- Главная
- Разное
- Дизайн
- Бизнес и предпринимательство
- Аналитика
- Образование
- Развлечения
- Красота и здоровье
- Финансы
- Государство
- Путешествия
- Спорт
- Недвижимость
- Армия
- Графика
- Культурология
- Еда и кулинария
- Лингвистика
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Маркетинг
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Introduction to research. Module 4 презентация
Содержание
- 1. Introduction to research. Module 4
- 2. Issues... Why are we interested in research?
- 3. Why must we understand research?
- 4. Why is research a valued source
- 5. What is Science, the Scientific Method,
- 6. What is Science, the Scientific Method,
- 7. What is Science, the Scientific Method,
- 8. What is Science, the Scientific Method,
- 9. Characteristics of Research objective precise verifiable parsimonious empirical logical probabilistic
- 10. Types of Research Trochim’s Classifications… descriptive
- 11. Types of Research Other Common Classifications…
- 12. Key Concepts and Issues time in
- 13. Time in Research cross-sectional vs. longitudinal
- 14. Variables variable… any observation that can
- 15. Examples
- 16. Examples
- 17. Examples
- 18. Examples
- 19. Examples
- 20. Examples
- 21. Types of Variables independent variable (IV)…
- 22. Examples exercise participation
- 23. The purpose of the study was to…
- 24. Types of Relationships correlational vs. causal
- 25. Types of Relationships patterns of relationships… no relationship positive relationship negative relationship curvilinear relationship
- 26. - + - +
- 27. Hypotheses hypothesis… a specific statement of
- 28. Hypotheses alternative hypothesis (HA)… An effect
- 29. Hypotheses hypothesis there is a relationship
- 30. Hypotheses hypothesis an incentive program will
- 31. Types of Data quantitative vs. qualitative
- 32. Research Fallacies fallacy… an error in
- 33. Structure of Research begin with
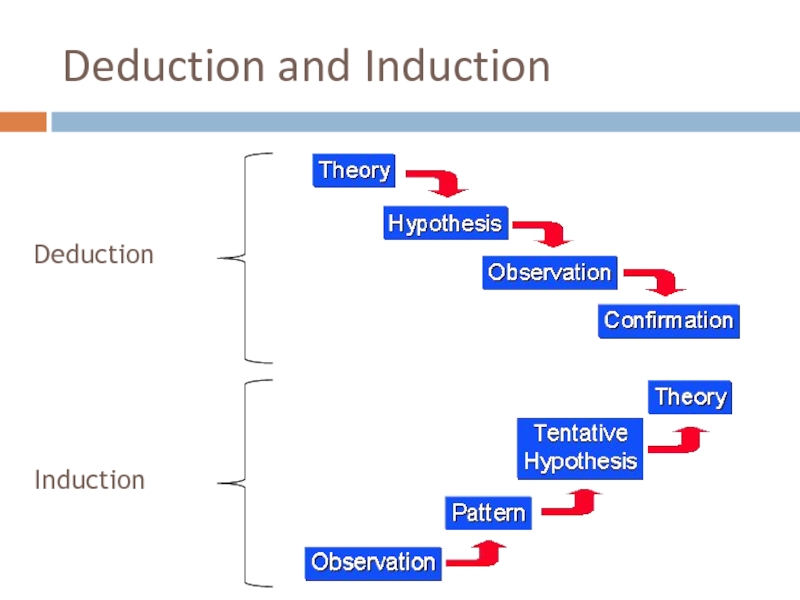
- 34. Deduction and Induction
- 35. Ethics in Research balance between protecting
- 36. Practice Questions Is the study descriptive,
- 37. Practice Questions A. The purpose of
- 38. Practice Questions B. The purpose of
- 39. Practice Questions C. The study examined
- 40. Practice Questions D. Participants at the
- 41. Practice Questions E. A researcher was
- 42. Introduction to Validity validity… the best
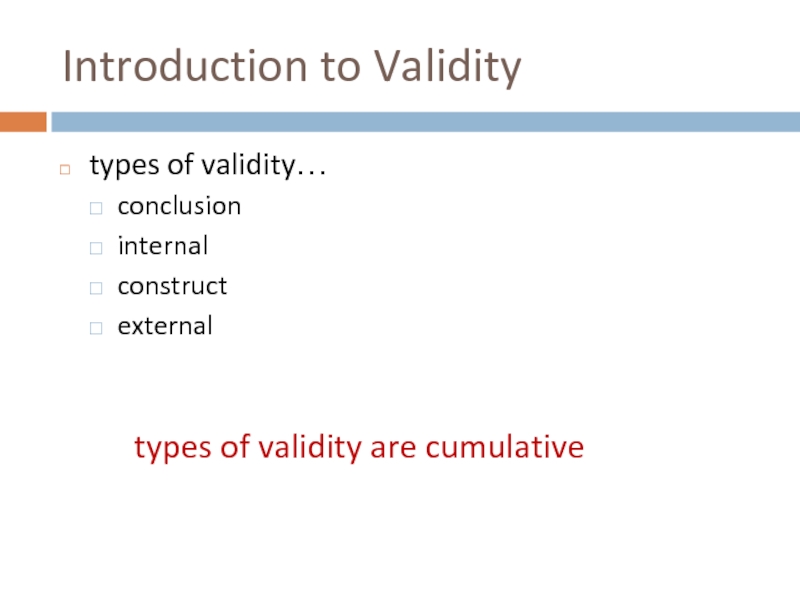
- 43. Introduction to Validity types of validity…
- 44. Introduction to Validity for each type
- 45. Additional Information Describing Refereed Articles Sharing Research Findings with Clients
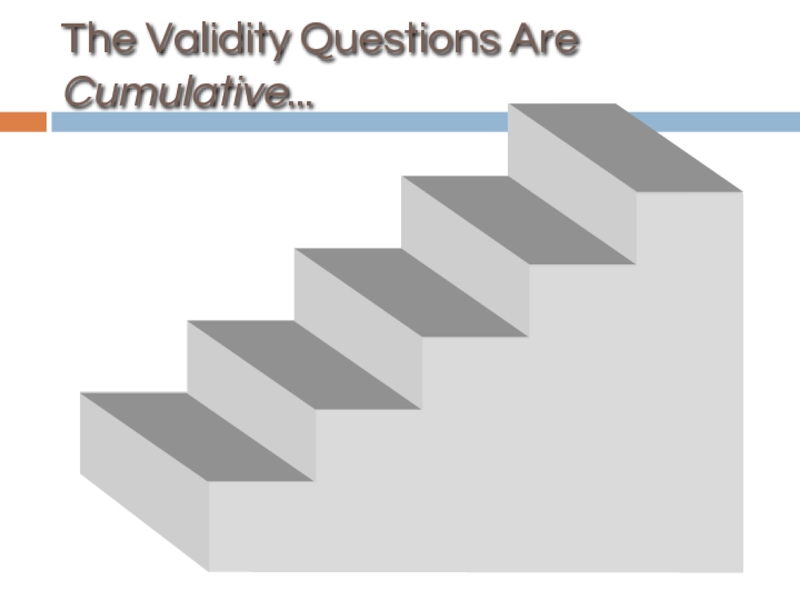
- 47. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative...
- 48. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... In this
- 49. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... Conclusion Is
- 50. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... In theory
- 51. The Validity Questions Are Cumulative... Construct Is
- 52. The Validity Questions are cumulative... Is there
- 53. Validity Questions are Cumulative Is there a
Слайд 2Issues...
Why are we interested in research?
What is research?
Key concepts and issues
Introduction
Слайд 3
Why must we understand research?
help make informed decisions
need to produce
evaluating research in the media
assist in classes
Слайд 4
Why is research a valued source of knowledge?
Common ways of
personal experience/intuition
experts/traditions/authority
scientific method
Слайд 5
What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research?
Science…
a body of established
the observation, identification, investigation, and theoretical explanation of natural phenomenon
usually the ultimate goal is theory generation and verification
Слайд 6
What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research?
Theory…
a set of inter-related
should be simple, consistent with observed relationships, tentative and verifiable
Слайд 7
What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research?
Scientific Method…
involves the principles
process or approach to generating valid and trustworthy knowledge
Слайд 8
What is Science, the Scientific Method, and Research?
Research…
the application of the
a systematic process of collecting and logically analyzing information (data)
Research Methods (Methodology)…
the ways one collects and analyzes data
methods developed for acquiring trustworthy knowledge via reliable and valid procedures
Слайд 9
Characteristics of Research
objective
precise
verifiable
parsimonious
empirical
logical
probabilistic
Слайд 10
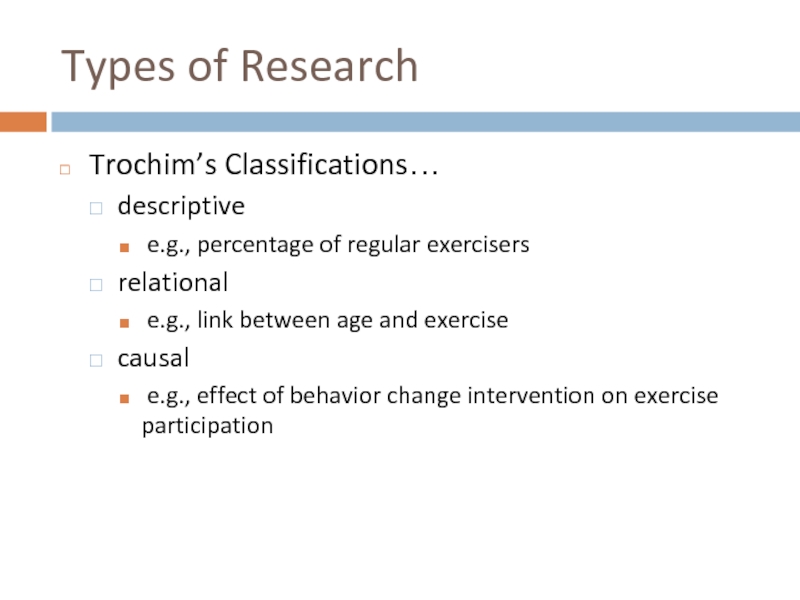
Types of Research
Trochim’s Classifications…
descriptive
e.g., percentage of regular exercisers
relational
e.g., link
causal
e.g., effect of behavior change intervention on exercise participation
Слайд 11
Types of Research
Other Common Classifications…
basic vs. applied vs. evaluation
experimental vs. non-experimental
analytical
Слайд 12
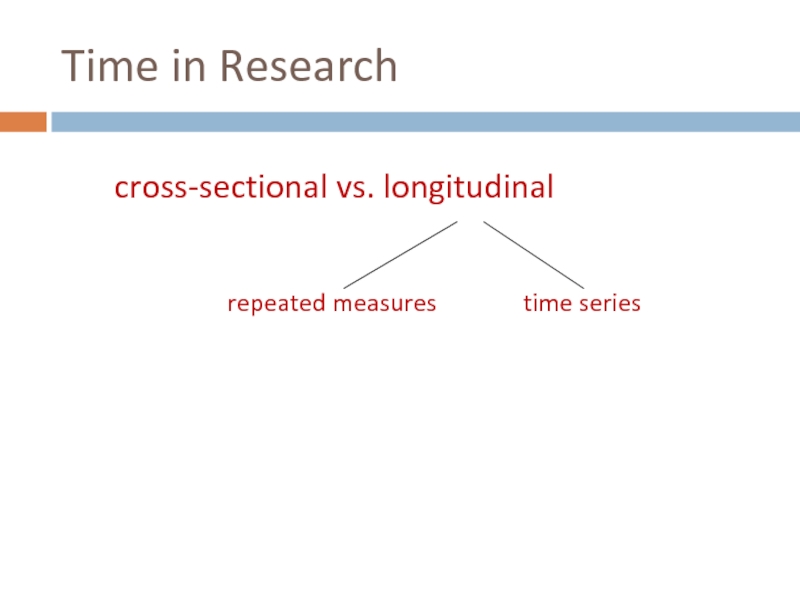
Key Concepts and Issues
time in research
variables
types of relationships
hypotheses
types of data
fallacies
structure or
deduction and induction
ethics
validity
Слайд 14
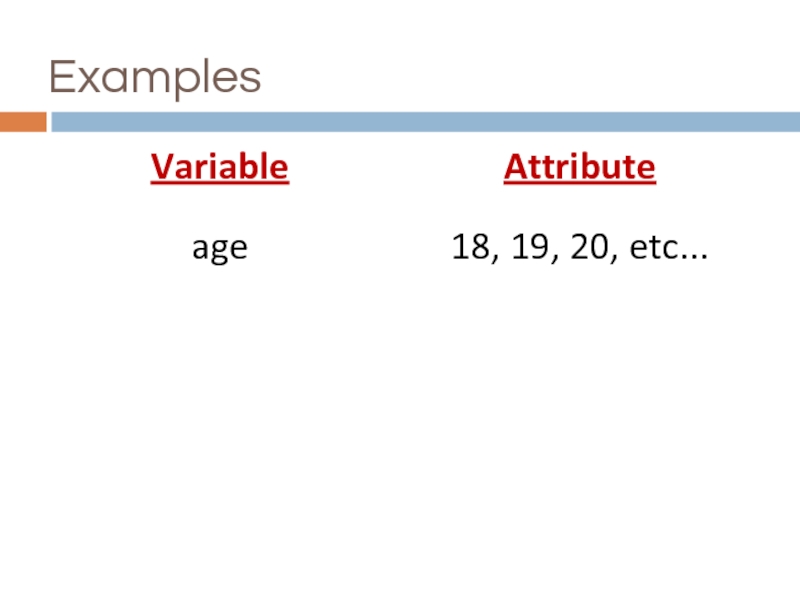
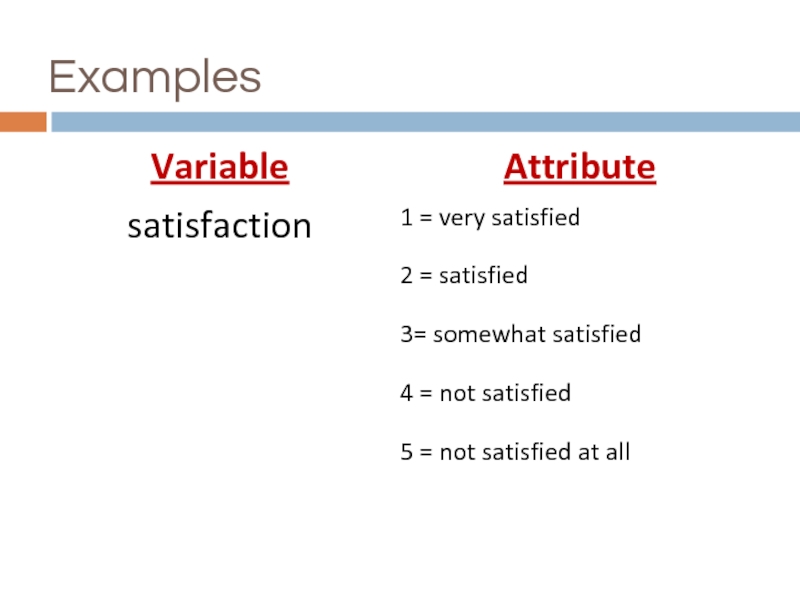
Variables
variable…
any observation that can take on different values
attribute…
a specific value on
Слайд 21
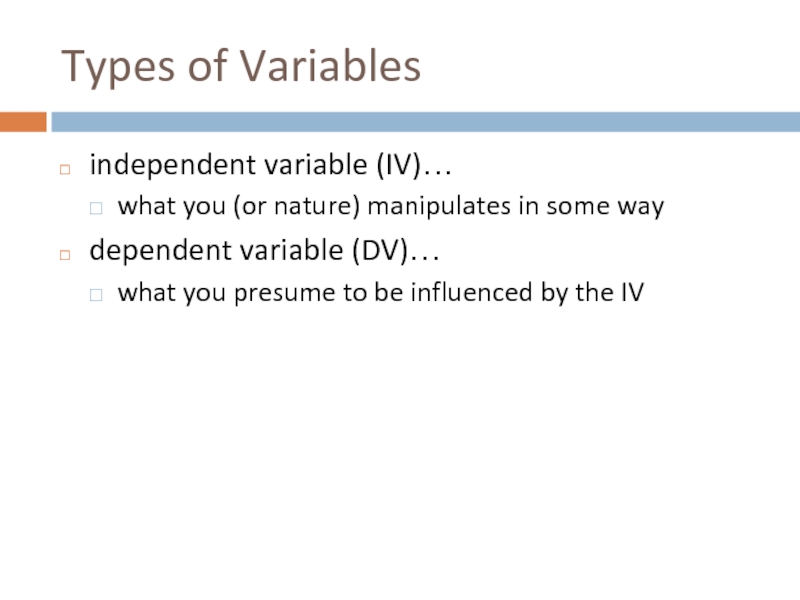
Types of Variables
independent variable (IV)…
what you (or nature) manipulates in some
dependent variable (DV)…
what you presume to be influenced by the IV
Слайд 23The purpose of the study was to…
test whether the “Fair Play
examine the relationship between age and VO2max.
test whether there are gender differences the value placed on sport participation
determine whether students’ perceptions of the amount of positive, negative, and informational feedback provided by their teachers is predictive of their self-esteem and level of achievement
IV, DV?
Слайд 24
Types of Relationships
correlational vs. causal relationships
correlation does not imply causation!
(it’s necessary
variables perform in a synchronized manner
one variable causes the other variable
Слайд 25
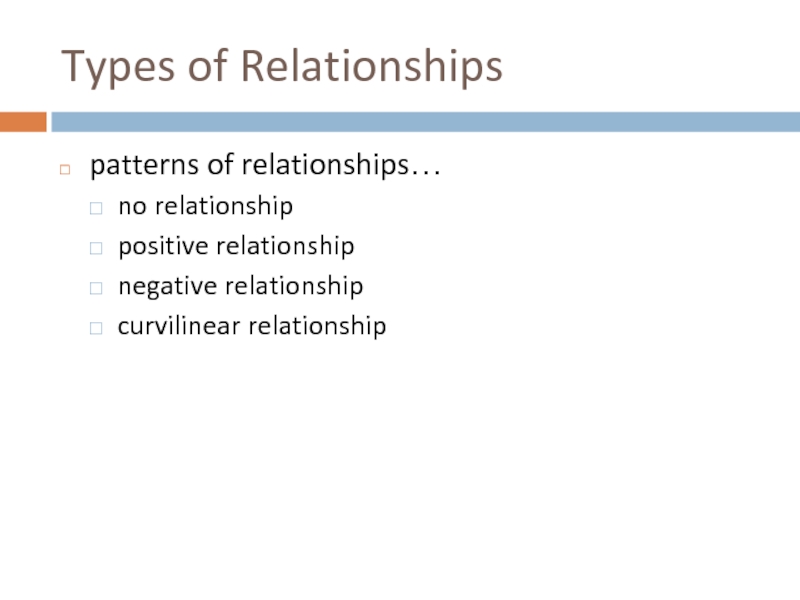
Types of Relationships
patterns of relationships…
no relationship
positive relationship
negative relationship
curvilinear relationship
Слайд 27
Hypotheses
hypothesis…
a specific statement of prediction
types of hypotheses
alternative vs. null
one-tailed vs. two-tailed
Слайд 28
Hypotheses
alternative hypothesis (HA)…
An effect (that you predict)
null hypothesis (HO) …
Null effect
Слайд 29
Hypotheses
hypothesis
there is a relationship between age and exercise participation
HA
there is a
HO
there is not a relationship
this is a two-tailed hypothesis as no direction is predicted
Слайд 30
Hypotheses
hypothesis
an incentive program will increase exercise participation
HA
participation will increase
HO
participation will not
this is a one-tailed hypothesis as a specific direction is predicted
Слайд 32
Research Fallacies
fallacy…
an error in reasoning (logic or premise)
types of fallacies described
ecological
exception
Слайд 33
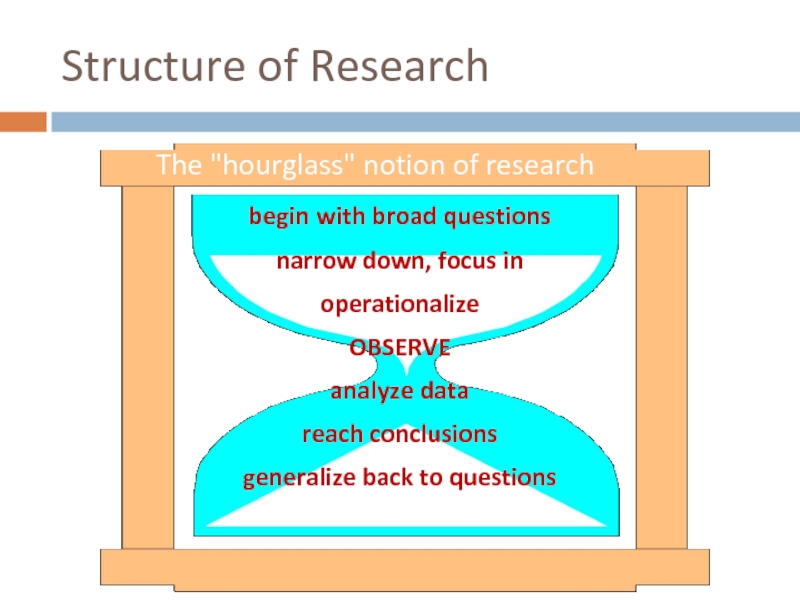
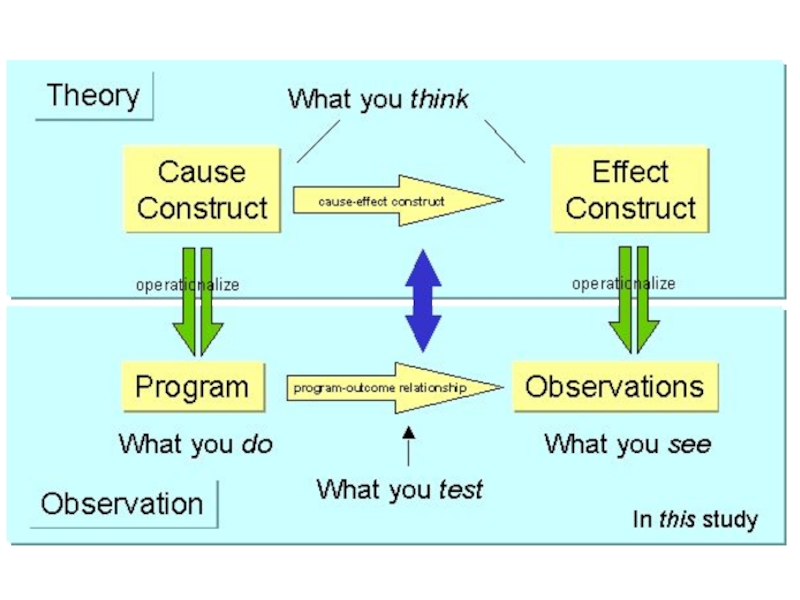
Structure of Research
begin with broad questions
narrow down, focus in
operationalize
OBSERVE
analyze data
reach conclusions
generalize
The "hourglass" notion of research
Слайд 35
Ethics in Research
balance between protecting participants vs. quest for knowledge
IRB provides
informed consent/assent
confidentiality and anonymity
justification of procedures
right to services
http://www.rsp.ilstu.edu/policy/IRB/IRB_policy.pdf
Слайд 36
Practice Questions
Is the study descriptive, relational, or causal?
Is the study cross-sectional
What is (are) the IV (IVs)?
What is (are) the DV (DVs)?
What are the alternative and null hypotheses?
Слайд 37
Practice Questions
A. The purpose of the study was to examine the
Слайд 38
Practice Questions
B. The purpose of the study was to determine whether
Слайд 39
Practice Questions
C. The study examined the effects of an acute bout
Слайд 40
Practice Questions
D. Participants at the 2009 Chicago Marathon were polled to
Слайд 41
Practice Questions
E. A researcher was interested in the role of caffeine
Слайд 42
Introduction to Validity
validity…
the best available approximation to the truth of a
Слайд 43
Introduction to Validity
types of validity…
conclusion
internal
construct
external
types of validity are cumulative
Слайд 44
Introduction to Validity
for each type of validity there are typical threats,
this provides our framework for critiquing the overall validity (= worth) of studies
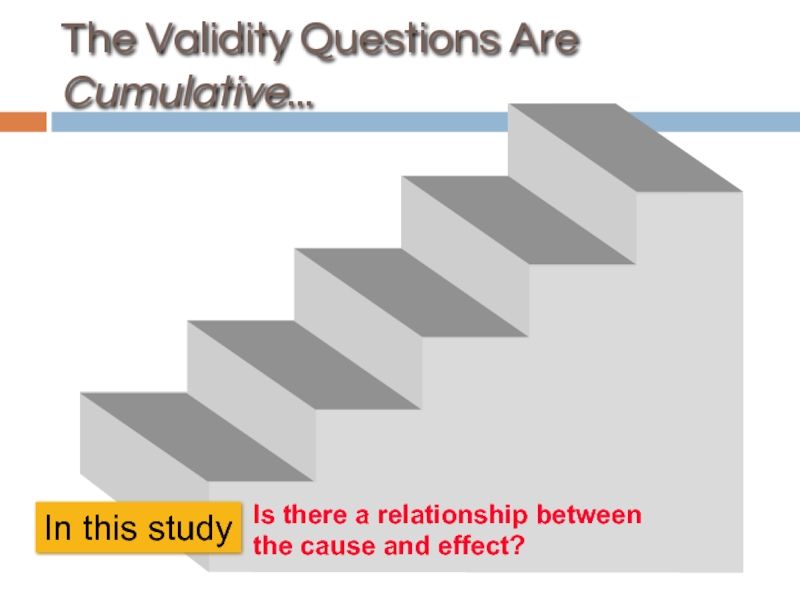
Слайд 48The Validity Questions Are Cumulative...
In this study
Is there a relationship between
Слайд 49The Validity Questions Are Cumulative...
Conclusion
Is there a relationship between the cause
Is the relationship causal?
In this study
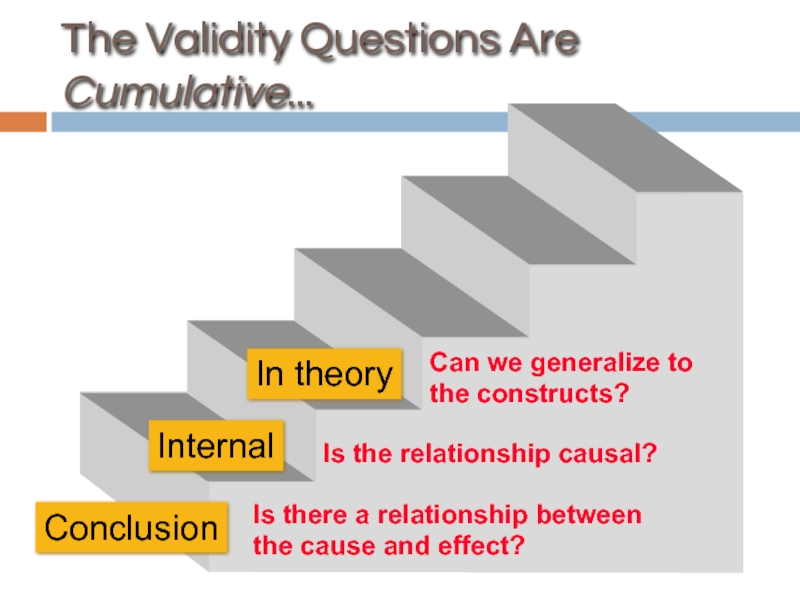
Слайд 50The Validity Questions Are Cumulative...
In theory
Is there a relationship between the
Is the relationship causal?
Can we generalize to the constructs?
Conclusion
Internal
Слайд 51The Validity Questions Are Cumulative...
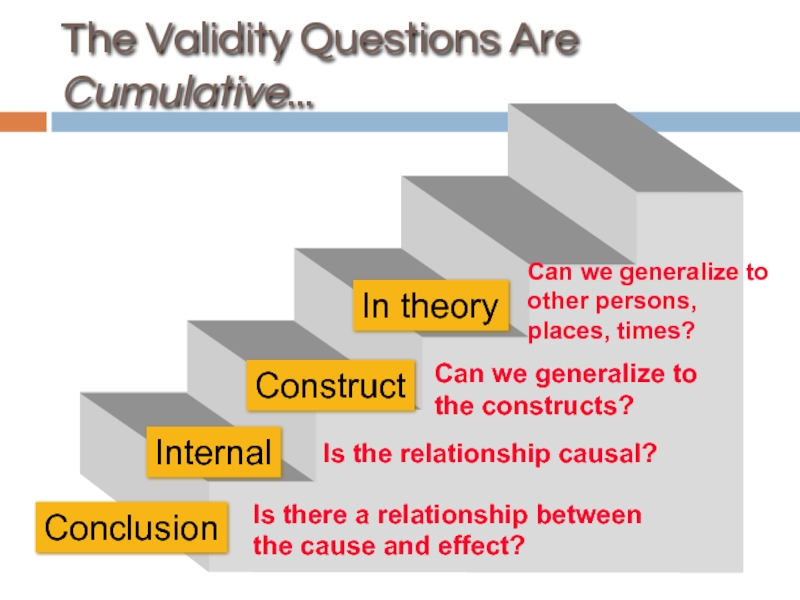
Construct
Is there a relationship between the cause
Is the relationship causal?
Can we generalize to the constructs?
Can we generalize to other persons, places, times?
In theory
Conclusion
Internal
Слайд 52The Validity Questions are cumulative...
Is there a relationship between the cause
Is the relationship causal?
Can we generalize to the constructs?
Can we generalize to other persons, places, times?
External
Validity
Conclusion
Internal
Construct
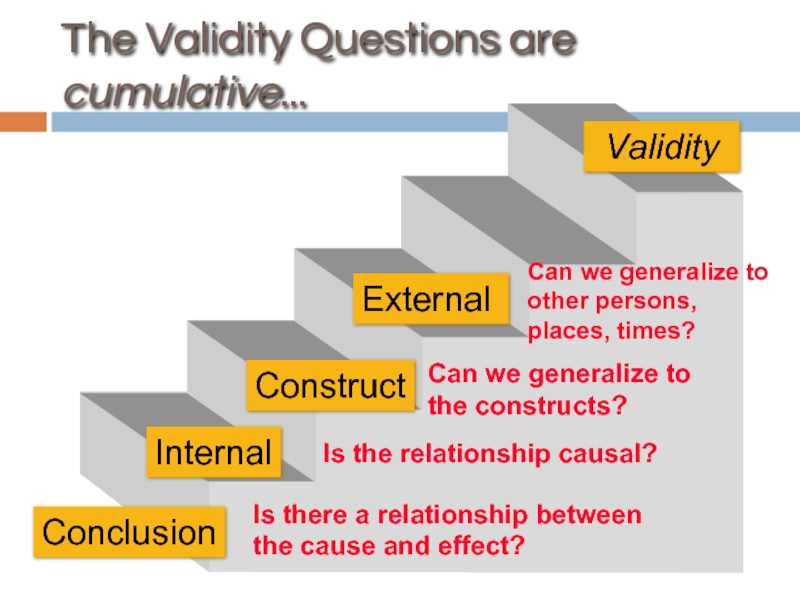
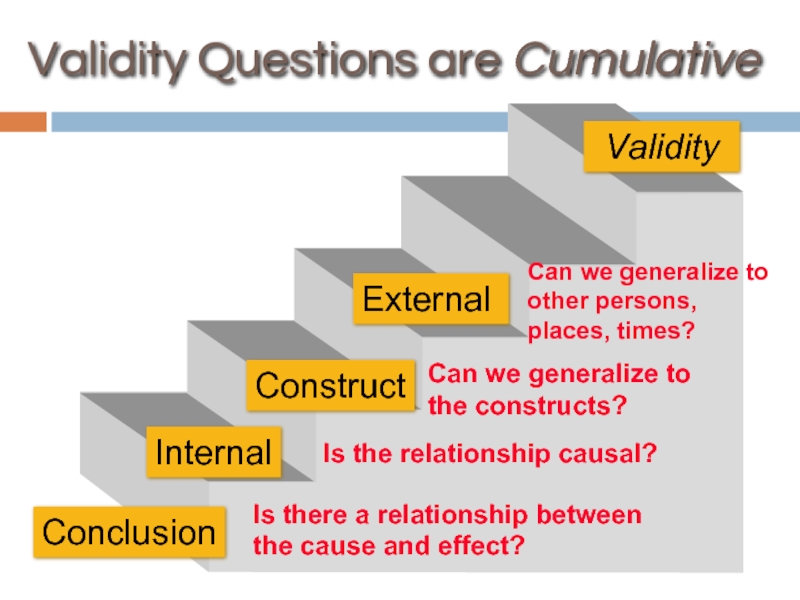
Слайд 53Validity Questions are Cumulative
Is there a relationship between the cause and
Is the relationship causal?
Can we generalize to the constructs?
Can we generalize to other persons, places, times?
External
Validity
Conclusion
Internal
Construct