- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Convolutional Codes Mohammad Hanaysheh Mahdi Barhoush презентация
Содержание
- 1. Convolutional Codes Mohammad Hanaysheh Mahdi Barhoush
- 2. * A convolutional code is
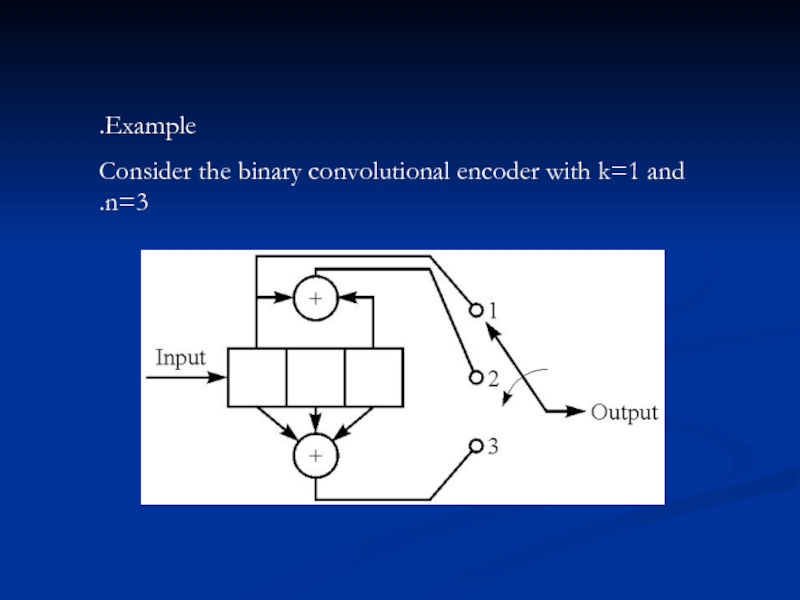
- 3. Example. Consider the binary convolutional encoder with k=1 and n=3.
- 4. >>> Initially, the shift register is assumed
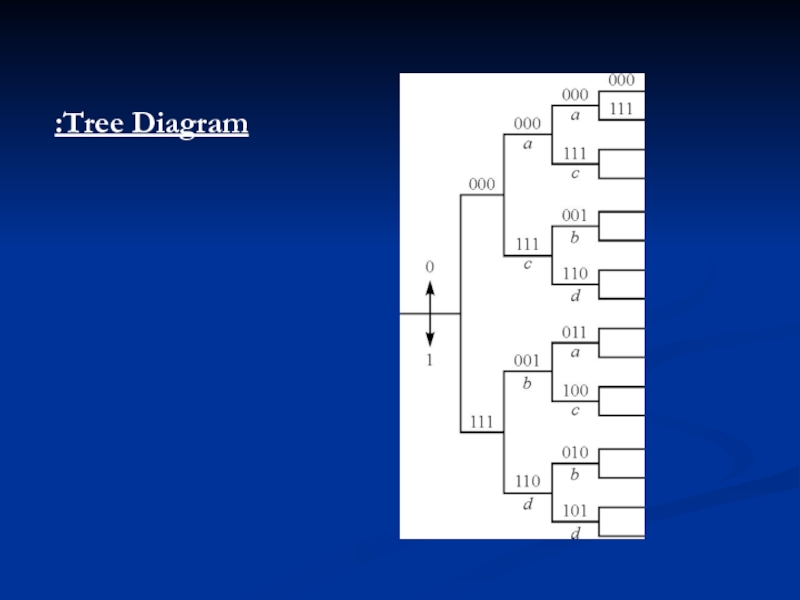
- 5. Tree Diagram:
- 6. Information bit 0 or 1 Register
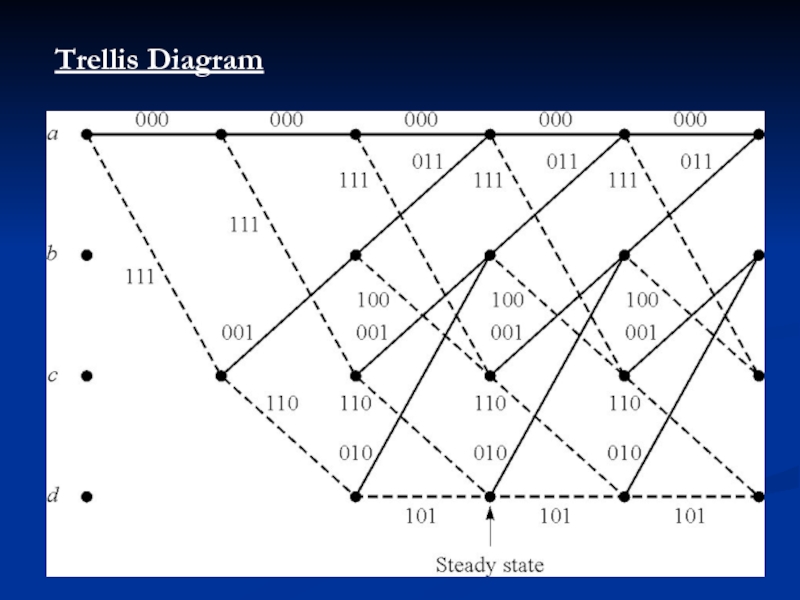
- 7. Trellis Diagram
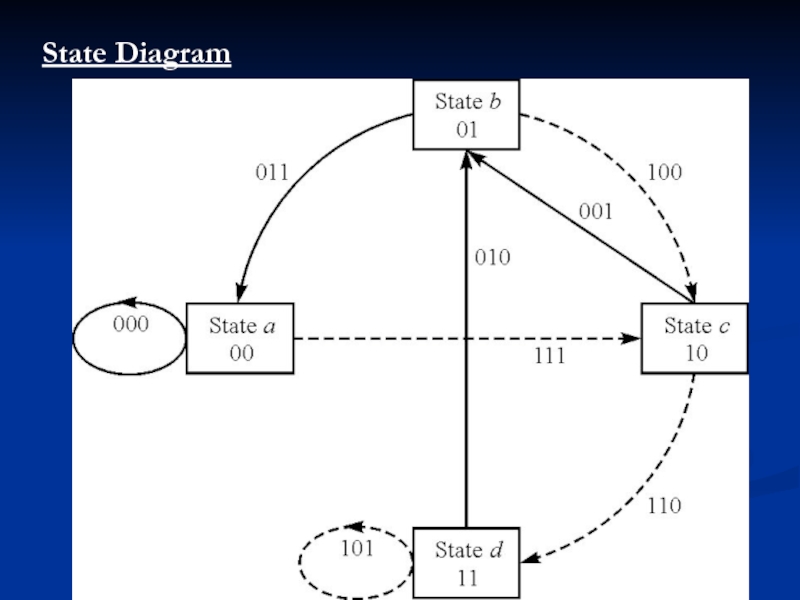
- 8. State Diagram
- 9. Decoding A message m is encoded into
- 10. The Viterbi Algorithm: * The viterbi
- 12. THANK YOU
Слайд 2
* A convolutional code is generated by passing the information sequence
to be transmitted through a linear finite shift register.
* The input data to the encoder, which is assumed to be binary is shifted into and along the shift register k bits at a time. The number of output bits for each k bit sequence is n bits.
R = k / n.
* The input data to the encoder, which is assumed to be binary is shifted into and along the shift register k bits at a time. The number of output bits for each k bit sequence is n bits.
R = k / n.
Слайд 4>>> Initially, the shift register is assumed to be in the
all-zero state. suppose the first input is a 1.then the output sequence of three bits is 111.suppose the second bit is 0.the output sequence will be 001.if the third bit is 1,the output will be 100,and so on.
>>> There are three alternative methods that are often used to describe a convolutional code:
1. Tree diagram.
2. Trellis diagram.
3.State diagram.
>>> There are three alternative methods that are often used to describe a convolutional code:
1. Tree diagram.
2. Trellis diagram.
3.State diagram.
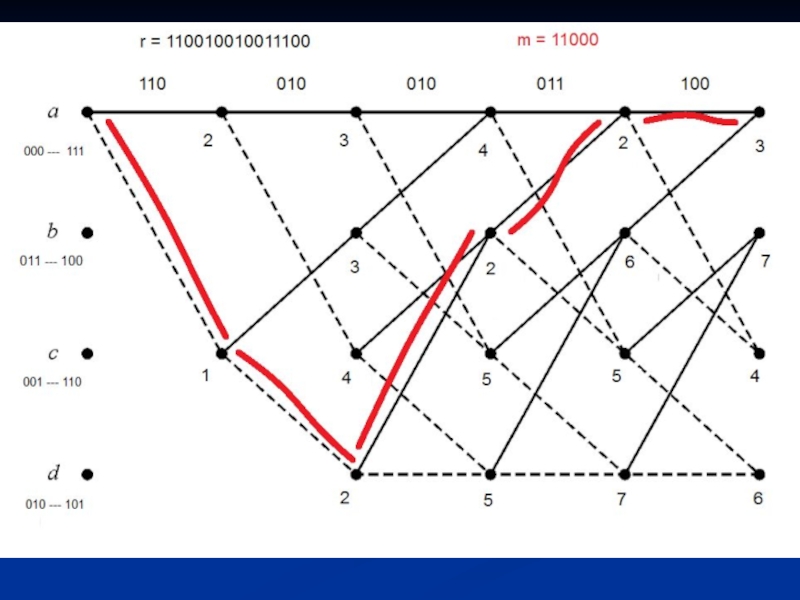
Слайд 9Decoding
A message m is encoded into the code sequence c.
Each code
sequence represents a path in the trellis diagram.
Minimum Distance Decoding
Upon receiving the received sequence r, search for the path that is closest ( in Hamming distance) to r .
Minimum Distance Decoding
Upon receiving the received sequence r, search for the path that is closest ( in Hamming distance) to r .
Слайд 10The Viterbi Algorithm:
* The viterbi algorithm is used to decode convolutional
codes and any structure or system that can be described by a trellis.
* It is a maximum likelihood decoding algorithm that selects the most probable path that maximizes the likelihood function.
* The algorithm is based on add-compare-select the best path each time at each state.
* It is a maximum likelihood decoding algorithm that selects the most probable path that maximizes the likelihood function.
* The algorithm is based on add-compare-select the best path each time at each state.