- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Building Your First Android App Using Xamarin презентация
Содержание
- 2. Building your first Android app using Xamarin Gill Cleeren - @gillcleeren
- 3. Building your first Android app using Xamarin Gill Cleeren @gillcleeren
- 4. Hi, I’m Gill! Gill Cleeren MVP
- 5. I’m a Pluralsight author! Courses on Windows 8, social and HTML5 http://gicl.me/mypscourses
- 6. Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android
- 7. Targets of this talk Understanding the fundamentals
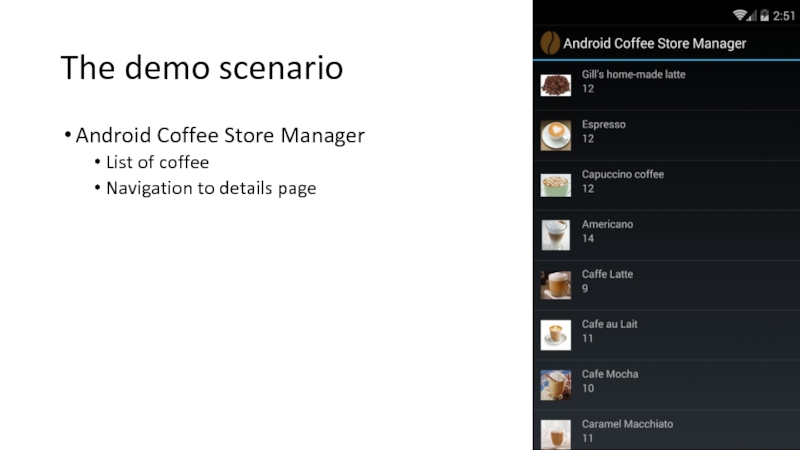
- 8. The demo scenario Android Coffee Store Manager List of coffee Navigation to details page
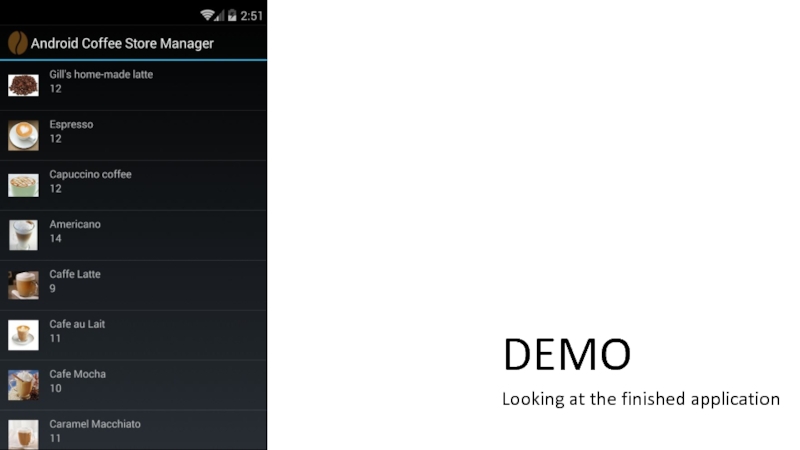
- 9. DEMO Looking at the finished application
- 10. Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android
- 11. Hello Xamarin Xamarin enables developers to reach
- 12. Advantages of Xamarin Full control Familiar development
- 13. Disadvantages of Xamarin You need a licence
- 14. Write Everything in C#
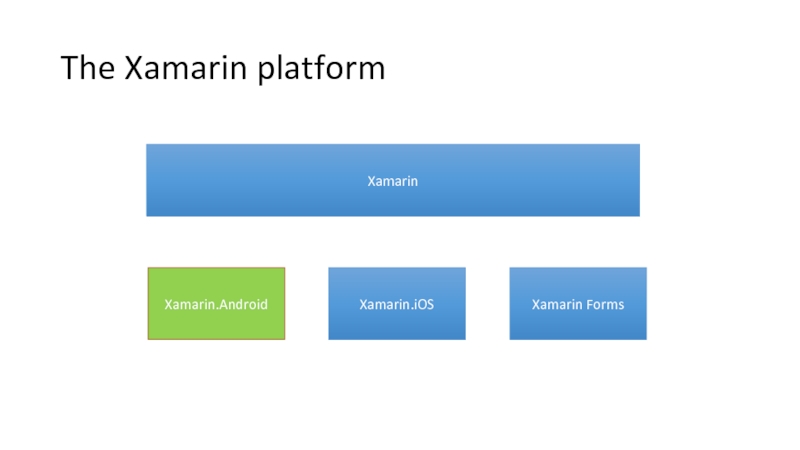
- 15. The Xamarin platform Xamarin Xamarin.Android Xamarin.iOS Xamarin Forms
- 16. Xamarin.Android exposes many extra device types
- 17. Xamarin.Android Anything you can do in Java/Android
- 18. How Xamarin works on Android Mono VM
- 19. A word on code-sharing Xamarin brings development
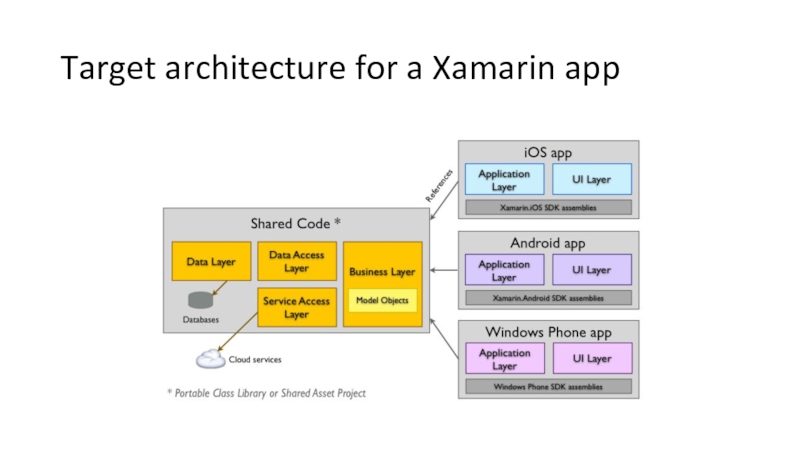
- 20. Target architecture for a Xamarin app
- 21. Preparing for Android development
- 22. What you need for Xamarin.Android development Xamarin
- 23. Installing Xamarin.Android
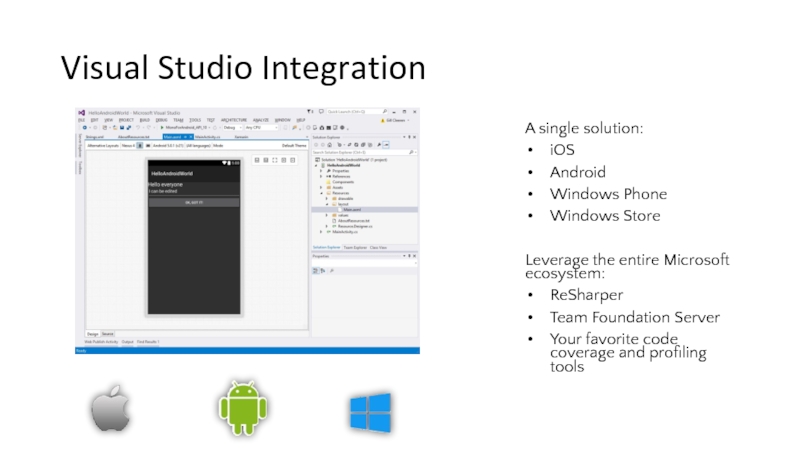
- 24. Visual Studio Integration A single solution: iOS
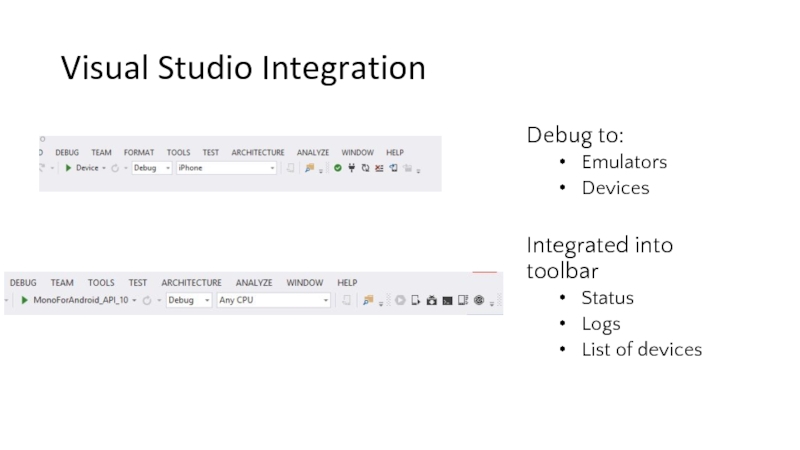
- 25. Visual Studio Integration Debug to: Emulators Devices
- 26. Alternative: Xamarin Studio Optimized for cross-platform mobile
- 27. A word on emulators Setup will install
- 28. Alternatives for the default emulators Possible options
- 29. Developing with a device 3 steps Enable
- 30. Enable device debugging Tap the Build number 7 times to reveal developer options
- 31. Install USB drivers
- 32. Xamarin setup DEMO A quick look at the development setup
- 33. Xamarin.Android fundamentals
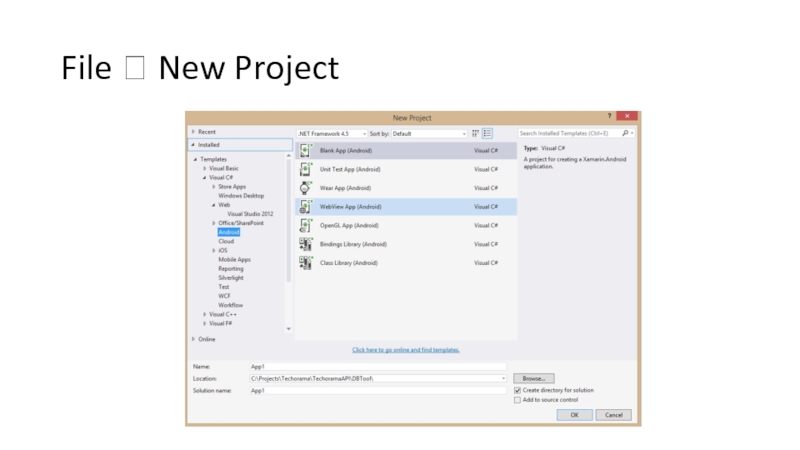
- 34. File ? New Project
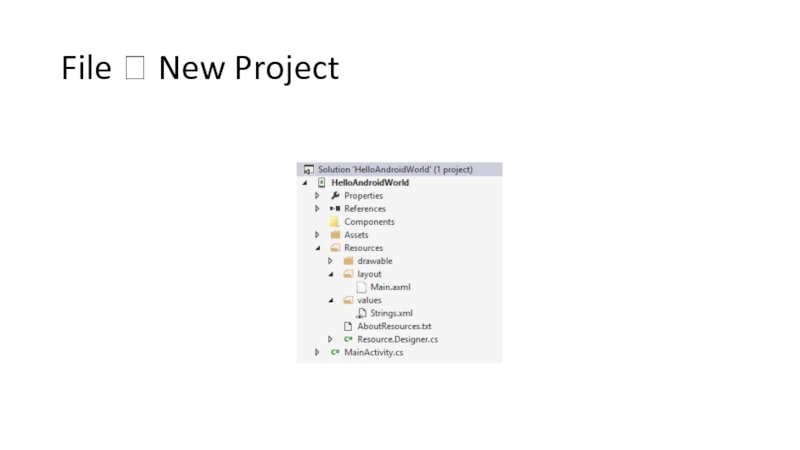
- 35. File ? New Project
- 36. Fundamental #1: Activities Apps are collections of
- 37. Fundamental #1: Activities When opening an application,
- 38. Fundamental #1: Activities One activity needs to
- 39. Fundamental #1: Activities Often, the first activity
- 40. Activity lifecycle
- 41. Activity lifecycle We can of course override
- 42. Activity lifecycle in effect
- 43. Fundamental #2: Views The layout of the
- 44. The designer for Xamarin.Android views
- 45. The designer for Xamarin.Android views
- 46. View code
- 47. Connecting and accessing controls from code Linking
- 48. Connecting and accessing controls from code We
- 49. Connecting and accessing controls from code Once
- 50. Fundamental #3: Application manifest An Android app
- 52. DEMO Creating our first Android application together!
- 53. Navigation and lists
- 54. Fundamental #4: ListViews and adapters Used very
- 55. Fundamental #4: ListViews and adapters
- 56. Important classes ListView ListActivity BaseAdapter ArrayAdapter & ArrayAdapter
- 57. ListActivity and the built-in ArrayAdapter [Activity(Label
- 58. Implementing your own adapter In most cases,
- 59. Using row views Row views need to
- 60. public class CoffeeAdapter : BaseAdapter { List items; Activity context;
- 61. Fast scrolling on the ListView Fast Scrolling
- 62. Sectioning the ListView We need to implement
- 63. Handling row clicks To handle row clicks,
- 64. DEMO Adding a ListView and an adapter
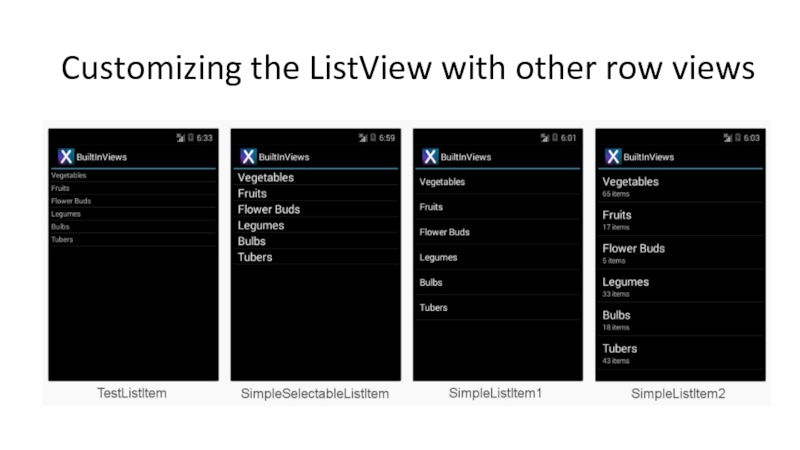
- 65. Customizing the ListView with other row views
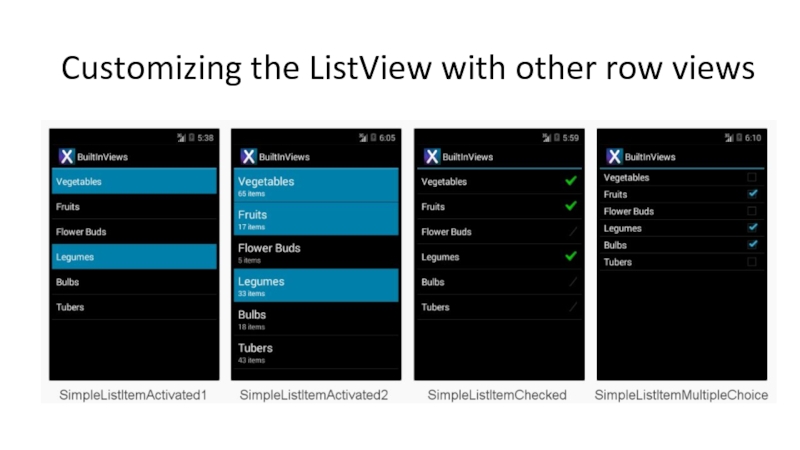
- 66. Customizing the ListView with other row views
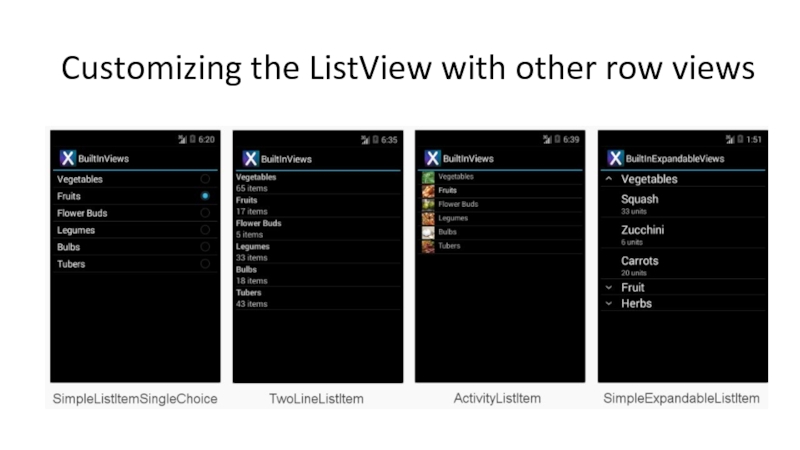
- 67. Customizing the ListView with other row views
- 68. DEMO Using the built-in row views
- 69. Creating your own row views Custom row
- 70. Creating your own row view
- 71. Using your custom row view public override View GetView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
- 72. DEMO Adding our own custom row view
- 73. Fundamental #5: Intents An Intent is an
- 74. Intent of making a phone call ActionCall
- 75. Intent of navigating to another screen StartActivity
- 76. Receiving information from the intent protected override void OnCreate (Bundle bundle)
- 77. DEMO Navigating from the List to the Detail page
- 78. Adding Fragments
- 79. The need for Fragments Larger screen: more
- 80. The need for Fragments
- 81. FragmentManager To help an Activity coordinate and
- 82. Creating a fragment A Fragment inherits from
- 83. Adding a fragment to an Activity We
- 84. DEMO Refactoring to Fragments
- 85. Optimizing the application
- 86. Managing strings in strings.xml We can have
- 87. Making the app multi-language
- 88. Application drawables We can add drawables: application
- 89. Application drawables We can select an image
- 90. DEMO Adding resources and drawables to the application
- 91. Deploying to the store
- 92. Publishing your work Marketplace is most common
- 93. Summary Xamarin.Android leverages your C# knowledge to
- 94. Thanks!
- 95. Q&A
- 96. Building your first Android app using Xamarin Gill Cleeren - @gillcleeren
- 97. Your feedback is important! Scan the QR
- 98. Building your first Android app using Xamarin Gill Cleeren @gillcleeren
Слайд 4Hi, I’m Gill!
Gill Cleeren
MVP and Regional Director
.NET Practice Manager @ Ordina
Trainer
@gillcleeren
gill@snowball.be
Слайд 6Agenda
Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android
Xamarin.Android fundamentals
Creating a detail screen
Lists and navigation
Navigating
(Optional) Intro to using Fragments
Optimizing the application
Preparing for store deployment
Слайд 7Targets of this talk
Understanding the fundamentals of Android app development with
See how a fully working app can be built
Слайд 11Hello Xamarin
Xamarin enables developers to reach all major mobile platforms!
Native User
Native Performance
Shared Code Across Platforms
C# & .NET Framework
Toolset on top of Visual Studio
Enables VS to create native iOS and Android apps
Commercial product
Слайд 12Advantages of Xamarin
Full control
Familiar development environment
Native controls
Native performance
Code reuse
Active component
Слайд 13Disadvantages of Xamarin
You need a licence
It’s not a shared UI Platform
You
Слайд 17Xamarin.Android
Anything you can do in Java/Android can be done in C#
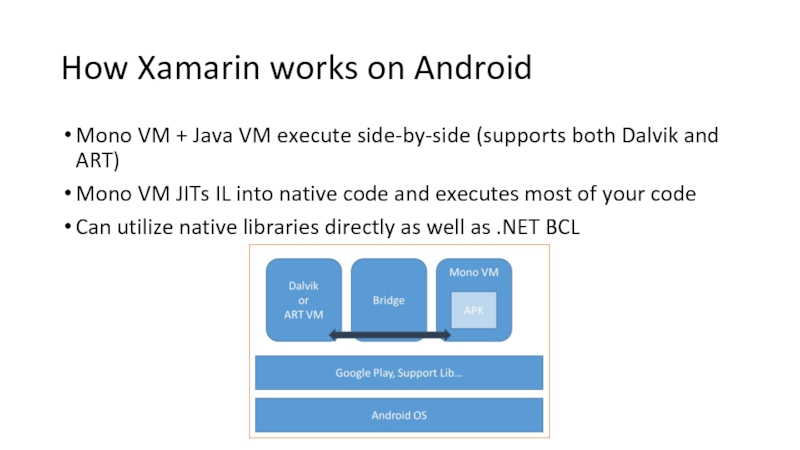
Слайд 18How Xamarin works on Android
Mono VM + Java VM execute side-by-side
Mono VM JITs IL into native code and executes most of your code
Can utilize native libraries directly as well as .NET BCL
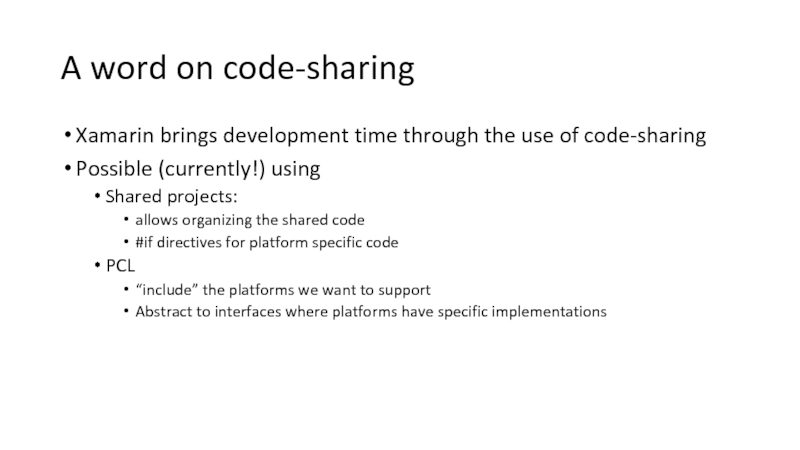
Слайд 19A word on code-sharing
Xamarin brings development time through the use of
Possible (currently!) using
Shared projects:
allows organizing the shared code
#if directives for platform specific code
PCL
“include” the platforms we want to support
Abstract to interfaces where platforms have specific implementations
Слайд 22What you need for Xamarin.Android development
Xamarin license (Xamarin.Android)
PC or Mac
Visual Studio
Android SDK and Emulators (installed via Xamarin setup)
Emulator
Device (not really required but...)
Слайд 24Visual Studio Integration
A single solution:
iOS
Android
Windows Phone
Windows Store
Leverage the entire Microsoft ecosystem:
ReSharper
Team
Your favorite code coverage and profiling tools
Слайд 25Visual Studio Integration
Debug to:
Emulators
Devices
Integrated into toolbar
Status
Logs
List of devices
Слайд 26Alternative: Xamarin Studio
Optimized for cross-platform mobile development
Explore native APIs with code
World class Android and iOS designers
Powerful debugging on simulator or device
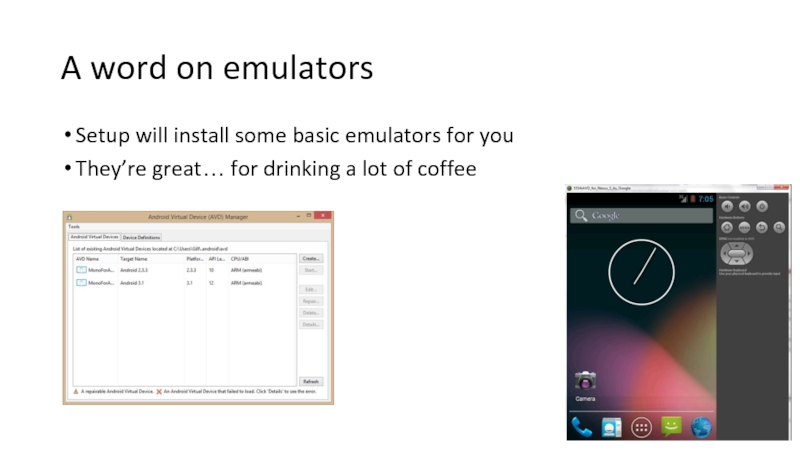
Слайд 27A word on emulators
Setup will install some basic emulators for you
They’re
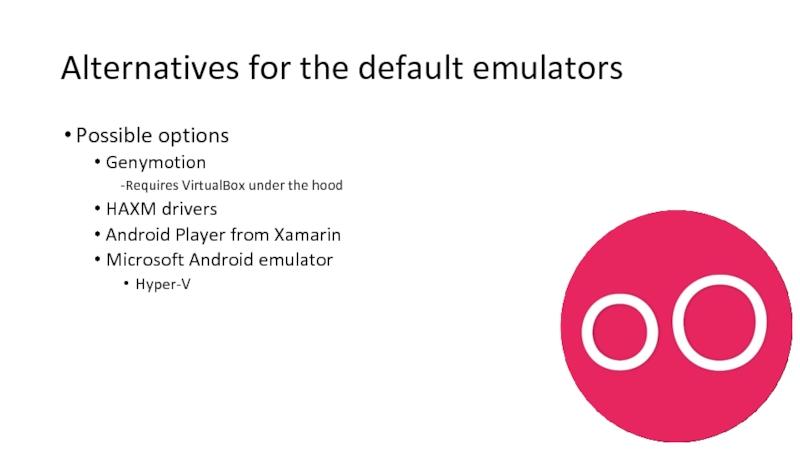
Слайд 28Alternatives for the default emulators
Possible options
Genymotion
-Requires VirtualBox under the hood
HAXM drivers
Android
Microsoft Android emulator
Hyper-V
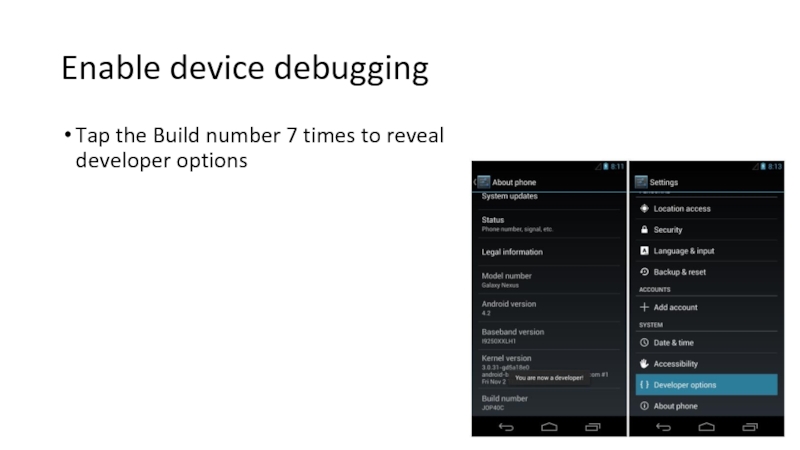
Слайд 29Developing with a device
3 steps
Enable Debugging on the Device
Install USB
Connect the Device to the Computer
Слайд 36Fundamental #1: Activities
Apps are collections of activities
A view == an activity
Apps don’t have an “entry point”
No single code line which is called by the OS
Apps start when Android creates one of the classes of the app
App then gets loaded into memory
Слайд 37Fundamental #1: Activities
When opening an application, the OS creates the first
Activity is a specific class
Defines UI and behaviour for a single task
Corresponds to a single app screen
App gets loaded in memory
OS
User launches app
Activity
Android loads app
In memory
Слайд 38Fundamental #1: Activities
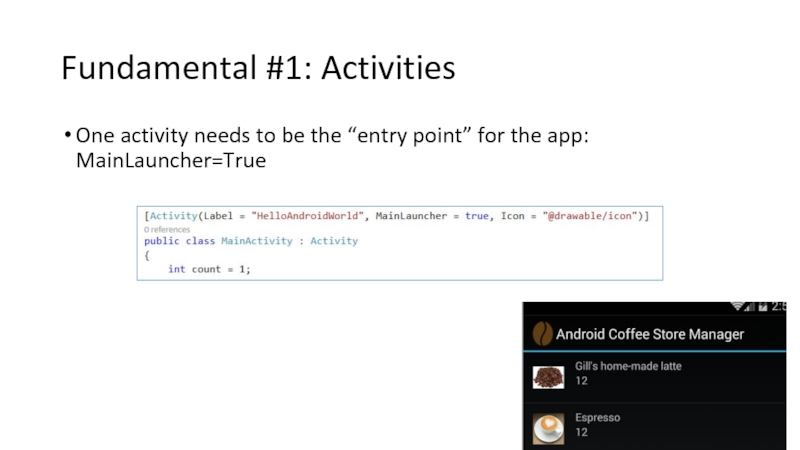
One activity needs to be the “entry point” for
Слайд 39Fundamental #1: Activities
Often, the first activity is named MainActivity
Is also a
Makes sure that activity gets registered with the manifest to let Android know that the class is part of the application
Label is the title of the screen
Icon can be used to customize the displayed icon
Слайд 41Activity lifecycle
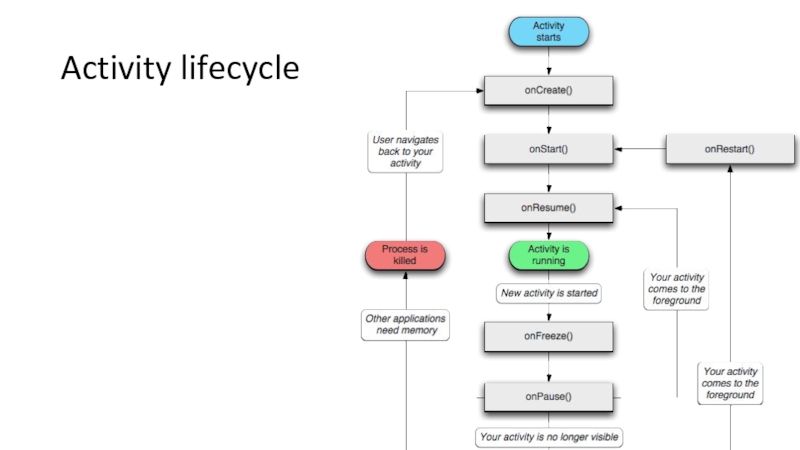
We can of course override these methods
OnCreate:
Create views, initialize variables,
This method is called only once when the Activity is loaded into memory
OnResume
Perform any tasks that need to happen every time the Activity returns to the device screen
OnPause
Perform any tasks that need to happen every time the Activity leaves the device screen
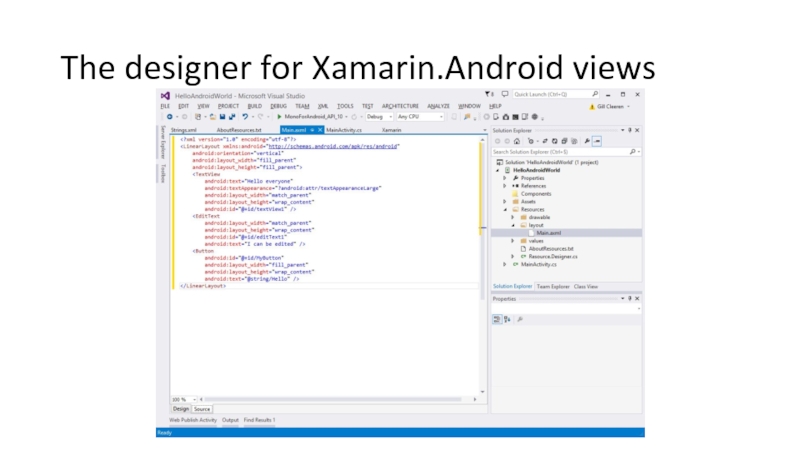
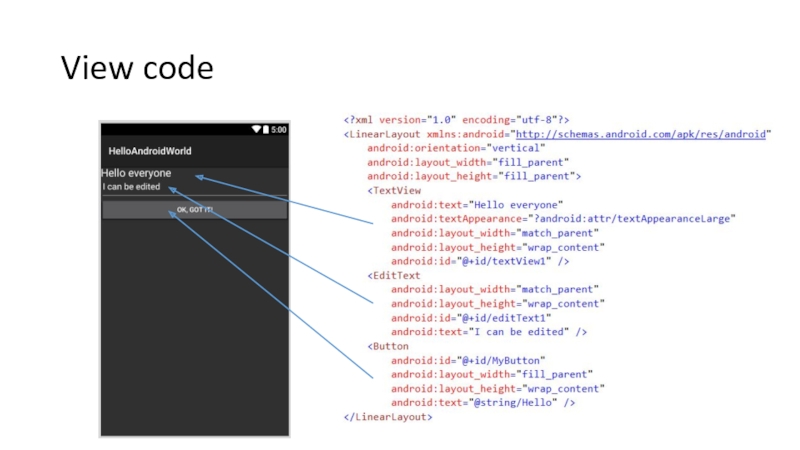
Слайд 43Fundamental #2: Views
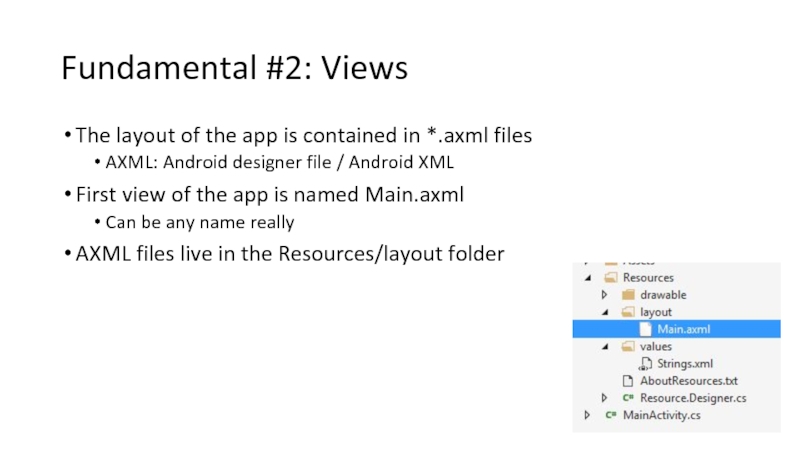
The layout of the app is contained in *.axml
AXML: Android designer file / Android XML
First view of the app is named Main.axml
Can be any name really
AXML files live in the Resources/layout folder
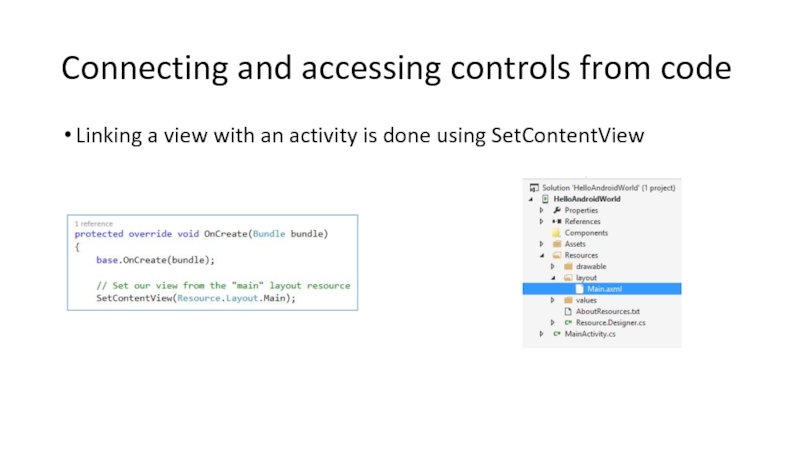
Слайд 47Connecting and accessing controls from code
Linking a view with an activity
Слайд 48Connecting and accessing controls from code
We can name controls using the
The Android designer maps the control to the Resource class and assigns it a resource ID
The code representation of a control is linked to the visual representation of the control in the designer via the Id property
Слайд 49Connecting and accessing controls from code
Once we have created the controls,
Field name is used for lookup
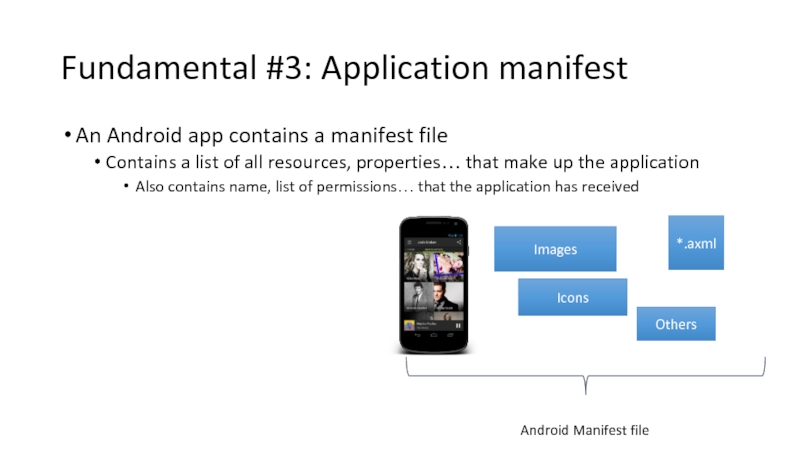
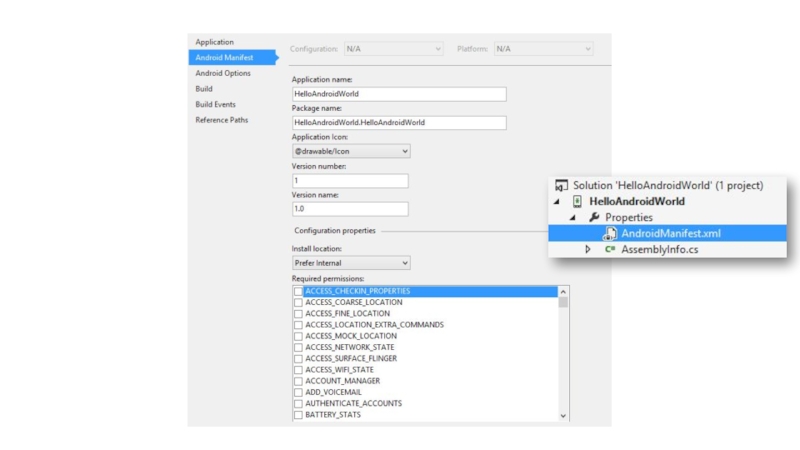
Слайд 50Fundamental #3: Application manifest
An Android app contains a manifest file
Contains a
Also contains name, list of permissions… that the application has received
Images
Icons
*.axml
Others
Android Manifest file
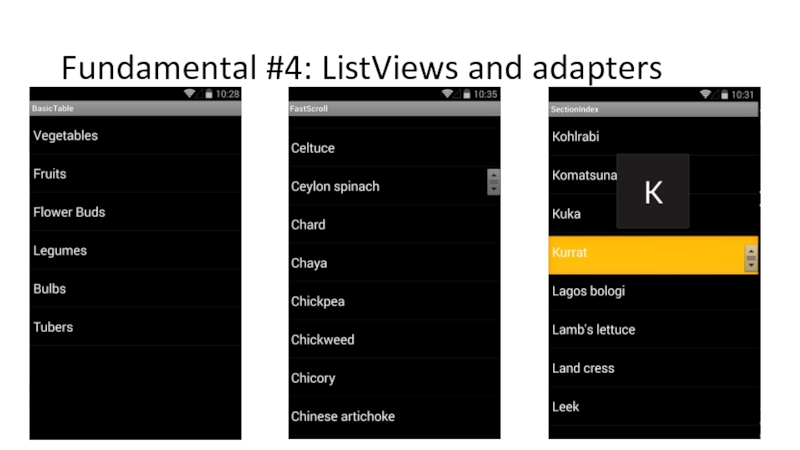
Слайд 54Fundamental #4: ListViews and adapters
Used very commonly in Android
Common way to
Each row is represented using a standard style or customized
Consists out of
ListView: visual part
Adapter: feeds data to ListView
Слайд 57ListActivity and the built-in ArrayAdapter
[Activity(Label = "Coffees", MainLauncher = true, Icon
public class CoffeeScreenActivity: ListActivity
{
string[] coffees;
protected override void OnCreate(Bundle bundle)
{
base.OnCreate(bundle);
coffees= new string[] { "Coffee 1","Coffee 2", "Coffee 3"};
ListAdapter = new ArrayAdapter
this,
Android.Resource.Layout.SimpleListItem1,
coffees);
}
}
Слайд 58Implementing your own adapter
In most cases, the ArrayAdapter won’t be enough
We’ll
Inherits from BaseAdapter
Things we need to implement
Count:
To tell the control how many rows are in the data
GetView:
To return a View for each row, populated with data. This method has a parameter for the ListView to pass in an existing, unused row for re-use
GetItemId:
Return a row identifier (typically the row number, although it can be any long value that you like)
this[int] indexer:
To return the data associated with a particular row number
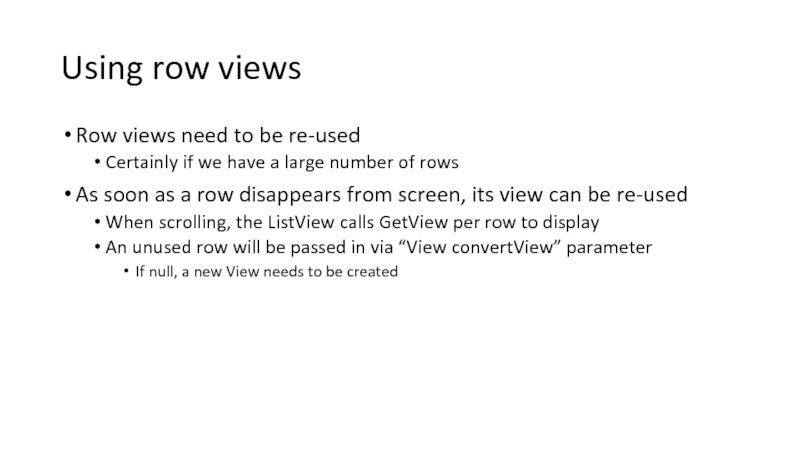
Слайд 59Using row views
Row views need to be re-used
Certainly if we have
As soon as a row disappears from screen, its view can be re-used
When scrolling, the ListView calls GetView per row to display
An unused row will be passed in via “View convertView” parameter
If null, a new View needs to be created
Слайд 60
public class CoffeeAdapter : BaseAdapter
{
List items;
Activity context;
public CoffeeAdapter(Activity context, List items): base()
{
this.items = items;
this.context = context;
}
public override long GetItemId(int position)
{
return position;
}
public override Coffee this[int position]
{
get
{
return items[position];
}
}
public override int Count
{
get
{
return items.Count;
}
}
public override View GetView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
{
var item = items[position];
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = context.LayoutInflater.Inflate (Android.Resource.Layout.SimpleListItem1, null);
}
convertView.FindViewById (Android.Resource.Id.Text1).Text = item.CoffeeName;
return convertView;
}
}
Слайд 61Fast scrolling on the ListView
Fast Scrolling helps the user to scroll
Can be enabled by using
ListView.FastScrollEnabled = true;
Слайд 62Sectioning the ListView
We need to implement on the adapter:
GetSections:
Provides the
GetPositionForSection:
Returns the first row position for a given section index
GetSectionForPosition:
Returns the section index to be displayed for a given row
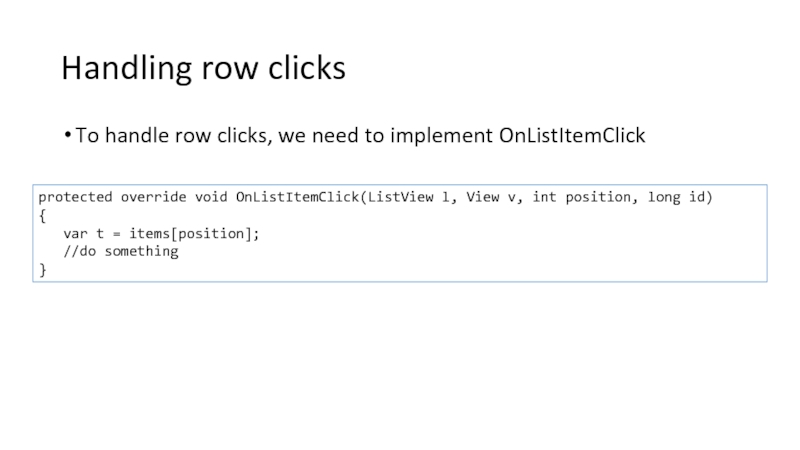
Слайд 63Handling row clicks
To handle row clicks, we need to implement OnListItemClick
protected
{
var t = items[position];
//do something
}
Слайд 69Creating your own row views
Custom row layouts are AXML files in
Are loaded by Id using a custom adapter
View can contain any number of display classes with custom colors, fonts…
Слайд 71Using your custom row view
public override View GetView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent)
{
//custom view
var item = items[position];
if (convertView == null)
{
convertView = context.LayoutInflater.Inflate (Resource.Layout.CoffeeRowView, null);
}
(Resource.Id.CoffeeImageView).SetImageResource(
imageRepository.ImageNameToResourceInt(item.ImageId.ToString())); convertView.FindViewById
(Resource.Id.CoffeeNameText).Text = item.CoffeeName; convertView.FindViewById
(Resource.Id.PriceText).Text = item.Price.ToString(); return convertView; }
Слайд 73Fundamental #5: Intents
An Intent is an abstract concept for some sort
Navigating to another activity
Often, launching an external application (= built-in) with the intent of doing something
Make a phone call
Launch a URI
Map an address
An intent often consist out of
What the intent is
The data needed for the intent
Phone number to call
Слайд 75Intent of navigating to another screen
StartActivity can be used to start
PutExtra() is used to pass data from one activity to the other
var intent = new Intent ();
intent.SetClass (this, typeof(CoffeeDetailActivity));
intent.PutExtra ("selectedCoffeeId", t.CoffeeId);
StartActivity (intent);
Слайд 76Receiving information from the intent
protected override void OnCreate (Bundle bundle)
{
base.OnCreate (bundle);
SetContentView (Resource.Layout.Main);
var selectedCoffeeId = Intent.Extras.GetInt ("selectedCoffeeId", 0);
Coffee coffee = DataService.GetCoffeeById (selectedCoffeeId);
}
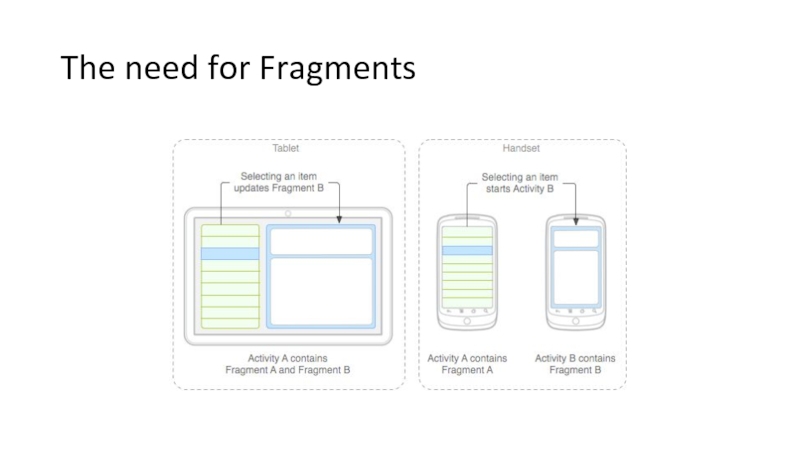
Слайд 79The need for Fragments
Larger screen: more complex to build UIs that
Layouts which look good on a small screen may not look good on a large tablet screen
Android V3.0 introduced Fragments
Fragment is a UI module
UI gets divided into reusable parts
Each “part” is an separate activity
At run time, the Activities themselves will decide which Fragments to use
Also work in older versions through Support packages
Слайд 81FragmentManager
To help an Activity coordinate and manage all these Fragments, Android
Each activity has an instance of the FragmentManager
Allows finding, adding and removing fragments
Слайд 82Creating a fragment
A Fragment inherits from Android.App.Fragment
Must override the OnCreateView
OnCreateView is
Returns a View
OnCreateView will create the View (of the fragment) by inflating a layout file and attaching that to the parent container
Will apply the same parameters as the parent container
public override View OnCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
return inflater.Inflate(Resource.Layout.CoffeeFragment, container, false);
}
Слайд 83Adding a fragment to an Activity
We can add the Fragment to
Declaratively:
Fragments can be used declaratively within .axml layout files by using the
Programmatically
Fragments can also be instantiated dynamically by using the FragmentManager class’s API
Слайд 86Managing strings in strings.xml
We can have Android store string values for
Слайд 88Application drawables
We can add drawables: application icons
Adding all resolutions makes sure
Filenames are the same
Folder name identifies the resolution
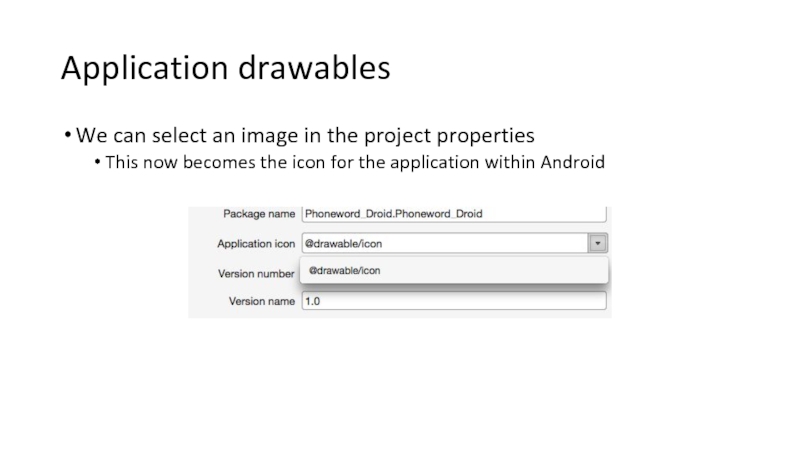
Слайд 89Application drawables
We can select an image in the project properties
This now
Слайд 92Publishing your work
Marketplace is most common option
Often, more than one is
Email or website is often for a more closed distribution
Also require less work to prepare the application for distribution
Google Play is best known store
Allows users to discover, download, rate, and pay for applications by clicking a single icon either on their device or on their computer
Google Play also provides tools to assist in the analysis of sales and market trends and to control which devices and users may download an application
Слайд 93Summary
Xamarin.Android leverages your C# knowledge to build apps for Android
Concepts of
Слайд 97Your feedback is important!
Scan the QR Code and let us know
Laat ons weten wat u van de sessie vindt via de TechDays App!
Scan de QR Code.
Bent u al lid van de Microsoft Virtual Academy?! Op MVA kunt u altijd iets nieuws leren over de laatste technologie van Microsoft. Meld u vandaag aan op de MVA Stand. MVA biedt 7/24 gratis online training on-demand voor IT-Professionals en Ontwikkelaars.






























![public class CoffeeAdapter : BaseAdapter { List items; Activity context; public CoffeeAdapter(Activity context, List items): base() { this.items = items; this.context = context; } public override long GetItemId(int position) { return position; } public override Coffee this[int position] {](/img/tmb/3/283181/05000cd93e8a25cf17926459b3d1b759-800x.jpg)





![Using your custom row viewpublic override View GetView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent){ //custom view var item = items[position]; if (convertView == null) { convertView = context.LayoutInflater.Inflate (Resource.Layout.CoffeeRowView, null); } convertView.FindViewById](/img/tmb/3/283181/02b0325cdfb7456948712471d78e4711-800x.jpg)