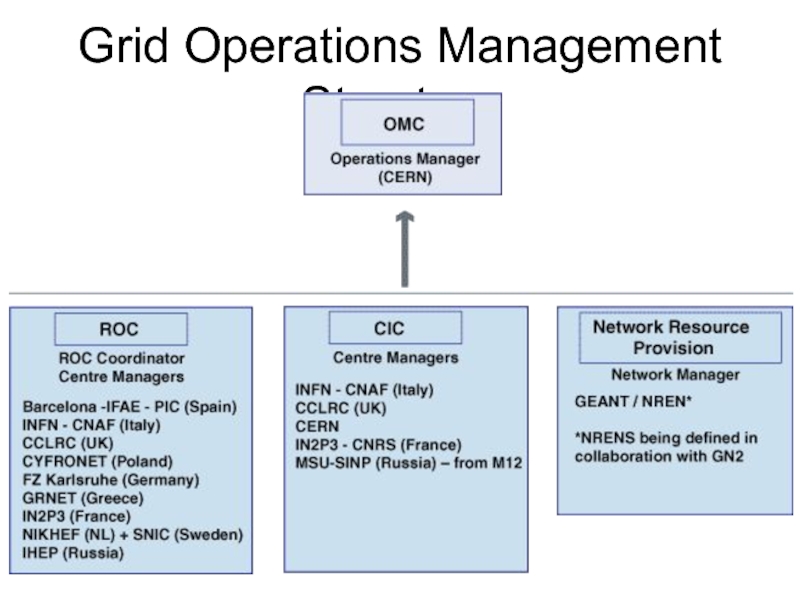
- 17. Grid Operations Management Structure
- 18. Активности России в EGEE
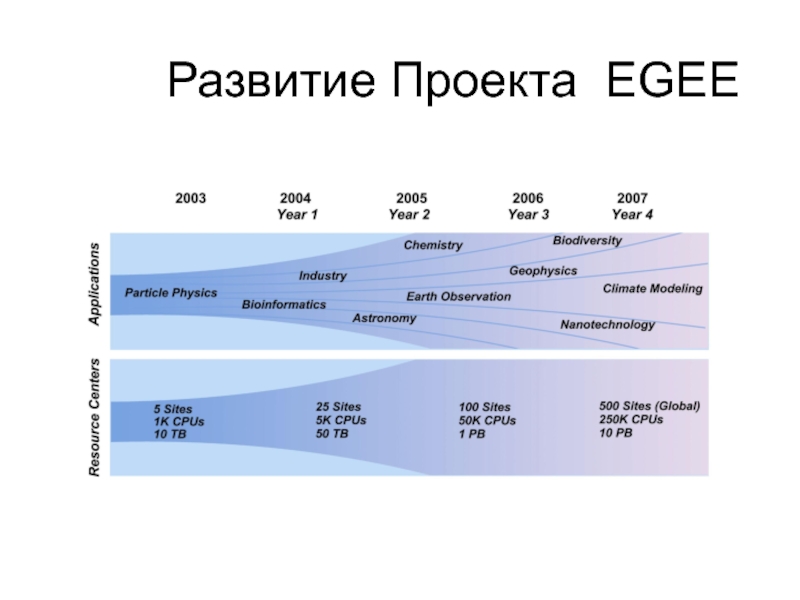
- 19. Развитие Проекта EGEE
- 20. Developing Grid Standards Increased functionality, standardization Custom
- 21. Полезные ссылки: European DataGrid (EDG)
- 22. СПАСИБО ЗА ВНИМАНИЕ. ВАШИ ВОПРОСЫ ?
Слайд 2 План выступления
Ранние определения GRID
Понятие о Виртуальной Организации
Область зарождения и применения
Перспективы для развития
Минимальная архитектура для участия в GRID
Проект EGEE и участие в нем России
Слайд 3
„We will probably see the spread of ´computer utilities‘,
electric and telephone utilities, will service individual homes and offices
across the country.“ Leonard Kleinrock (1969)
Мы, вероятно, увидим распространение «компьютерных услуг», которые, подобно электричеству и телефону, придут в дома и офисы по всей стране.
„A computational grid is a hardware and software infrastructure that
provides dependable, consistent, pervasive, and inexpensive access to
high-end computational capabilities.“ I. Foster, C. Kesselmann (1998), “The Grid: Blueprint for a New Computing Infrastructures”.
Вычислительный Grid - это аппаратно-программная инфраструктура, которая обеспечивает надежный, устойчивый, повсеместный и недорогой доступ к высокопроизводительным вычислительным ресурсам.
Первые определения GRID
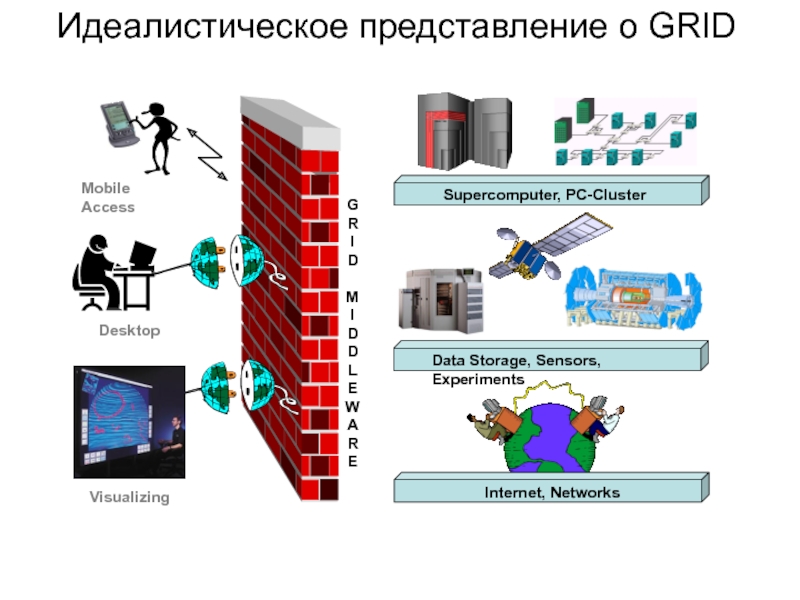
Слайд 4 Идеалистическое представление о GRID
G
R
I
D
M
I
D
D
L
E
W
A
R
E
Visualizing
Supercomputer, PC-Cluster
Data Storage, Sensors,
Internet, Networks
Desktop
Mobile Access
Слайд 5Скоординированное разделение ресурсов -
Виртуальная Организация
„The sharing that we are
Разделение (ресурсов), о котором мы говорим, - это не просто обмен файлами, а еще и прямой доступ к компьютерам, программному обеспечению, данным и другим ресурсам, как это требуется для совместного решения задач и стратегий выделения ресурсов. принятых в промышленности, науке и инженерии. Разделение должно тщательно контролироваться поставщиками и потребителями ресурсов, быть ясно и тщательно определено, что распределяется, кому разрешается пользоваться и на каких условиях. Отдельные пользователи и/или институты, подчиняющиеся таким правилам, образуют то, что мы называем Виртуальной Организацией.
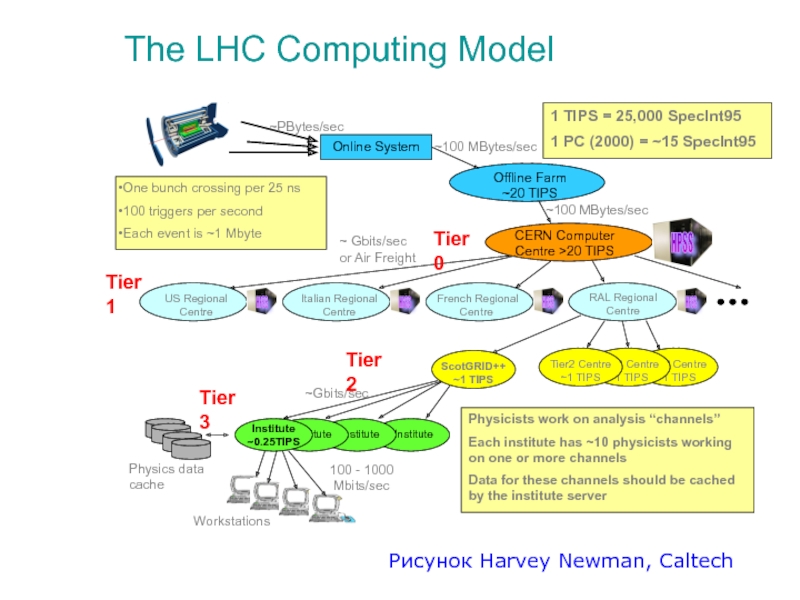
Слайд 6The LHC Computing Model
Tier2 Centre ~1 TIPS
Online System
Offline Farm
~20 TIPS
CERN Computer
RAL Regional Centre
US Regional Centre
French Regional Centre
Italian Regional Centre
Institute
Institute
Institute
Institute ~0.25TIPS
Workstations
~100 MBytes/sec
~100 MBytes/sec
100 - 1000 Mbits/sec
HPSS
HPSS
One bunch crossing per 25 ns
100 triggers per second
Each event is ~1 Mbyte
Physicists work on analysis “channels”
Each institute has ~10 physicists working on one or more channels
Data for these channels should be cached by the institute server
Physics data cache
~PBytes/sec
~ Gbits/sec or Air Freight
HPSS
HPSS
HPSS
Tier2 Centre ~1 TIPS
Tier2 Centre ~1 TIPS
~Gbits/sec
Tier 0
Tier 1
Tier 3
1 TIPS = 25,000 SpecInt95
1 PC (2000) = ~15 SpecInt95
Tier 2
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
Рисунок Harvey Newman, Caltech
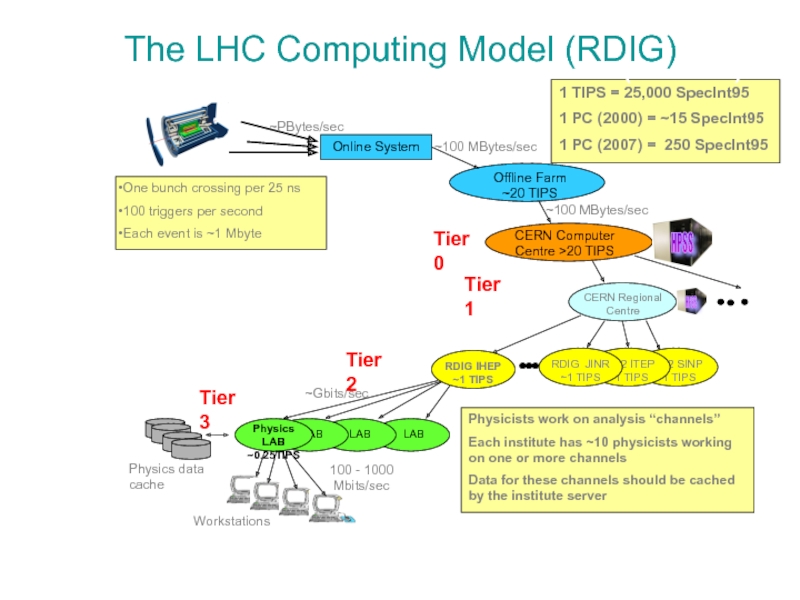
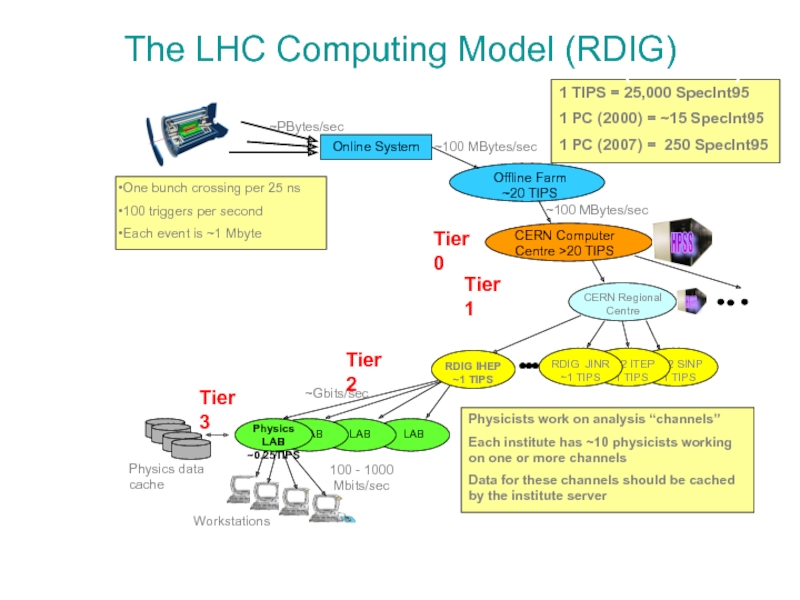
Слайд 7The LHC Computing Model
Tier2 SINP ~1 TIPS
Online System
Offline Farm
~20 TIPS
CERN Computer
CERN Regional Centre
LAB
LAB
LAB
Physics LAB ~0.25TIPS
Workstations
~100 MBytes/sec
~100 MBytes/sec
100 - 1000 Mbits/sec
HPSS
HPSS
One bunch crossing per 25 ns
100 triggers per second
Each event is ~1 Mbyte
Physicists work on analysis “channels”
Each institute has ~10 physicists working on one or more channels
Data for these channels should be cached by the institute server
Physics data cache
~PBytes/sec
Tier2 ITEP ~1 TIPS
RDIG JINR ~1 TIPS
~Gbits/sec
Tier 0
Tier 3
1 TIPS = 25,000 SpecInt95
1 PC (2000) = ~15 SpecInt95
1 PC (2007) = 250 SpecInt95
Tier 2
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model (RDIG)
The LHC Computing Model (RDIG)
Tier 1
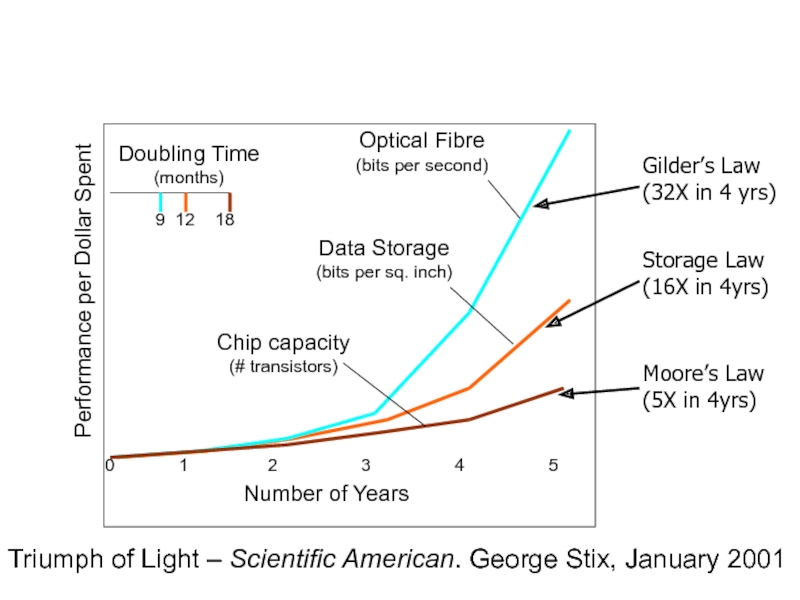
Слайд 8Gilder’s Law
(32X in 4 yrs)
Storage Law
(16X in 4yrs)
Moore’s Law
(5X in
Triumph of Light – Scientific American. George Stix, January 2001
Performance per Dollar Spent
Optical Fibre
(bits per second)
Chip capacity
(# transistors)
Data Storage
(bits per sq. inch)
Number of Years
0 1 2 3 4 5
Doubling Time
(months)
Слайд 9Перспективы развития ресурсов для GRID
С 1986 по 2000 годы производительность вычислений
Сейчас в мире около 500 млн. РС. Из них не более 30% имеют выход в Интернет
Средний коэффициент использования вычислительного ресурса не превышает 5%!
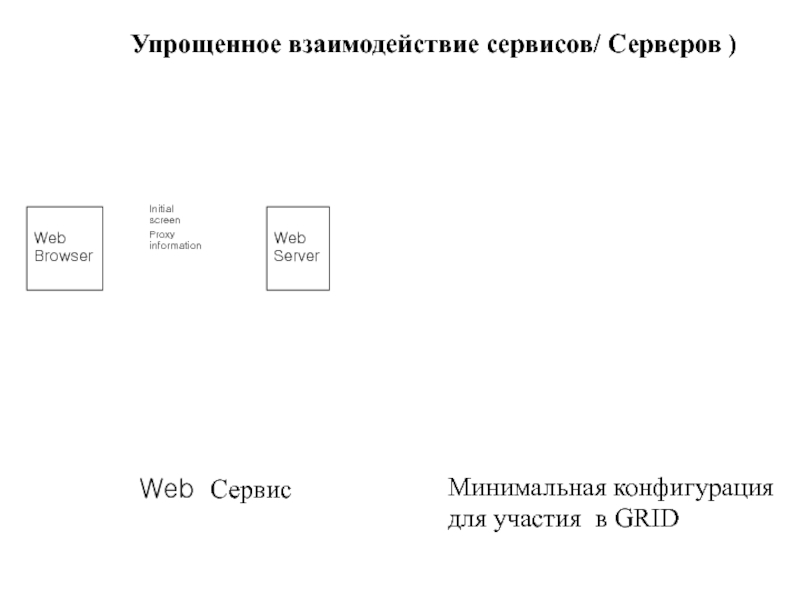
Слайд 11Упрощенное взаимодействие сервисов/ Серверов )
Web
Browser
Web
Server
Web Сервис
Минимальная конфигурация
для участия в
Initial screen
Proxy information
Слайд 12The LHC Computing Model
Tier2 SINP ~1 TIPS
Online System
Offline Farm
~20 TIPS
CERN Computer
CERN Regional Centre
LAB
LAB
LAB
Physics LAB ~0.25TIPS
Workstations
~100 MBytes/sec
~100 MBytes/sec
100 - 1000 Mbits/sec
HPSS
HPSS
One bunch crossing per 25 ns
100 triggers per second
Each event is ~1 Mbyte
Physicists work on analysis “channels”
Each institute has ~10 physicists working on one or more channels
Data for these channels should be cached by the institute server
Physics data cache
~PBytes/sec
Tier2 ITEP ~1 TIPS
RDIG JINR ~1 TIPS
~Gbits/sec
Tier 0
Tier 3
1 TIPS = 25,000 SpecInt95
1 PC (2000) = ~15 SpecInt95
1 PC (2007) = 250 SpecInt95
Tier 2
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model
The LHC Computing Model (RDIG)
The LHC Computing Model (RDIG)
Tier 1
Слайд 13EGEE: Partners
Leverage national resources in a more effective way for broader
70 leading institutions in 27 countries organised into regional federations
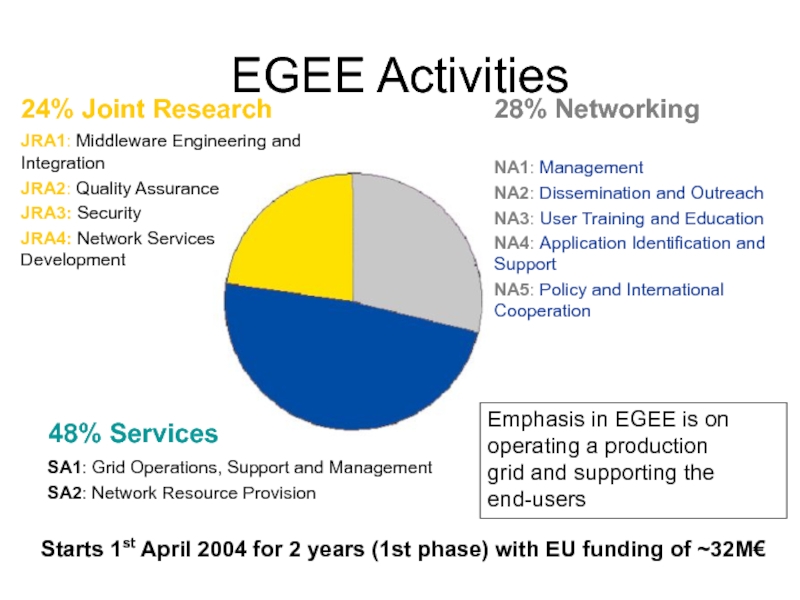
Слайд 15EGEE Activities
JRA1: Middleware Engineering and Integration
JRA2: Quality Assurance
JRA3: Security
JRA4: Network Services
SA1: Grid Operations, Support and Management
SA2: Network Resource Provision
NA1: Management
NA2: Dissemination and Outreach
NA3: User Training and Education
NA4: Application Identification and Support
NA5: Policy and International Cooperation
24% Joint Research
28% Networking
48% Services
Emphasis in EGEE is on operating a production
grid and supporting the end-users
Starts 1st April 2004 for 2 years (1st phase) with EU funding of ~32M€
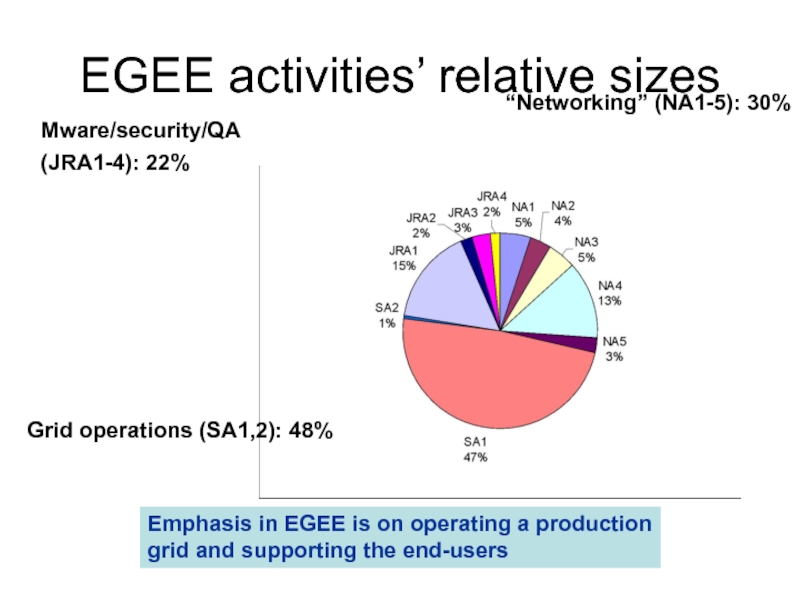
Слайд 16EGEE activities’ relative sizes
“Networking” (NA1-5): 30%
Emphasis in EGEE is on operating
grid and supporting the end-users
Mware/security/QA
(JRA1-4): 22%
Grid operations (SA1,2): 48%
Слайд 18Активности России в EGEE (Общая координация -
NA2 - Dissemination and Outreach (Руководит Т. Стриж, ОИЯИ)
Operate the dissemination Web site, support mail lists and Web base collaborative tools, organize presentations, visits, 2 project conferences and showcases per year, publication of dissemination material.
NA3 – User Training and Induction (Руководит Е. Слабоспицкая, ИФВЭ)
Produce training and course material. Deliver on-site courses and support distributed courses in the project.
NA4 – Application Identification and support (Рук. Е. Тихоненко, ОИЯИ)
Support HEP and Bio pilot applications. Identify early users. Introduction of new user communities. Definition of common application interfaces and tools. Creation of an Industry Forum.
SA1 – European Grid Support, Operation and Management (Руководят А. Крюков, НИИЯФ МГУ и Ю. Лазин, ИФВЭ)
Core infrastructure services. Grid monitoring and control. Middleware deployment and resource induction. Resource and user support. Grid management.
SA2 – Network Resource Provision (Рук. В.Добрецов, КИ)
Definition in collaboration with RN Geant,...
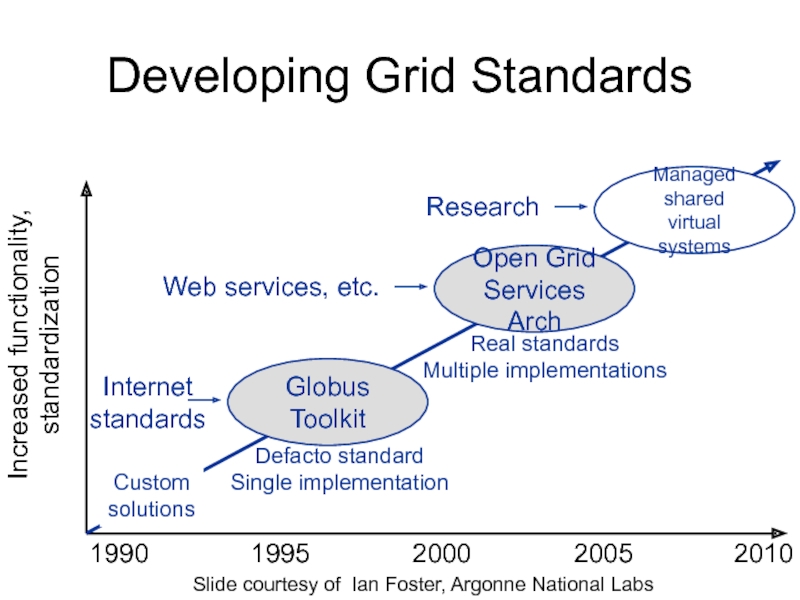
Слайд 20Developing Grid Standards
Increased functionality,
standardization
Custom
solutions
1990
1995
2000
2005
2010
Slide courtesy of Ian Foster, Argonne National Labs
Слайд 21Полезные ссылки:
European DataGrid (EDG) www.edg.org
LHC
GridLab www.gridlab.org
EGEE public.eu-egee.org
RDIG www.egee-rdig.ru
GRIDCLUB www.gridclub.ru
GRID в ИФВЭ www.ihep.su/egee